Extracting metals and equilibria
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
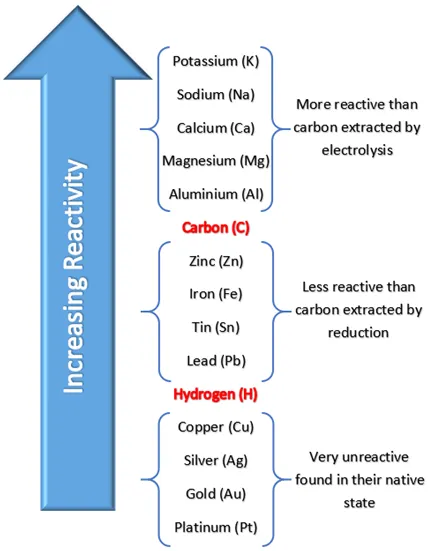
Reactivity series image on the other side
* Bacteria grown on low grade ore and produces a solution containing metal ions called a leachate
* Metal extracted from leachate by displacement using scrap iron and purified by electrolysis
* no harmful gases
* Doesn’t require high temperature
* Very slow
What is phytoextraction?
Plants are grown that absorb metal compounds into its roots
Plant concentrates metal compounds in shoots and leaves
Plants burned and from the ash the metal is extracted
* Less damage to landscape
* Can extract metals from contaminated soil
* more expensive than mining
* Plants depend on weather
How can we extract some metals using carbon?
You can heat some metals with carbon. If they are less reactive than carbon they will be displaced by it so they will no longer be in a compound. This can be done using a blast furnace.
what is an electrode?
A solid electrical conductor through which and electric current enters or leaves an electrolytic solution
What is the positive electrode called?
Anode
What is the negative electrode called?
Cathode
What kind of ions do anodes attract?
Anions (negative ions)
What kind of ions do cathodes attract?
Cations (positive ions)
What is oxidation?
Gains oxygen
Loss of electrons
What is reduction?
Loss of oxygen
Gain of electrons
What happens to cations at the cathode during electrolysis?
Metal ions (which are always cations) are always attracted to the negative cathode where they gain electrons and because neutral metal atoms
What happens to non-metal ions at the anode in electrolysis?
Non-metal ions (Which are always anions) are always attracted to the positive anode where they lose electrons to become neutral atoms
What is produced at the cathode in electrolysis (if in solution)?
Metals below hydrogen in the reactivity series are discharged (produced)
Metals above hydrogen are NOT discharged and hydrogen is produced instead
What is produced at the anode in electrolysis (if in solution)
Chloride, bromide and iodide ions give chlorine, bromine and iodine respectively
Solutions containing other ions give oxygen gas instead
What happens if the substance electrolysed is molten instead of a solution?
The metal ion and non-metal will stay the same and hydrogen and oxygen will never be produced.
What are reactions where both oxidation and reduction reactions occur?
Redox reactions
When is electrolysis used?
When a metal is more reactive than carbon, it cannot be displaced by it. Because of this we need to use electricity to separate a metal from it’s compound
Why does resistance to corrosion increase as you go down the reactivity series?
The metals get less reactive, so the ones at the bottom will not react with oxygen or water at all
Disadvantages of extracting metals?
Uses up limited resources
Uses a lot of energy
damages environment
What are the advantages and disadvantages of recycling?
Metal ores last longer
Less energy is needed
Fewer quarries and mines are needed
Less land is needed
Used metal items must be collected and transported to recycling centre
Different metals must be removed from used items and sorted
Recycling saves different amounts of energy depending on the metal
What are the stages of a life-cycle assessment?
Obtaining raw materials
Manufacturing the product
Using the product
Disposing of the product
What data is needed for a life-cycle assessment?
The use of energy
The release of waste materials
Transport and storage
If the raw materials are renewable or not
If any part of the product can be recycled
How the product is disposed of