OpenStax Psychology 2E - Full (edited)
1/767
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
768 Terms
Optic nerve
large bundle of nerve fibers that carries impulses from the retina to the brain and is where the blind spot occurs
behaviorism
focus on observing and controlling behavior
biopsychology
study of how biology influences behavior
biopsychosocial model
perspective that asserts that biology, psychology, and social factors interact to determine an individual's health
cognitive psychology
study of cognitions, or thoughts, and their relationship to experiences and actions
forensic psychology
area of psychology that applies the science and practice of psychology to issues within and related to the justice system
functionalism
focused on how mental activities helped an organism adapt to its environment
humanism
perspective within psychology that emphasizes the potential for good that is innate to all humans
personality psychology
study of patterns of thoughts and behaviors that make each individual unique
personality trait
consistent pattern of thought and behavior
psyche
Greek word for soul
psychoanalytic theory
focus on the role of the unconscious in affecting conscious behavior
structuralism
understanding the conscious experience through introspection
Wilhelm Wundt
established the first psychology laboratory at the University of Leipzig, Germany
Plato
Socrates' most well known pupil. Founded an academy in Athens.
Descartes
French philosopher, nativist, and dualist
Dualism
the presumption that mind and body are two distinct entities that interact
William James
founder of functionalism; studied how humans use perception to function in our environment
Erik Erikson
famous for his 8-stage model of psychosocial development; neo-Freudian
John B. Watson
developed behaviorism (the study of observable behavior)
Ivan Pavlov
discovered classical conditioning; trained dogs to salivate at the ringing of a bell
Lawrence Kohlberg
Theory of Moral Development
Naomi Weisstein
Credited with starting the feminist revolution in psychology
Anna Freud
Continued her father's work in psychoanalysis with an emphasis on children.
Charles Darwin
English natural scientist who formulated a theory of evolution by natural selection (1809-1882)
Democritus
Greek philosopher that said all matter is made of tiny particles called "atomos" or atoms
behaviorist perspective
the psychological perspective primarily concerned with observable behavior that can be objectively recorded and with the relationships of observable behavior to environmental stimuli
evolutionary psychology
the study of the evolution of behavior and the mind, using principles of natural selection
cognitive perspective
how we encode, process, store, and retrieve information
The Interpretation of Dreams
the Bible of Psychoanalysis by Freud
sociocultural perspective
perspective that focuses on the relationship between social behavior and culture
Hypothesis
A testable prediction, often implied by a theory
Stanley Milgram
obedience to authority; had participants administer what they believed were dangerous electrical shocks to other participants; wanted to see if Germans were an aberration or if all people were capable of committing evil actions
Albert Ellis
rational emotive behavior therapy
Introspection
examination of one's own thoughts and feelings
Herman Ebbinghaus (1850-1909)
created the forgetting curve and serial position effect in memory
Solomon Asch
Conducted famous conformity experiment that required subjects to match lines.
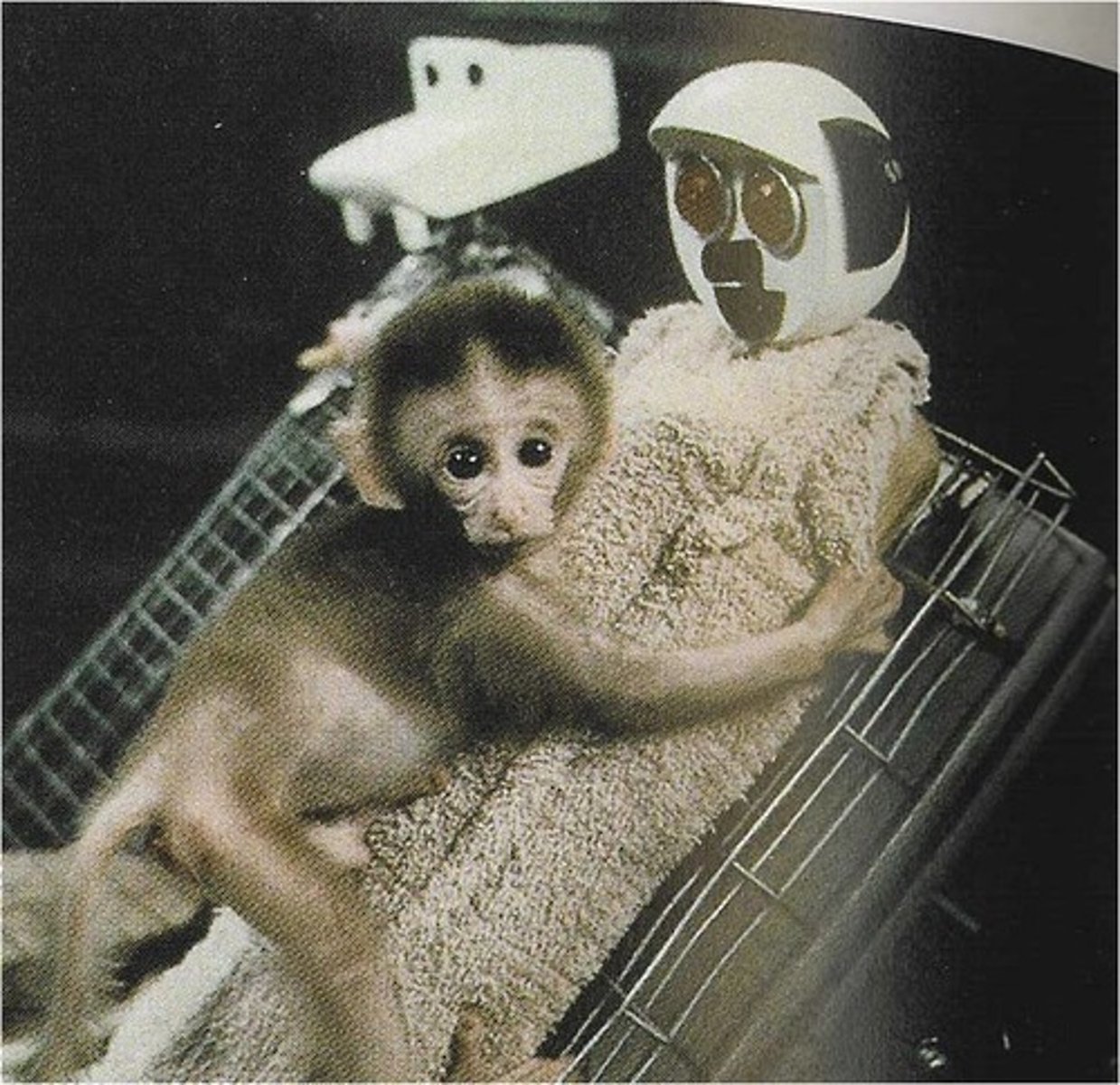
Harry Harlow
Studied attachment in monkeys with artificial mothers

Prefrontal Lobotomy
example of what happens when we rely on our subjective impressions; brain damage before and after the surgery remained the same
Heuristics
mental shortcuts or rules of thumb
Theory
a well-developed set of ideas that propose an explanation of observed phenomena
Case Study
in depth study of rare cases (does not tell cause and effect); ex: Phineas Gage, H.M., Little Albert
Naturalistic Observation
watching behavior in real-world settings
High Degree of External Validity
extent to which we can generalize our findings to the real world
Low Degree of Internal Validity
extent to which we can draw cause-and-effect inferences
Observer Bias
the tendency of the observer to unconsciously skew observations to fit the research goal/expectations
Operational Definition
being specific about what is being observed; important to specify how we're measuring our variables ahead of time
Self-Report Measures and Surveys
surveys and questionnaires;
advantages:
-easy to administer
-subtle information
disadvantages:
-may not have insight
-may not be honest
Population
everyone in a particular group
Halo Effect
tendency of ratings of one positive characteristics to spill over to influence the ratings of other positive characteristics
Leniency Effect
tendency of raters to provide ratings that are overly generous (opposite of Halo Effect)
Attrition Rates
dropouts/people lost over the course of the study
Cross-sectional Research
a "snapshot;" a researcher compares multiple segments of the population at a given time
Cohort Effect
an effect that different age groups give different reaction results not necessarily due to their age
Confirmation Bias
looking for evidence to support a preexisting belief and ignoring evidence that contradicts it
Confounds
any difference between the experimental and control groups, other than the independent variable; makes it impossible to interpret any findings
Hawthorne Effect
phenomenon in which participant's knowledge that they're being studied can affect their behavior
Demand Characteristics
cues that participants pick up from a study that allow them to generate guesses regarding the researcher's hypotheses
Glial Cell
cell in the nervous system that: plays a role in formation of myelin and blood brain barrier, responds to injury, removes debris, enhances learning and memory
Neuronal Membrane
covers entire cell and separates the inside from the outside environment
Dendrite
receiving end of the neuron
Cell Body
soma/central area; maintains cell's vital functions
Axon
extends from cell body, sends messages to other neurons (messages go one-way only)
Axon Terminal
end of axon; where neurotransmitter production and release happens
Action potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
Brain-communication
electro-chemical
Synaptic Vesicles
small capsules that make neurotransmitter and release into the synaptic cleft
Pre-synaptic Membrane
semi-permeable covering on the end of the axon terminal
Synaptic Cleft
small space between axon and dendrite
Post-synaptic Membrane
semi-permeable covering on the end of the dendrite
Myelin
fat covering on axon
Chemical Messengers
Neurotransmitters
Serotonin
happy mood
Dopamine
motor function and rewarding feeling
Acetylcholine
muscle control and cortical (cortex) arousal
Anadamide
pain reduction, increase appetite
Norepinephrine
mood, hunger, sleep, adrenaline
GABA
inhibitory
Glutamate
information and learning
Localization of Function
researcher's attempts to identify the function of each individual brain area (but areas likely work together to produce our perceptions)
Forebrain (including cerebral cortex)
the site of most of the brain's conscious functions; containins the cerebral cortex, the thalamus, and the limbic system,among other structures
Corpus Callosum
bundle of nerve fibers connecting the cerebrum's two hemispheres
Thalamus
area that relays nerve signals to the cerebral cortex; sensory gateway
Hypothalamus
forebrain structure that regulates sexual motivation and behavior and a number of homeostatic processes; serves as an interface between the nervous system and the endocrine system
Cerebellum
hindbrain structure that controls our balance, coordination, movement, and motor skills, andit is thought to be important in processing some types of memory
Brain Stem
regulates control of involuntary functions, breathing, heart rate
Frontal Lobe
part of the cerebral cortex; involved in motor function, language, memory, and executive function
Motor Cortex
voluntary movement
Prefrontal Cortex
area in the frontal lobe responsible for higher-level cognitive functioning; thinking, planning, language, etc.
Broca's Area
language production
Parietal Lobe
somatosensory cortex: touch, pressure, pain information; spatial perception; object shape/orientation; integrates vision and touch input w/ motor output
Temporal Lobe
hearing, understanding language, autobiographical memories
Wernicke's Area
understanding speech
Occipital Lobe
visual cortex: vision
The Limbic System
emotional center
Amygdala
threat sensor (sometimes hippocampus)
Midbrain
contains limbic system
Reticular Activating System (RAS)
regulates cortical arousal
Hindbrain (brainstem)
division of the brain containing the medulla, pons, and cerebellum
Medulla
regulation of critical functions (heart rate, breathing, etc.)