CHAPTER 7 lecture
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/28
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
1
New cards
chromosome
A structure found inside the nucleus of a cell. A chromosome is made up of proteins and DNA organized into genes. Each cell normally contains 23 pairs of chromosomes.
2
New cards
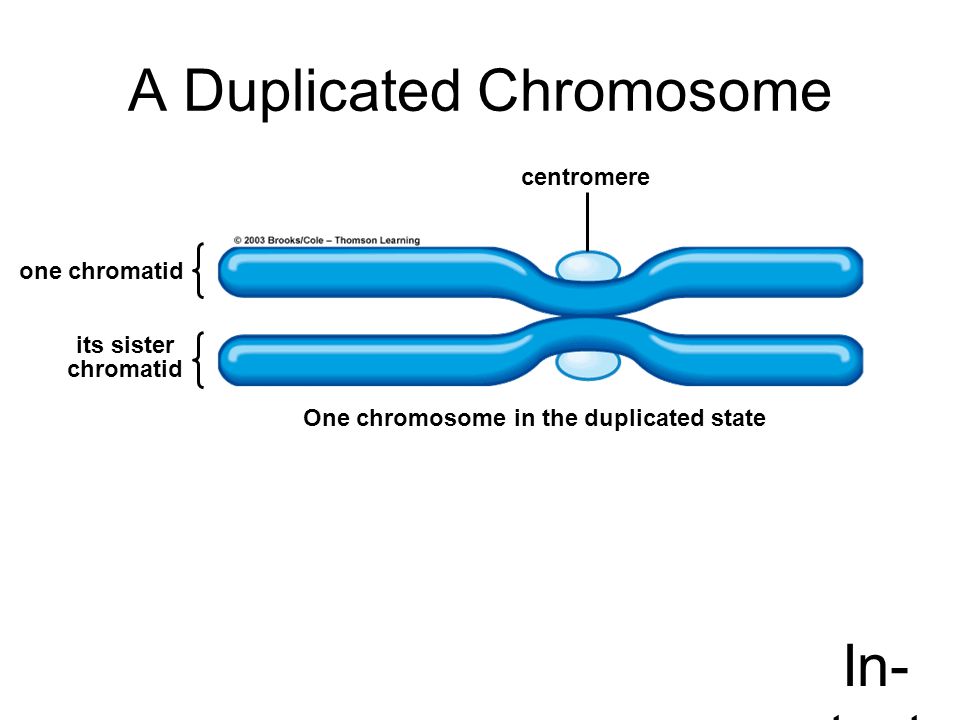
Sister chromatid
One of two attached members of a duplicated eukaryotic chromosome/BOTTOM
3
New cards
Centromere
Constricted region in a eukaryotic chromosome where sister chromatids are attached/MIDDLE
4
New cards
\
5
New cards
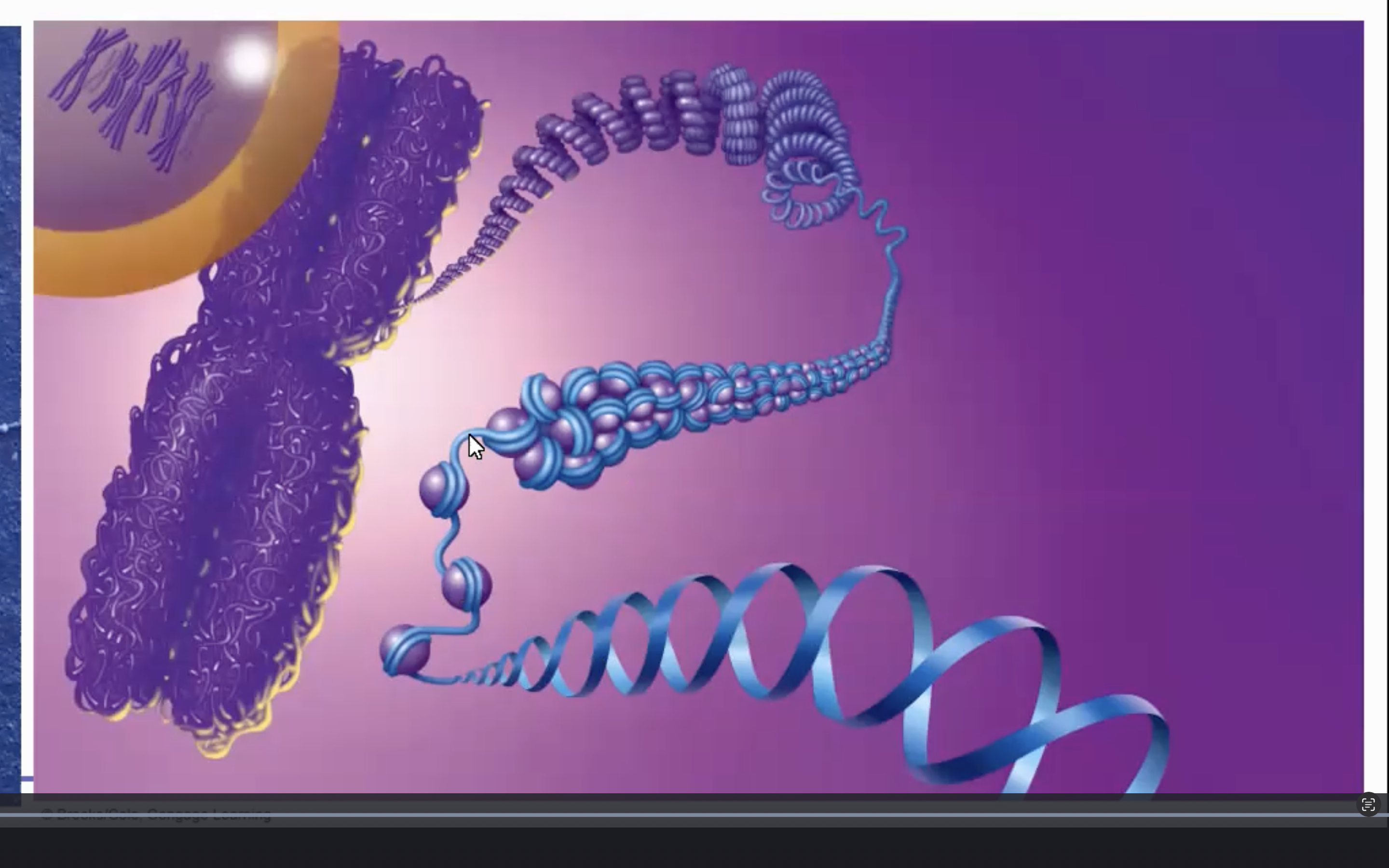
Nucleosome
• A length of DNA wound around a spool of histone proteins
6
New cards
How many chromosomes are in a human body cell
46/23pairs
7
New cards
Diploid
Cells having two of each type of chromosome characteristic of the species (2n)
8
New cards
haploid
a cell that contains a single set of chromosomes. The term haploid can also refer to the number of chromosomes in egg or sperm cells, which are also called gametes
9
New cards
autosomal chromosomes
Any chromosome other than a sex chromosome
• Paired chromosomes with the same length, shape, centromere location, and genes
• Paired chromosomes with the same length, shape, centromere location, and genes
10
New cards
sex chromosomes
Members of a pair of chromosomes that differ between males and females
11
New cards
karyotype
Image of an individual’s chromosomes arranged by size, length, shape, and centromere location
12
New cards
mutation
A permanent change in DNA sequence
13
New cards
Erwin Chargaff
A = T and C = G Proportions of A and G vary among species
14
New cards
Rosalind Franklin
▪ Discovered the basic structure of DNA by x-ray crystallography
15
New cards
Maurice Wilkins \n ▪ James Watson, and Francis Crick
▪ Built the first accurate model of a DNA molecule
16
New cards
DNA Molecule
Consists of two strands of nucleotide monomers
• running in opposite directions
• coiled into a double helix
• held together by hydrogen bonds between nucleotide
• running in opposite directions
• coiled into a double helix
• held together by hydrogen bonds between nucleotide
17
New cards
The double helix
a term used to describe the physical structure of DNA. A DNA molecule is made up of two linked strands that wind around each other to resemble a twisted ladder in a helix-like shape. Each strand has a backbone made of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate groups.
18
New cards
DNA nucleotide
A five-carbon sugar (deoxyribose)
• Three phosphate groups
• One nitrogen-containing base (adenine, thymine, guanine, or cytosine)
• Three phosphate groups
• One nitrogen-containing base (adenine, thymine, guanine, or cytosine)
19
New cards
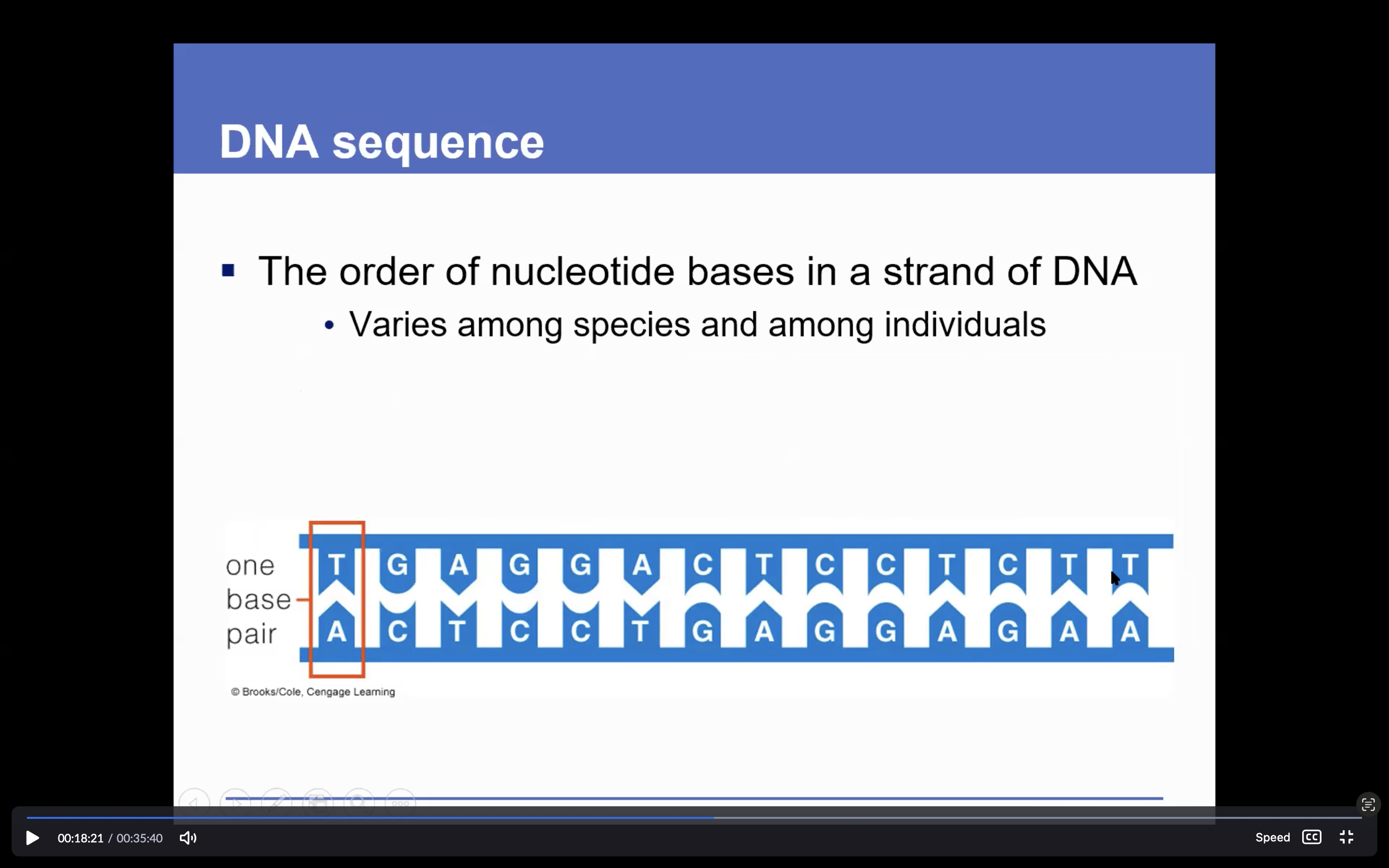
DNA sequence
The order of nucleotide bases in a strand of DNA
• Varies among species and among individuals
• Varies among species and among individuals
20
New cards
DNA Replication
Duplication of a cell’s DNA before cell division
▪ The double-helix unwinds
▪ The double-helix unwinds
21
New cards
DNA polymerase
• uses each strand as a template to assemble new, complementary strands of DNA
22
New cards
DNA ligase
• seals any gaps to form a continuous strand
23
New cards
DNA repair mechanisms
Proofreading by DNA polymerase corrects most base-pairing errors
24
New cards
Clones
Exact genetic copies of DNA or an organism
▪ Now a common practice in research and animal husbandry
▪ Now a common practice in research and animal husbandry
25
New cards
Reproductive cloning
Technology that produces genetically identical individuals
▪ Produced by somatic cell nuclear transfer
▪ Produced by somatic cell nuclear transfer
26
New cards
Somatic cell nuclear \n transfer (SCNT)
• Method of reproductive cloning in which nuclear DNA from an adult somatic cell is transferred into an unfertilized, enucleated egg
• Common practice for livestock breeders
• Common practice for livestock breeders
27
New cards
reasons of Therapeutic cloning
▪ To learn about molecular basis of genetic diseases
▪ To make replacement tissues or organs for people with fatal diseases
▪ Save endangered animals from extinction
▪ To make replacement tissues or organs for people with fatal diseases
▪ Save endangered animals from extinction
28
New cards
The Hershey Chase Experiments
the DNA of a virus needs to enter a bacterium to infect it.
29
New cards