Dental Anatomy Quiz Maxillary 1st & 2nd Molars
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
3, 14 vs 2, 15
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
The 1st maxillary molar can be identified through which of the following characteristics
a. concavity on the lingual root
b. a fifth cusp
c. a prominently divergent lingual root
d. all of the above
e. none of the above
d. all of the above
Which characteristics accurately distinguish maxillary 1st and 2nd molars
a. roots are more divergent on the 1st than on the 2nd
b. mesiodistal crown dimension narrower on the 1st than on the 2nd
c. DL cusp larger on the 1st than on the 2nd
d. a and c
e. b and c
d. a and c
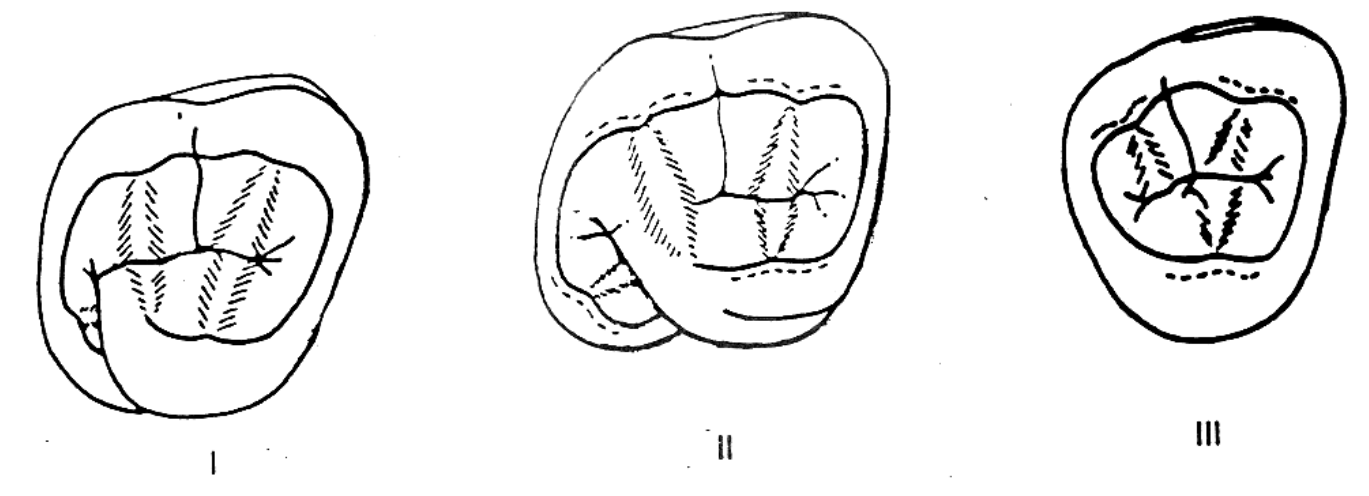
How would you arrange these occlusal views to identify the maxillary molars in the proper sequence
II, I, II
Which group of cusps on #2 or #3 is correctly arranged in order of decreasing size
a. ML, DL, MB, DB
b. DL, ML, MB, DB
c. ML, MB, DB, DL
d. MB, ML DB, DL
e. none of the above
c. ML, MB, DB, DL
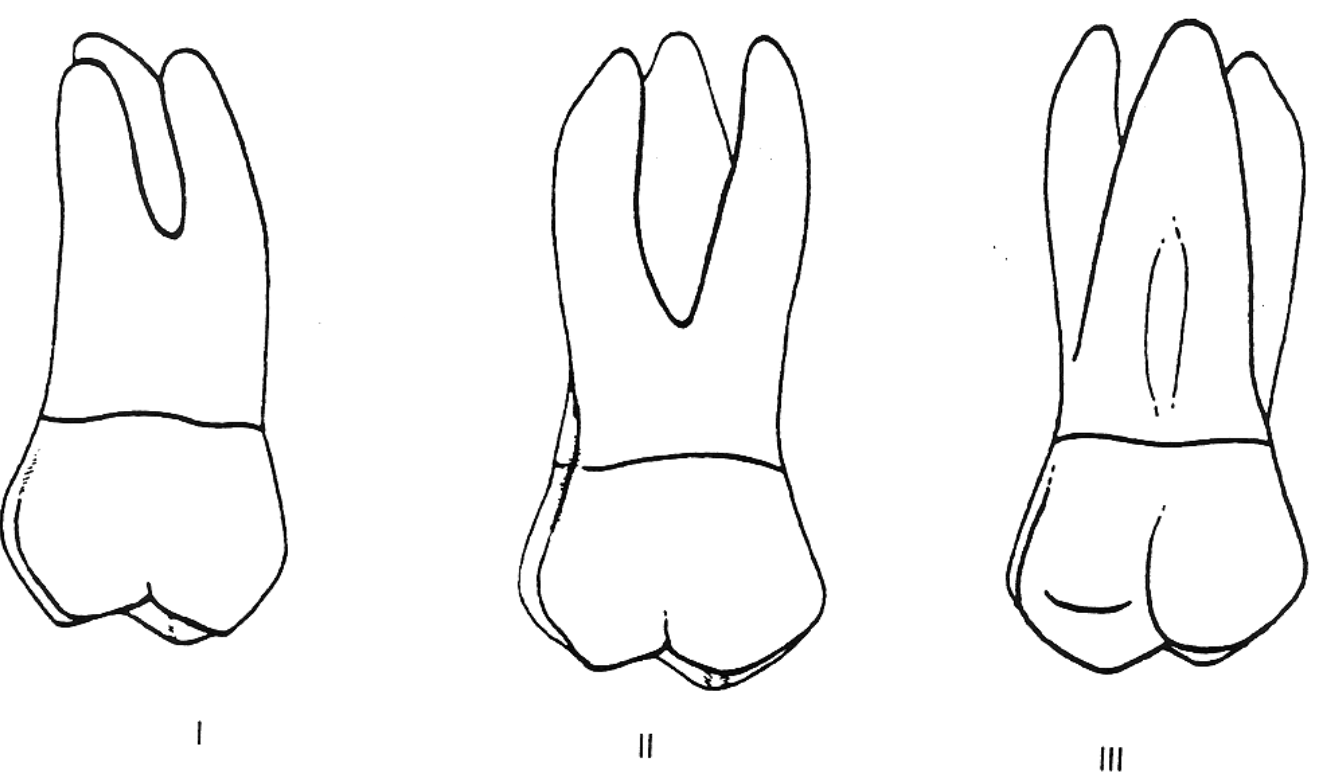
Which of these is the buccal view of #2?
I
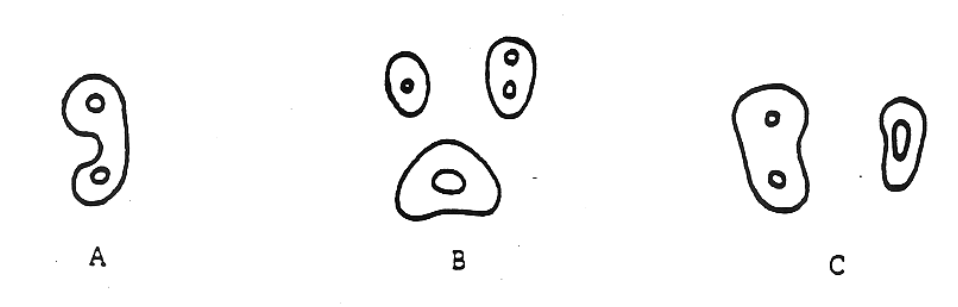
which of these cervical views in the mid-root section of #14?
B
The oblique ridge on a maxillary molar runs or extends:
a. from the MB root to the ML root
b. across the transverse ridge
c. from the ML cusp to the DL cusp
d. from the triangular ridge of the DB cusp to the distal lingual cusp ridge of the ML cusp
d. from the triangular ridge of the DB cusp to the distal lingual cusp ridge of the ML cusp
In normal occlusion, the maxillary 1st molars occlude with which teeth?
mandibular first and second molars
In maxillary molars which root is usually the shortest with the least amount of curvature?
distobuccal
Fist Evidence of Calcification in Maxillary 1st Molars
birth
Fist Evidence of Calcification in Maxillary 2nd Molars
2 ½ - 3 years
Crown Completion of Maxillary 1st Molars
2 ½ - 3 years
Crown Completion of Maxillary 2nd Molars
7-8 years
Tooth Eruption of Maxillary 1st Molars
6-7 years
Tooth Eruption of Maxillary 2nd Molars
12-13 years
Root Completion of Maxillary 1st Molars
9-10 years
Root Completion of Maxillary 2nd Molars
14-16 years
Which is present in a maxillary 1st molar but not in a maxillary second molar
a. ML cusp
b. oblique ridge
c. large F-L dimension
d. cusp of Carabelli
d. cusp of Carabelli
A left maxillary 1st molar would be identified by the universal and international tooth number system as ___.
14, 26
Which of the following is true of maxillary 1st and 2nd molars
a. ML cusp is the largest
b. they always have 4 cusps
c. the mesial contact is centered, and more cervical and distal contact is to the facial and more occlusal
d. they are relatively small in the F-l dimension
a. ML cusp is the largest
What is the correct order of anatomic landmarks of a tooth with two roots from the root tip to the cementoenamel junction?
Apex, furcation, trunk, cervix
What is the correct rank from longest to shortest of the roots on maxillary 1st and 2nd molars?
P>MB>DB
Distinctive characteristics of a maxillary 1st molar
similar buccal cusps, greater F-L than M-D dimension, oblique ridge, 3 roots, is not a succedaneous tooth
In the occlusal view, which of the following may be present in a 3 cusp “heart shaped” maxillary 2nd molar
distolingual cusp
oblique ridge
central groove
mesial fossa
3,4
From which view are only two roots visible on a maxillary 1st molar?
mesial
How many root canals do maxillary 1st and 2nd molars have?
four (MB, MB2, DB, P)
Which of the following is present in a 3-cusp maxillary 2nd molar
a. distal oblique groove
b. oblique ridge
c. distolingual cusp
d. central groove
d. central groove
Which of the following statements are true of marginal ridges
They are not responsible for maintaining arch alignment
They protect interproximal areas from food impaction
They produce a lack of occlusion
They need to be aligned with adjacent marginal ridges
2,4