Biology Lab Exam 1 professor Hughes
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms

Cell Counter Slide


Transfer Pipette

Micropipette

Micropipette tip


Microcentrifuge tube

Slide

Cover slip

Forceps

Erlenmeyer flask


Beaker


Ocular Lens

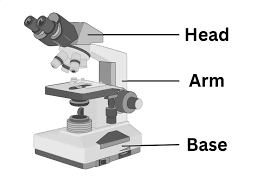
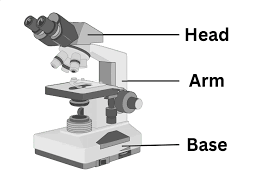
Arm

fast focusing
Coarse Adjustment Knob


precise adjustments
Fine Adjustment


Rotating/Revolving Nosepiece


Objective Lenses

Low Power
This objective lens provides the lowest magnification, 4 x

Stage


Mechanical Stage


Iris Diaphragm of the Condenser
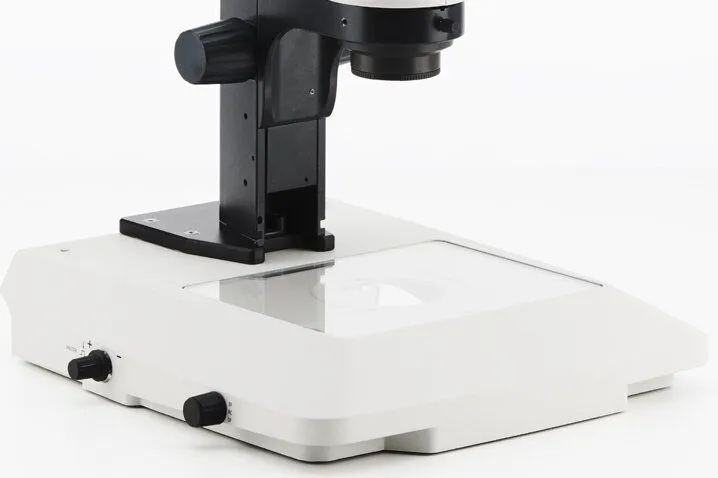


Base
Stage
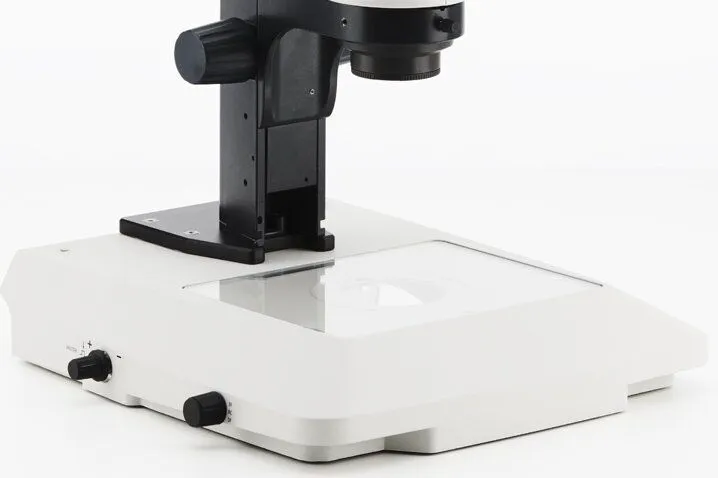

Light Source/ illuminator

Condenser Lens

Always carry the microscope by: the arm with the other hand supporting the base

Substage Light
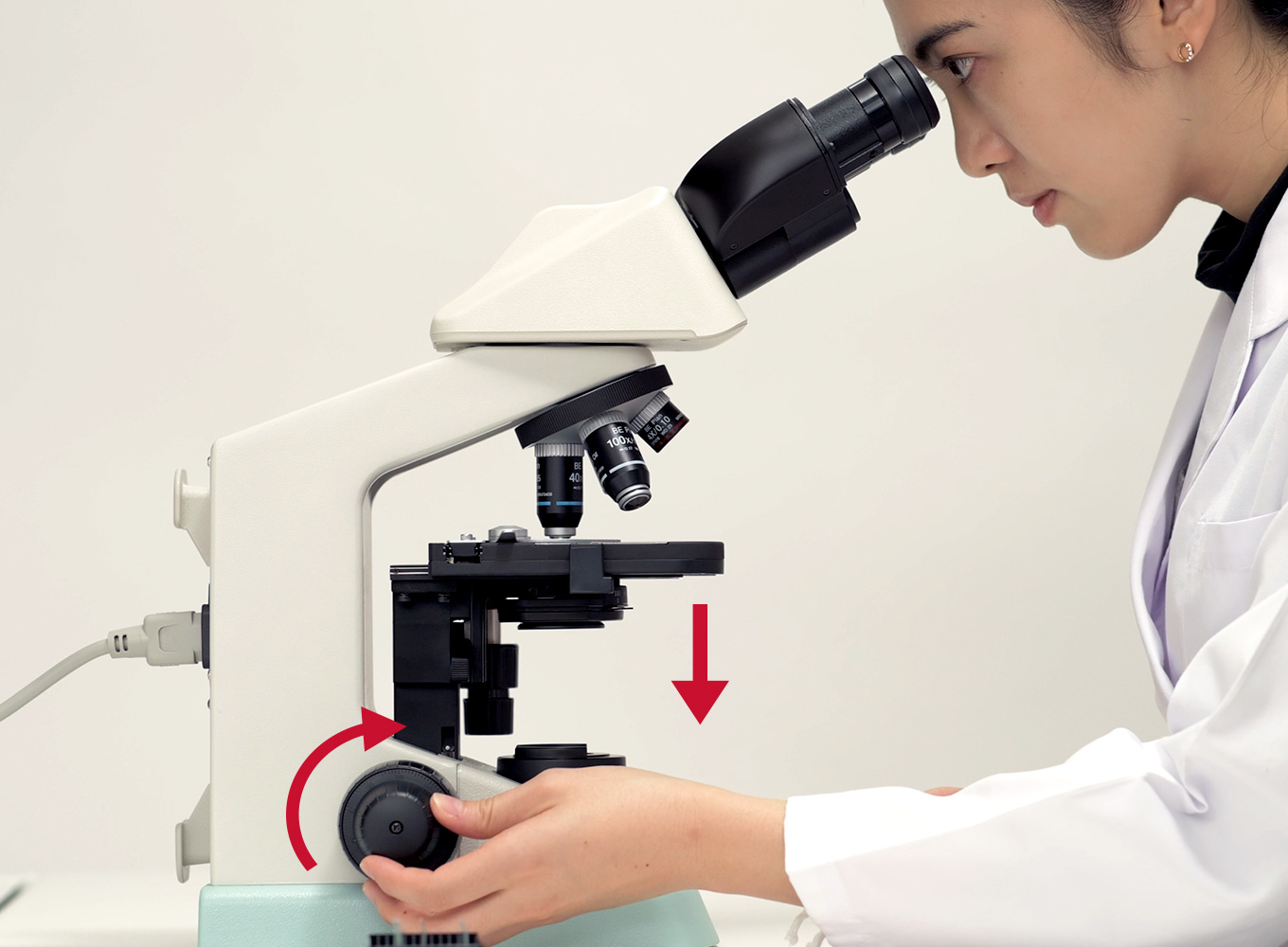


Adjustment Knob
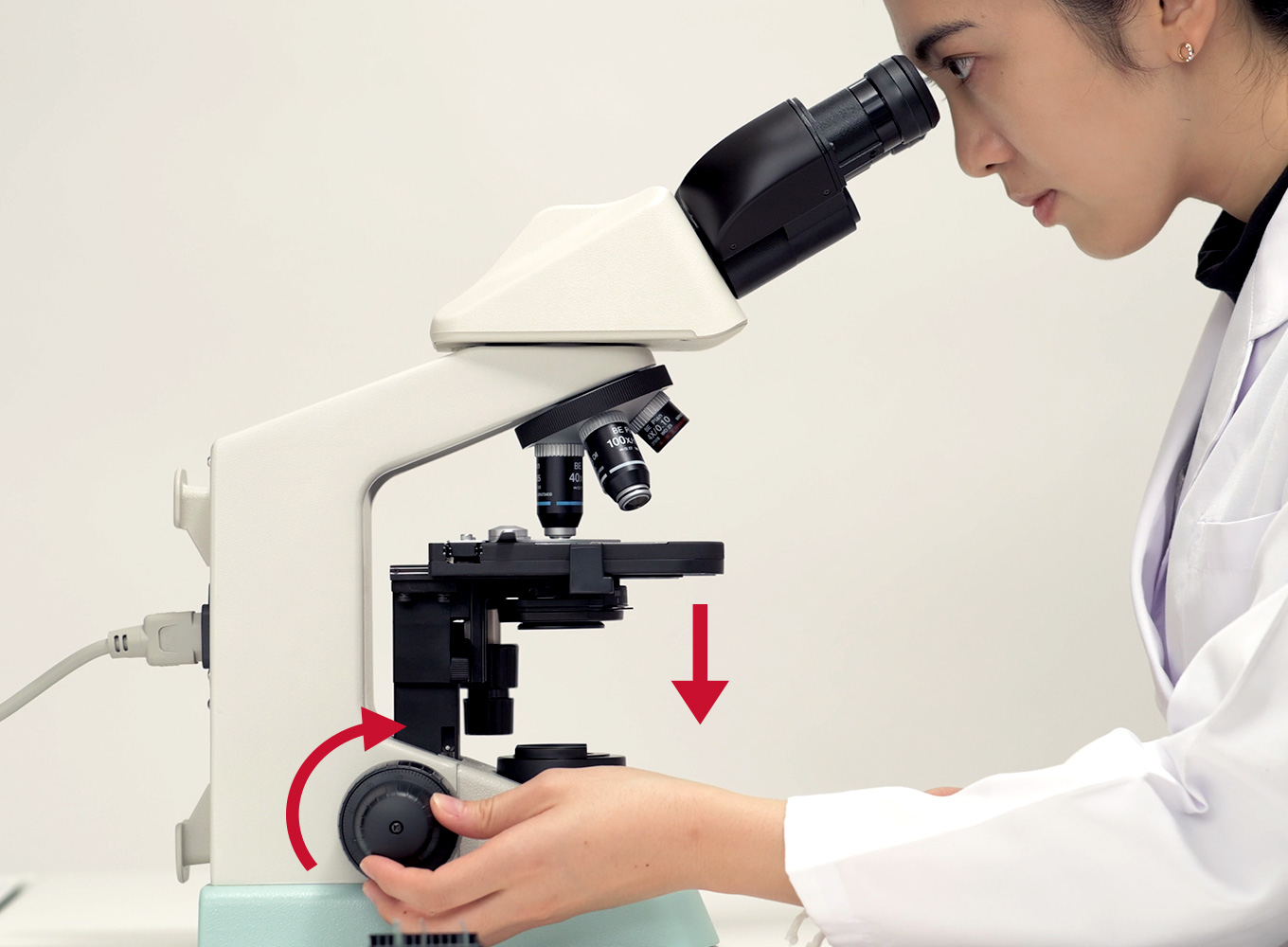


Light Control Knob


Mechanical Stage Control Knobs


What is used to clean the microscope after use?
Lens Paper, if using oil, use lens cleaner.

Where should the stage be moved after use?
It should be lowered and returned to the lowest position. This prevents damage to the objectives and ensures safe storage.
What objective should be in place after use?
4X The lowest power objective lens should be in place after use. This helps prevent damage to the slides and objectives.
There are four objectives but only THREE are used in lab
4x (also called scanning lens), 10x, 40x. There is an ocular magnification of 10x for every microscope in lab, thus the total magnification is found by multiplying the objective magnification times 10.
Cheek cells
What type of stain is used?
A methylene blue stain is used to highlight the cheek cells under a microscope, making the nuclei more visible.
● Colored thread slide
○ How does this demonstrate depth of field and working distance?
The colored thread slide demonstrates that as magnification increases, the depth of field decreases, requiring careful focusing to see all layers of the specimen clearly. And the working distance also decreases with higher magnification, affecting how close the lens must be to the slide.
● Letter "e"
○ If the stage moves right, what direction will the specimen move when viewed through the microscope?
The specimen will move left.
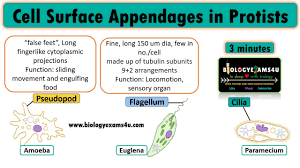
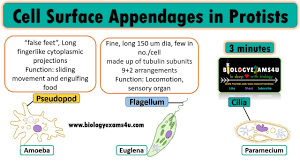
What are three main forms of movement or locomotion for protists? (cilia, flagellum, and pseudopodia)
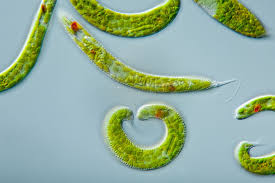
Three main forms of movement for protists include: cilia, flagella, and pseudopodia. Cilia are short hair-like structures that beat in a wave; flagella are longer whip-like structures that propel the cell; pseudopodia are temporary projections used for movement and feeding that allow the protist to "crawl”.

Algea:
Closterium

Algea:
Volvox
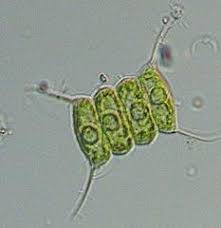
Algea: (connected)
Scenedesmus
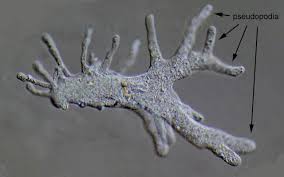
Protists:
Amoeba (pseudopodia)
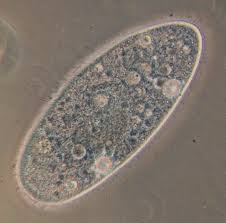
Protists:
Paramecium (cilia)
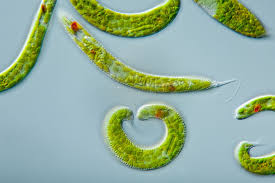
Protists: (red dot)
Euglena (flagellum)
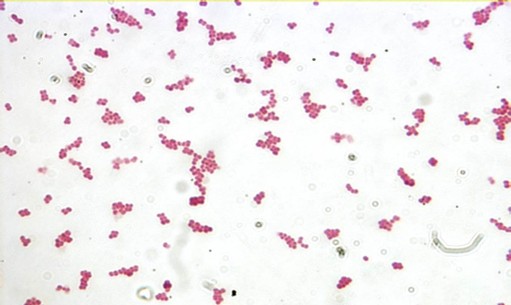
Coccus
spherical
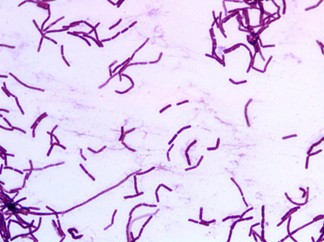
Bacillus
rod- shaped
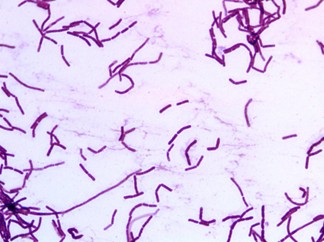
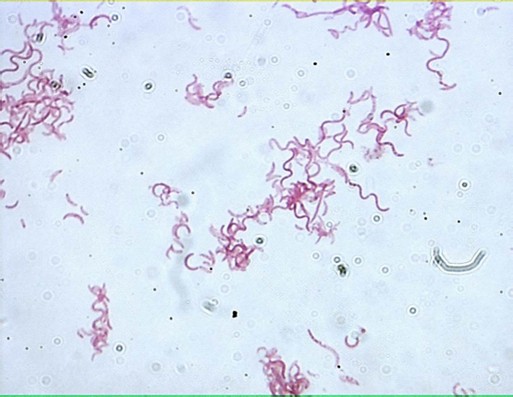
Spirillum
corkscrew- shaped
Prokaryotic cells
Consists of Bacteria and Archaea.
● Prokaryotic cells are smaller in size, less complex, and have no membrane-bound organelles.
● Outer covering of prokaryotic cells: Cell wall surrounding the plasma membrane.
Eukaryotic cells
Consists of protists, fungi, plants, and animals.
● Eukaryotic cells are generally larger, have a well-defined nucleus that is separated by a double membrane from the cytoplasm, and contain many specialized membrane-bound organelles.
● Outer covering of eukaryotic cells: Cell membranes surrounding the cytoplasm.
Differentiate between methylene blue and Trypan blue. Which is used for cell counting? Which is used for staining cheek cells?
Methylene blue is a dye used for staining cheek cells, while Trypan blue is used for cell counting, specifically to assess cell viability.
What designates a control, experimental, or variable flask?
In experiments, a control flask contains no variables, while an experimental flask contains one or more variables for testing. A variable flask is used to manipulate specific factors to observe their effects.
A
Eudorina
Z
Volvox
R
Replication
What is diffusion?
Diffusion is the flow or transport of molecules or substances down their concentration gradient.
What is osmosis?
When water diffuses across the cell membrane from an area of high water concentration (low solute concentration) to an area of low water concentration (high solute concentration).
Active transport
Active transport requires ATP for the movement of molecules against the concentration gradient from a low to high concentration.
Passive transport
Passive transport does NOT require ATP for the transport of molecules down the concentration gradient from a high to low concentration.
Plasmolysis
Plasmolysis is the shrinking of the cytoplasm of plant cells away from the cell wall. This occurs when plant cells are placed in solutions with very high solute concentrations (i.e. hypertonic solutions) causing the water inside the cell to flow outward.
pond water, 10% salt water, Distilled water.
Pond water: Isotonic
10% salt water: Hypertonic solution causing plasmolysis in plant cells.
Distilled water: Hypotonic solution.
Isotonic, Hypertonic,Hypotonic.
Isotonic solutions maintain equal concentration, Hypertonic solutions have a higher solute concentration, and Hypotonic solutions have a lower solute concentration.
What is the scientific method?
The scientific method is a systematic process used for experimentation and observation, involving steps such as asking questions, forming hypotheses, conducting experiments, analyzing data, and drawing conclusions.
What is a null hypothesis?
A null hypothesis is a statement that there is no effect or no difference, positing that any observed effect is due to random chance. It serves as the basis for statistical testing.
What is an alternate hypothesis?
An alternate hypothesis is a statement that contradicts the null hypothesis, proposing that there is a significant effect or relationship in a study. It suggests a difference or change due to the independent variable being tested.
What is replication?
Repeating a process or experiment to verify results or understand biological mechanisms.
What are the controlled variables in your algae experiment?
Culture medium (Bold Basal Medium) and nutrients; light intensity (200-700 foot candles) and duration (12:12); temperature (22 ̊ C)
What are the independent variables in your experiment?
type of Algea
What are the dependent variables?
Average number of cells, colony size, cells per colony, etc.
What is your research question?
What are the differences in cellular growth (= population size) and
colonial characteristics of Eudorina and Volvox under similar conditions?