Blood Bank Reagents
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Polyclonal antibodies
made from several different clones of B cells that secrete antibodies of different specificity
recognize multiple epitopes
mixture of IgM and IgG antibodies
Monoclonal antibodies
made from single clones of B cells that secrete antibodies of same specificity
recognize single epitope
one immunoglobulin class (IgG or IgM)
ABO typing
reagents are formulated to give strong reaction
testing performed in the immediate-spin (IS) phase
confirmation testing should check for expected ABO antibodies
D antigen typing
negative control ensures that false-positive result has not occurred (low protein reagent control)
false-positive agglutination can result from strong cold autoantibodies or protein abnormalities
Reagent RBCs
contain known antigens to confirm the presence of antibodies in pt serum or plasma
procedures: ABO serum testing, screening test, antibody ID
A1 and B cells
resuspended to 2-5% concentration
negative for Rh antigen
should not be used if red cells darken, agglutinated in vial, or show hemolysis
Screening cells
used in antibody screen (detection) tests for unexpected antibodies
each vial may be from single donor or two donors
polled cells can be used for donor testing, but only single donor vials are used in transfusion
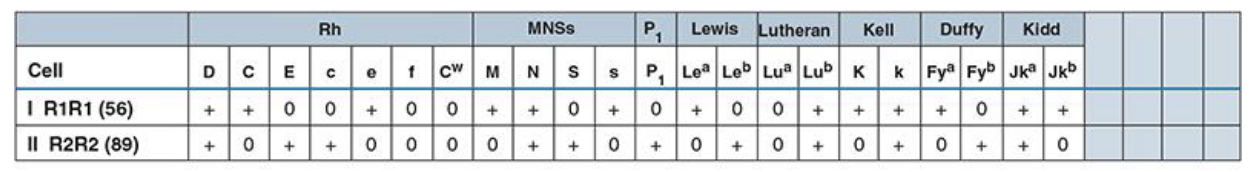
Panel cells
used for identifying antibodies in a procedure called an antibody panel
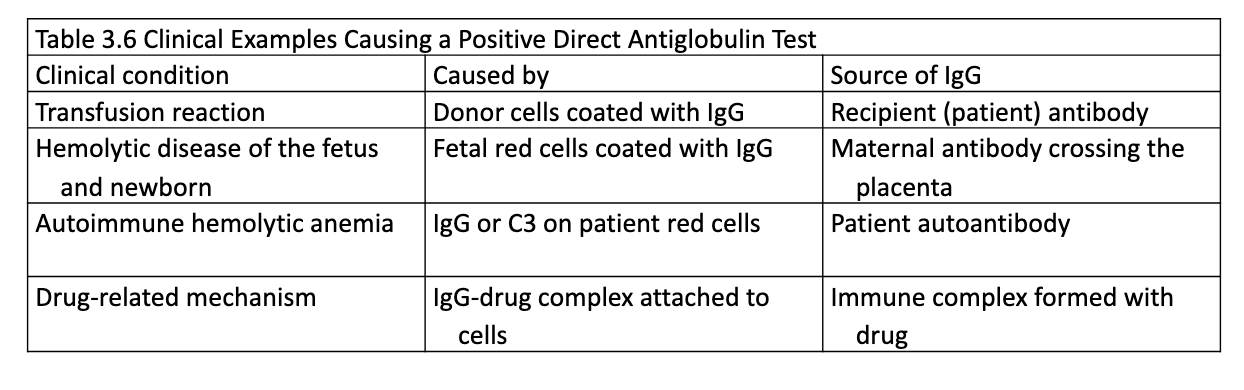
Antiglobulin Test
Commercial antibody with a specificity toward human globulins is used to agglutinate antibody-coated RBCs
Direct Antiglobulin Test (DAT)
detects IgG or complement bound to RBCs in vivo
AHG reagent added after RBCs have been washed
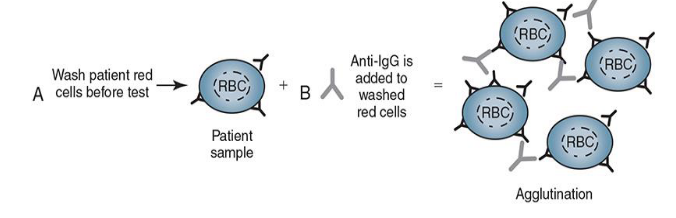
Positive DAT
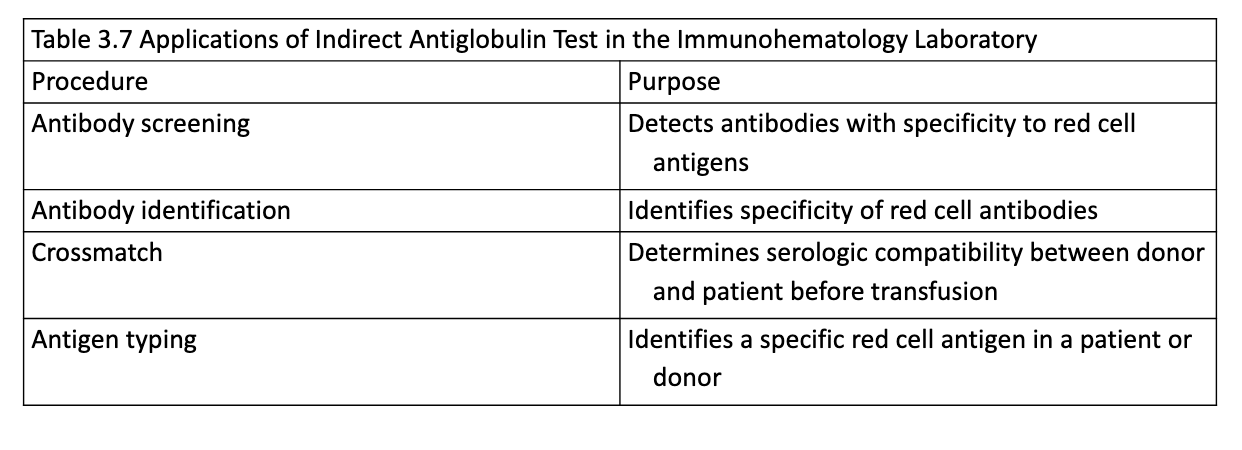
Indirect Antiglobulin Test (IAT)
detects IgG or complement bound to RBCs in vitro
antibodies are incubated at 37C with RBC antigens in vitro then washed and combined with AHG reagent to detect agglutination
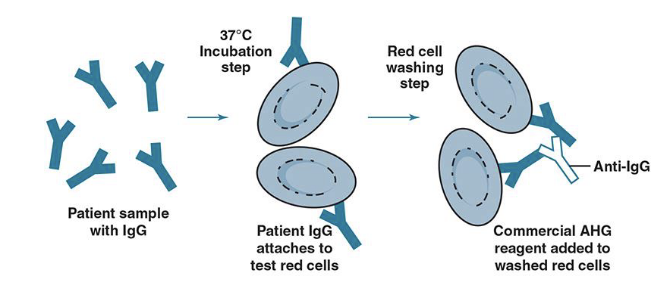
Application of IAT
Polyspecific AHG
contains both anti-IgG and anti-C3d antibodies
agglutination indicates that IgG or complement is coating RBCs
different DAT performed if positive
Monospecific AHG
Contains either anti-IgG or anti-C3b/C3d, but not both
Anti-C3b/C3d specifically detects complement proteins as a result of activation of the classical pathway
IgG-Sensitized Cells
when added to a negative AHG test, reagent should cause agglutination
Commercial reagents are type O RBCs prepared with IgG antibodies attached
False-negative results are caused by
failure to add AHG reagent
failure of AHG reagent to react
failure to wash RBCs adequately
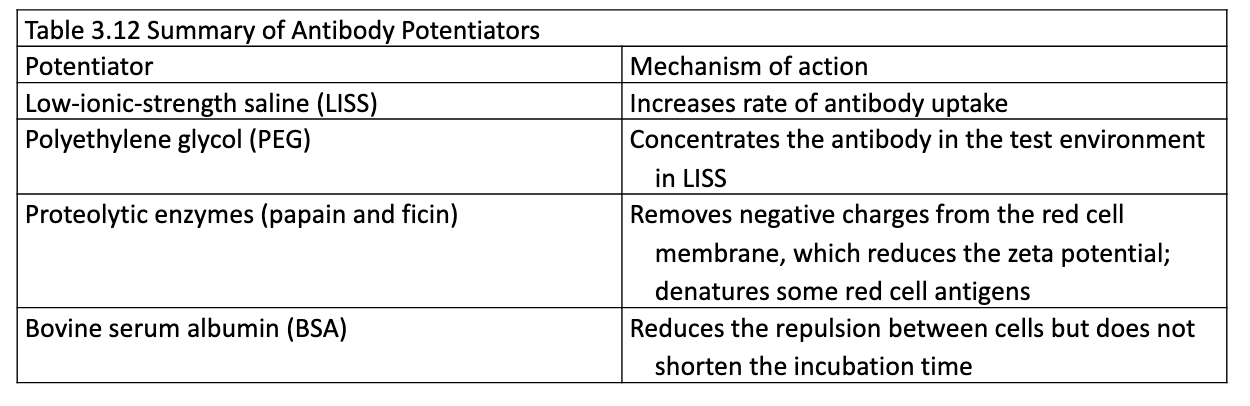
Potentiators
Reagents that enhance detection of IgG antibodies by increasing reactivity
Gel Technology
Uses dextran acrylamide gel particles to trap agglutinated cells
Microplate
microliter plate replaces test tubes, same principles
Solid Phase
Uses microplate wells with immobilized reagent
cells adhere to sides and bottom = positive
cells that settle to bottom = negative