ap bio unit 2: cell structure function
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
what does larger surface area entail?
more efficient resource exchange
purpose of membrane-bound organelles in eukaryotes (compartmentalization)
to increase surface area (e.g. mitochondria double membrane)
nucleus
stores genetic info in eukaryotes
nucleolus
produces/assembles ribosomes
endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
structure connected to nuclear membrane
smooth ER
produces lipids
rough ER
covered with ribosomes used to make proteins
golgi apparatus
helps process and package things, especially proteins to be exported
appears as a series of stacked membranes near cell membrane
think ____ = fat = bouncer
lysosomes
contains digestive enzymes, destroys viruses, break down excess or worn out cell parts, carries out apoptosis (____ = clean)
vacuole
contains fluid/food, there is a huge one in plant cells
mitochondria
powerhouse of cell
cristae
folds on mitochondria inner membrane that inc. SA
cell wall
rigid, semipermeable barrier for plant cells and some bacteria (cellulose)
chloroplasts
have green pigment that absorbs sunlight in photosynthesis
chlorophyll
green pigment in chloroplast
chromoplast
have colorful pigments, found in flowers and fruit
plastid
chloroplast, chromoplasts, and leucoplasts (plant organelles containing pigment or food)
differing pigments = differing light absorption frequencies
carotenoids
colorful (red, orange, yellow) pigments in chromoplasts
leucoplast
has no pigment, is used to store starch
apoplastic pathways
go thru cell wall (comms)
sympoplastic pathways
go thru cytoplasm (comms)
stem cells
can turn into a lot of different specialized cells
phospholipid components
hydrophilic glycerol+phosphate head, hydrophobic fatty acid tails
fluid mosaic model
the membrane is like a jelly soup of phospholipids, proteins, and cholesterol, and carbohydrates that kind of float near each other
glycolipids
carb chains that stick out of the membrane, allowing for cell to cell comms
cholesterol purpose
modulates fluidity with changing temperature (fixes excess rigidity or fluidity)
receptor protein
sticks out of membrane w/ tentacles (e.g GPCR) so it can recognize things
adhesion protein
sticks out of membrane with a hook that allows it to stick to other cells
passive transport/simple diffusion
no energy needed, goes down gradient without help until dynamic equilibrium is reached
facilitated diffusion
passive transport but with a channel protein
active transport
pumps against conc. gradient
channel protein
lets charged or big substances through membrane through facilitated diffusion
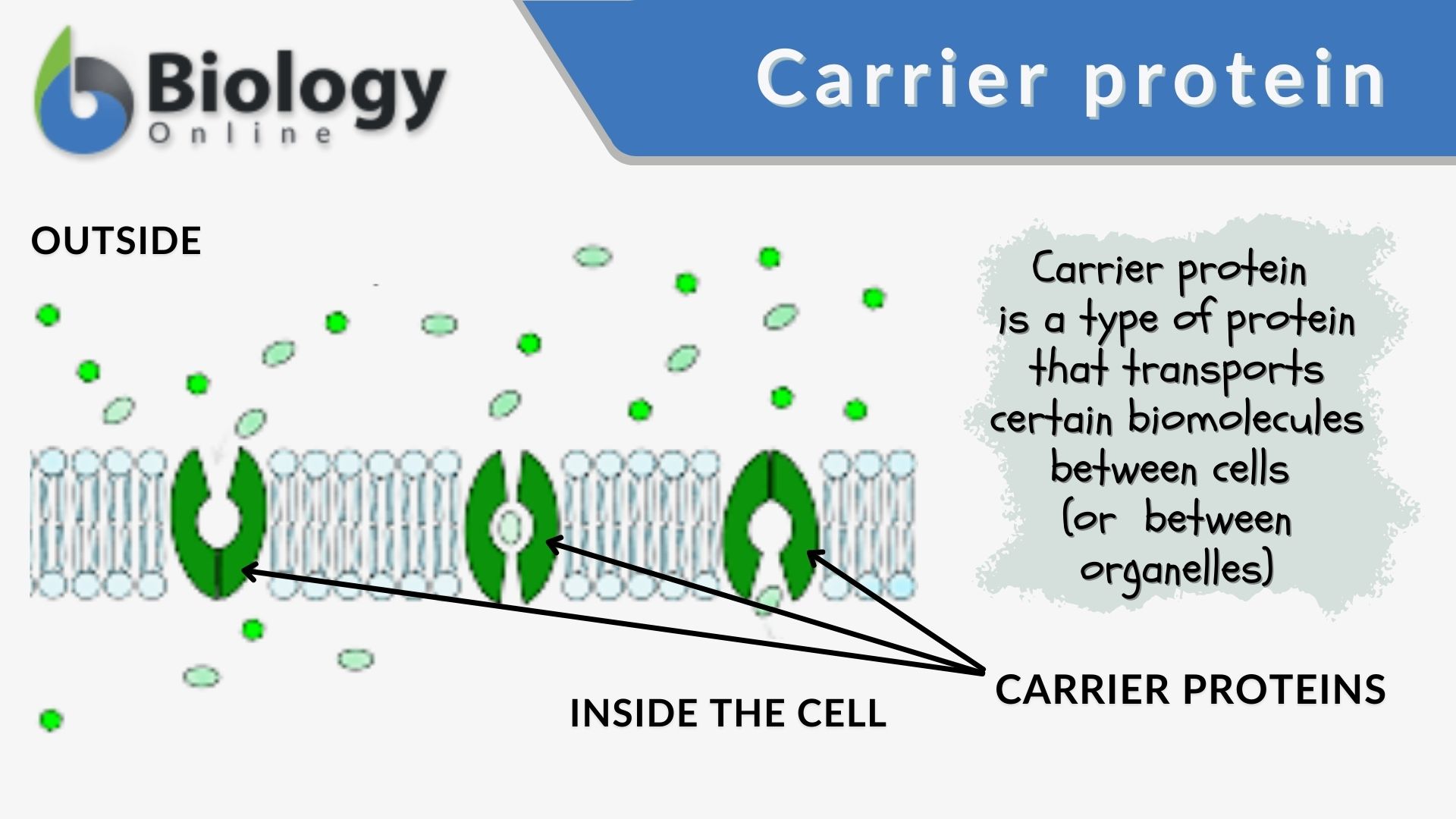
carrier protein
gated diffusion of materials (passive and active transport depending on the situation)
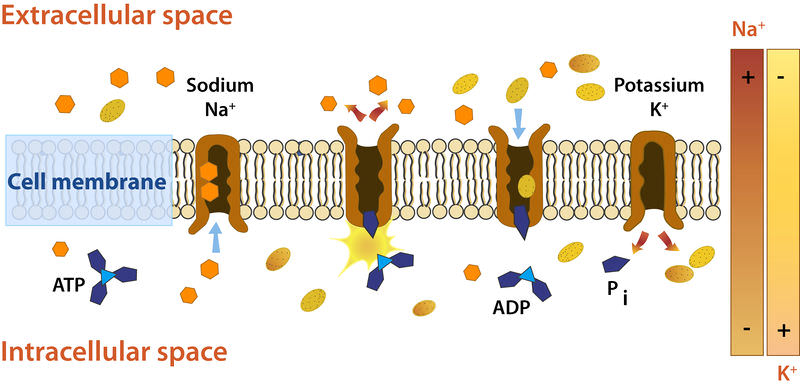
Na+ and K+ pump steps
na+ and atp bind to pump
atp hydrolysis (atp → adp + phosphorylated protein) changes pump conformation
shape change discharges na+ and k+ can bind to pump
phosphorylated protein from 2 is released and k+ can go into cell against k+ conc. gradient
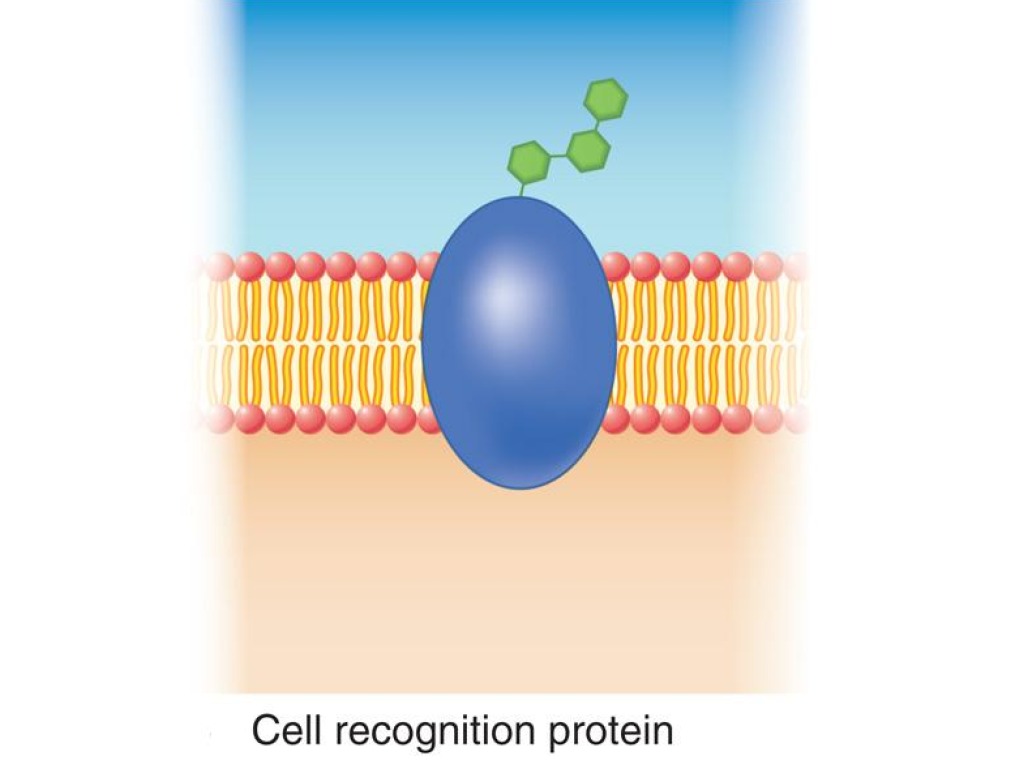
recognition protein
immune system, recognizes diseased cell
primary active transport
requires atp and active transport creates a membrane potential
secondary active transport
uses electrochemical gradient as energy source as atp
when two ions have opposite gradients, one is transported passively, which provides the voltage for the active transport of the other
uniporter
allows one molecules through membrane (either passive or active)
cotransporter
allow two mcules through membrane at same time (secondary active transport with a nonpolar solute and ion)
symporter
cotransporter where both are in same dir
antiporter
cotransporter where both are in opp dir
where does water move toward?
high solute conc. (low solvent conc.)
hypertonic
surroundings are more conc. w solute
plasmolysis
when plant cells shrivel in hypertonic solution
hypotonic
surroundings are less conc. w/ solute
isotonic
surroundings are same solute conc
aquaporin
protein channel for water
plasmodesmata
narrow channels between cell walls of neighboring plant cells
stomata
openings in plant cells for co2 and h2o regulation (opens when there is light)
water potential
describes the potential energy of water, moves from high potential to low potential (measured in kPa)
water potential = pressure potential + solute pot
pressure potential
the pressure a closed container exerts on its contents, 0 for open container, usually +
solute potential
measures solute content, always 0 for pure water, adding solute lowers solute pot, always (-)
solute pot = iCRT
i = ionization const.
R = gas cons.t
T = temp (K)
C = conc. (M)
phagocytosis
intake of big mcules (eating)
pinocytosis
small mcules suspended in fluid (drinking)
receptor mediated transport
regulated entry of mcules (messaging)