ES 3033 Exam 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/147
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:20 PM on 12/7/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
148 Terms
1
New cards
natural selection
differential survival/reproduction within a population that result from interactions with the environment
2
New cards
adaptation
heritable trait of an organism that has evolved over time by natural selection; contributes to fitness of an organism
3
New cards
fitness
measurement of the contribution of an individual to future generations
4
New cards
evolution
change in gene frequency over time
5
New cards
what caused the peppered moth to change color patterns?
industrial melanism
6
New cards
typica peppered moth

7
New cards
carbonaria peppered moth

8
New cards
what is evidence for evolutionary change?
fossil records, morphological convergence, morphological divergence, domestication, antibiotic resistant bacteria, GA cockroaches
9
New cards
simple organisms are found in _____ rocks, complex organisms are found in _____.
oldest; newer
10
New cards
what is morphological convergence?
independent evolution of similar morphological adaptations to similar environmental challenges in unrelated organisms
11
New cards
sharks/dolphins and birds/butterflies are examples of morphological ________.
convergence
12
New cards
what is morphological divergence?
over time, populations diverge in morphological traits that characterize their species; change from common ancestor body form; may or may not result in speciation.
13
New cards
the galapagos finches' beaks are an example of morphological _____.
divergence
14
New cards
what is artificial selection?
a process by which humans use animal/plant breeding to selectively develop particular traits or characteristics by choosing and controlling individual reproduction.
15
New cards
what are the requirements for evolution?
population, heritable traits, genetic variation, selective pressure, and time
16
New cards
what theory did jean baptiste lamarck come up with?
acquired characteristics-modifications produced in an individual as a result of an environmental influence
17
New cards
what is a genotype?
genetic makeup of an organism
18
New cards
what is a phenotype?
the physical/chemical expression of characteristics
19
New cards
what are alleles?
one of two or more alternate forms of a gene
20
New cards
what is the dominant allele?
the expressed allele; denoted with an uppercase letter
21
New cards
what is the recessive allele?
the masked allele; denoted with a lowercase letter
22
New cards
what does homozygous mean?
two identical alleles of a gene (AA or aa).
23
New cards
what does heterozygous mean?
two different alleles of a gene (Aa_
24
New cards
what does the hardy-weinburg principle state?
under certain conditions of stability, both allele frequencies and genotypic ratios remain constant from generation to generation in sexually reproducing populations
25
New cards
what are some conditions of stability?
a large population reduces genetic drift, no mutations, no immigration, no selective pressure, random mating
26
New cards
what is genetic drift?
change in allele frequencies due to chance or random events
27
New cards
what is a recessive disorder?
2 copies of an abnormal recessive allele must be present in order for disease or trait to develop
28
New cards
in hardy-weinburg, how are recessive disorders characterized?
q^2
29
New cards
in hardy-weinburg, how are carriers characterized?
2pq
30
New cards
in hardy-weinburg, what does p represent?
frequency of the dominant allele in the population
31
New cards
in hardy-weinburg, what does q represent?
frequency of the recessive allele in the population
32
New cards
in hardy-weinburg, what does p^2 represent?
frequency of homozygous dominant individuals in a population
33
New cards
in hardy-weinburg, what does 2pq represent?
frequency of heterozygous individuals in a population
34
New cards
in hardy-weinburg, what does q^2 represent?
frequency of homozygous recessive individuals in a population
35
New cards
what is the hardy-weinburg equation?
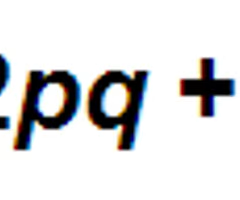
36
New cards
what is directional selection?
mean shifts
37
New cards
what is an example of directional selection?
galapagos finch beaks
38
New cards
what is stabilizing selection?
the mean does not change
39
New cards
what is an example of stabilizing selection?
human birth weight
40
New cards
what is disruptive selection?
the mean does not change
41
New cards
what is an example of disruptive selection?
mocker swallowtail butterflies
42
New cards
in mocker swallowtail butterflies, males are ____ and females are ____
monomorphic; polymorphic
43
New cards
which selection has bimodal distribution?
disruptive
44
New cards
what is the biological species concept?
a species is a group of organisms that can potentially interbreed with one another to produce vital, fertile offspring.
45
New cards
what are examples of prezygotic mechanisms of reproductive isolation?
habitat, temporal, behavioral, gametic, mechanical
46
New cards
what are examples of postzygotic mechanisms of reproductive isolation?
hybrids do not develop or are sterile
47
New cards
what is speciation?
occurs as a subset of an original population, and becomes reproductively isolated from other subsets of the original population by some mechanisms of reproductive isolation
48
New cards
what is the most common form of speciation?
allopatric speciation
49
New cards
which form of speciation needs a physical barrier such as mountains, deserts, glaciers?
allopatric speciation
50
New cards
which form of speciation involves populations getting separated by habitat changes, and may interbreed but develop differently?
parapatric speciation
51
New cards
which form of speciation involves reproductive isolation that occurs in the original population with no physical barrier?
sympatric speciation
52
New cards
what is polyploidy?
having more than two full sets of chromosomes.
53
New cards
Is polyploidy more common in plants or animals?
plants
54
New cards
polyploidy diagram
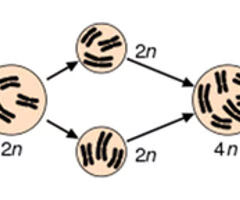
55
New cards
what is homeostasis?
regulation of internal environment, maintenance of appropriate conditions when faced with a changing external environment
56
New cards
temperature, pH, ion balance, water balance, dissolved oxygen, and glucose concentration are all examples of factors that are regulated by:
homeostasis
57
New cards
_________ is used to maintain conditions at a set point or optimal range
negative feedback
58
New cards
what is thermoregulation?
maintenance of an internal temperature within appropriate limits
59
New cards
the temperature coefficient can be denoted by
Q10
60
New cards
what is temperature coefficient?
measure of the rate of change of a system due to an increase in temperature by 10°C
61
New cards
what is the heat budget equation?
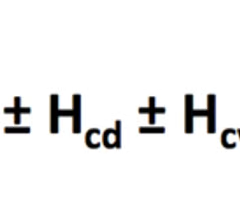
62
New cards
what is "Hm" in the heat budget equation?
metabolic heat
-generated internally
-oxidation of carbs, fats, proteins
-generated internally
-oxidation of carbs, fats, proteins
63
New cards
what is "Hcd" in the heat budget equation?
conduction
-direct physical contact
-temperature gradient
-direct physical contact
-temperature gradient
64
New cards
what is thermal conductivity?
measure of the ability of a material to conduct heat
65
New cards
what is "Hcv" in the heat budget equation?
convection
-solid body; moving fluid
-solid body; moving fluid
66
New cards
what is a fluid?
a substance that has no fixed shape and yields easily to external pressure
67
New cards
what are the two types of convection?
natural and forced
68
New cards
what is "Hr" in the heat budget equation?
radiation
69
New cards
what is "He" in the heat budget equation?
evaporation
70
New cards
what is the heat of vaporization?
energy required to change the state from liquid to vapor
71
New cards
what is the temperature regulation equation for plants?
Hs= ±Hcd±Hcv±Hr-He
72
New cards
how else can annual plants be classified as?
"stress avoidance"
73
New cards
why did we talk about the oval leaf fan petal?
dormancy during high temperatures
74
New cards
what is dormancy?
germination block; delayed germination to prevent emergence under unfavorable conditions
75
New cards
are seeds durable?
yes
76
New cards
why is the svalbard global seed vault important?
it stores the worlds' seeds
77
New cards
what is ICARDA?
international center for agriculture research in dry areas
78
New cards
how else can perennial plants be classified?
stress resistance
79
New cards
open growth form, small leaves, transpiration, drought deciduous, dense pubescence, and paraheliotropism are all adaptations to ____ temperatures.
high
80
New cards
why is open growth form a good adaptation for high temperatures?
reduces heat gain by conduction, maximizes air movement through plant, increases heat loss by convection
81
New cards
why are small leaves a good adaptation for high temperatures?
increases heat loss by convection due to large surface area to volume ratio; reduces moisture loss
82
New cards
why is transpiration a good adaptation for high temperatures?
loss of H20 from plant in form of water vapor; evaporative cooling
83
New cards
where can stomata be found on the plant?
the surface of the leaf
84
New cards
what is paraheliotropism?
plants orient leaves to minimize incoming solar exposure
85
New cards
what is heliotropism?
directional growth of a plant in response to sunlight
86
New cards
what is dense pubescence?
reflects IR; does not gain as much heat from sun; low solar absorptance
87
New cards
plants that use dense pubescence have more dense hairs in the _____, and less dense hairs in the _____.
summer; winter
88
New cards
parallel orientation is an adaptation for ____ temperatures.
high
89
New cards
what are some plant adaptations to cold temperatures?
dark pigments, cushion growth form, diaheliotropism, dense pubescence, supercooling, winter deciduous, dehydration/extracellular ice formation
90
New cards
cushion growth form

91
New cards
dark pigments on plants help to:
maximize heat gain
92
New cards
what is diaheliotropism?
maximizes solar exposure through leaf orientation
93
New cards
why did we talk about the eastern skunk cabbage?
it melts the snow around the plant during the winter
94
New cards
what happens during supercooling?
solutes help reduce ice formation, and ice-binding protein production occurs through cold acclimation
95
New cards
what is the temperature regulation equation for animals?
Hs=Hm±Hcd±Hcv±Hr-He
96
New cards
what is a poikilotherm?
body temperature fluctuates with environmental temperatures
97
New cards
what is a homeotherm?
maintenance of fairly constant body temperature within narrow range
98
New cards
what are ectotherms?
control of body temperature through heat exchange with external environment
99
New cards
what kind of animals does this describe?
-low energy lifestyle
-minimal "Hm" (metabolic heat)
-most are poikilothermic
-dependence on a stable environment for metabolic rate and activity
-low energy lifestyle
-minimal "Hm" (metabolic heat)
-most are poikilothermic
-dependence on a stable environment for metabolic rate and activity
ectotherms
100
New cards
true or false: ectotherms are larger in size than endotherms.
false: they are usually smaller.