DNA Cloning
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What are the common forms of DNA technology?
DNA sequencing
Polymerase chain reaction
DNA cloning
Gel electrophoresis
What is gene therapy?
This is a technique used to treat genetic disorders that are caused by a nonfunctional gene. It works be delivering the “missing” gene’s DNA to the cells of the body
PCR is a technique that has the ability to make many copies of what?
PCR can make many copies of DNA sequences
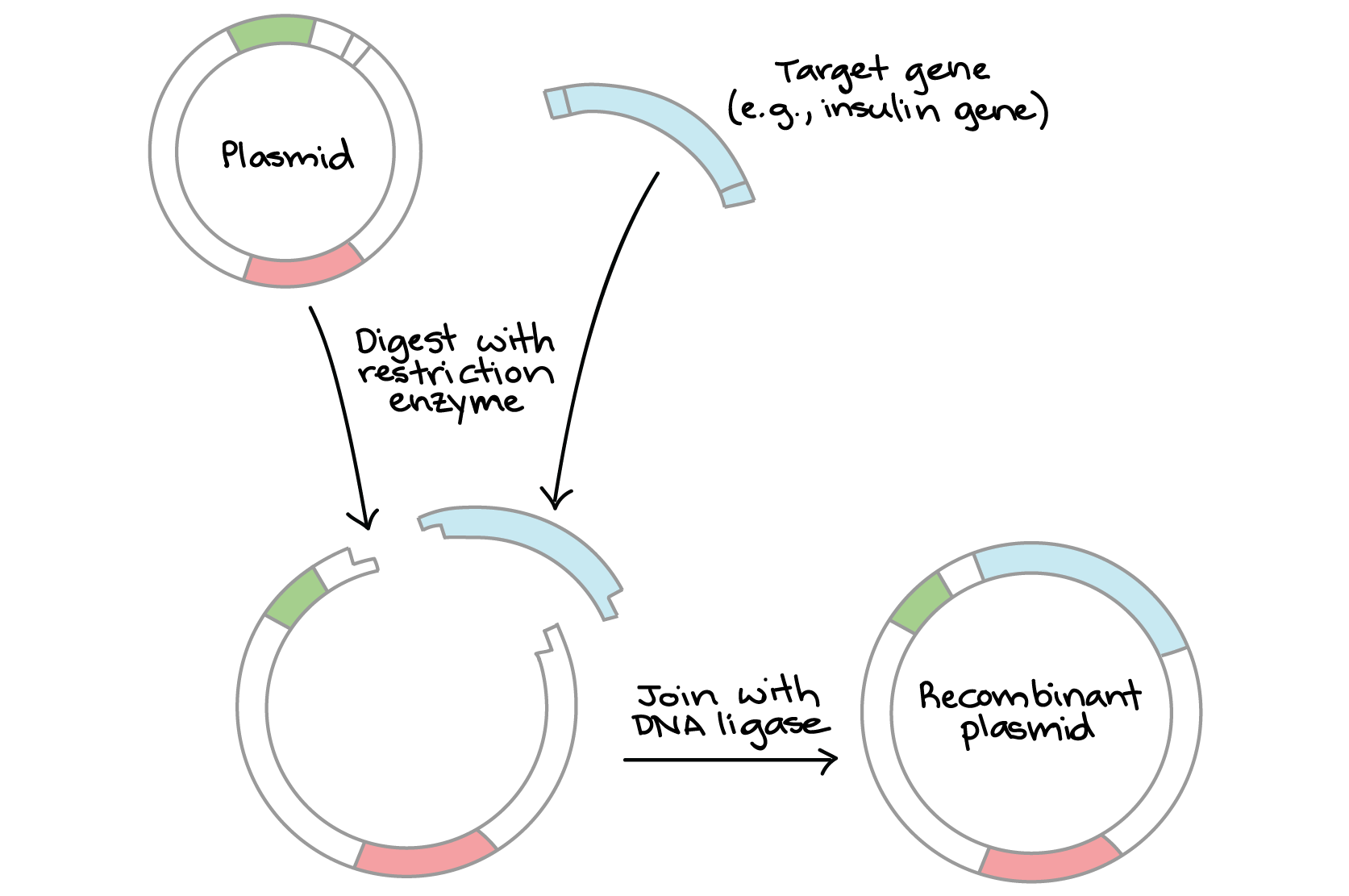
How does DNA cloning work?
DNA cloning-make many copies of the DNA fragment of interest (gene)- involves inserting a target gene into a circular DNA moilecules called a plasmid. The plasmis can be replicated in bacteria, making many copies of the gene of interest. In some cases, the gene is also expressed in bacteria, making a protein
What is PCR?
This is a technique used to amplify, or make copies of, a specific target region of DNA
What does PCR rely on?
PCR relies on a thermostable DNA polymerase (Taq polymerase), and requires DNA primers designed specifically for the DNA region of interest
What allows many copies of the target region to be produced in PCR?
The reactionn is repeatedly cycled through a series of temperature changes, allowing many copies of the traget region to be produced
PCR requires a DNA polymerase enzyme to make new strands of DNA, using existing strands as templates. What is enzyme?
Taq polymerase, after the heat-tolerant bacterium from which it was isolated from
What are the three basic steps of PCR?
Denaturation (96 C): Heat the reaction strongly to seperate, or denature, the DNA strands. This provides single-stranded templ;ate for the next step.
Annealing (55-65 C): Col the reaction so the primers can bind to their complementary sequences on the single-stranded template DNA
Extension (72 C): Raise the reaction temp so Taq polymerase extends the primers, synthesizing new strands of DNA
the resukts of a PCR reaction are visulized (made visable) through what technique?
Gel electrophoresis
What is gel electrophoresis?
This is a technique in which fragments of DNA are pulled through a gel matrix by an electric current, and it seperates DNA fragments according to size
What is DNA sequencing?
DNA sequencing involvces determining the sequence of nucleotide bases in a DNA molecule
How is DNA cloning done?
It creates identical copies of a specific gene uisng restriction enzymes to cut the desired gene, pasting it into a plasmid, and inserting it into bacteria like E.coli. the bacteria replicate the gene and can produce proteins, like insulin. Antibiotic resistance genes in plasmids help select bacteria containg the desired gene
What cuts out the gene in DNA cloning?
Restriction enzymes
What are the 4 essential features of cloning vectors?
Origin of replication
Selectable marker
Multiple Cloning Sites
Reporter genes (lacZ)
What does origin of replication do?
Allows independent replication in host cells
What does a selectable marker (amp) do in cloning vectors?
Allows selection of cells with plasmid (antibiotic resistance)
What does a Multiple cloning site do gor cloing vectors?
This is a region with multiple restriction sites to insert DNA
Reporter genes such as lacZ have what function for cloning vectors?
Reporter genes are used for screening clone (blue-white screening)
What are cloning vectors?
DNA molecules used to deliver genetic material into host cells
What are the types of cloning vectors?
Plasmids
Phages
Cosmids, BACs, and YACs
What is Recombinant DNA technology?
rDNA is a hybrid DNA molecule made by combing DNA from different sources
What are the key enzymes/tools used for rDNA?
Restrictive endonucleases
DNA ligase
Plasmid Vectors
Host cells
What is the purpose of restriction endonucleases in rDNA?
Cut DNA at specific sequences
What is the purpose of DNA ligase?
Joins DNA fragments together
What is the purpose of plasmid vectors in rDNA?
Circular DNA used to carry and replicate foreign genes
What do host cells (usally E. Coli) do for rDNA?
Provide the machinery for replication