Extraction & uses of metals
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Where are unreactive metals found?
in pure form in the Earths crust
(e.g. gold or silver)
Where are reactive metals found?
in ores from the Earths crust
What is an ore?
a material that contains a metal or metal compound in sufficient quantities so that its extraction is economic
(e.g. the iron ore haematite or the aluminium ore bauxite)
How does a metals reactivity impact its extraction method?
- metals more reactive than carbon are extracted by electrolysis
- metals less reactive than carbon are extracted by displacement reactions where carbon displaces the metal from its compound
Why are metals less reactive than carbon not extracted by electrolysis?
because electrolysis is very expensive due to the large amounts of energy used so it is better to use cheaper ways if possible (e.g. displacement reactions using carbon)
Explain the extraction of iron
- iron ore (haematite - contains iron oxide) is extracted in a blast furnace by a displacement reaction as iron is less reactive than carbon
- carbon monoxide is the reducing agent which reduces iron oxide
- iron(III) oxide + carbon monoxide → iron + carbon dioxide
- Fe2O3(s) + 3CO(g) → 2Fe(l) + 3CO2(g)
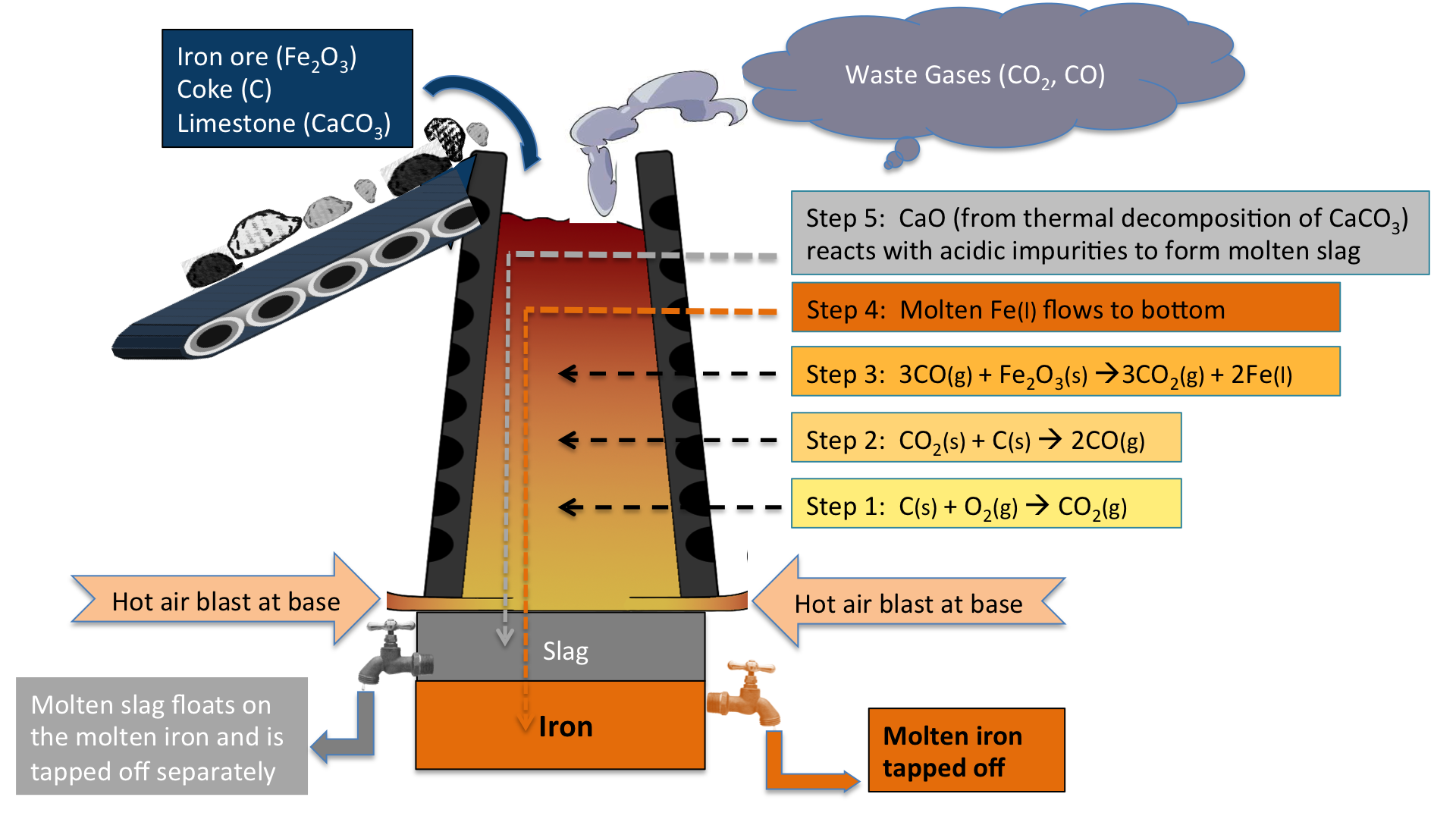
What are the raw materials & their uses in the extraction of iron?
Haematite → contains iron (III) oxide → ore that iron is extracted from
Coke → contains carbon → burns in air to produce heat & reacts to form carbon monoxide
Limestone → contains calcium carbonate → reactes to form slag which helps remove acidic impurities from the iron
Air → contains oxygen → allows coke to burn & therefore produce heat
What are the properties & uses of aluminium?
- low density, corrosion-resistant
- used for air crafts, trains, saucepans & cooking foil
What are the properties & uses of copper?
- soft, malleable, ductile, good conductor of electricity & heat, does not react with water
- used for electrical wiring, plumbing pipes, musical instruments
What are the properties & uses of iron?
Blast furnace iron: too hard & brittle for most uses so converted into steel
Pure iron: too soft for most uses
What are the properties & uses of steel?
Low carbon steel: 0.25% carbon, malleable, used for car body panels
High carbon steel: 2.5% carbon, hard, used for cutting tools
Stainless steel: resistant to corrosion, used for cutlery & sinks
What is an alloy?
a mixture of 2 or more metals or metal(s) + carbon
Why are alloys harder than pure metals?
Because in an alloy, the ions are different sizes which disrupts the regular arrangement & therefore prevents the layers from being able to easily slide over each other, making the alloy hard & brittle
However, in a pure metal, the ions are the same size & have a regular arrangement which makes them softer & more malleable because the layers can easily slide over each other