Menstruation - OB/GYN EOR
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Minus normal physiology and amenorrhea!! Listen to the violent nature album by I Prevail for the vibes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding (AKA abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB))
Uterine bleeding of abnormal quantity, duration, or schedule
3-80 mL
Average blood loss during menses
Menorrhagia
AUB defined as bleeding for 7+ days or more than 80 mLs
Cryptomenorrhea
AUB defined as light flow
metrorrhagia
AUB defined as bleeding between periods (spotting)
Polymenorrhea
AUB defined as less than 21 days between cycles (hella periods)
Oligiomenorrhea
AUB defined as more than 35 days between cycles
Menmetrorragia
AUB defined as excessive or prolonged bleeding at irregular intervals
Anovulation (ovaries produces estrogen but don’t ovulate, so there’s unopposed estrogen)
What causes 90% of AUB?
Luteal phase defect (results in difficulty achieving pregnancy)
An etiology of AUB in which ovulation occurs BUT the corpus luteum does not fully form to make sufficient progesterone (we never get to the secretory phase)
a sudden drop in estrogen that occurs mid-cycle at the time of ovulation
Mid Cycle spotting is related to
Polyp, adenomyosis, leiomyoma, malignancy/hyperplasia, coagulation, ovulatory disorder, endometrial, iatrogenic, not yet classified
What does PALM-COEIN stand for?
Preg (1st step DUH) → CBC, TSH, Iron studies, PT/PTT, progesterone, prolactin, FSH → TVUS (1st line imaging) → endometrial biopsy
Work up for AUB
Unopposed estrogen therapy, tamoxifen usage, menopause after 55, PCOS, 35+ with obesity/HTN/DM, if 45+, post menopausal bleeding
When is an endometrial biopsy indicated for AUB?
IV high dose estrogen, high dose OCs
Treatment for acute hemorrhage associated with AUB
OCPs, TXA (adjunctive), IUD, NSAIDs, hysterectomy (definitive), endometrial ablation
Chronic management of AUB
Leiomyoma (Fibroids)
A benign uterine smooth muscle tumors that derive from the muscle cells of the myometrium (most common benign gynecological tumor and most common cause of AUB)
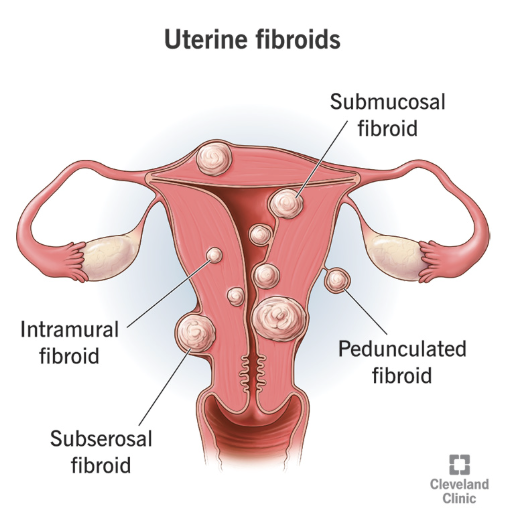
Intramural (most common), submucosal, subserosal, parasitic
Types of Fibroids
Increasing age, AA (5X more common), nulliparity, obesity, fam hx, HTN
Risk factors for Fibroids
Growth is estrogen dependent and may increase in size with relation to the menstrual cycle, anovulatory states, during pregnancy, and after menopause
Patho for fibroids
Menorrhagia and irregular bleeding (submucosal - watch for iron deficiency anemia), dysmenorrhea, pelvic pressure, pain, hydroureter/nephrosis (IF A MEGA FIBROID)
Clinical manifestation of leiomyomas (most asymptomatic)
palpable, firm, nontender asymmetric mobile mass in the abdomen or pelvis; enlarged mobile uterus with an irregular contour
PE findings for Leiomyomas
TVUS (focal heterogeneous hypoechoic, well circumscribed mass with shadowing), Hysteroscopy (submucosal), laparoscopy (r/o carcinoma)
Diagnostics for Leiomyomas
Observation, Leuprolide (most effective medical management), Levonorgestrel-releasing IUDs (dysmenorrhea), progestin, GnRH analogs, Hysterectomy (definitive), Myomectomy (fertility preservation)
Management plan for leiomyomas
Adenomyosis
Condition in which endometrial glandular tissue and stroma are present within the myometrium
Heavy menstrual bleeding, dysmenorrhea
Clinical manifestations of adenomyosis
Mobile, enlarged (glandular), boggy (soft) uterus that may be fixed if concurrent endometriosis
PE findings for adenomyosis
Hcg, H/H, STI testing (if pelvic pain), TVUS
Workup for Adenomyosis
asymmetric thickening of myometrium, myometrial cysts, linear striation, loss of endomyometrial border, increased heterogeneity
TVUS findings in adenomyosis
Levonorgestrel-releasing IUD, Total hysterectomy (definitive)
Management of adenomyosis
Polyp
A localized hyperplastic overgrowth of endometrial glandular/stromal tissue around a vascular core that forms a sessile or pedunculated projection from the endometrial surface
tamoxifen, obesity, HRT, lynch and cowden syndrome
Risk factors for endometrial polyps
OCPs, levonorgestrel containing IUD
Protective factors for endometrial polyps
intermenstrual bleeding
Clinical presentation of endometrial polyps
TVUS (1st line), sonohysterography/diagnostic hysterography, histology post polypectomy (diagnostics)
Diagnostics for endometrial polyps
Polypectomy
Treatment for endometrial polyps
Increased prostaglandins
Etiology for primary dysmenorrhea
menarche before 12, nulliparity, smoking, fam hx, obesity
Risk factors for primary dysmenorrhea
Pelvis/uterine pathology
Etiology of secondary dysmenorrhea
endometriosis, PID, adenomyosis, leiomyomas
Risk factors for secondary dysmenorrhea
Recurrent, crampy, midline lower abdominal/pelvic pain 1-2 days before menses that diminish over 12-72 hours, associated with HA, N/V/D
Clinical presentation for dysmenorrhea
Supportive care (heat, vitamin B/E, exercise), NSAIDs with OCPs (first line)
Management plan for dysmenorrhea
unresponsive to 3 cycles of initial therapy to r/o secondary causes
When is laparoscopy indicated for dysmenorrhea
Menopause
Cessation of menses for 1 year due to loss of ovarian function leading to a drop in estrogen and progesterone (average age is 51)
Perimenopause
Transition between reproductive capability and menopause that is characterized by irregular menses and lasts 3-5 years
Increased FSH, LH, estrone (predominates after menopause)
Decreases: Estradiol (hella), Progesterone
No Change: Testosterone
Hormonal changes in Menopause
hot flashes, night sweats, sleep disturbances, mood changes, skin/hair/nail changes, increased risk of CVD events, hyperlipidemia, osteoporosis, dyspareunia, vaginal atrophy
Signs of estrogen deficiency
HRT, SSRIs, Bisphosphonates (osteoporosis), Topical vaginal estrogens (vaginal atrophy)
Management of Menopause
H/o breast cancer, CHD, previous VTE/Stroke/TIA, active liver disease, unexplained vaginal bleeding, high risk endometrial cancer
Contraindications for HRT
Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS)
A cluster of physical, behavioral, and mood changes with cyclical occurrence during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle
Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD)
Severe PMS with functional impairment that must be present for 1 YEAR
A: at least 5 symptoms in the final week before menses
B: 1+ of theses → affective lability (mood swings), irritability, depressed, anxiety
C: 1+ of these → decreased interests, difficulty concentrating, lethargy, change in appetite, hypersomnia/insomnia, sense of being overwhelmed, breast tenderness or swelling, joint/muscle pain, bloating, weight gain
D: 2+ cycles
Diagnostics criteria for PMDD - DSM-V (if less than 5 its PMS)
Sxs occurring 1-2wks BEFORE menses (luteal phase), RELIEVED within 2-3days of the onset of menses + 7 sxs-free days during the follicular phase
Cycle timeline for PMDD
Lifestyle Modification (stress reduction + exercise, NSAIDs, vitamins B6/E limit caffeine/EtOH/cigarettes/salt), Spironolactone (bloating and tender breast), SSRIs (1st line - fluoxetine, sertraline, citalopram), OCPs (must contain drospirenone)
Management of PMDD