The Brain
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
What regions of the brain makes up the brainstem?
Midbrain
Pons
Medulla oblongata
Cerebrum
Largest part of adult brain
conscious thoughts, intellect, memory
Cerebral cortex
Surface layer of gray matter of cerebrum
Gyrus/ gyri- elevations that increase surface area
Gyri separated by shallow depressions (sulcus/sulci) and deep grooves (fissures)
Diencephalon
Located under cerebrum and cerebellum
thalamus
Hypothalamus
Epithalamus
Thalamus
Relays and processes sensory info
Hypothalamus
Involved with emotions, autonomic functions, and hormone production
Epithalamus
Involved with melatonin
Pituitary gland
Connected to hypothalamus via infundibulum
Brainstem
Relays info between spinal cord and cerebellum and cerebrum
Midbrain
Processes sight and sound
Pons
Connects cerebellum to brainstem
Connects tracts, relay centers, and nuclei for somatic and visceral motor control
Medulla oblongata
Connects brain to spinal cord
inferior portion has a narrow central canal
Regulates autonomic functions- HR, BP, and digestion
Cerebellum
Second largest part of brain
Coordinates repetitive movements
Covered by gray matter (cerebellar cortex)
Embryonic development
Neural tube- develops into CNS
Prosencephalon- (forebrain)
telencephalon
Diencephalon
Mesencephalon- (midbrain)
Rhombencephalon- (hindbrain)
metencephalon
Myelencephalon
Telecephalon
Forms cerebrum and lateral ventricles
Diencephalon
Diencephalon and third ventricle
Mesencephalon
Midbrain and cerebral aqueduct
Metencephalon
Forms cerebellum, pons, and upper fourth ventricle
Myelencephalon
Forms medulla oblongata and lower fourth ventricle
Neurocoel
Neural tube encloses neurocoel.
Expands to form chambers (ventricles) lined with ependymal cells
Ventricles of the Brain
Cranial Meninges
Dura mater
Arachnoid mater
Pia mater
Dura mater
meningeal cranial dura- inner fibrous layer
Periosteal cranial dura- outer fibrous layer
Dural folds
Extensions of meningeal dura into cranial cavity
Contains collecting veins called dural venous sinuses that drain deoxygenated blood and CSF into internal jugular veins
Flax cerebrum
Separates cerebral hemispheres
Contains superior sagittal sinus and inferior sagittal sinus
Tentorium cerebelli
Separates cerebrum and the cerebellum
contains transverse sinus and straight sinus
Flax cerebelli
Separates the cerebellar hemispheres
contains occipital sinus
Arachnoid mater
Covers brain
Attaches to dura mater
Separated by subdural space
Subarachnoid space
Between arachnoid mater and pia mater
CSF fills the space
Pia mater
Attached to brain surface by astrocytes
Choroid plexus
Produces CSF
Removes waste products from CSF
Arachnoid vili
Extensions of arachnoid membrane through meningeal layer of dura mater into superior sagittal sinus
Arachnoid granulations
Large clusters of arachnoid vili
absorbs CSF into venous circulation
Internal jugular veins and vertebral veins
Removes blood from dural venous sinuses
Blood Brain Barrier
Isolates CNS from circulation
Formed by tight junctions
O2, CO2, steroids, prostaglandins, small alcohols can diffuse
Astrocytes regulate BBB by releasing chemicals that control the permeability of endothelium
Blood CSF barrier
Formed by ependymal cells connected by tight junctions
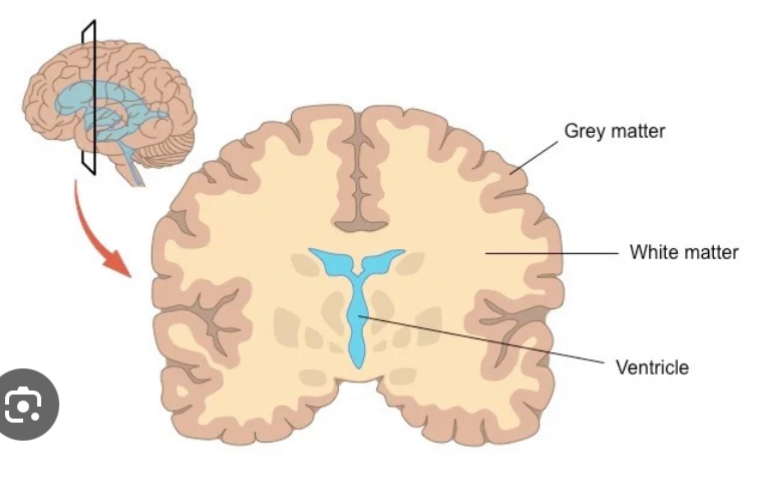
Gray matter in Cerebrum
In cerebral cortex and basal nuclei
White matter in cerebrum
Seep to cerebral cortex and around basal nuclei
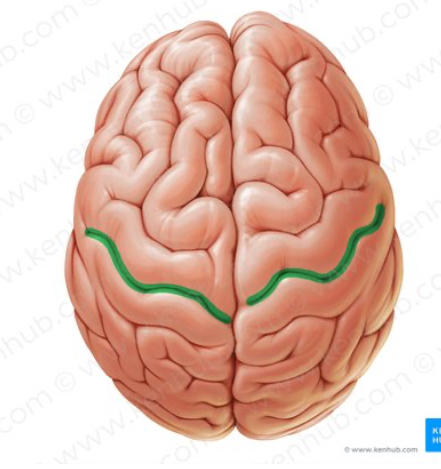
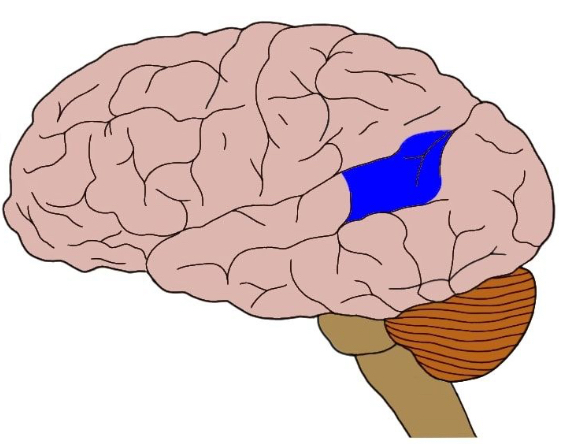
Central sulus
Divides the anterior frontal lobe from the posterior parietal lobe
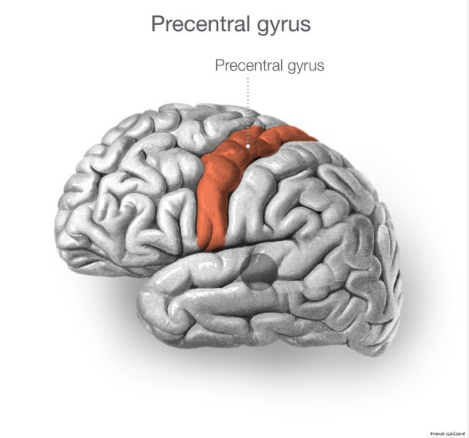
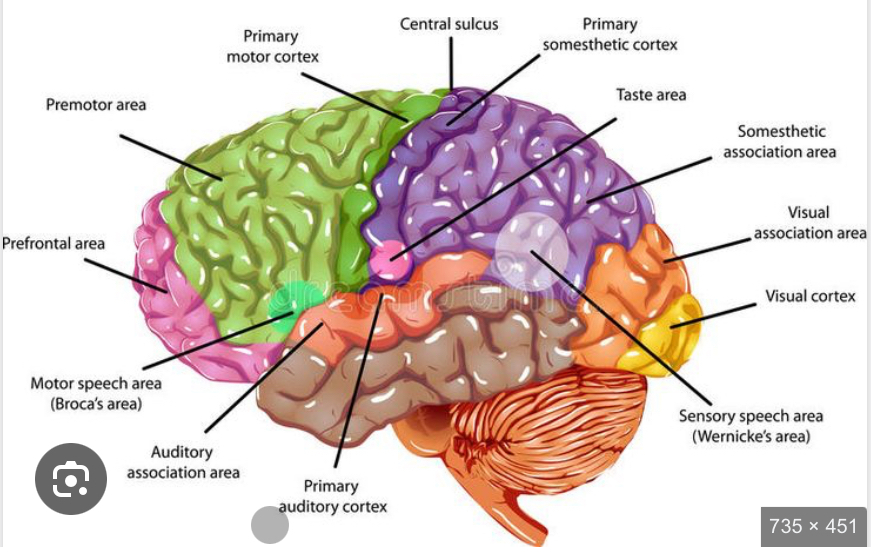
Precentral gyrus
Forms anterior border of central sulcus of frontal lobe
directs voluntary movements
Primary motor cortex is the surface
→ pyramidal cells are the neurons of the primary motor cortex
Postcentral gyrus
Forms posterior border of central sulcus of parietal lobe
receives somatosensory info (touch, pressure, pain, vibration, taste, temp)
Primary somatosensory cortex- surface of postcentral gyrus
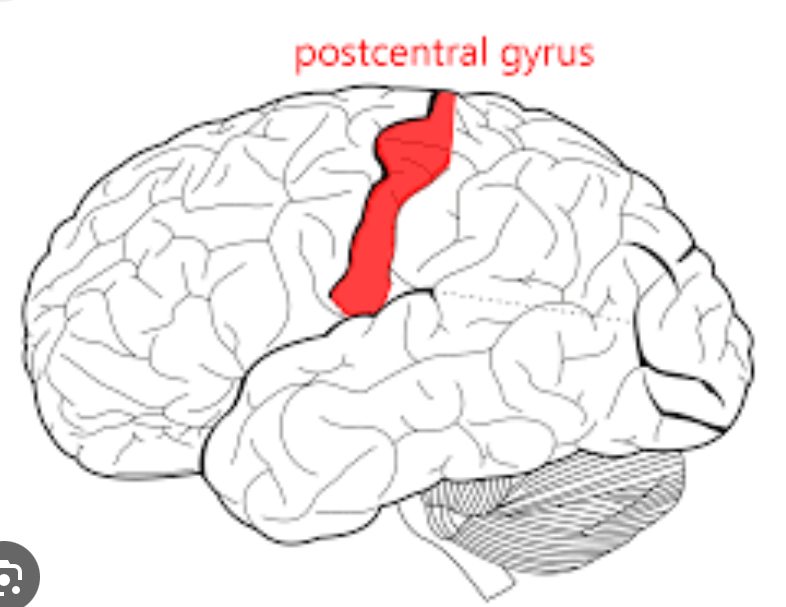
Lateral sulcus
Separates the frontal lobe form temporal lobe
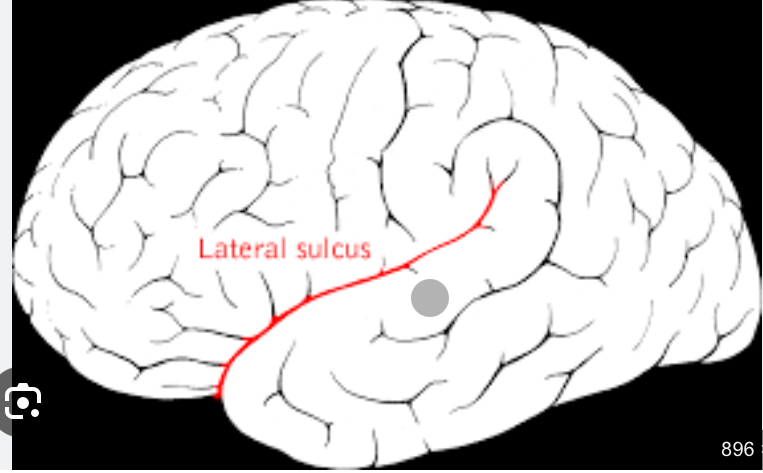
Insula of Cortex
Lies medial to lateral sulcus
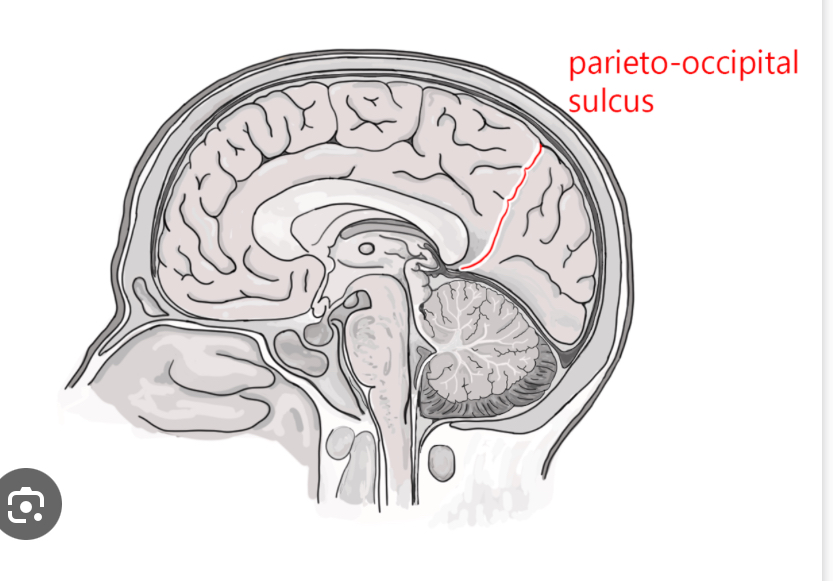
Parieto-occipital sulcus
Separates parietal lobe from occipital lobe
Premotor cortex
Anterior to the precentral gyrus
Controls learned, repetitious, patterned motor skills
Also called somatic motor association area
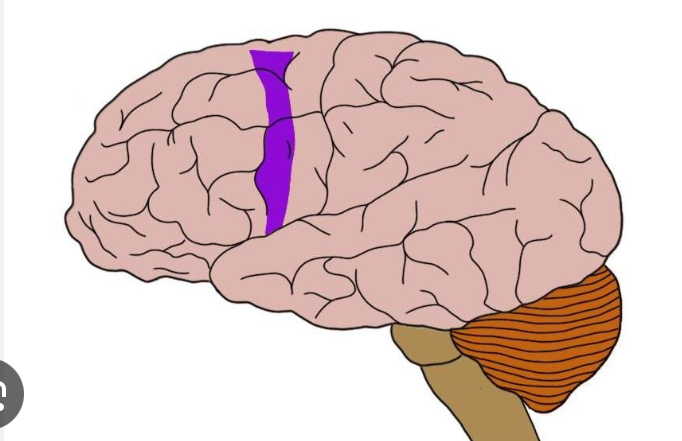
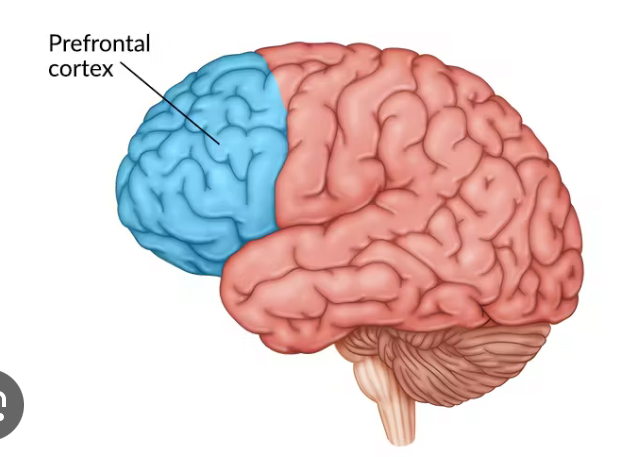
Prefrontal cortex
Most complicated
coordinates info from sensory association areas
Performs abstract intellectual activities
Intellect, recall, personality
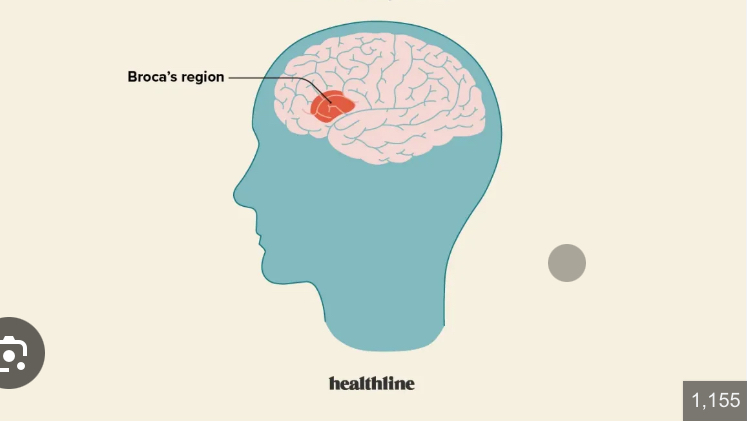
Broca’s Area
Anterior to inferior region of premotor area
Directs muscles of tongue
Speech area
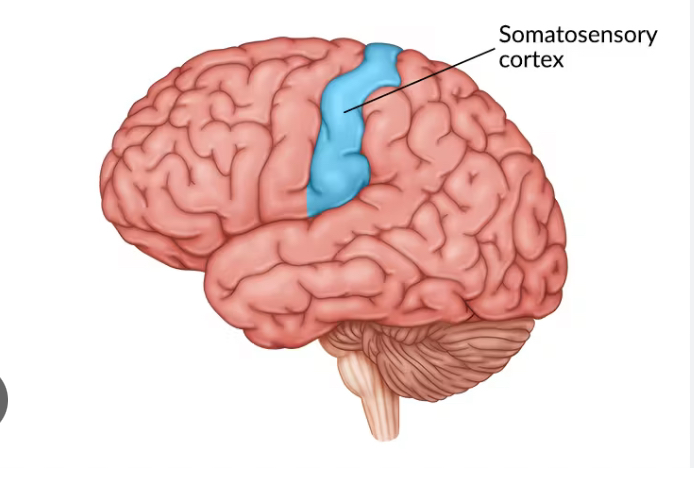
Primary somatosensory cortex
Receives somatic sensory info and is capable of spatial discrimination
Wernicke’s area
Understanding written and spoken language
Left hemisphere
Brain regions
Limbic System
Involved in emotional state, linking intellectual functions with unconscious and autonomic functions of brain stem and memory storage
What is the limbic lobe?
Cerebrum
cingulate gyrus
Dentate gyrus- hyppocampus storage and retrieval of long term memory
Parahyppocampus gyrus
Amygdala
What is in the Diencephalon?
Thalamus and hypothalamus
What is hemispheric lateralization?
Functional differences between the left and right hemispheres
What is the left hemisphere responsible for?
Reading, writing, math, logic
What is the right hemisphere responsible for?
Analyzes sensory info
Recognizes faces and voices
Insight, visual-spatial skills, artistic skills
What is an EEG?
Observes electrical patterns of brain
Alpha waves
Normal resting
Beta waves
Accompany intense concentration
Theta waves
Seen in children and frustrated adults
Delta waves
Occurs in deep sleep
Association fibers
Interconnect cortical areas within the same hemisphere
Arcuate fibers
Interconnect gyri within a lobe
Short fibers
Longitudinal fascicle
Interconnects the frontal lobes with other cerebral lobes
Longer bundles
Commissural fibers
White matter of Bands of fibers connecting the two hemispheres
Corpus callosum
White matter that Connects the two hemispheres
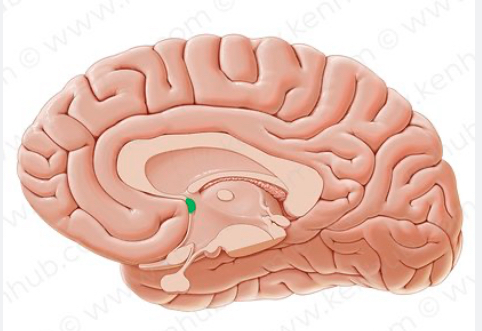
Anterior commissaries
White matter that connects hemispheres
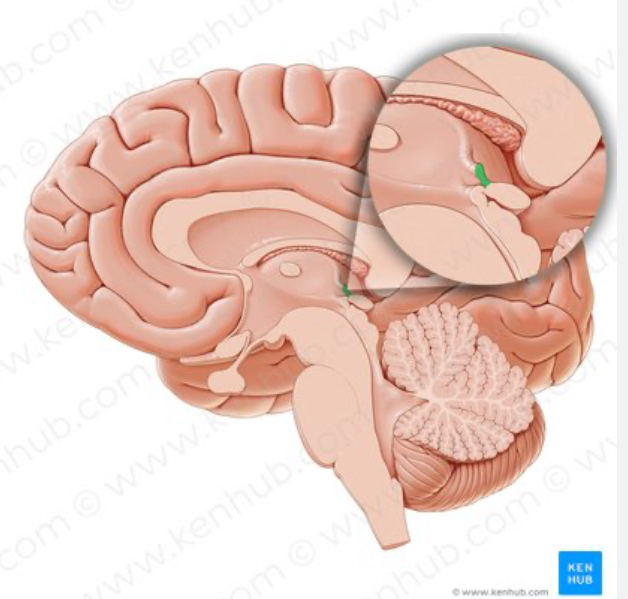
Posterior commissure
White matter that connects the hemispheres
Projection fibers
White matter that links cerebral cortex to Diencephalon, brainstem, cerebellum, and spinal cord.
Passes through Diencephalon
Internal capsule
All ascending and descending projection fibers
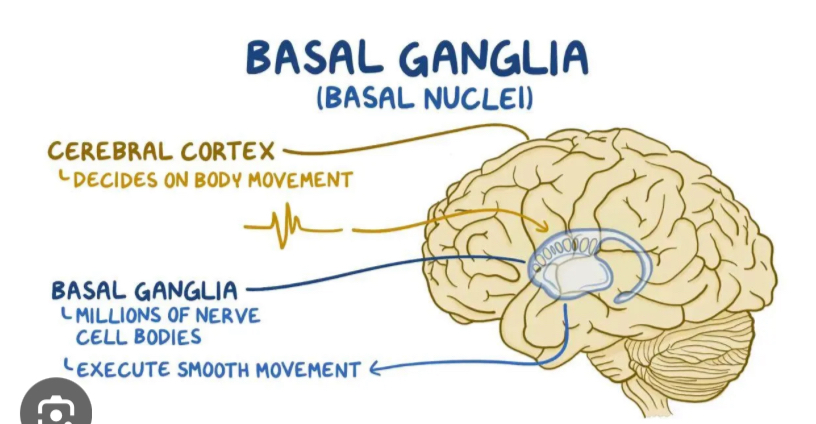
Basal nuclei
Masses of gray matter embedded in the white matter of the cerebrum
Directs subconscious activities
What are the parts of the basal nuclei?
caudate nucleus
Lentiform nucleus→ putamen and globes pallidus
Claustrum
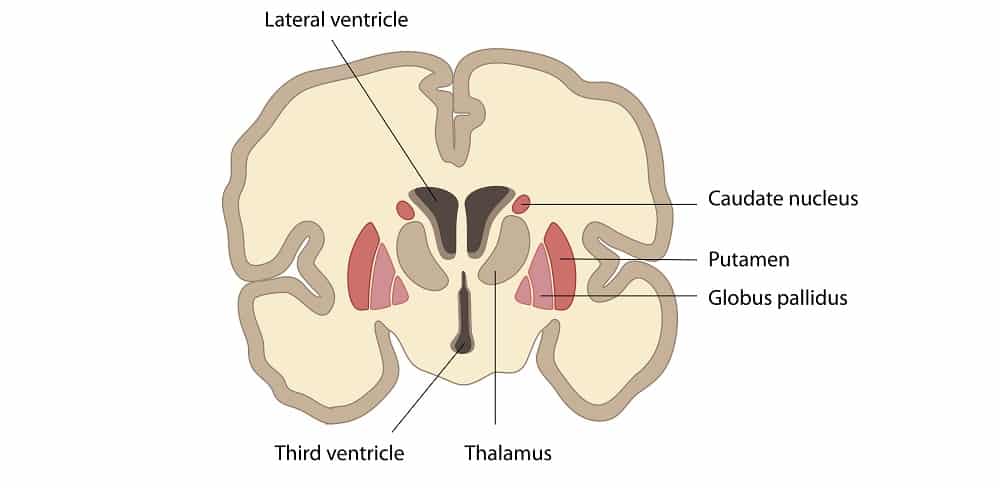
What causes the symptoms of Parkinson’s?
Increased activity of basal nuclei
What is the function of the basal nuclei?
Subconscious control of skeletal muscle and coordination of learned movement patterns (walking, lifting)
What are the parts of the Diencephalon?
Epithalamus, thalamus, hypothalamus
What is the function of the Epithalamus?
Contains pineal gland which secretes melatonin for sleep
What is the function of the thalamus?
Relays ascending sensory info
Where is the third ventricle located?
Separates left and right sides of thalamus
What are the parts of hypothalamus?
mammillary bodies
Infundibulum
Tuber cinereum
What do mammillary bodies do?
Controls reflex eating movements (licking, swallowing)
What does the infundibulum do?
Connects hypothalamus to pituitary gland
What does the tuber cinereum do?
Lies between infundibulum and mammillary bodies
Produces hormones that affect pituitary gland
What does the hypothalamus secrete?
ADH and oxytocin
Regulates body temp
Control satiety and thirst
What are the corpora quadrigemina?
Two pairs of sensory nuclei in midbrain
Superior colliculi function
Receives visual input from lateral geniculate bodies of thalamus
Inferior colliculi function
Receives auditory signals form pons and medulla oblongata and passes through medial geniculate body of thalamus
Red nucleus function
Receives info from cerebrum and cerebellum and is responsible for subconscious muscle adjustments
Substantial migration function
Releases dopamine and inhibits activity of basal nuclei
Cerebral peduncles
Contains descending fibers to cerebellum and motor command fibers
RAS increases alertness and attention
Pons contains
Motor and sensory nuclei of cranial nerves V, VI, VII, VIII
involved in respiration→ apneustic center and pneumotaxic center: processes info in respiratory rhythm centers of medulla oblongata
Transverse pontine fibers
Axons link nuclei of pons with opposite cerebellar hemisphere
Reticular formation
Gray and white matter with embedded nuclei
Regulates autonomic functions
Medulla oblongata cranial nerves
VIII, IX, X, XI, XII
Gracile nucleus and cuneate nucleus
Pass somatic info to thalamus
Decussation of pyramids
Crossing over site of gracile nucleus and cuneate nucleus
Solitary nuclei
Receives visceral sensory info from spinal and cranial nerves
Inferior olivary complex
Relay info to the cerebellar cortex
Folia
Folds in cerebellar cortex
Anterior and posterior lobes of cerebellum is separated by
Primary fissure
Vermis of the cerebellum
Separates cerebellar hemispheres at midline