G9 Semester 2 Exam 2025
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
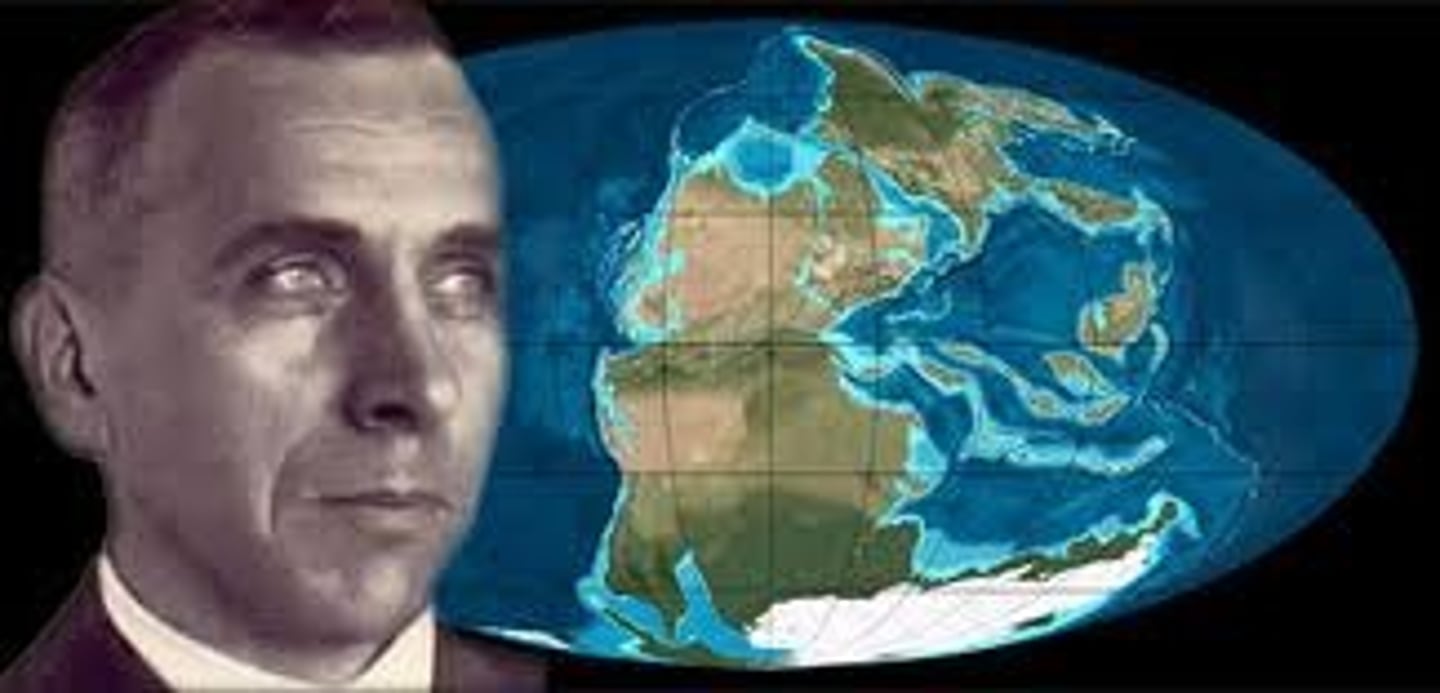
Alfred Wegener
A German scientist who proposed the theory of continental drift
Harry Hess
A naval scientist who proposed the theory of sea-floor spreading
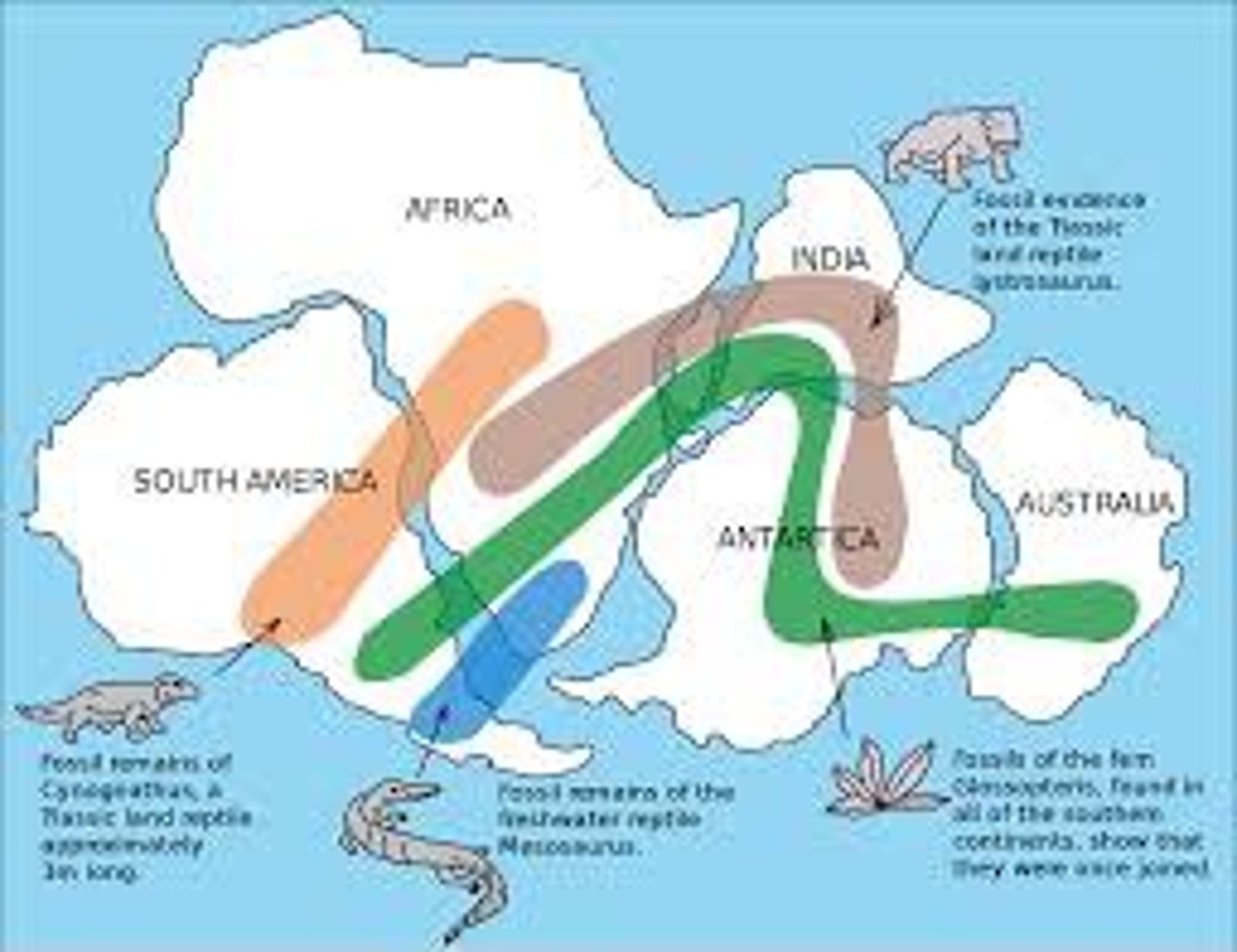
evidence for Alfred Wegener's theory of continental drift
Fossil Evidence, Fit of the Continents
evidence for Harry Hess' theory of seafloor spreading
Magnetic Striping, Age of Seafloor, Sediment Thickness
magnetic striping
The pattern of alternating normal and reversed magnetic polarities found in the seafloor on either side of the spreading center.
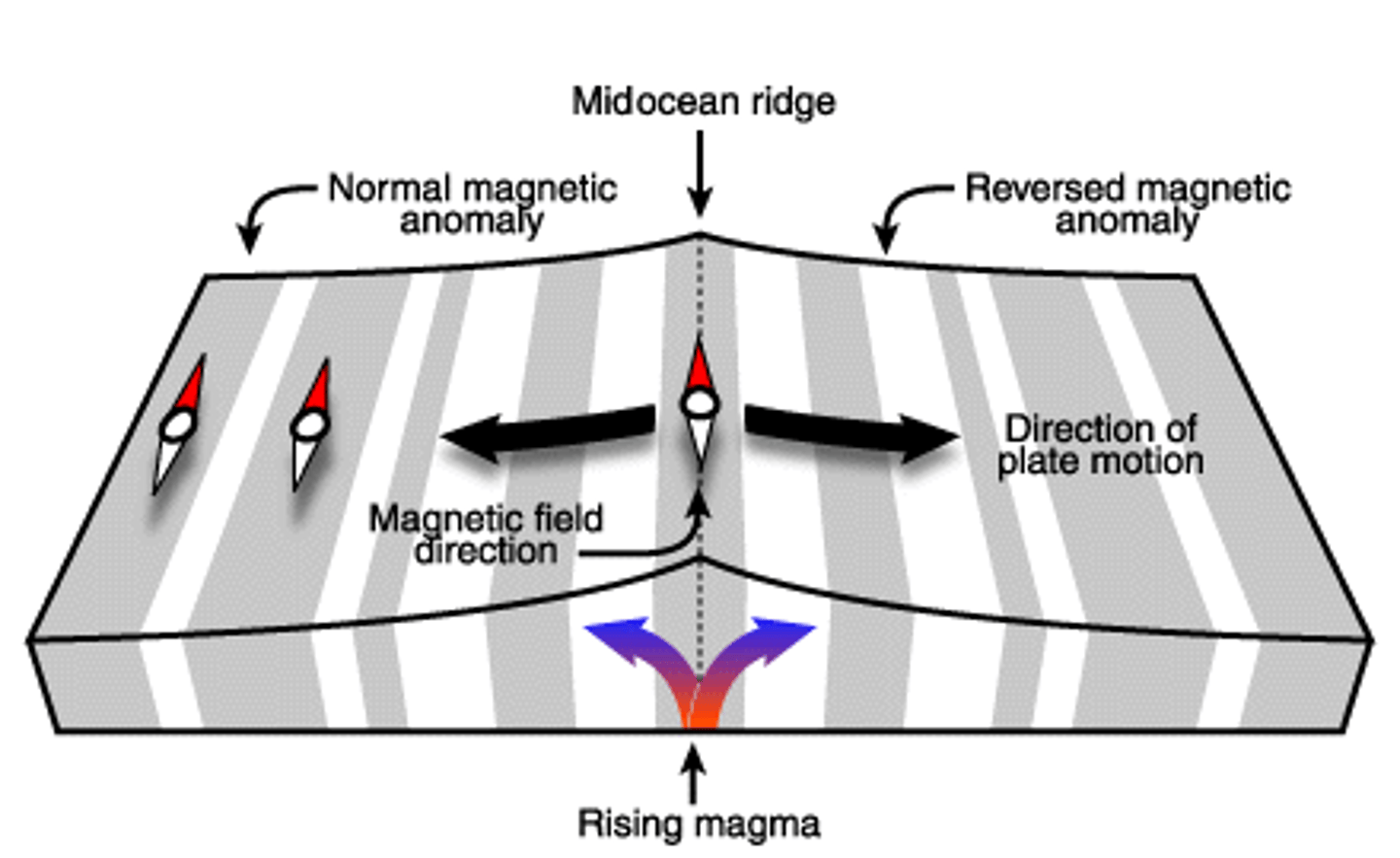
Magnetite
magnetic material found in the seafloor
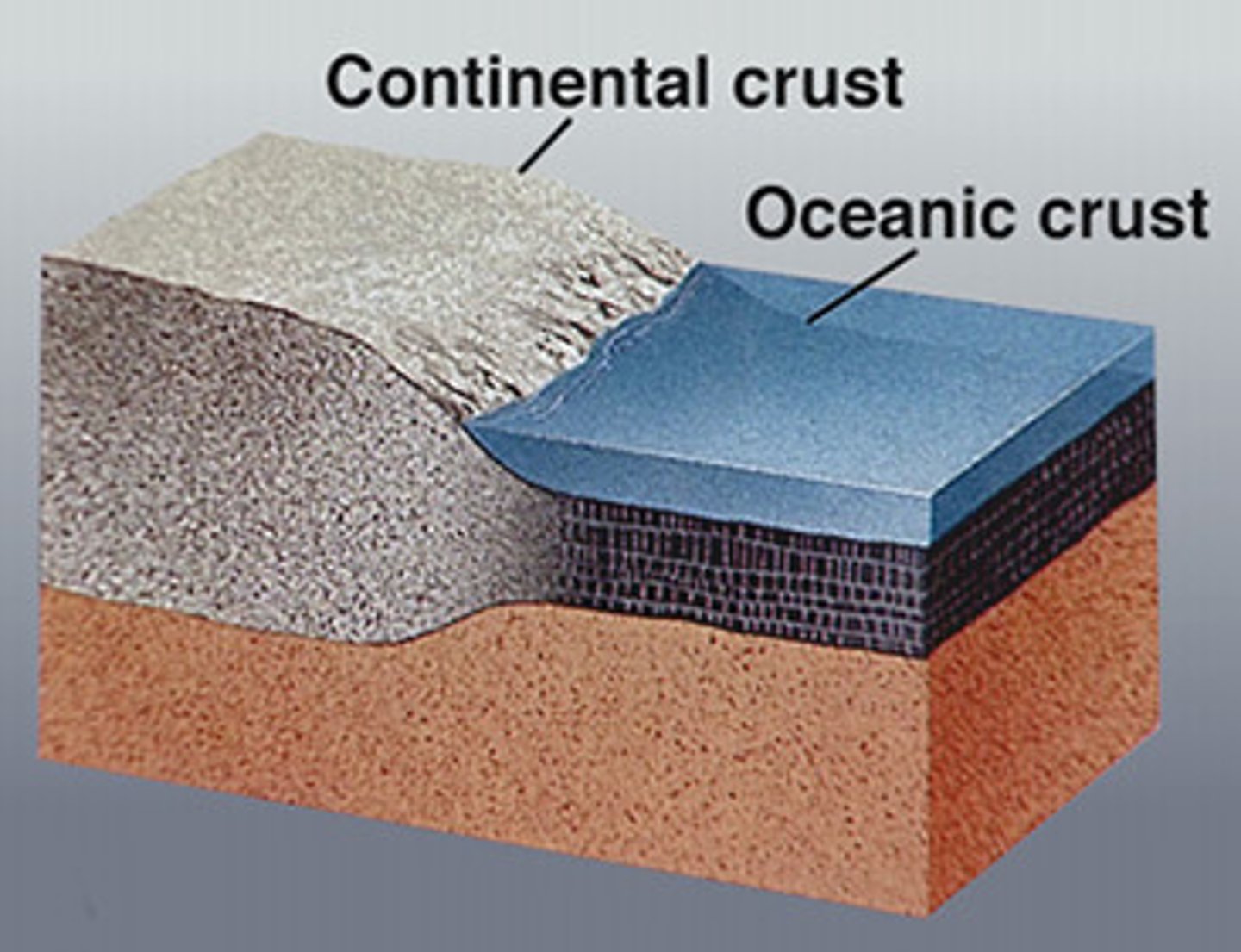
continental crust
crust that lies beneath the Earth's continents and is about 25-70 km thick. Less dense.
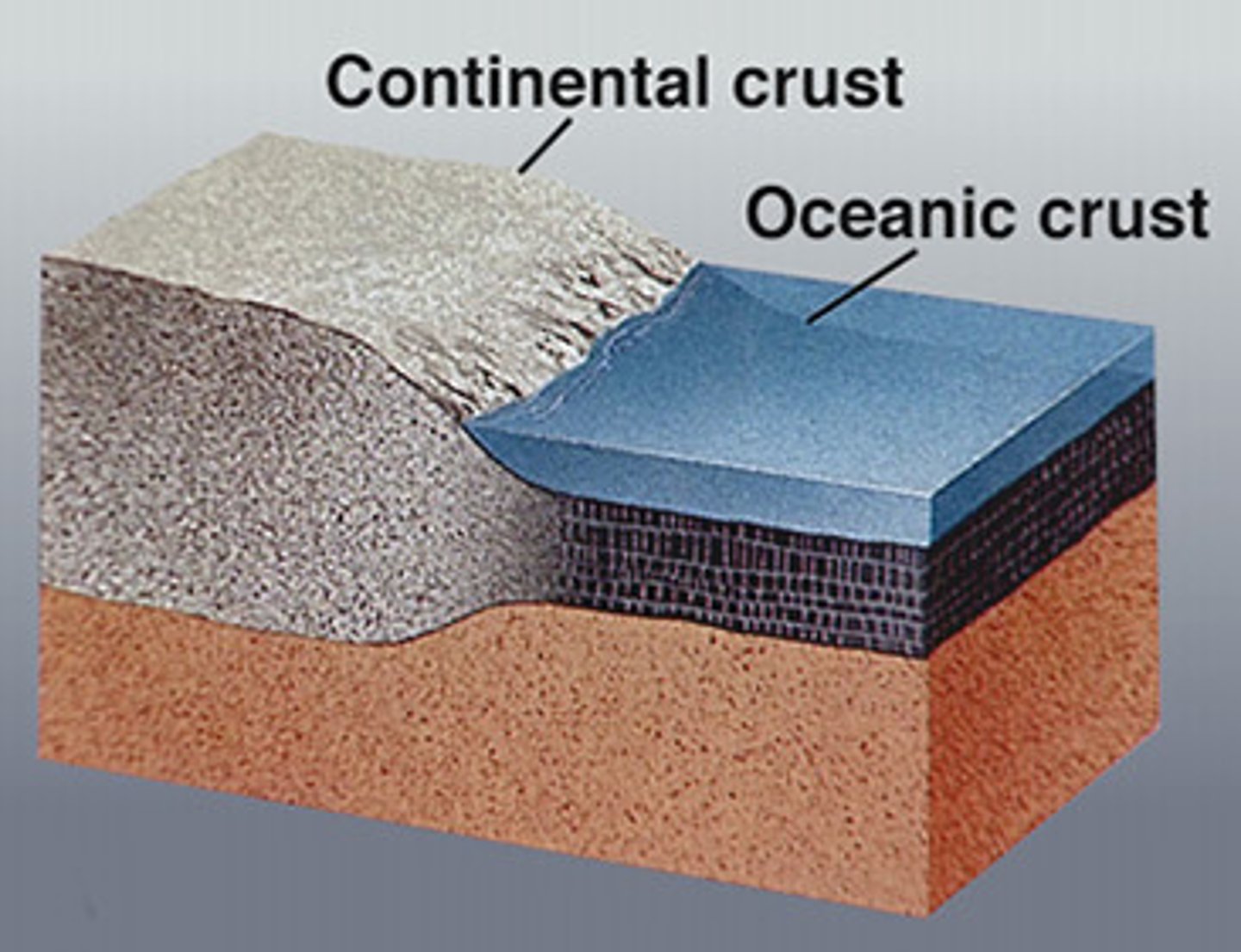
oceanic crust
crust that lies beneath the ocean and is usually 7-10 km thick. More dense.
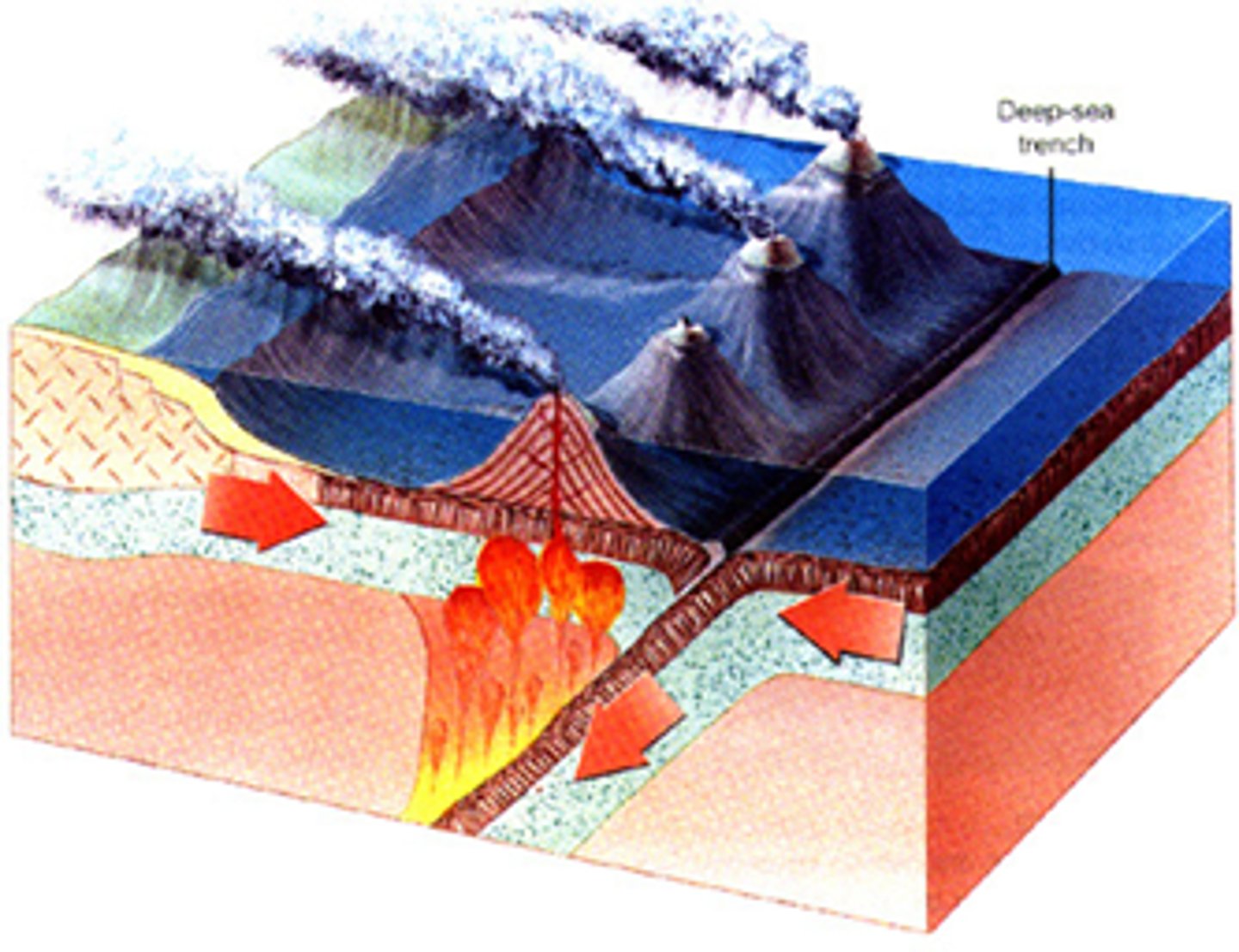
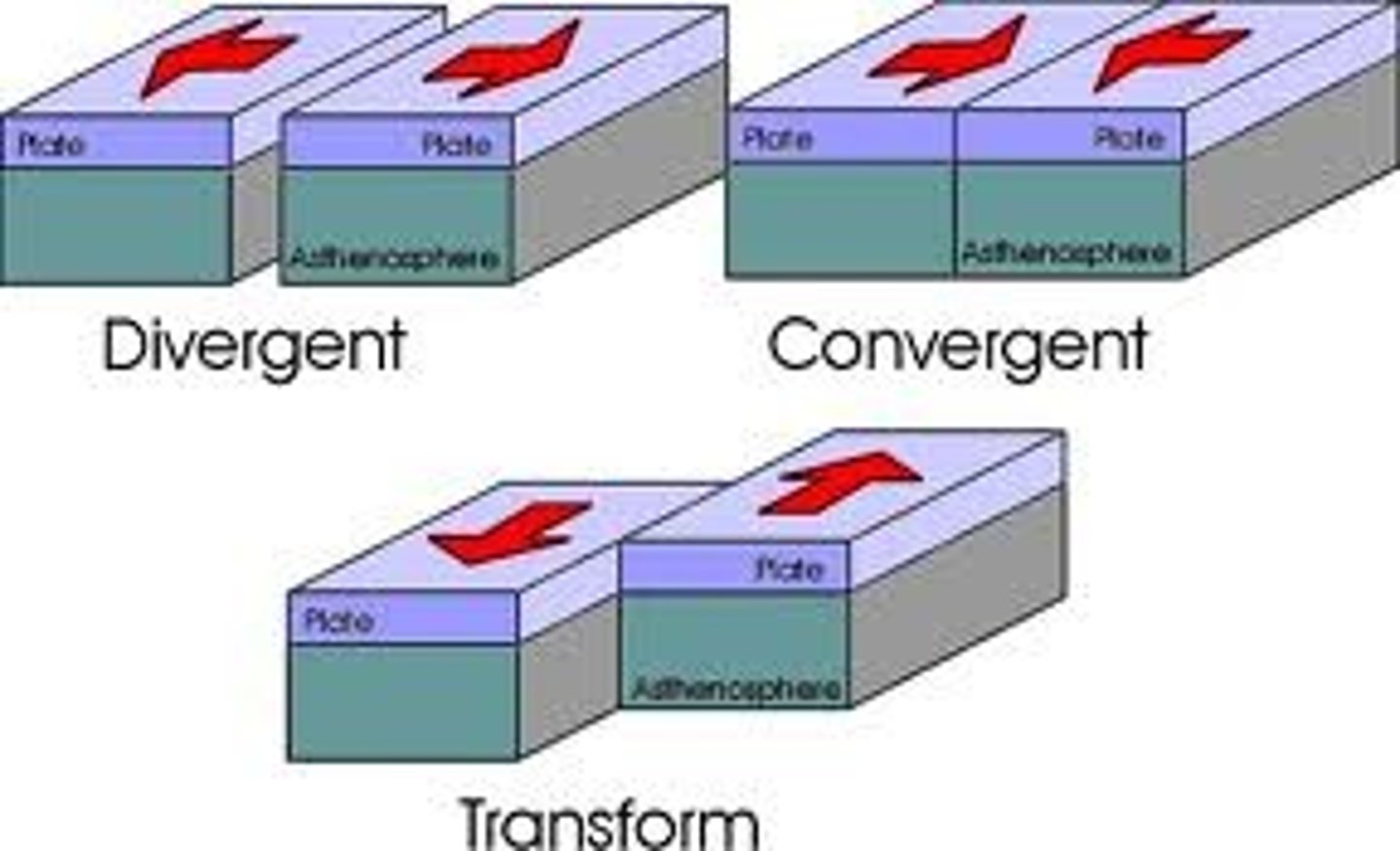
convergent boundary
A plate boundary where two plates move toward each other.
oceanic trench
Deep, narrow trough in the ocean floor where subduction is taking place.
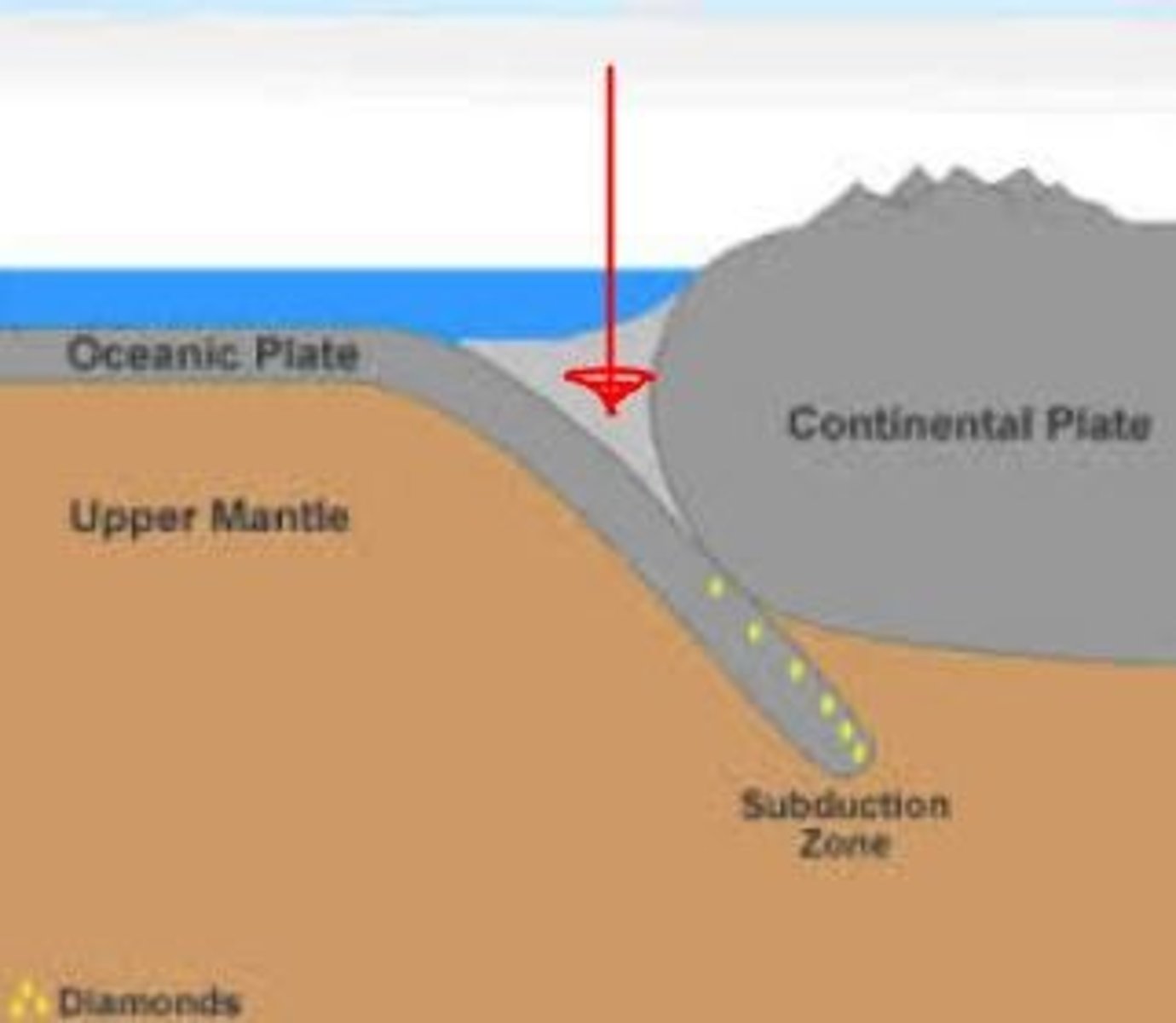
Subduction
The process by which one plate is pushed underneath another plate at a convergent boundary
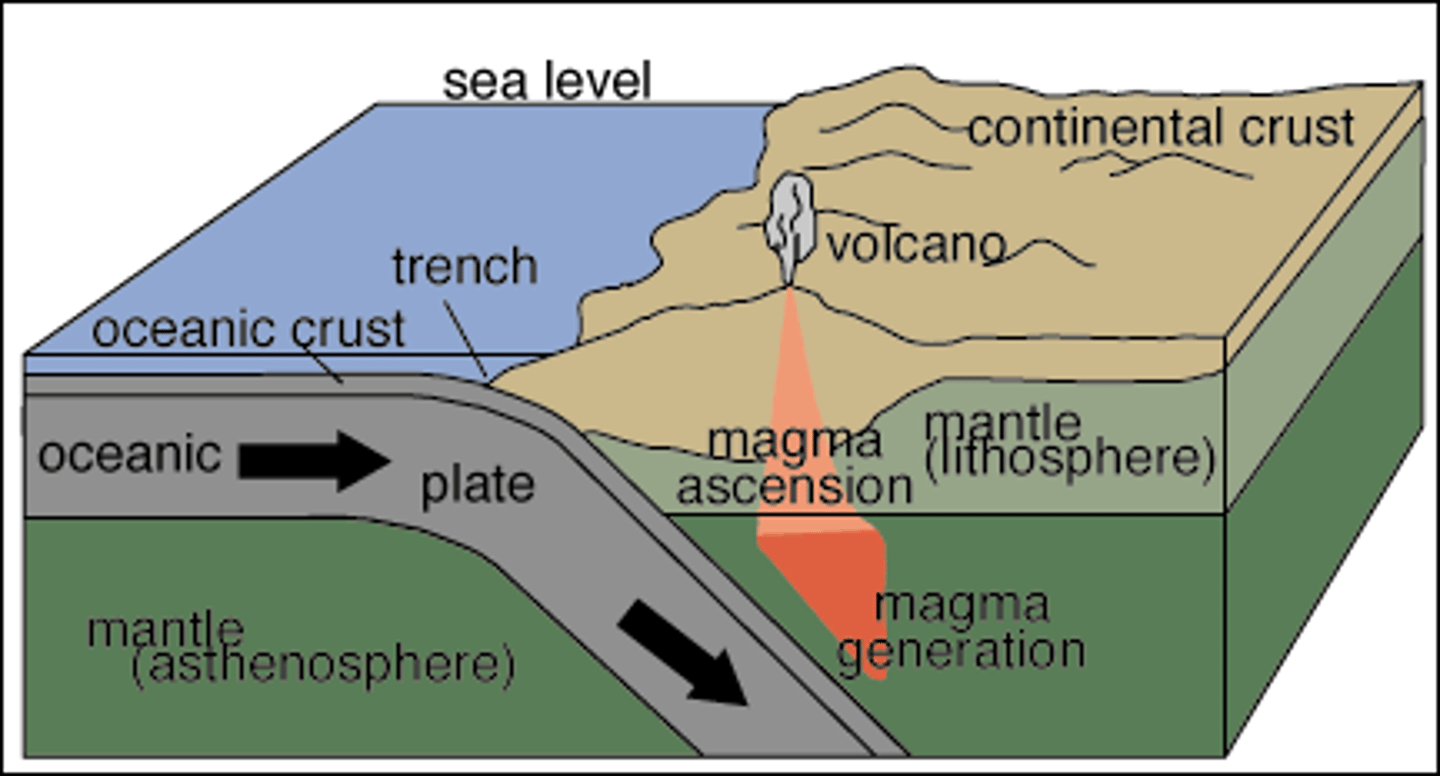
volcanic island arc
a series of volcanoes formed at a subduction zone at a oceanic-oceanic convergent boundary.
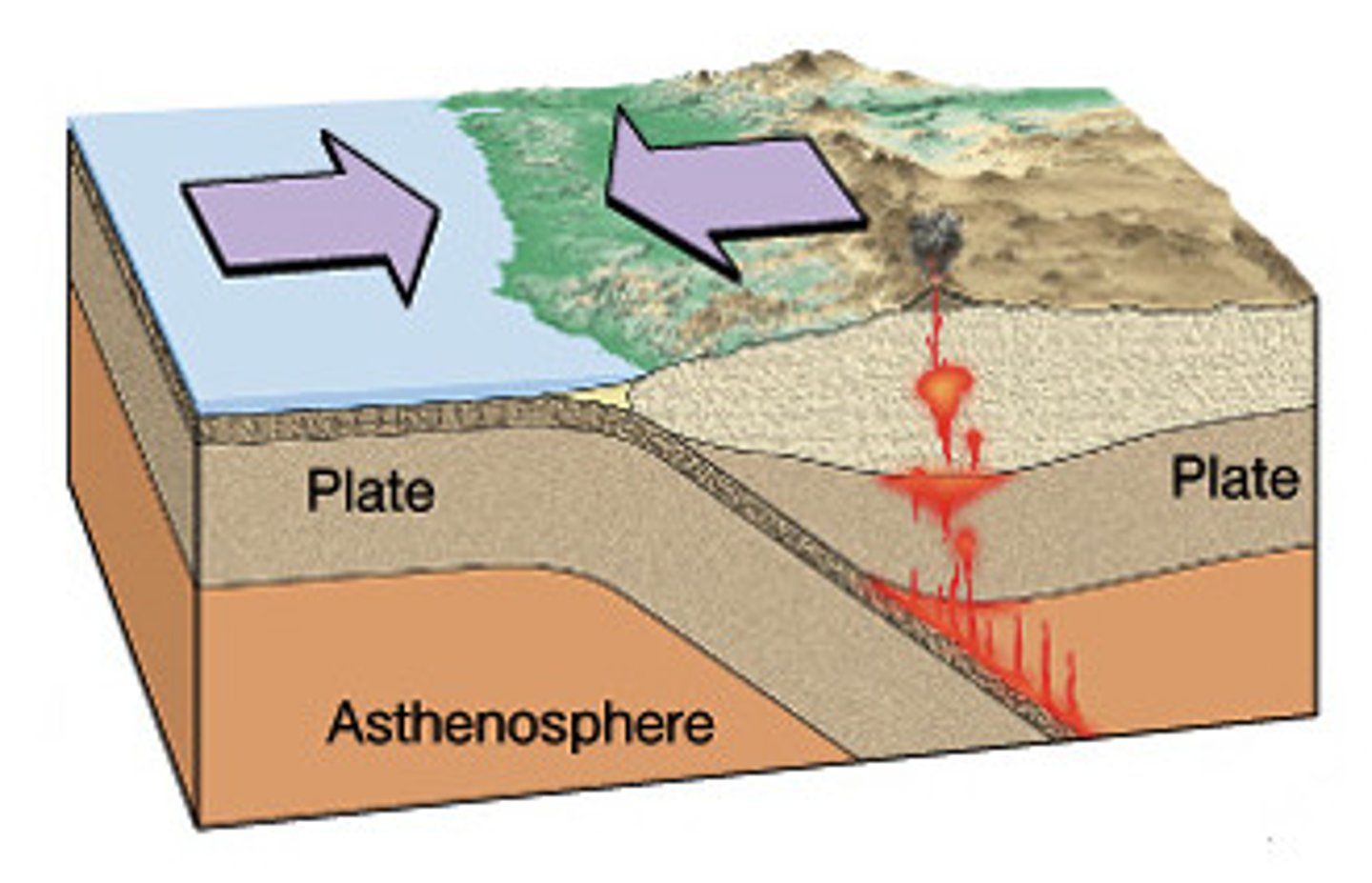
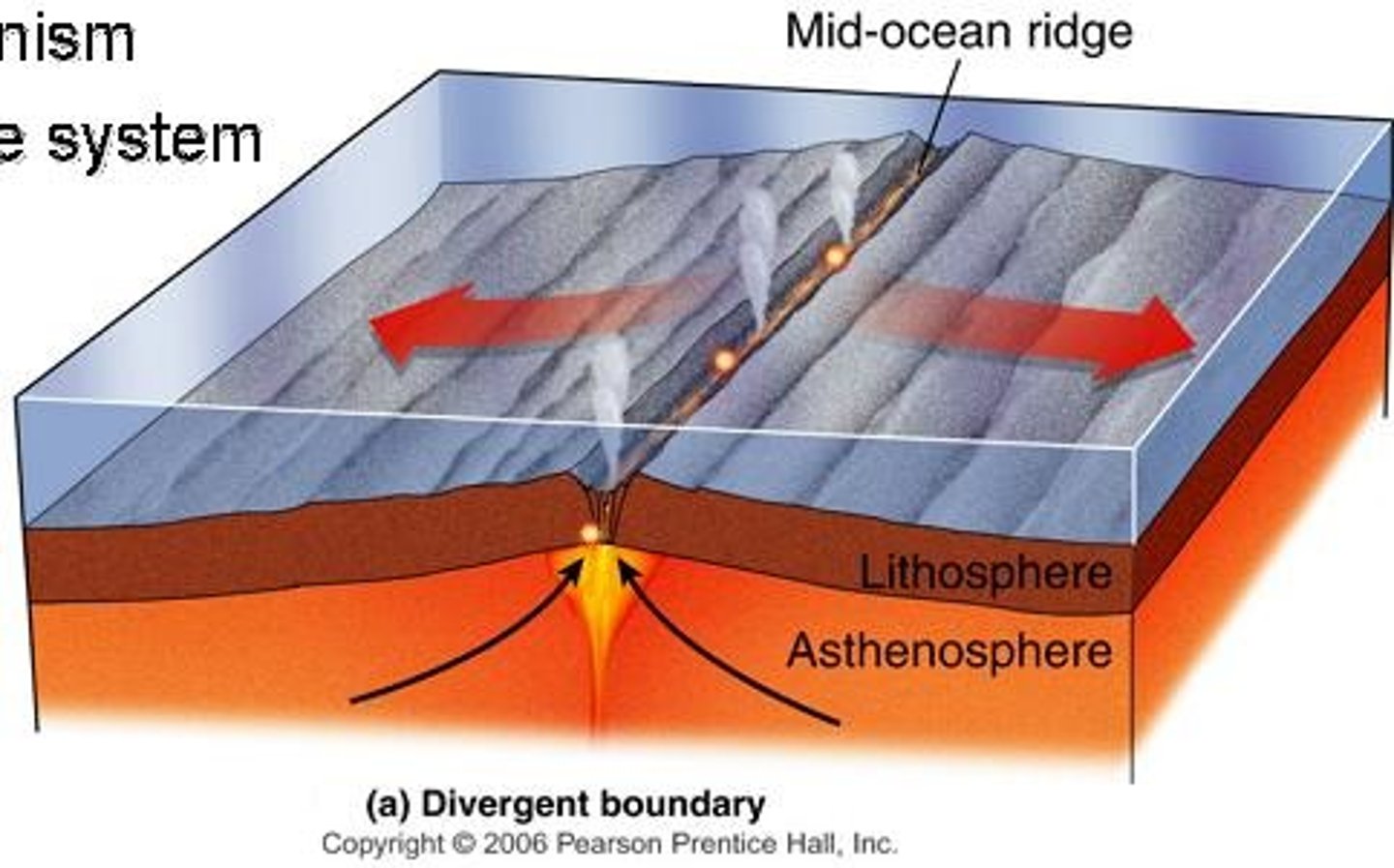
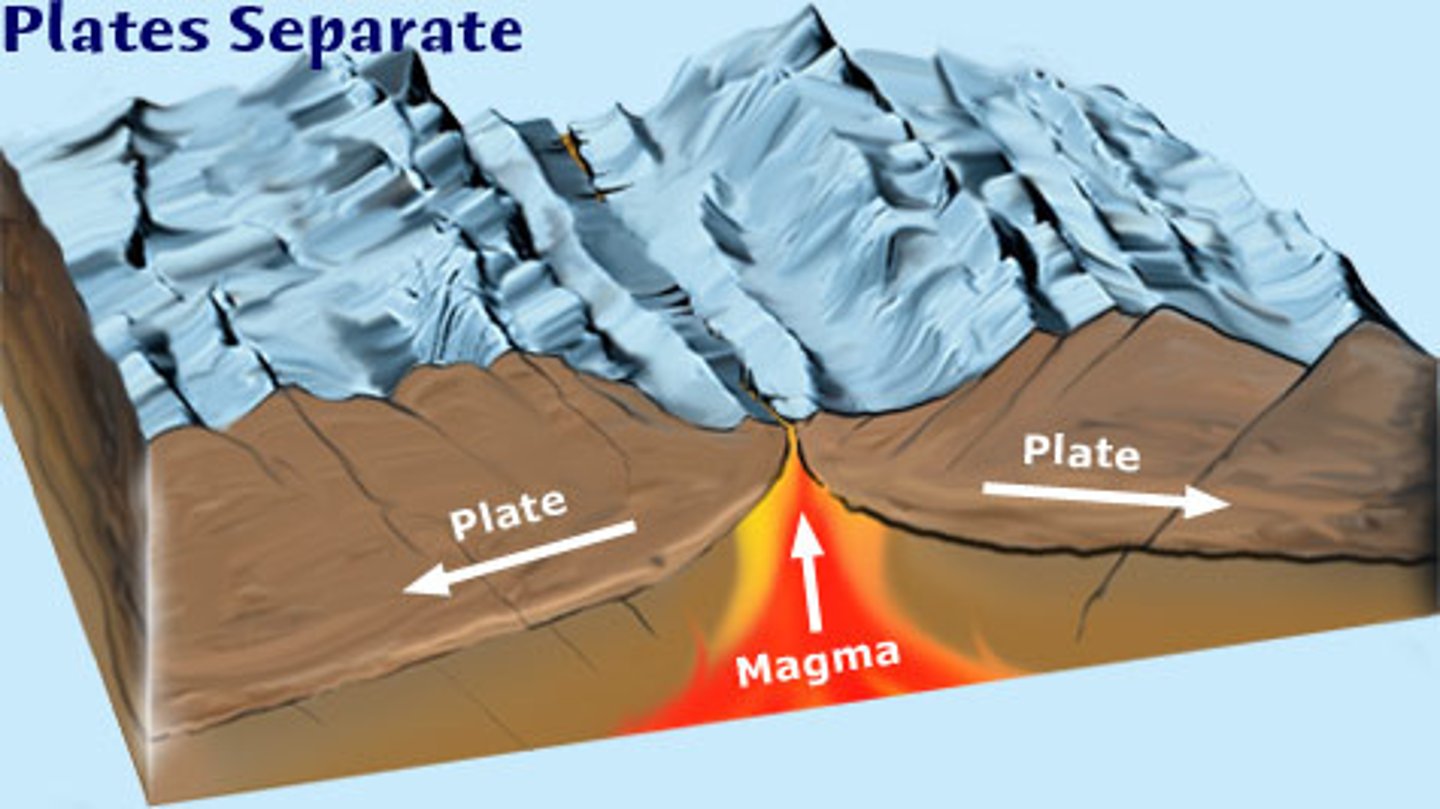
divergent boundary
A plate boundary where two plates move away from each other.
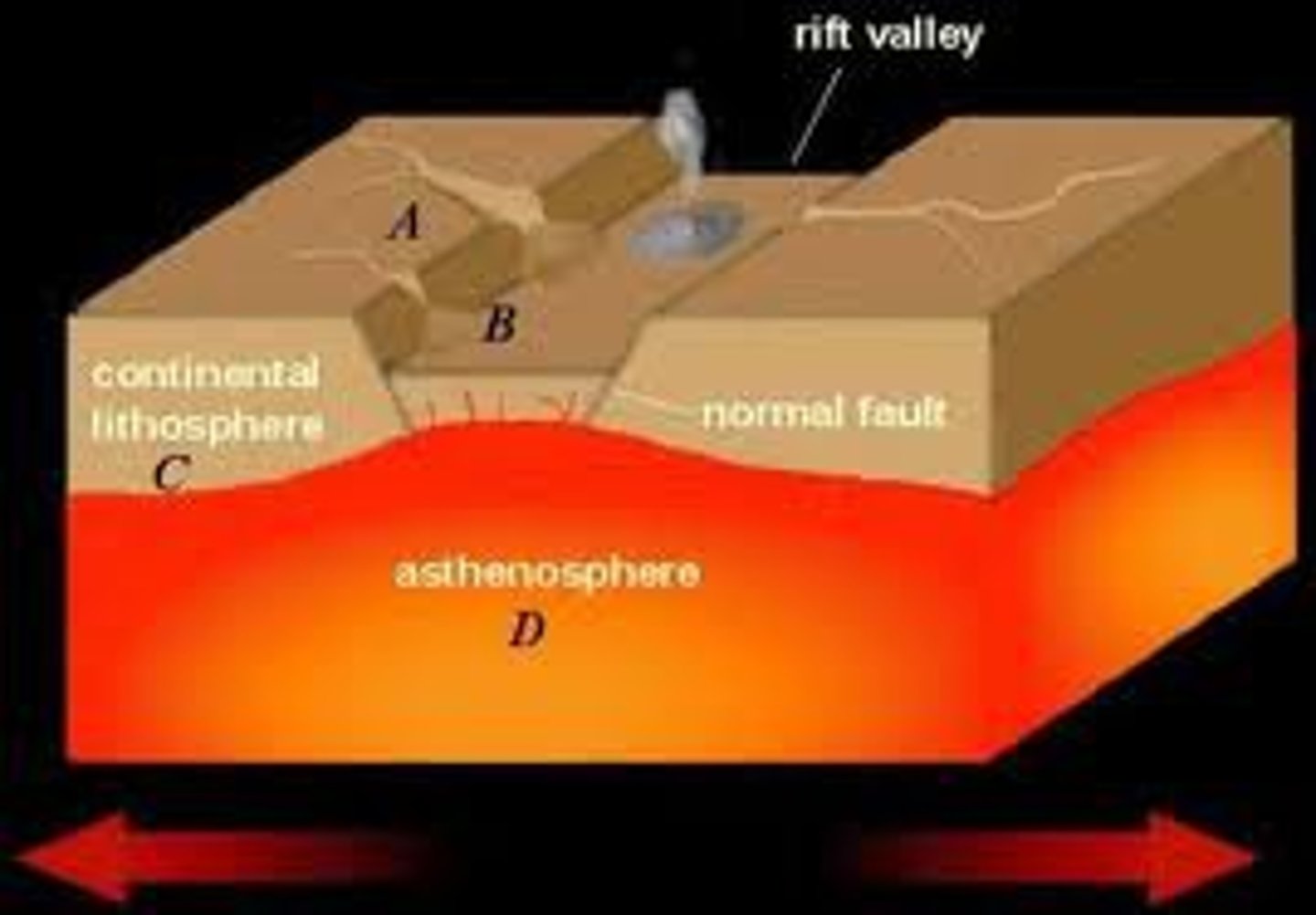
Rifting
the process by which Earth's crust breaks apart; can occur within continental crust or oceanic crust
mid-ocean ridge
An underwater mountain chain where new ocean floor is formed
transform boundary
A plate boundary where two plates move past each other in opposite directions
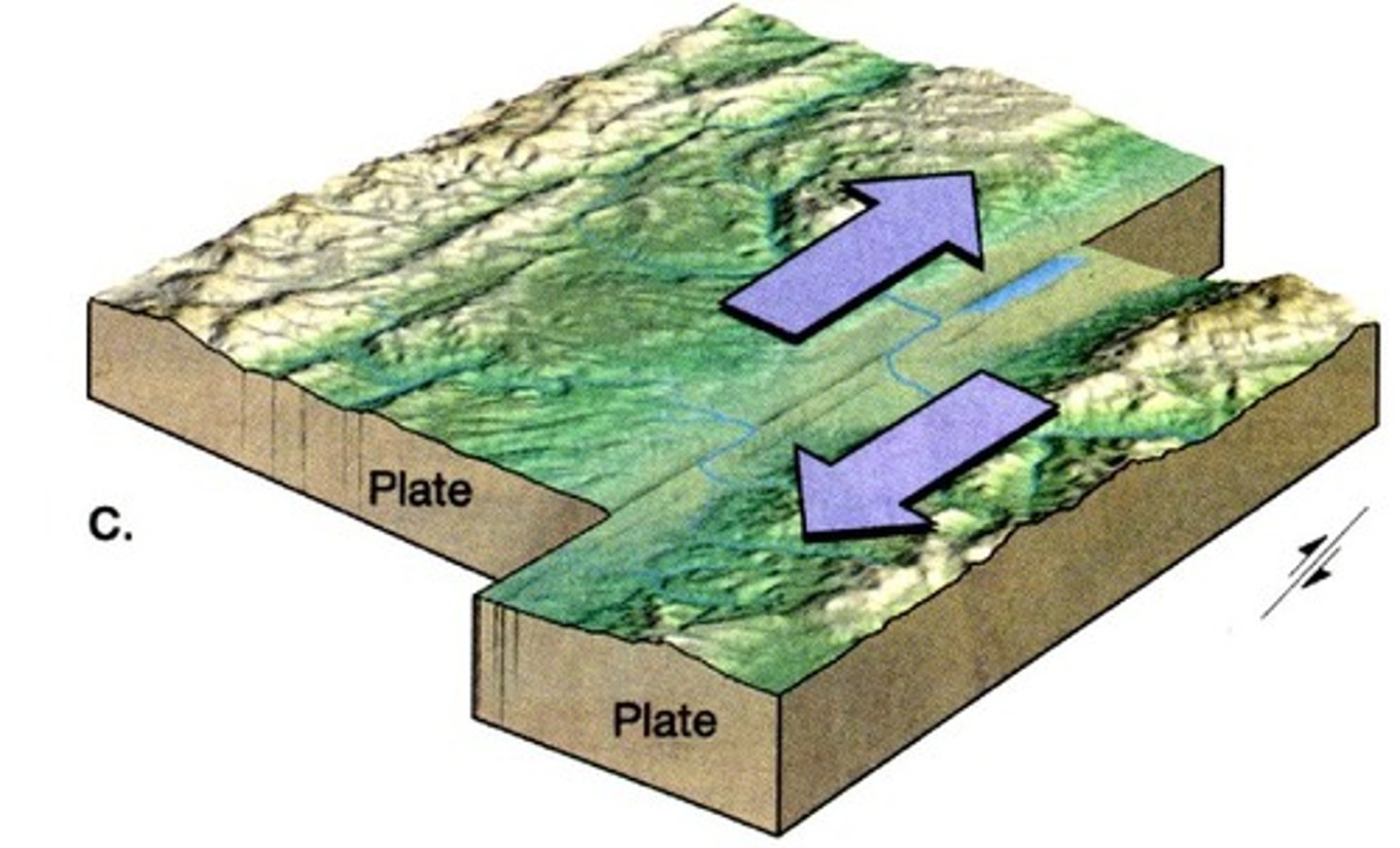
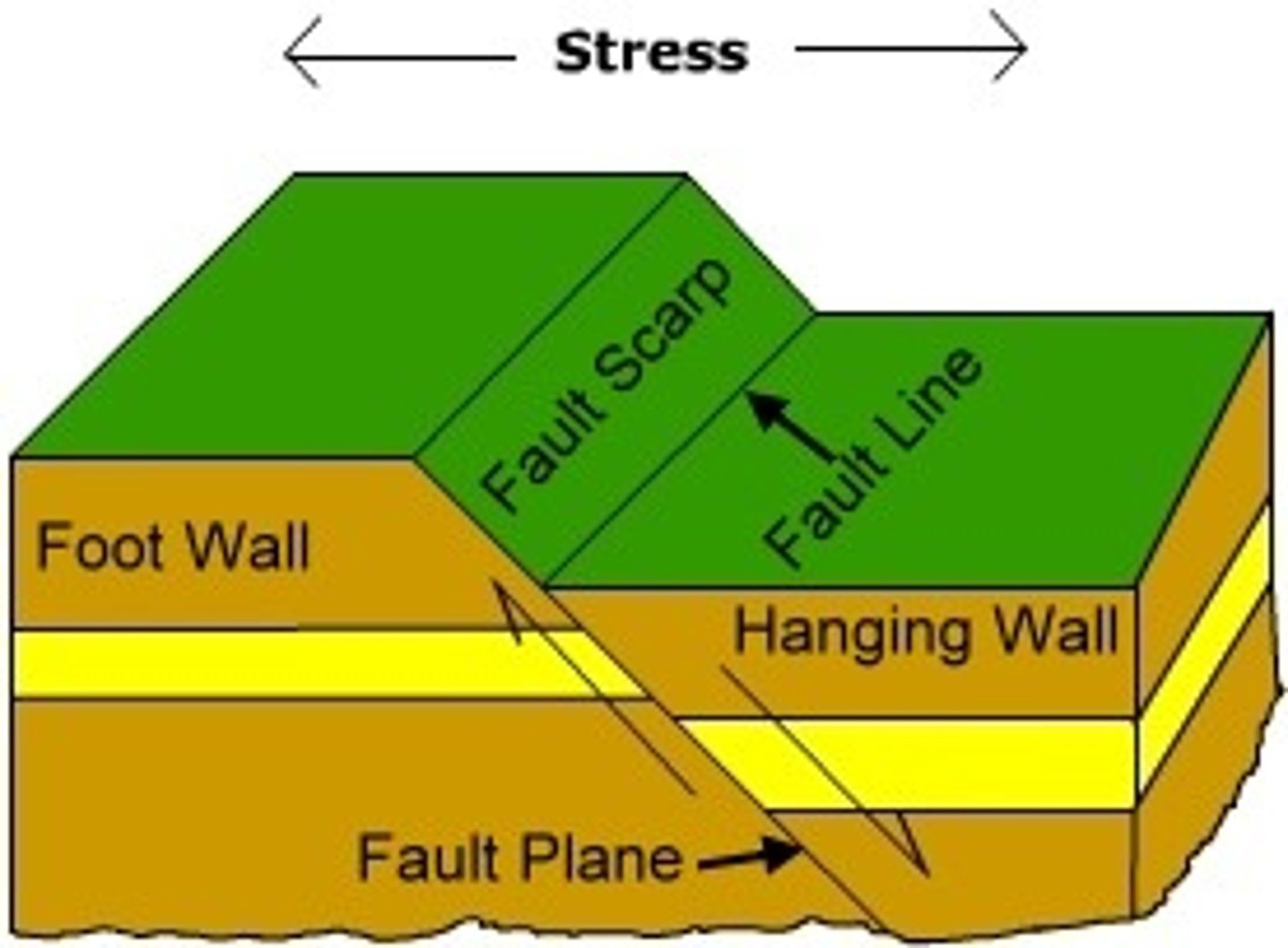
fault line
a crack in Earth's surface caused by moving plates
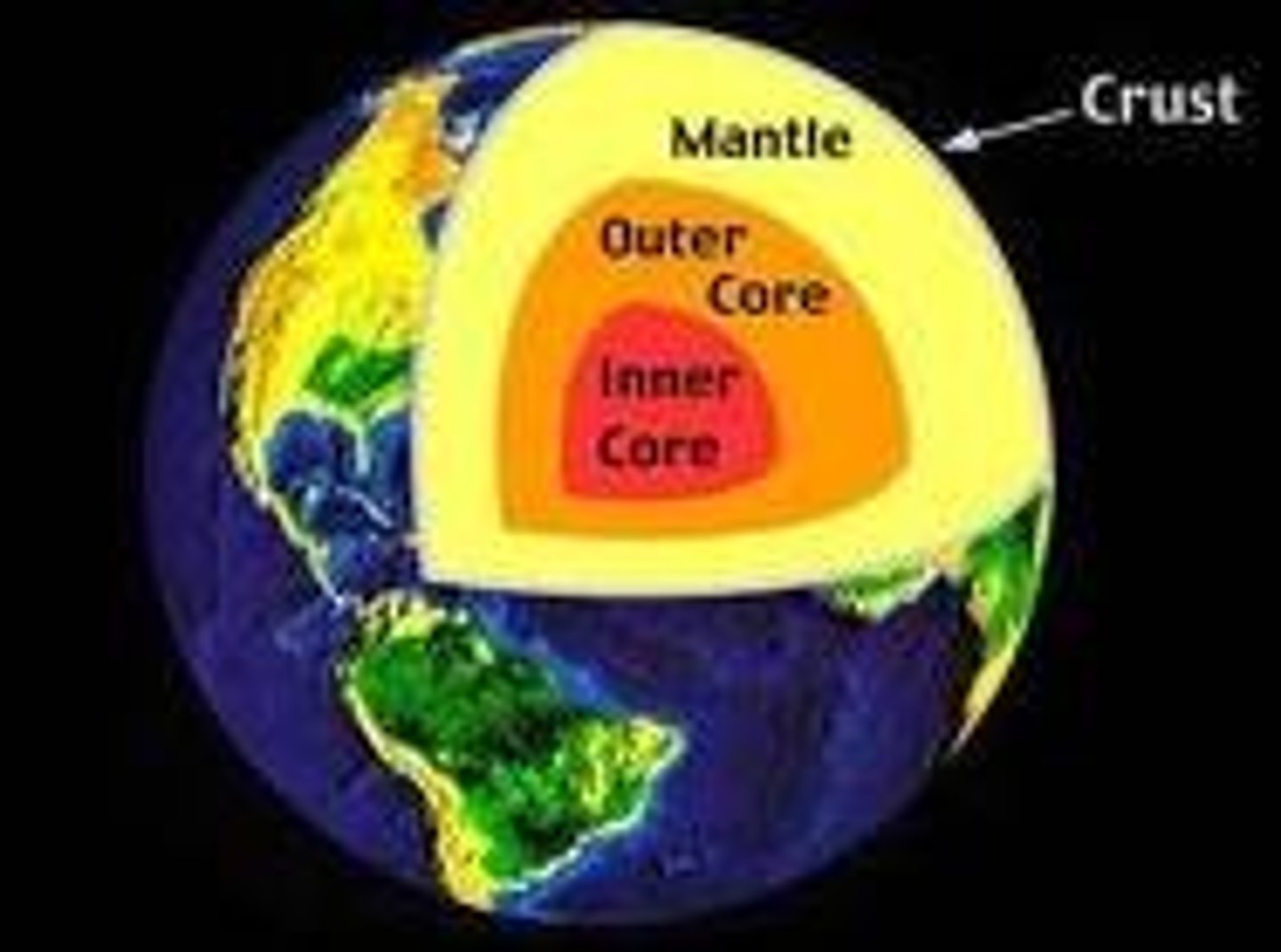
Mantle
The layer of hot, solid material between Earth's crust and core.
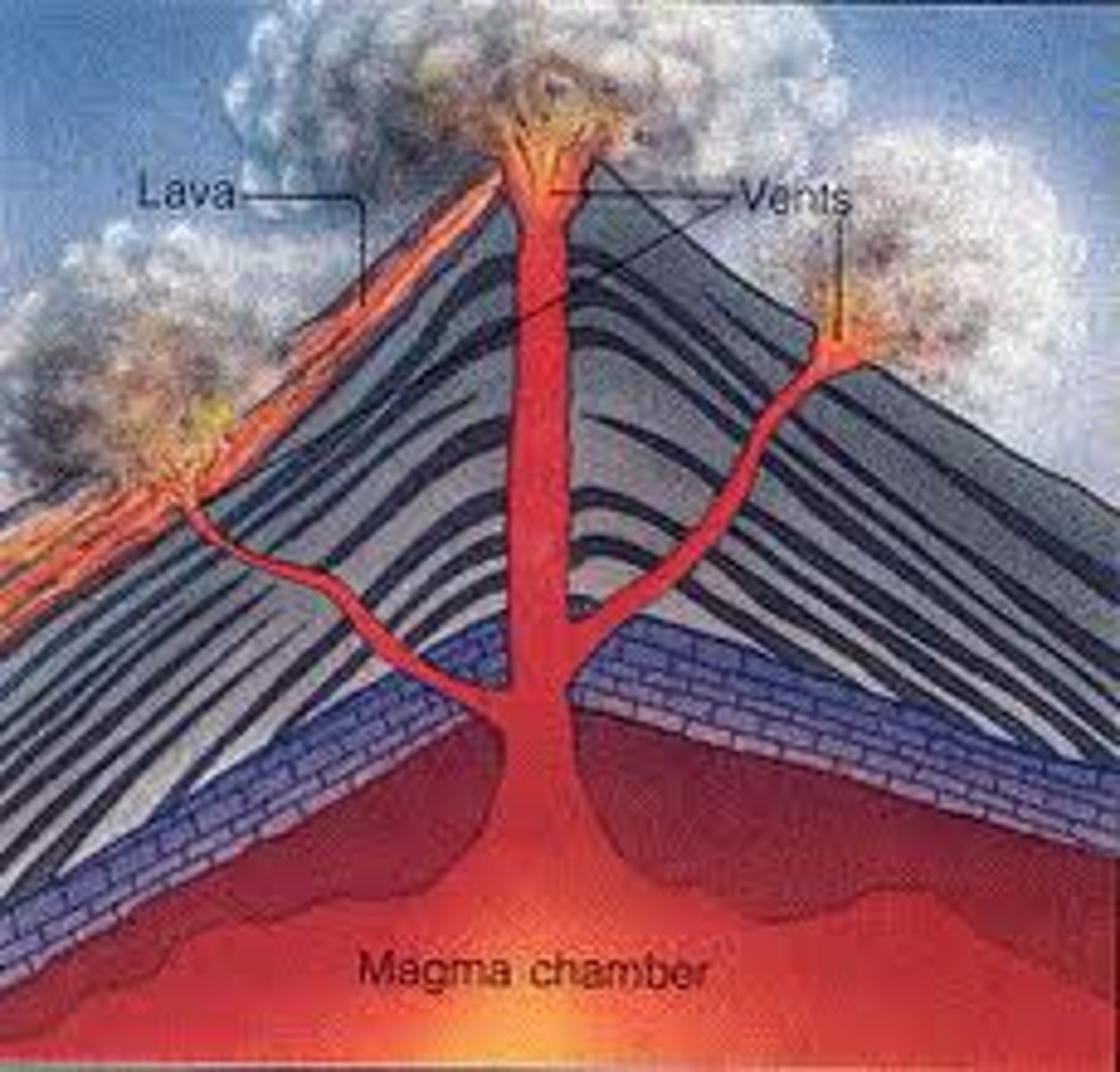
Magma
A molten mixture of rock-forming substances, gases, and water from the mantle
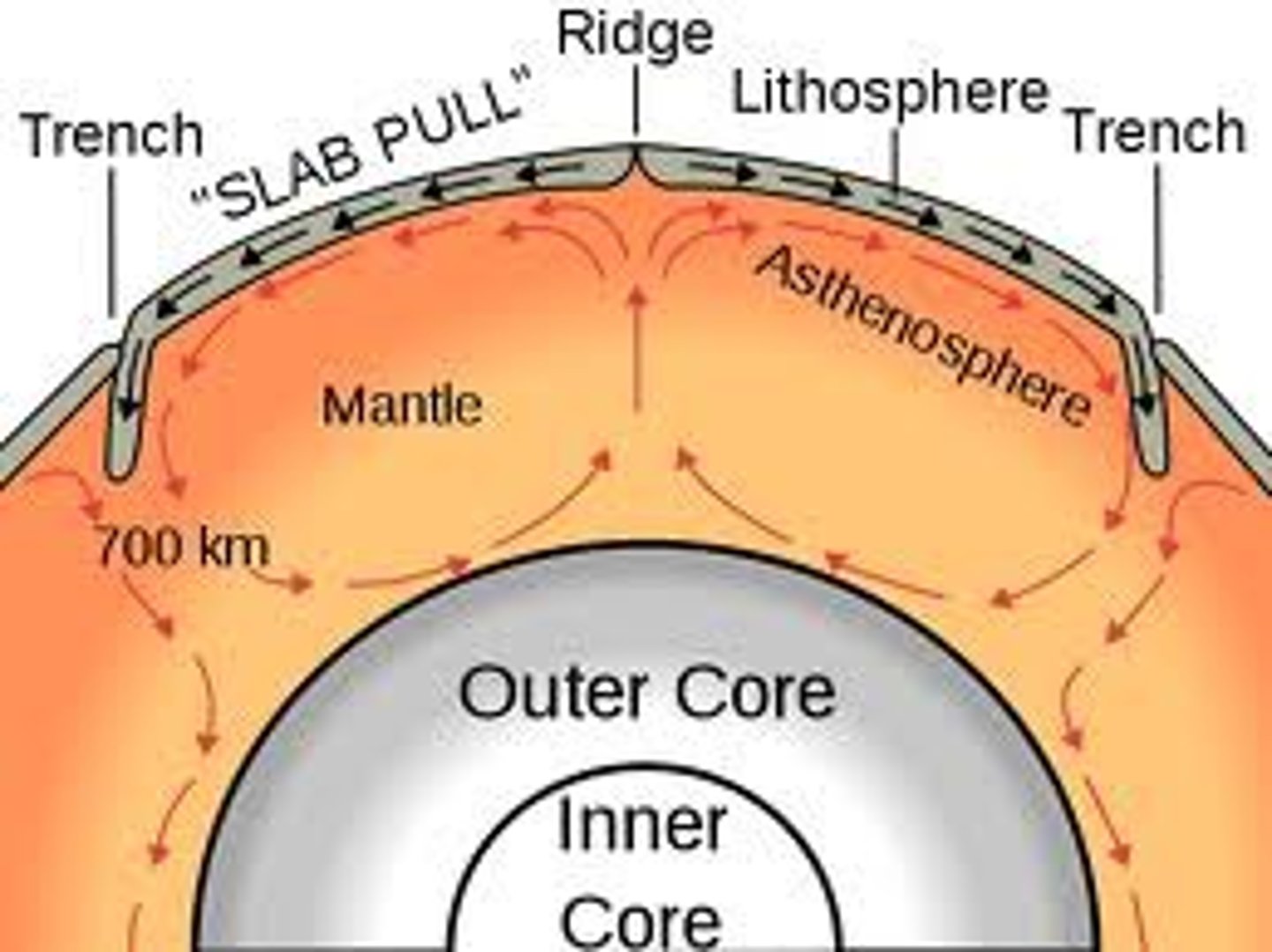
slab pull
the pulling of a tectonic plate as its edge subducts deep into the mantle
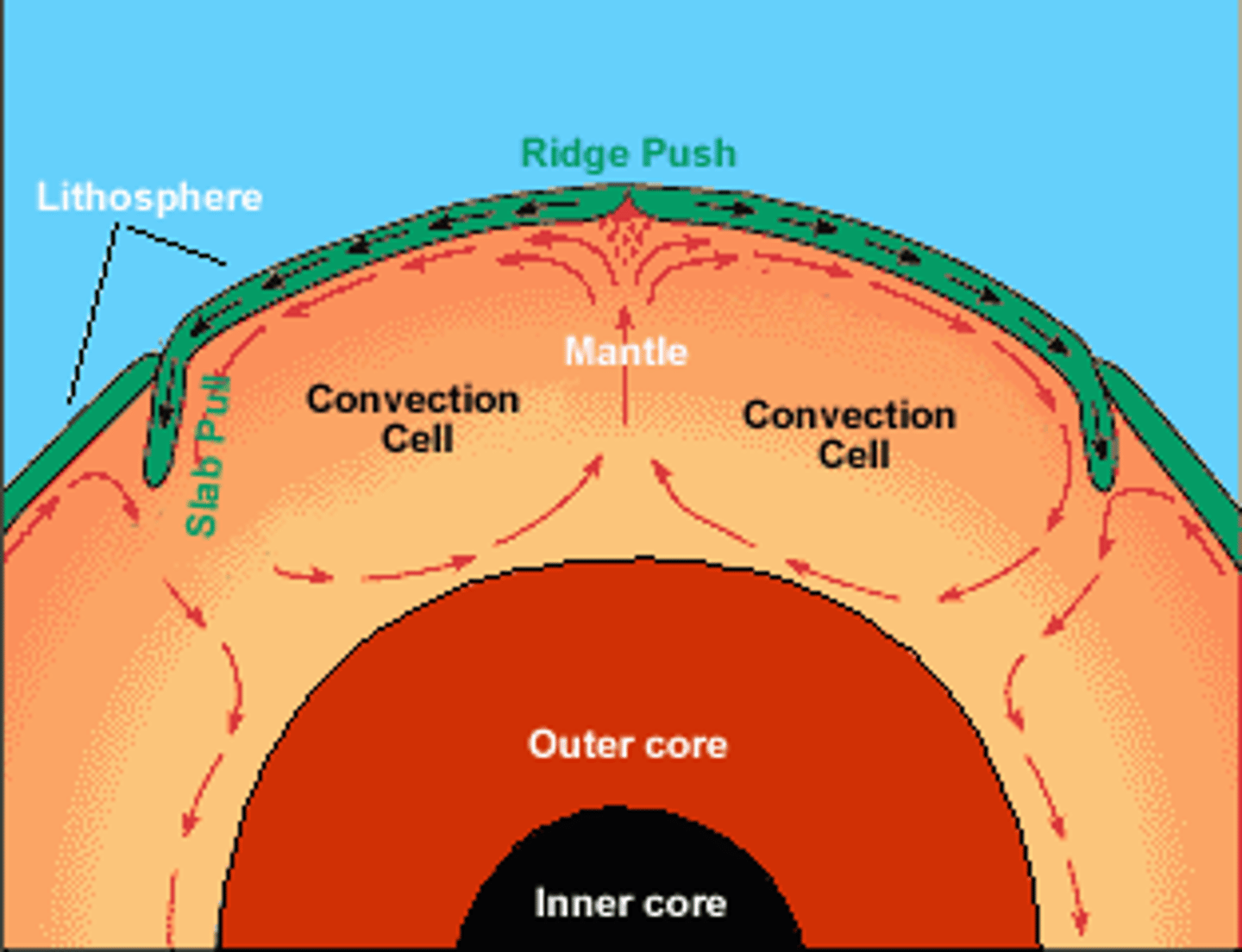
ridge push
when the force of gravity moves a plate downward and away from a ridge
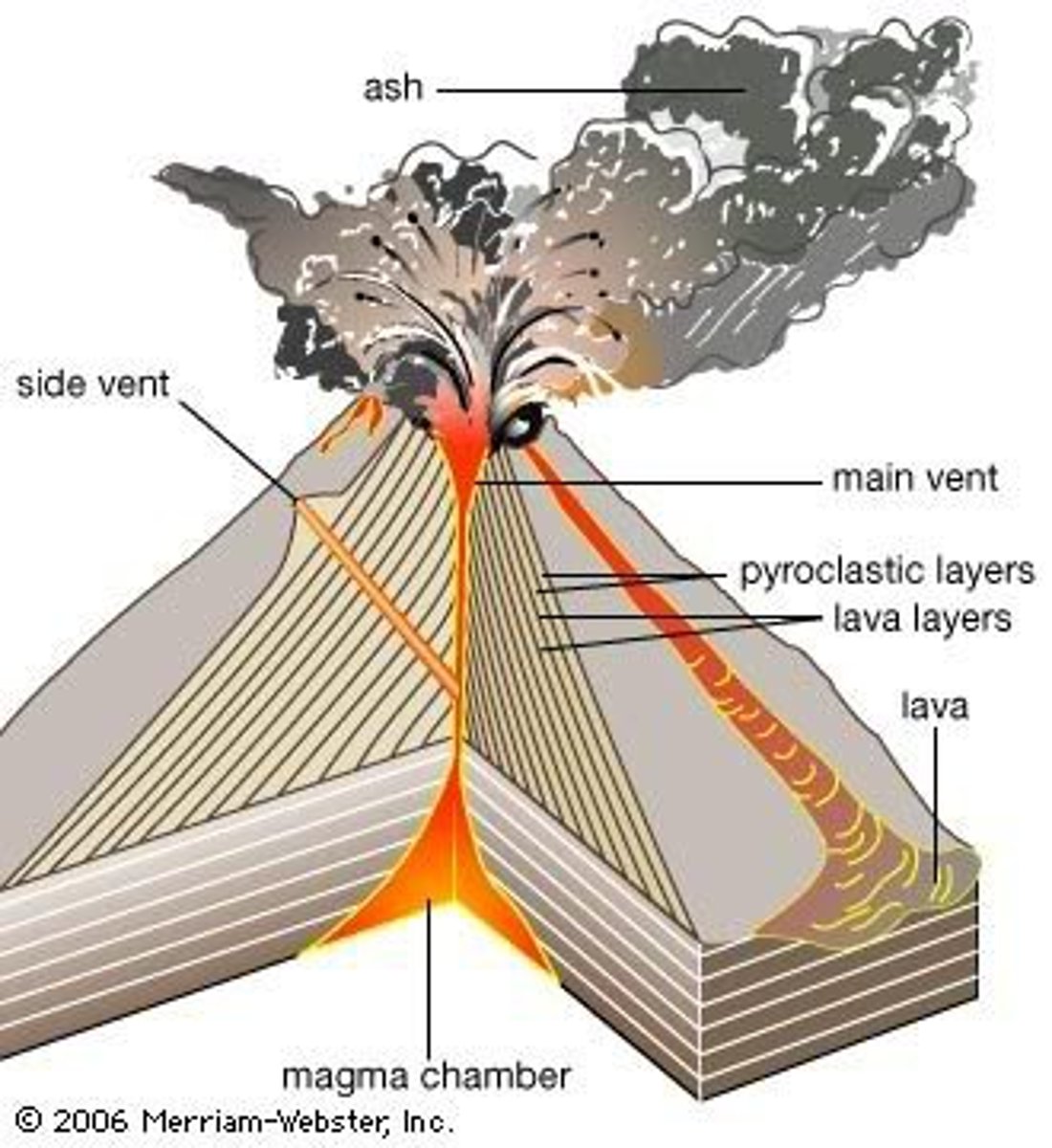
Volcanoes
an opening in the Earth's crust through which molten lava, ash, and gases are ejected.
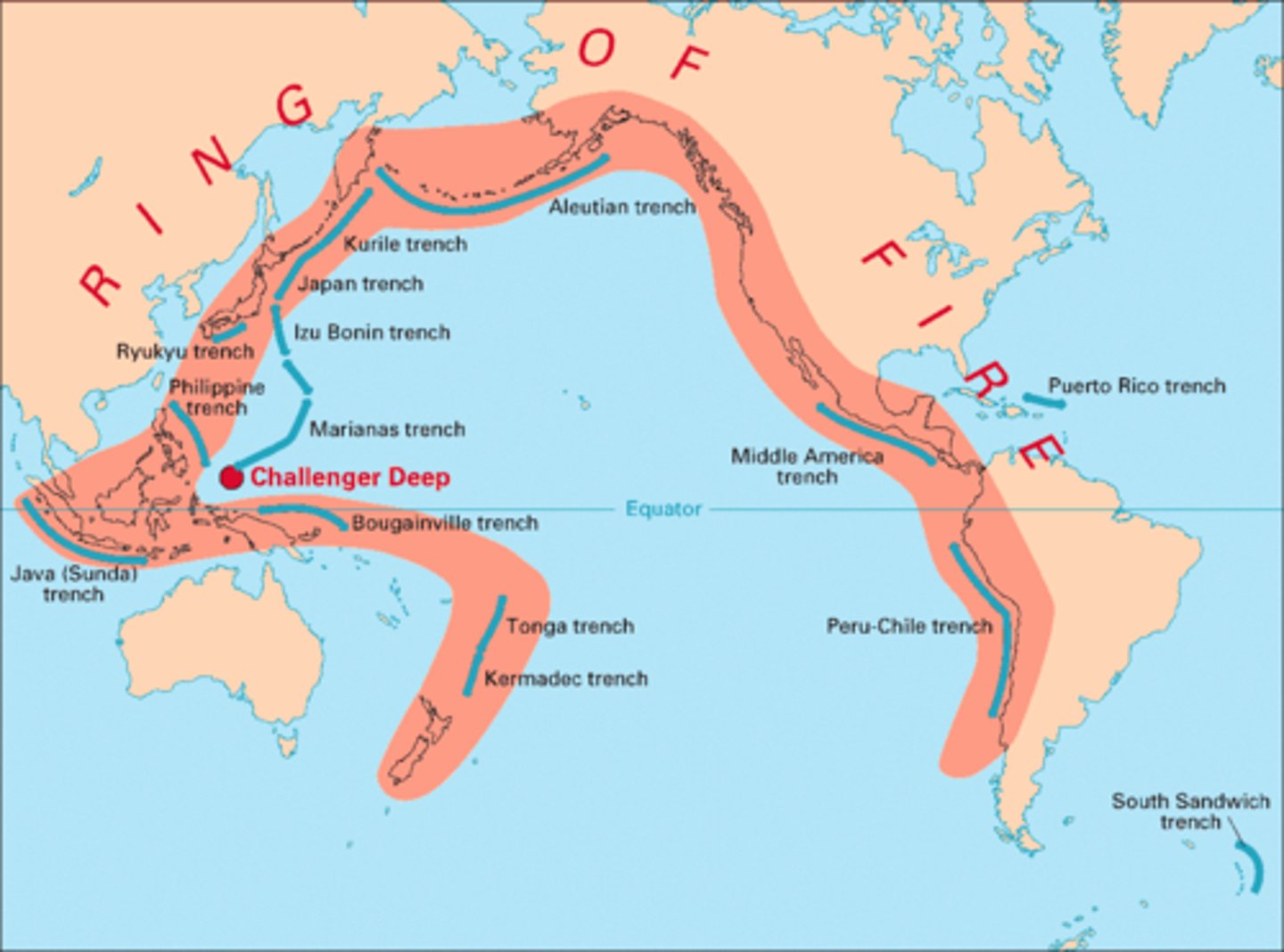
Ring of Fire
A zone of intense volcanic activity a the boundary between the Pacific plate and surrounding continental plates
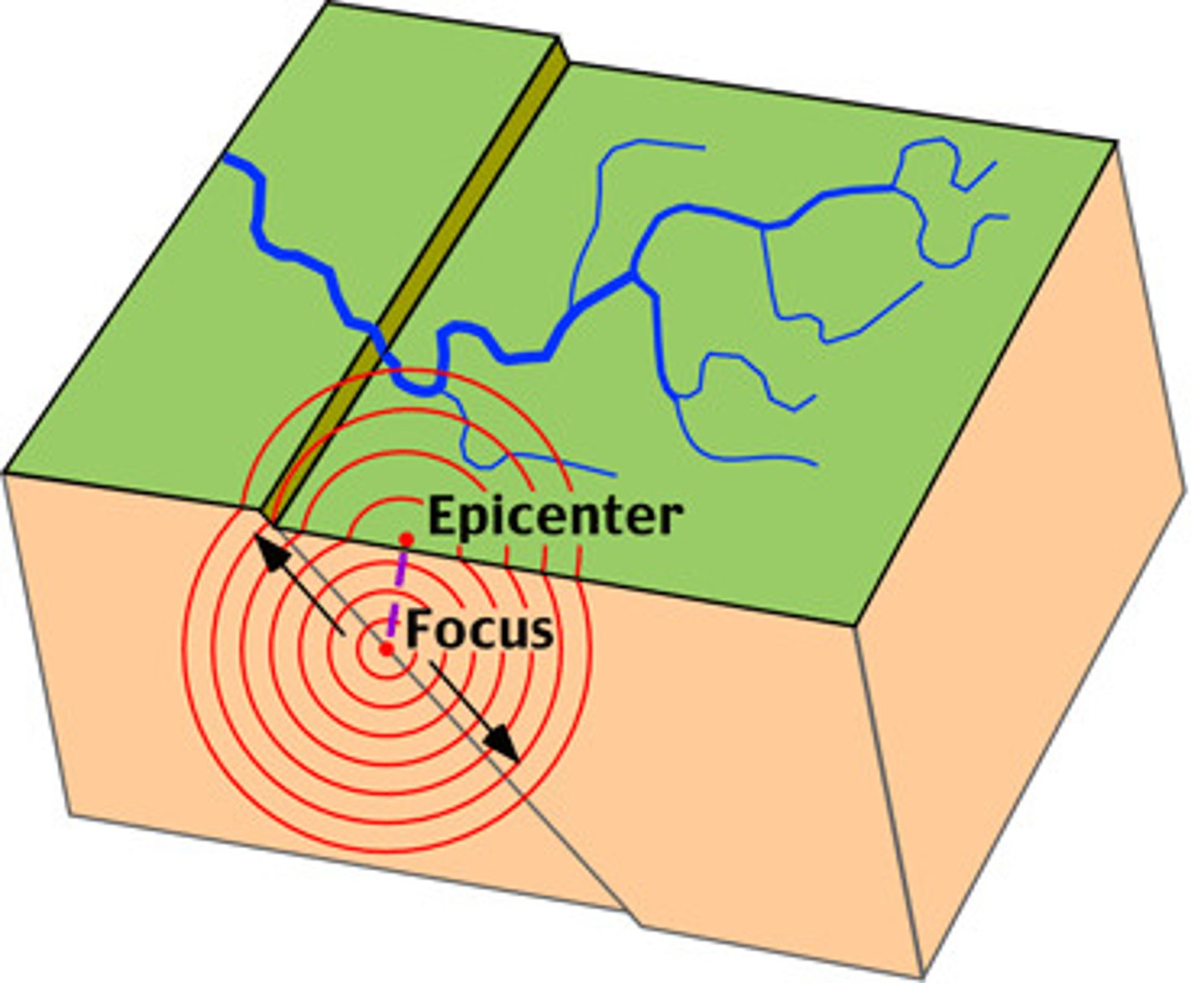
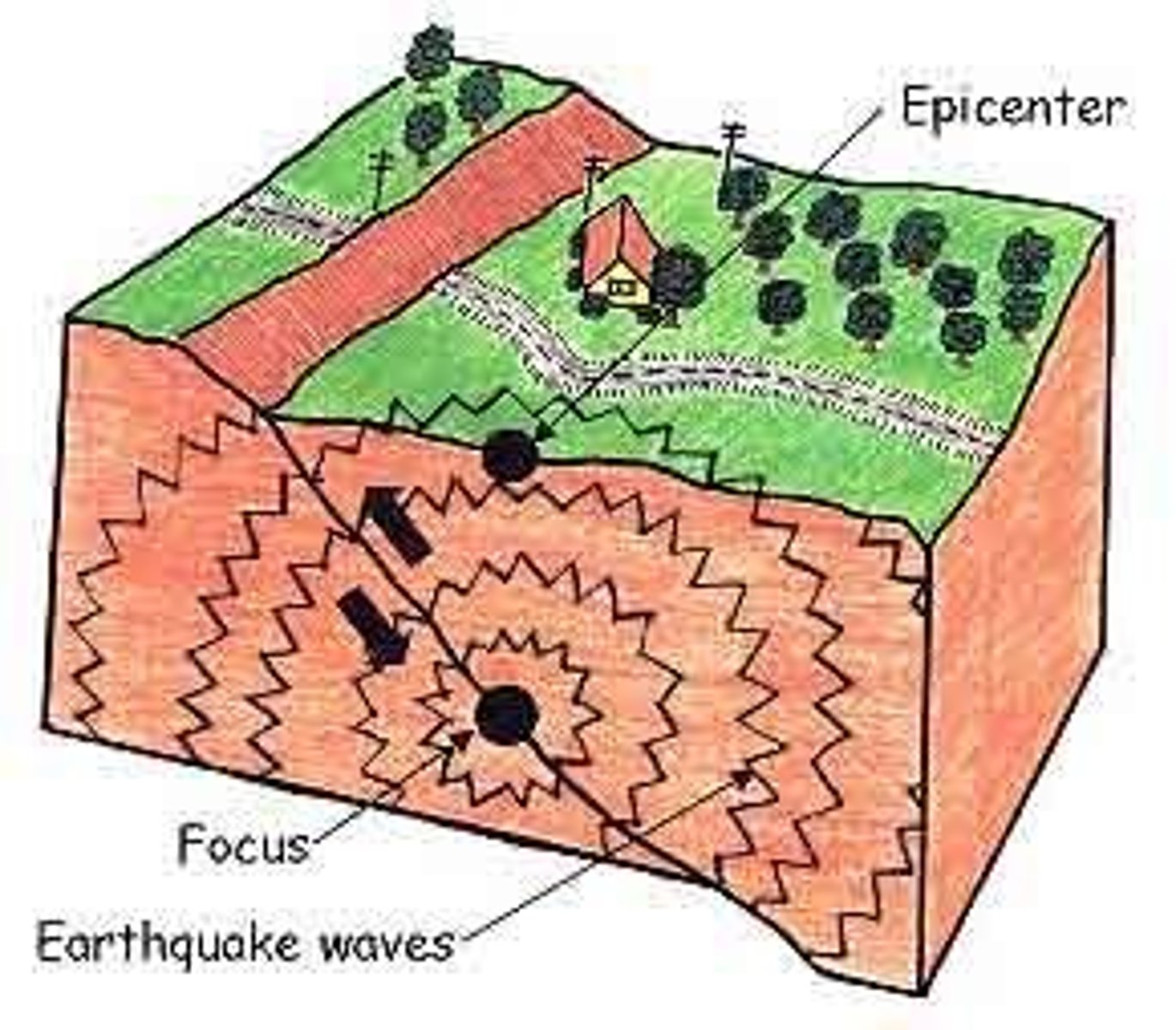
Focus
The point beneath Earth's surface where rock breaks under stress and causes an earthquake
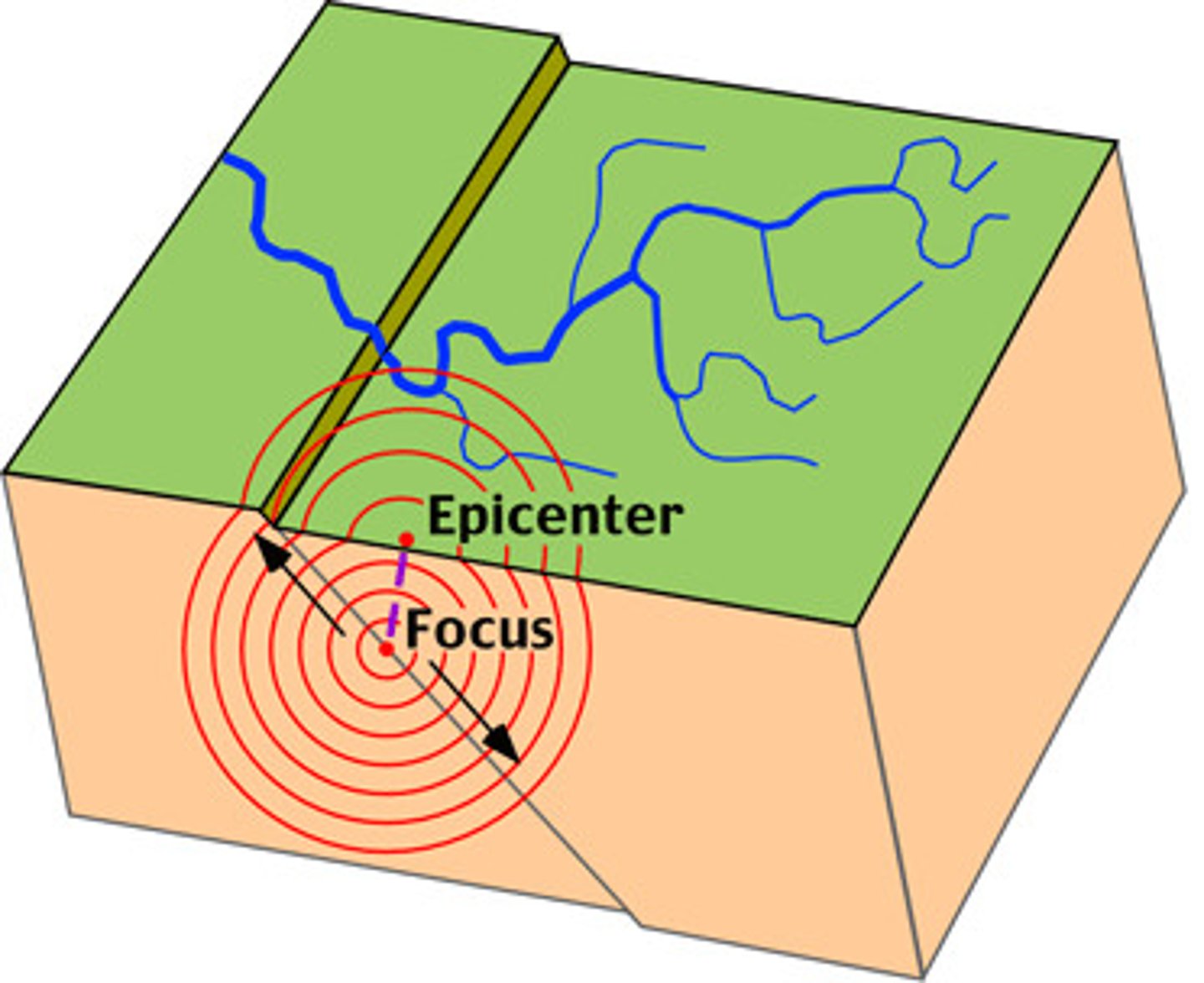
Epicentre
the point on the Earth's surface directly above the focus of an earthquake
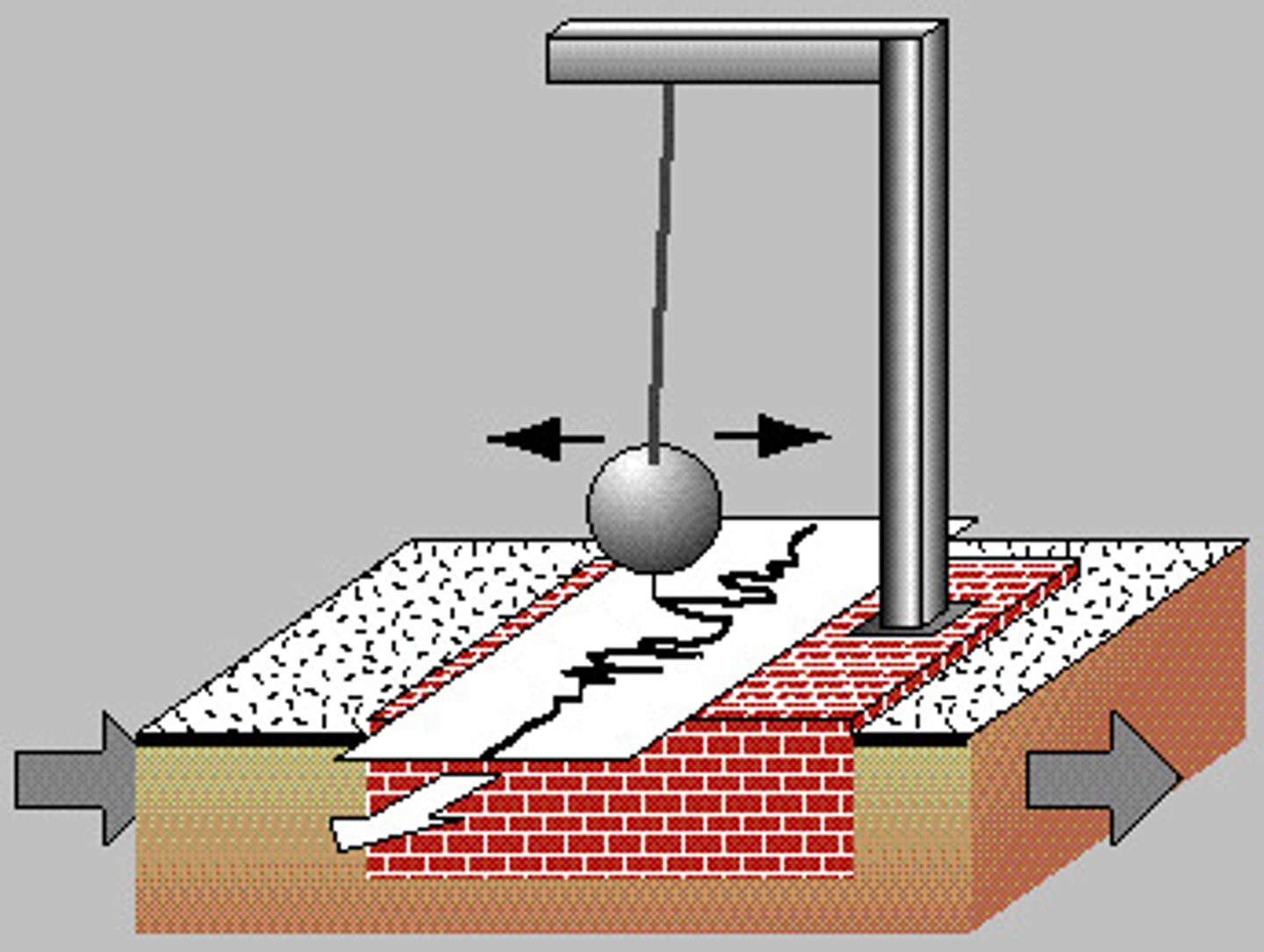
Seismometer
Instrument used to measure horizontal or vertical motion during an earthquake.
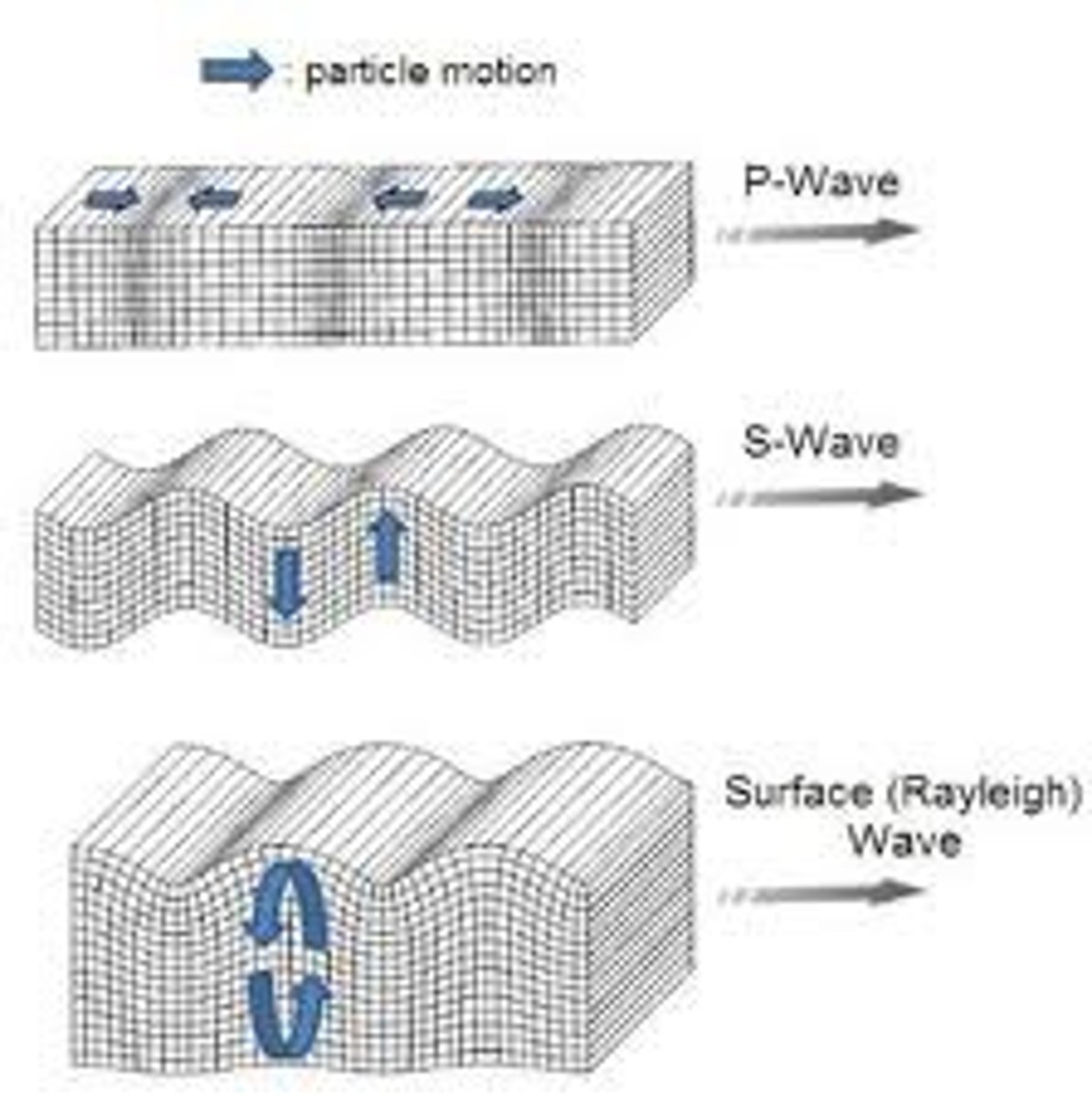
P (primary) waves
longitudinal waves (back and forth) that travel fast.
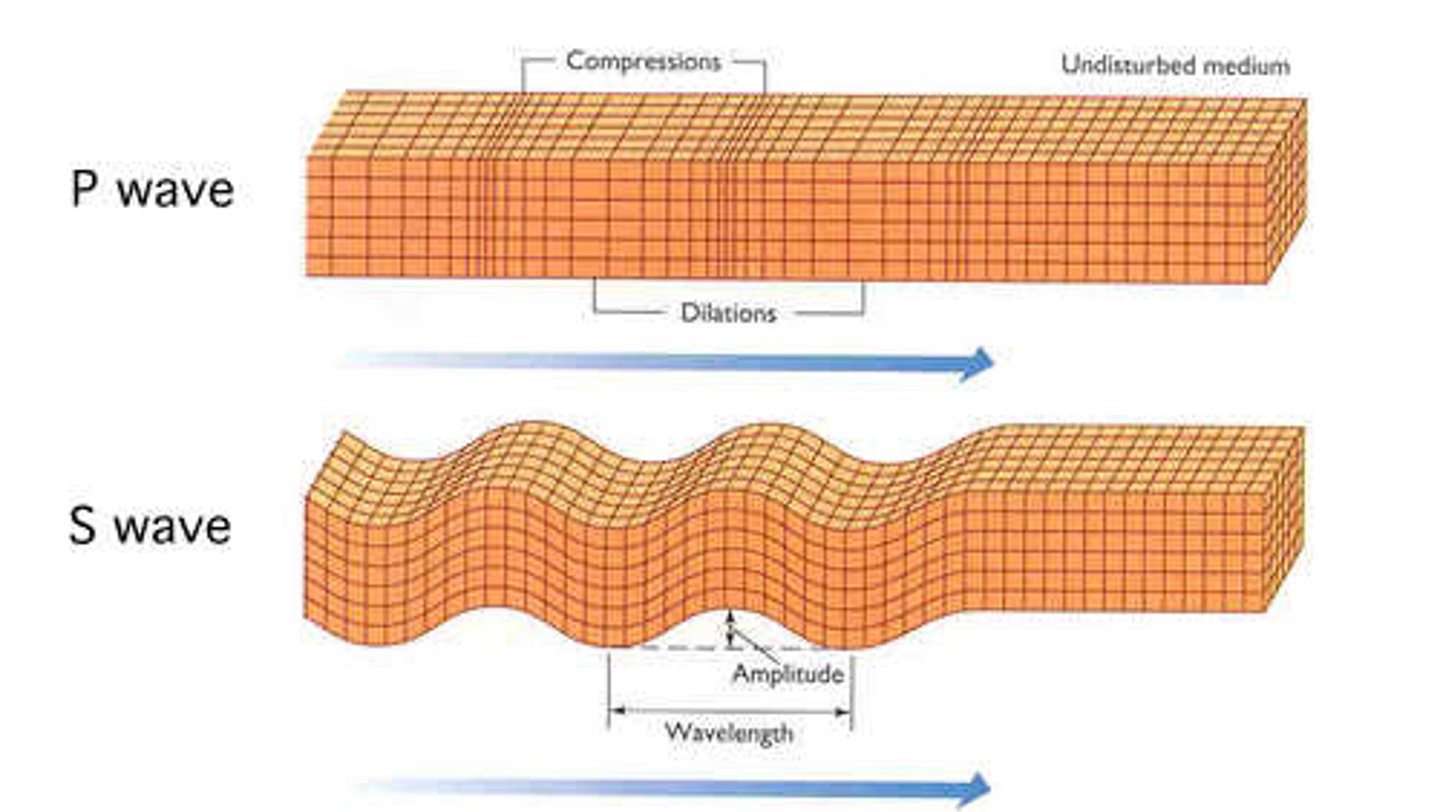
S (secondary) waves
transverse waves (up and down) travel slower than P-waves.
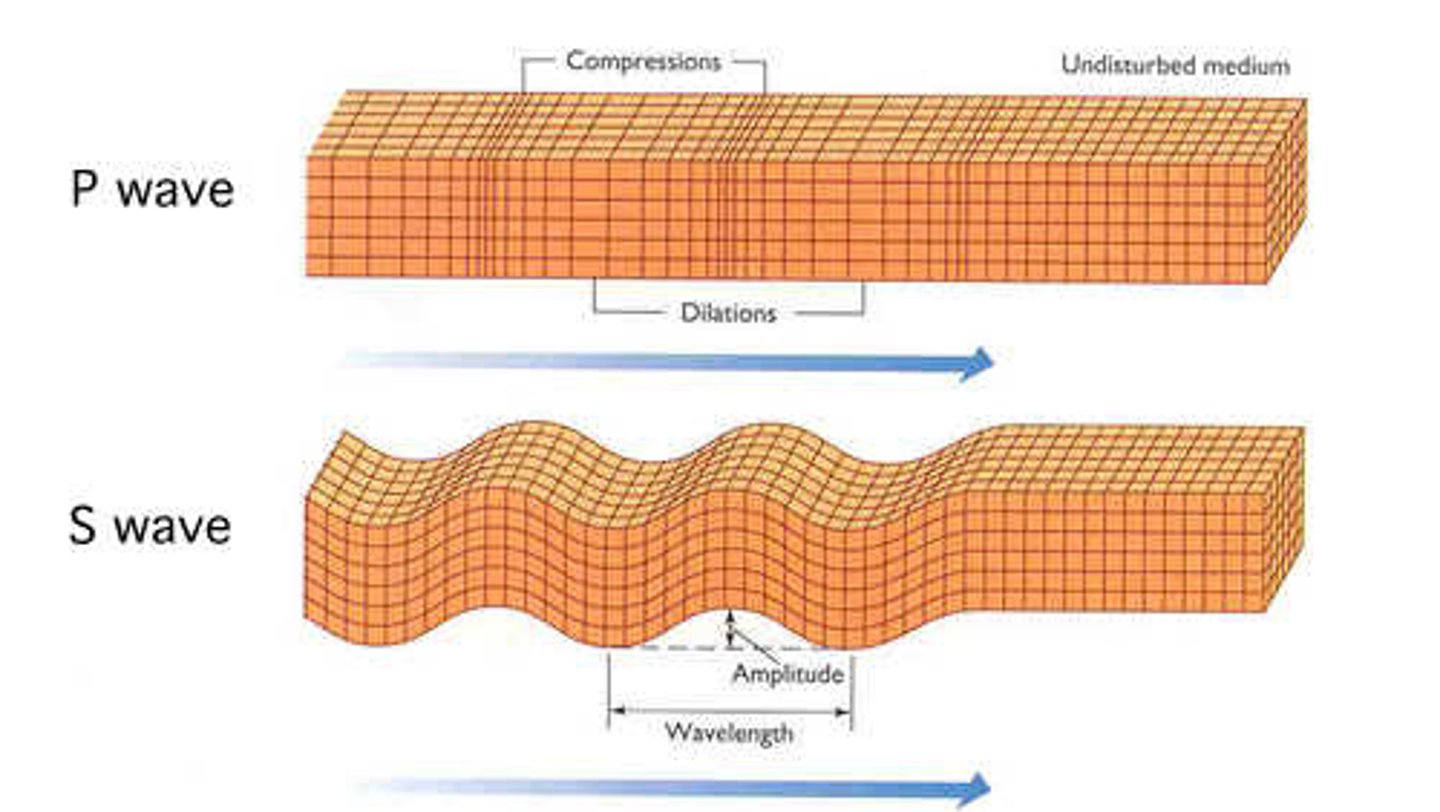
surface waves
seismic waves that travel along the Earth's surface. Causes the most destruction.
earthquake
The shaking that results from the movement of rock beneath Earth's surface.
Richter scale
A scale that rates an earthquake's magnitude based on the size of its seismic waves.

tectonic plates
Sections of the Earth's crust that move due to convection currents.

plate boundary
the region where two tectonic plates are in contact
Hot spot
A hot spot is an localized area where magma from deep in the mantle rises, not necessarily associated with a plate boundary
Proton
A subatomic particle that has a positive charge, a relative weight of 1, and found in the nucleus of an atom
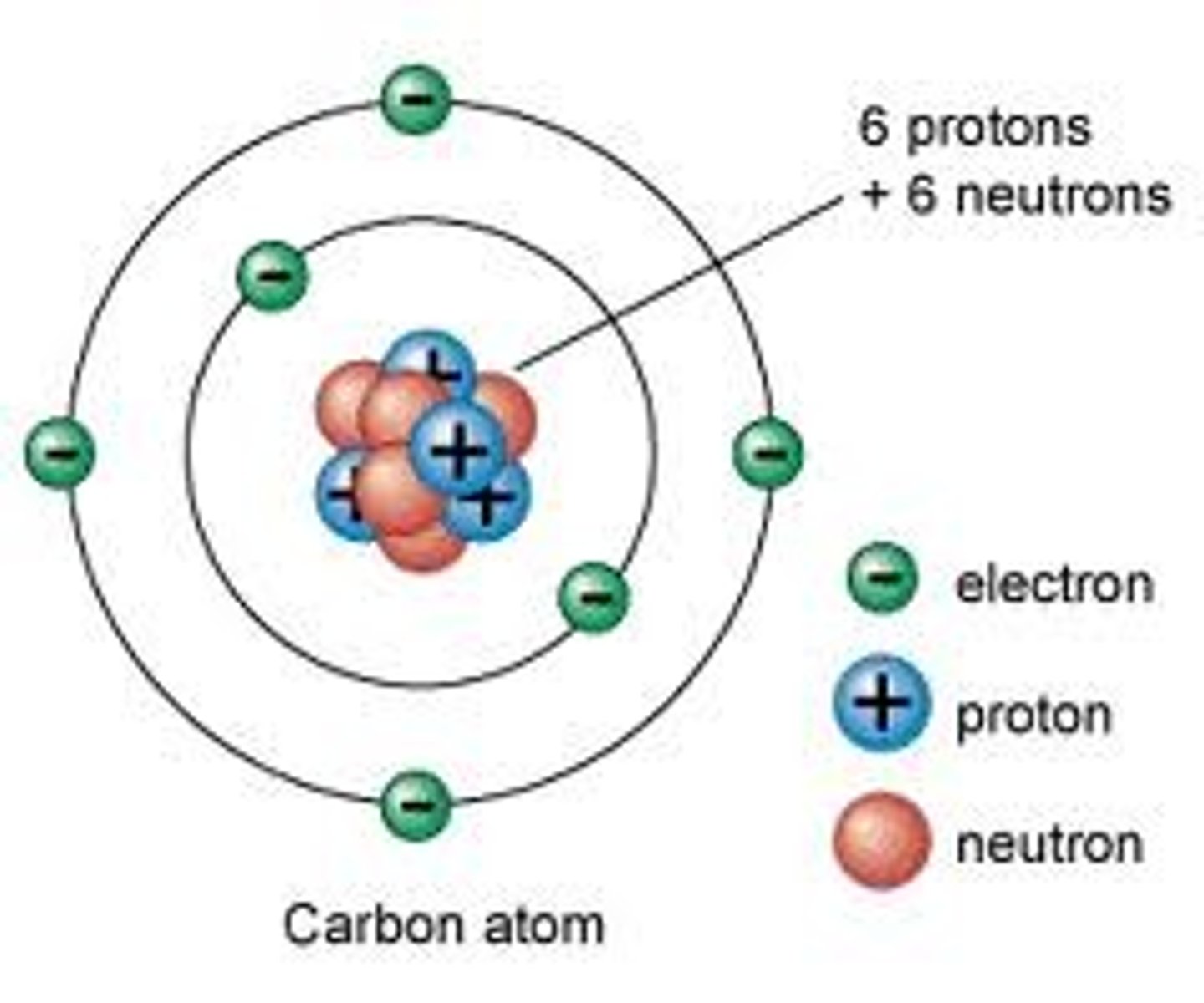
Neutron
A subatomic particle that has no charge, relative weight of 1, and found in the nucleus of an atom
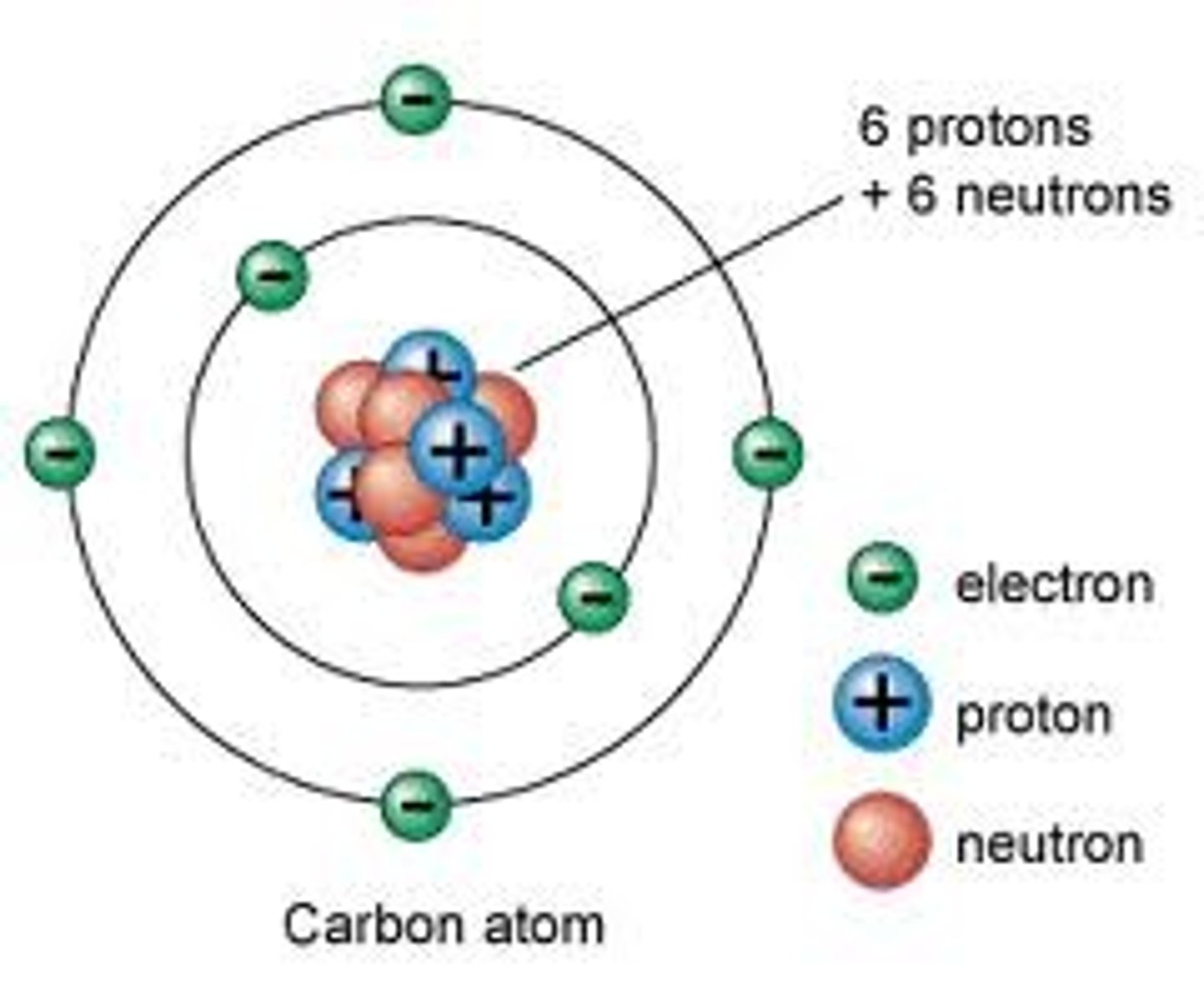
Electron
A subatomic particle that has a negative charge, no weight and orbits the nucleus
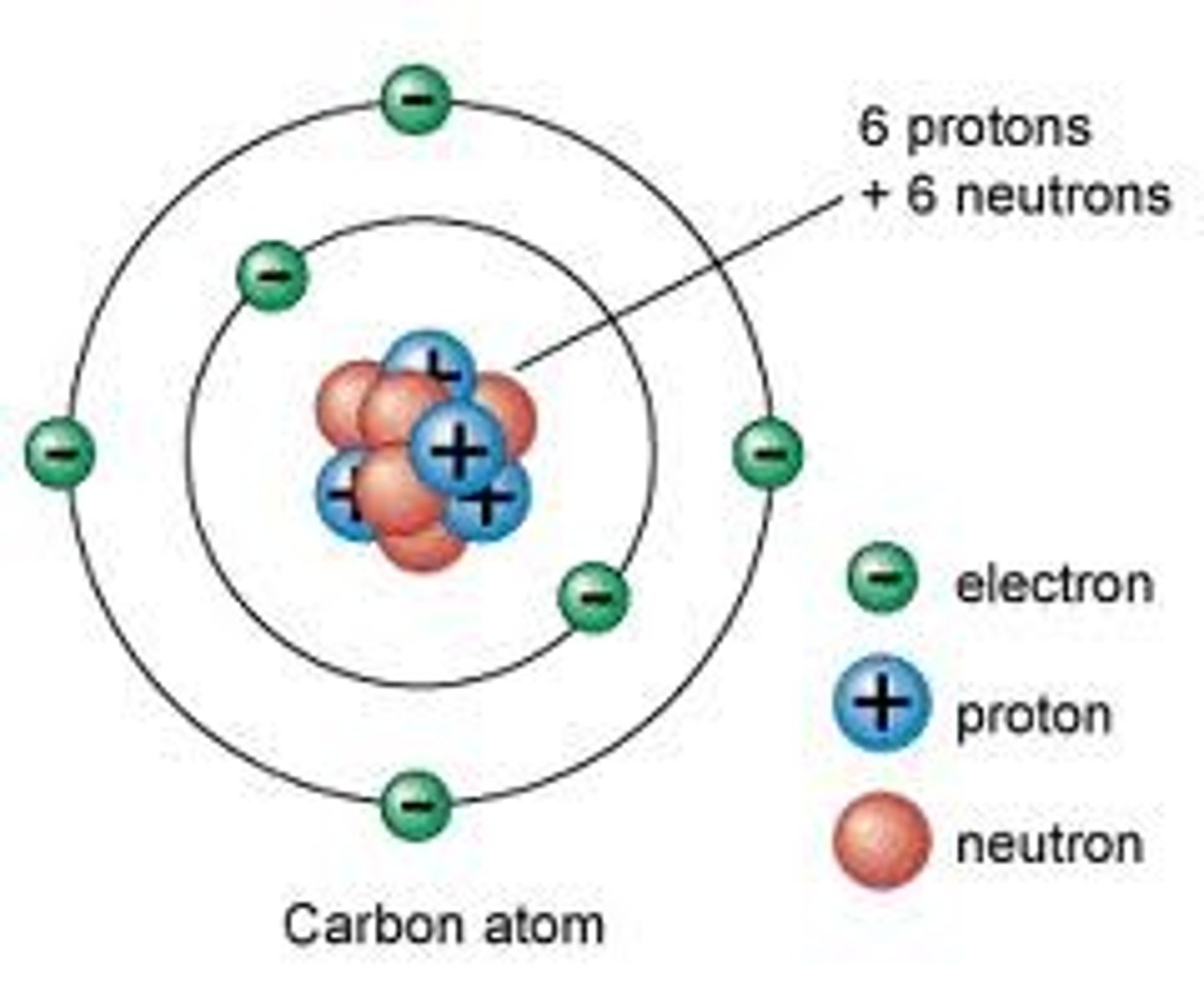
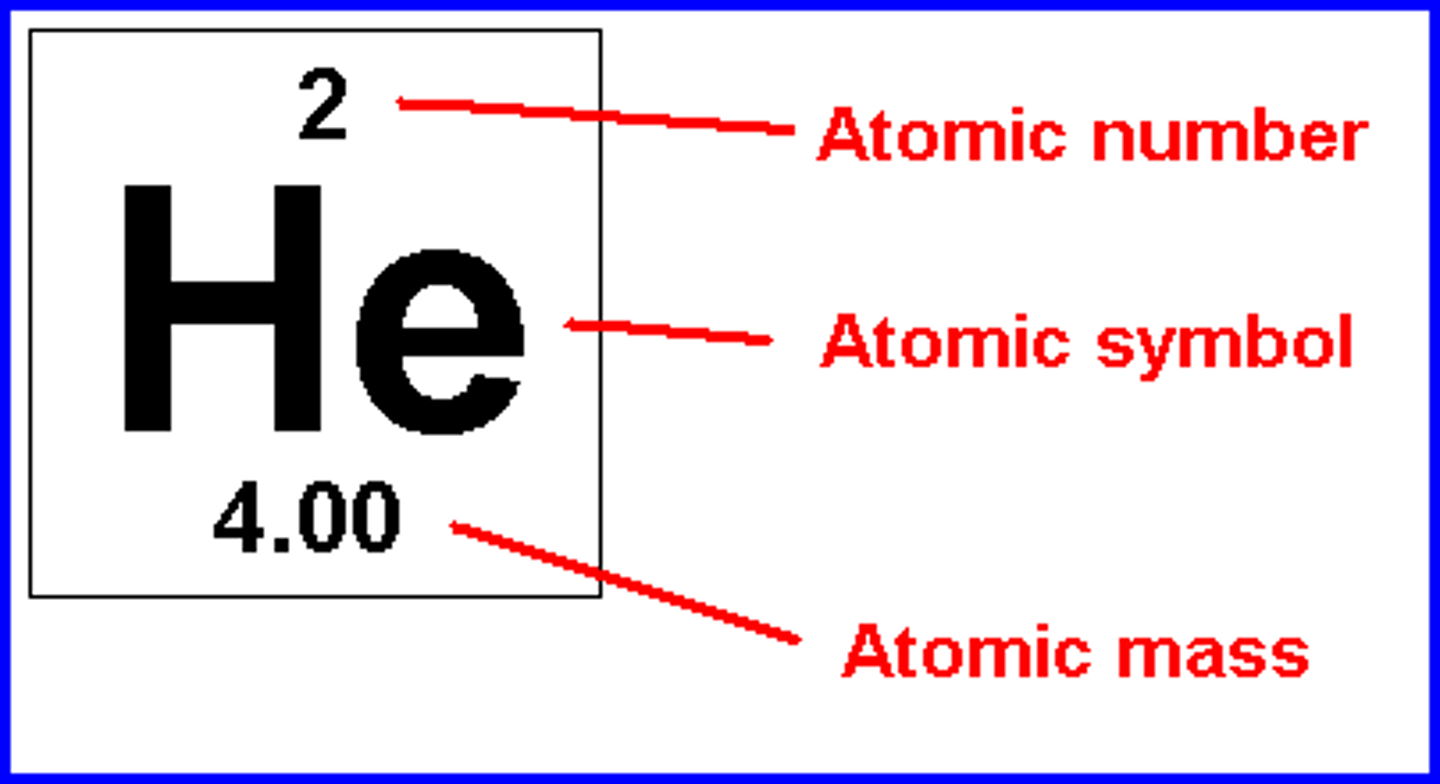
atomic number
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
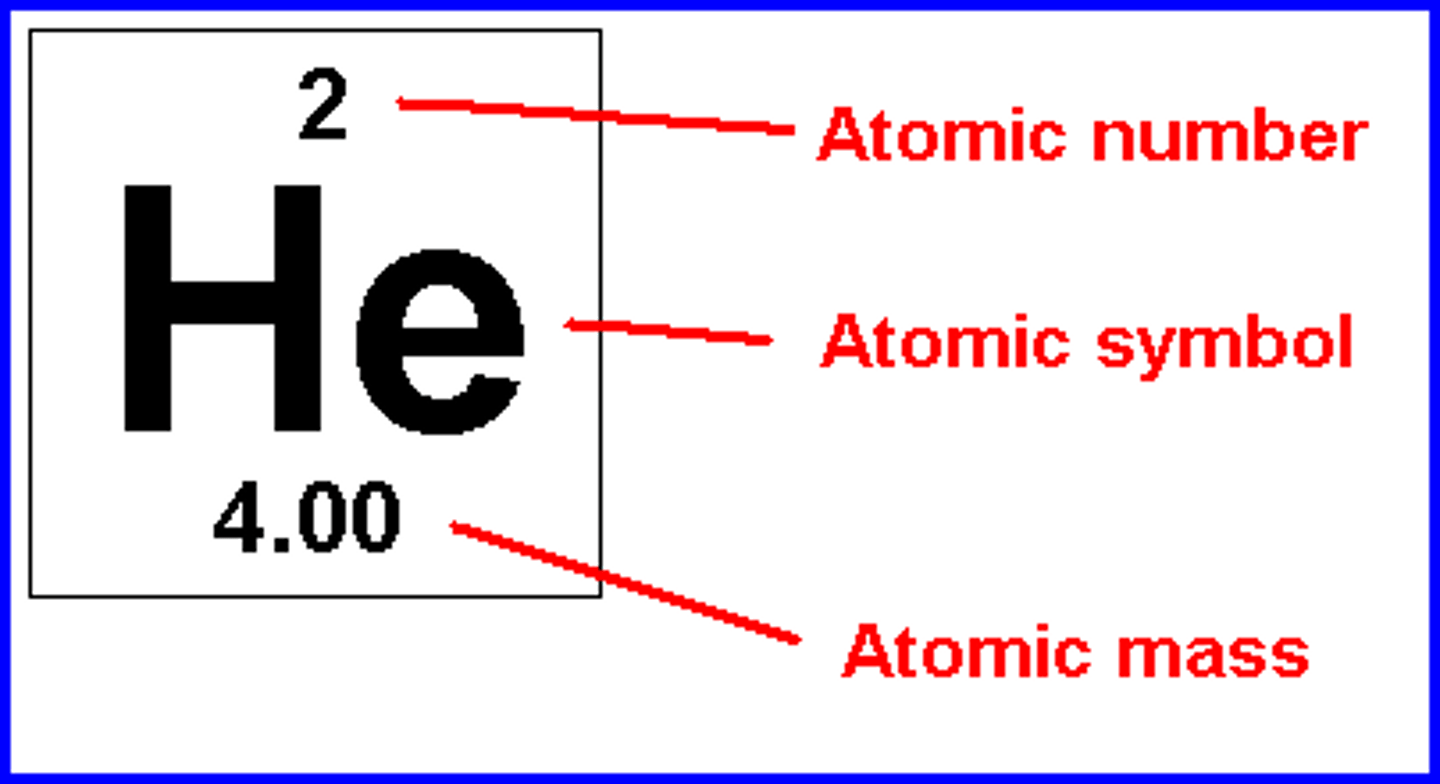
mass number
the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom
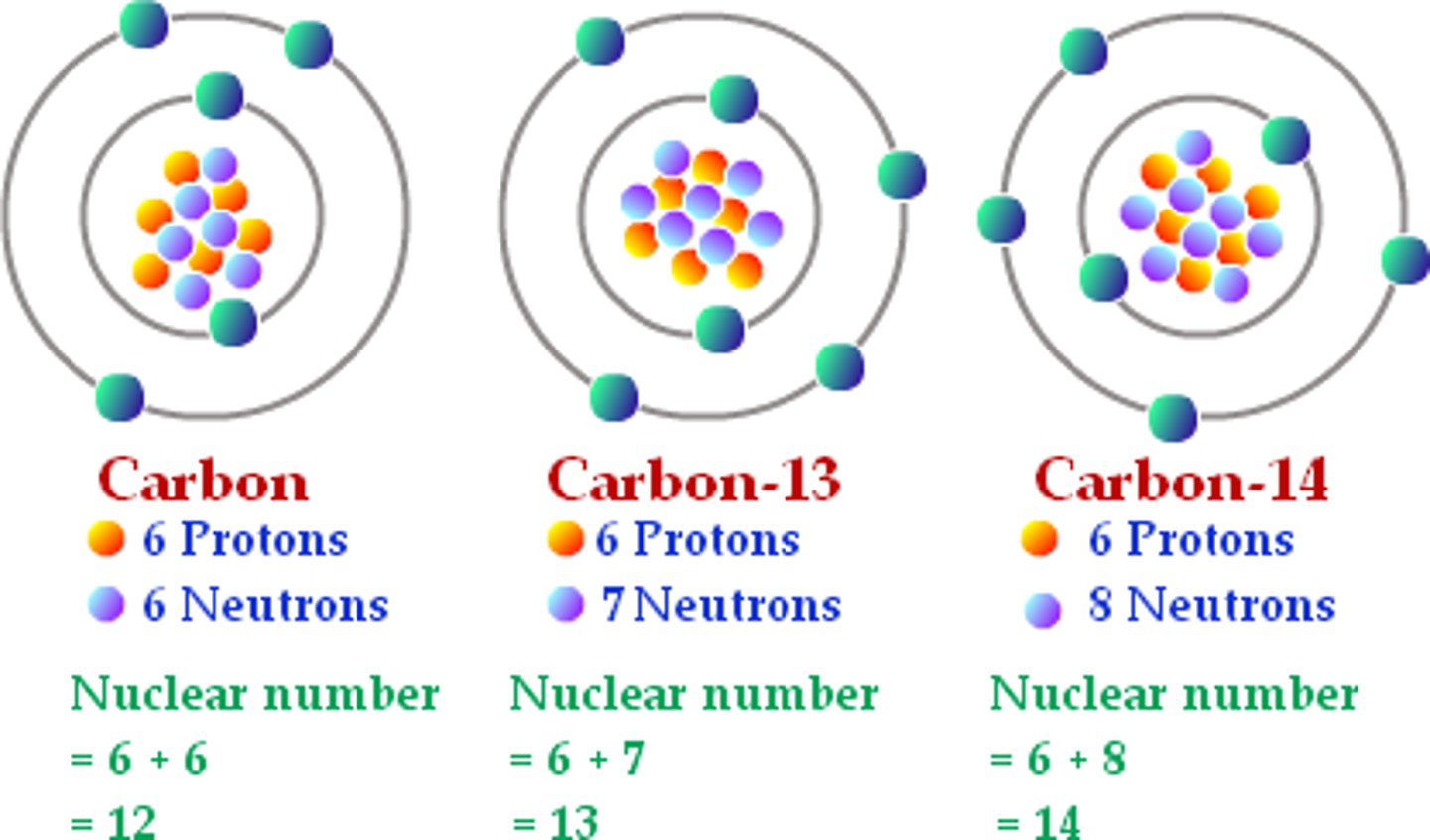
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element (same no. of protons) that have different numbers of neutrons
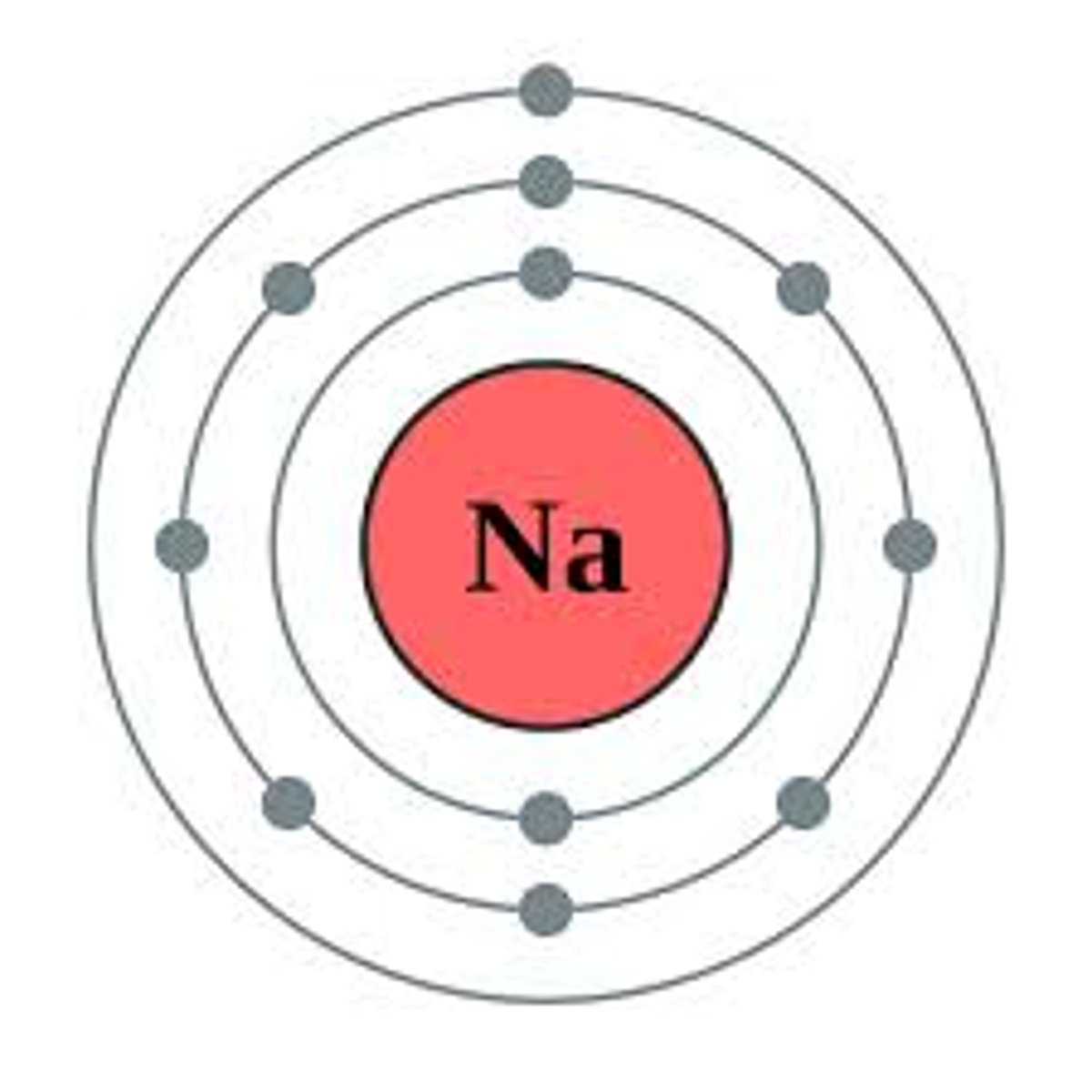
electronic configuration
The arrangement of electrons in shells around the nucleus of an atom, e.g. sodium = 2, 8, 1
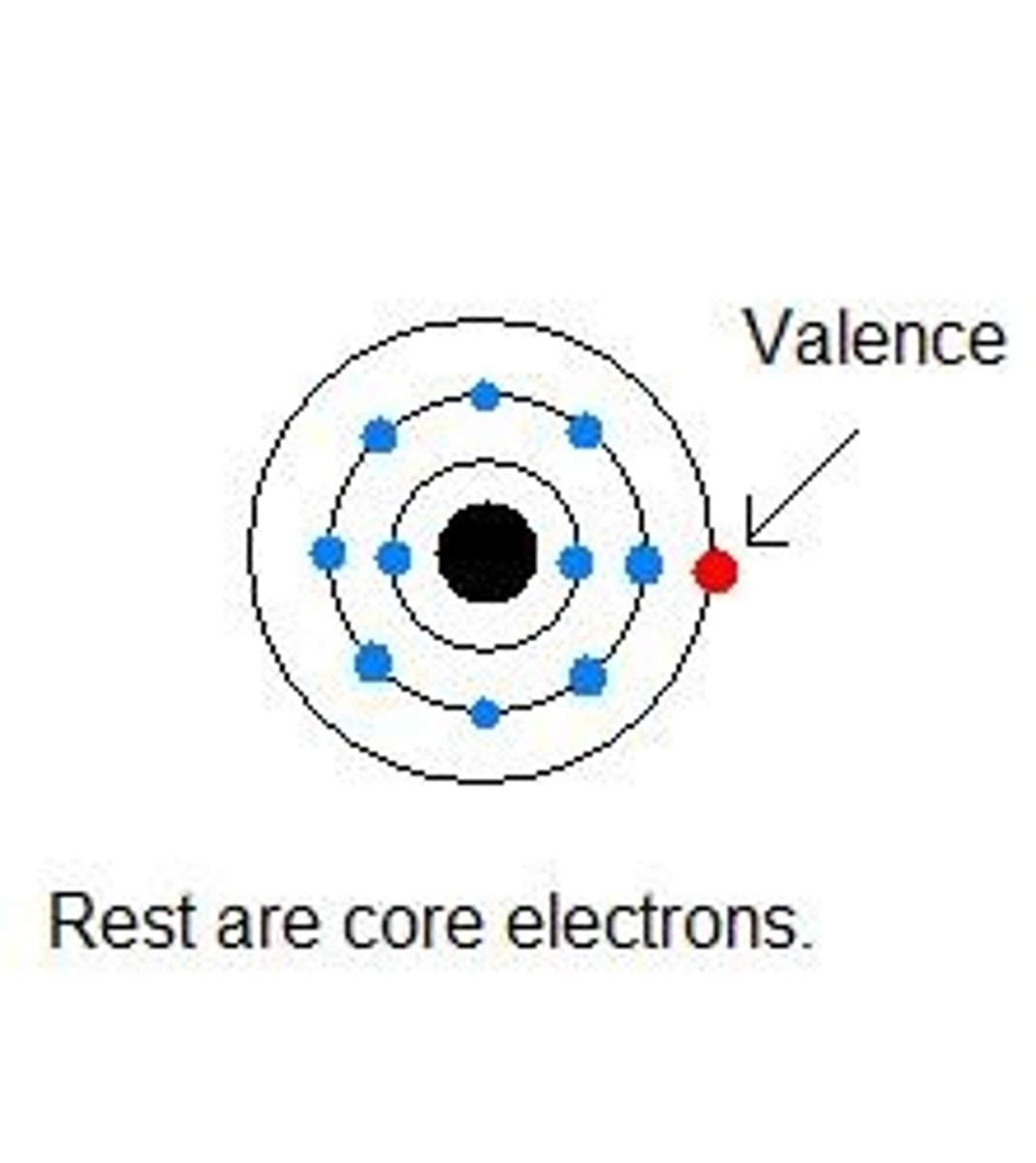
electron shells
paths electrons travel to orbit the nucleus; each can hold a max no. of electrons: 2, 8, 8, 18
Valence electrons
Electrons on the outermost shell of an atom
Cation
A positively charged ion
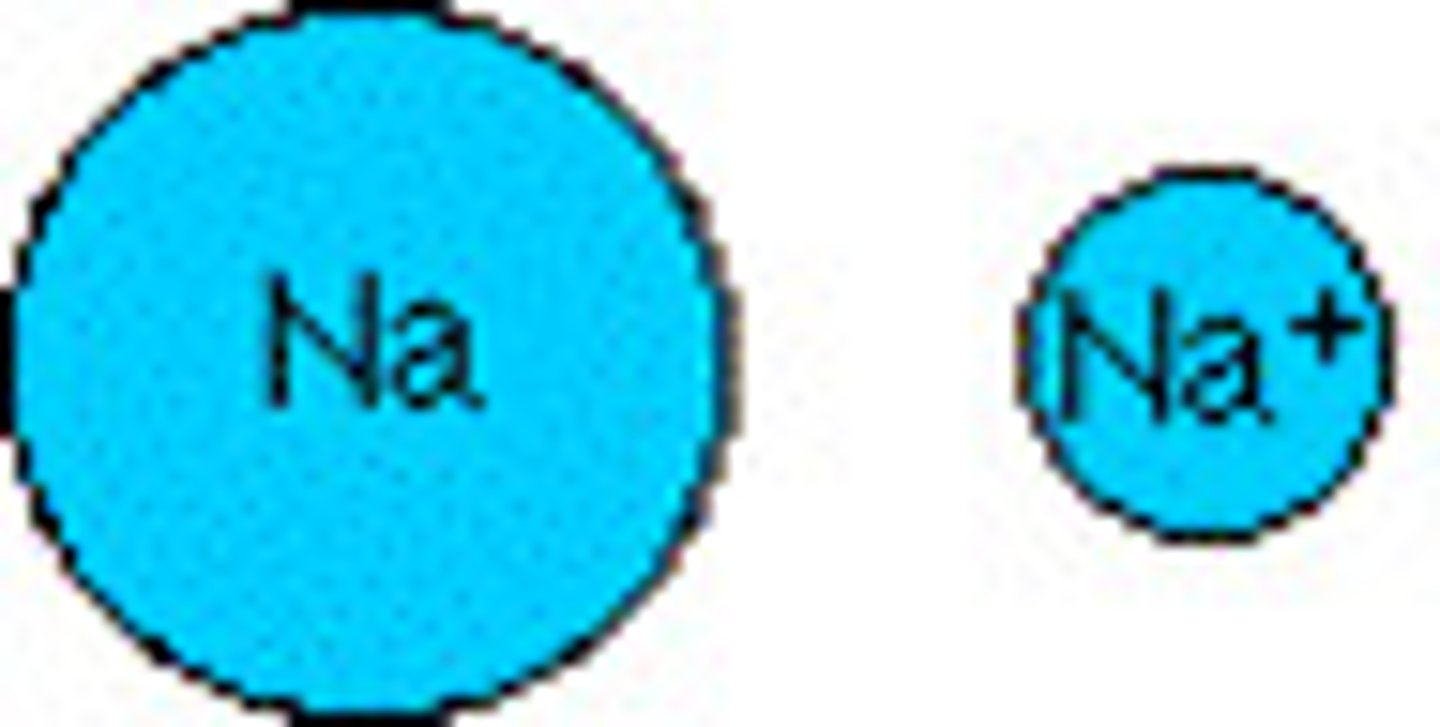

Anion
A negatively charged ion
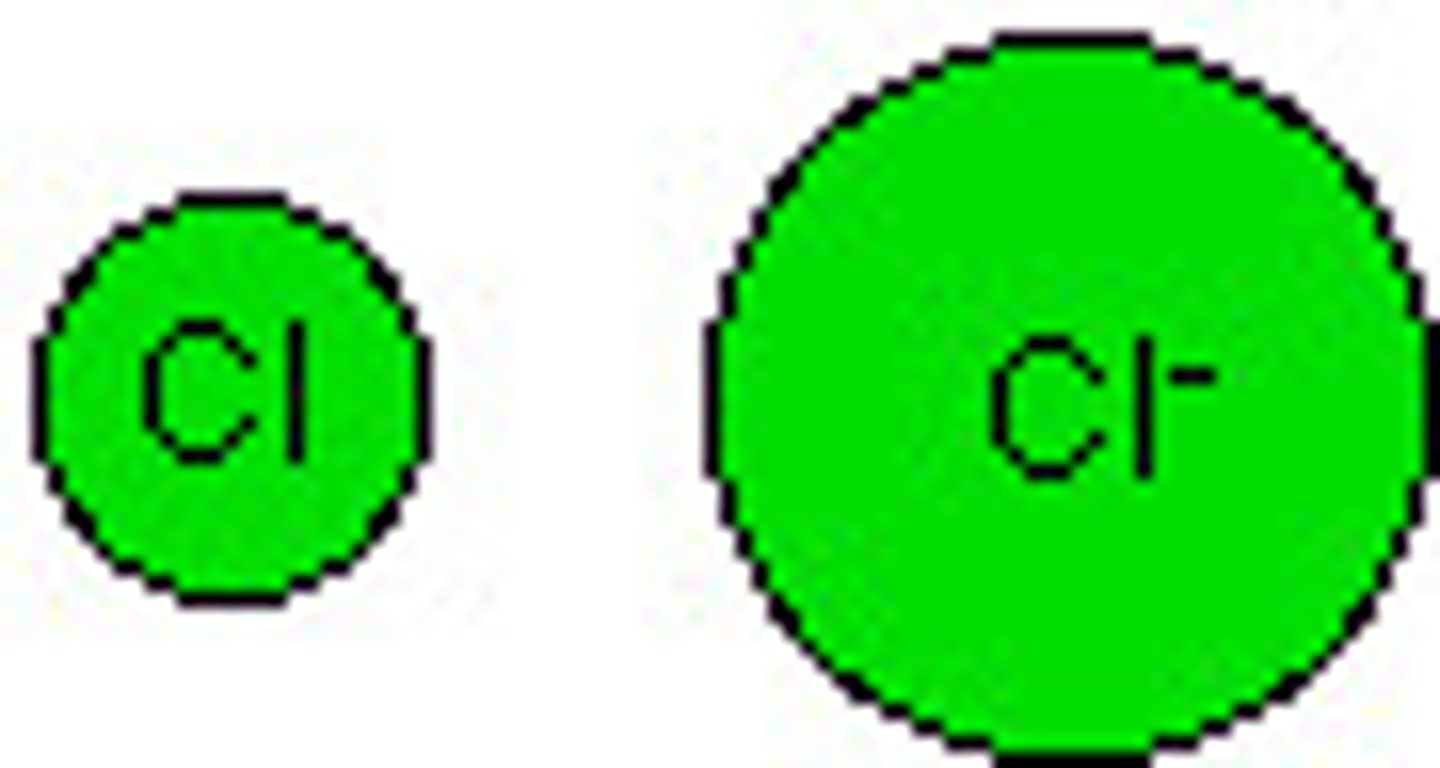
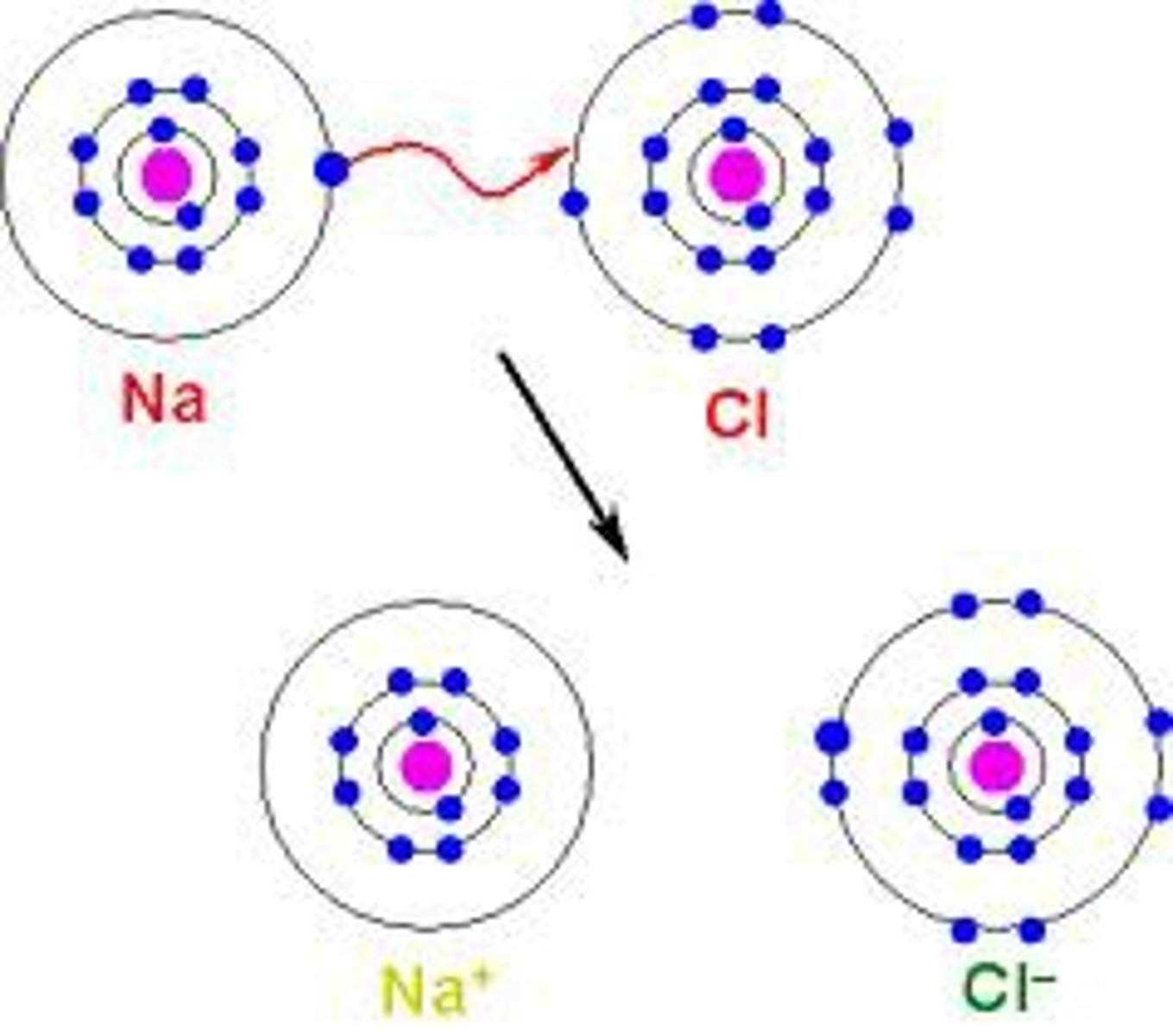
ionic bonding
Chemical bonding that involves the transfer of electrons, resulting in attraction between cations and anions
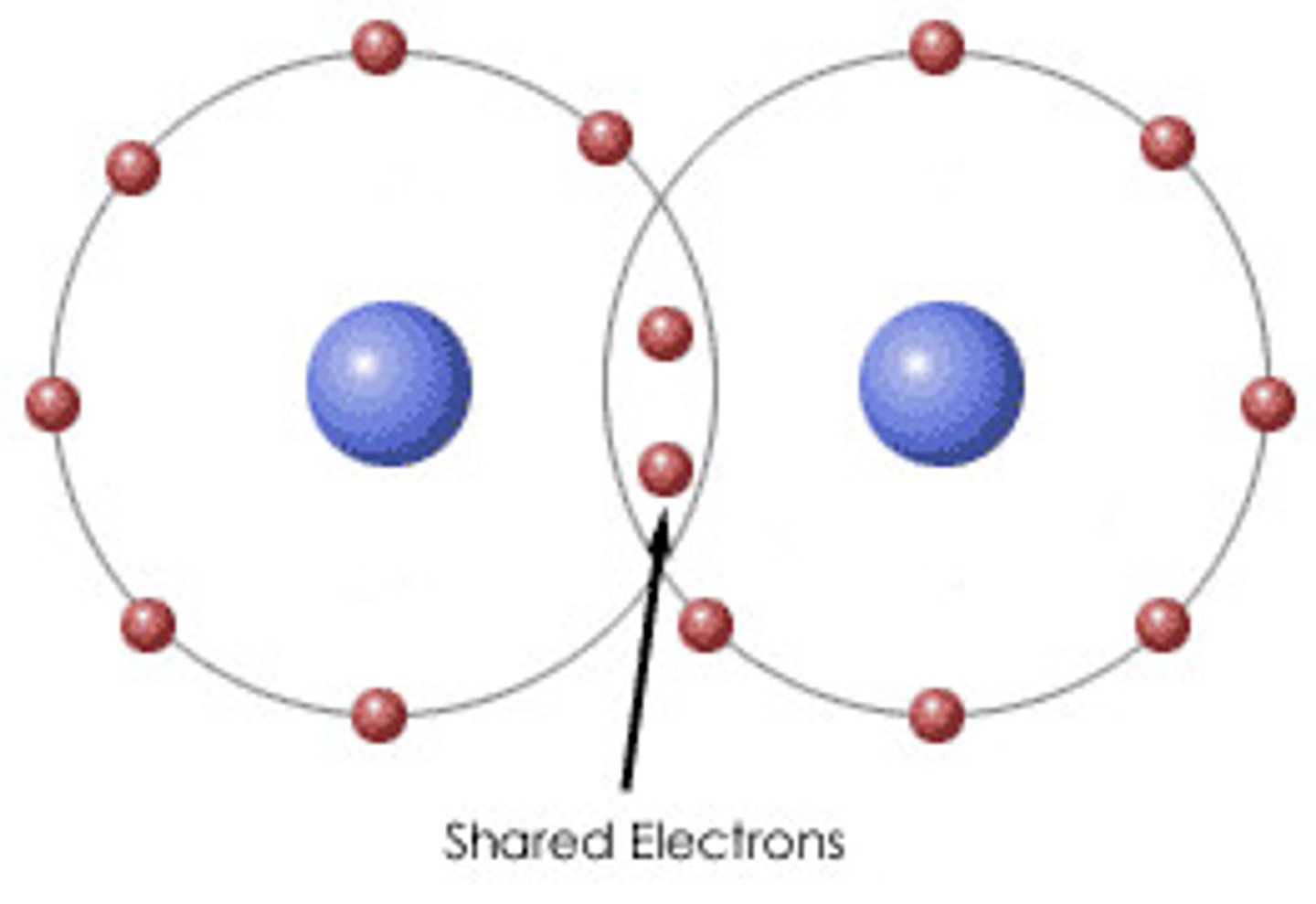
covalent bonding
Chemical bonding resulting from the sharing of electron pairs between two non-metal atoms
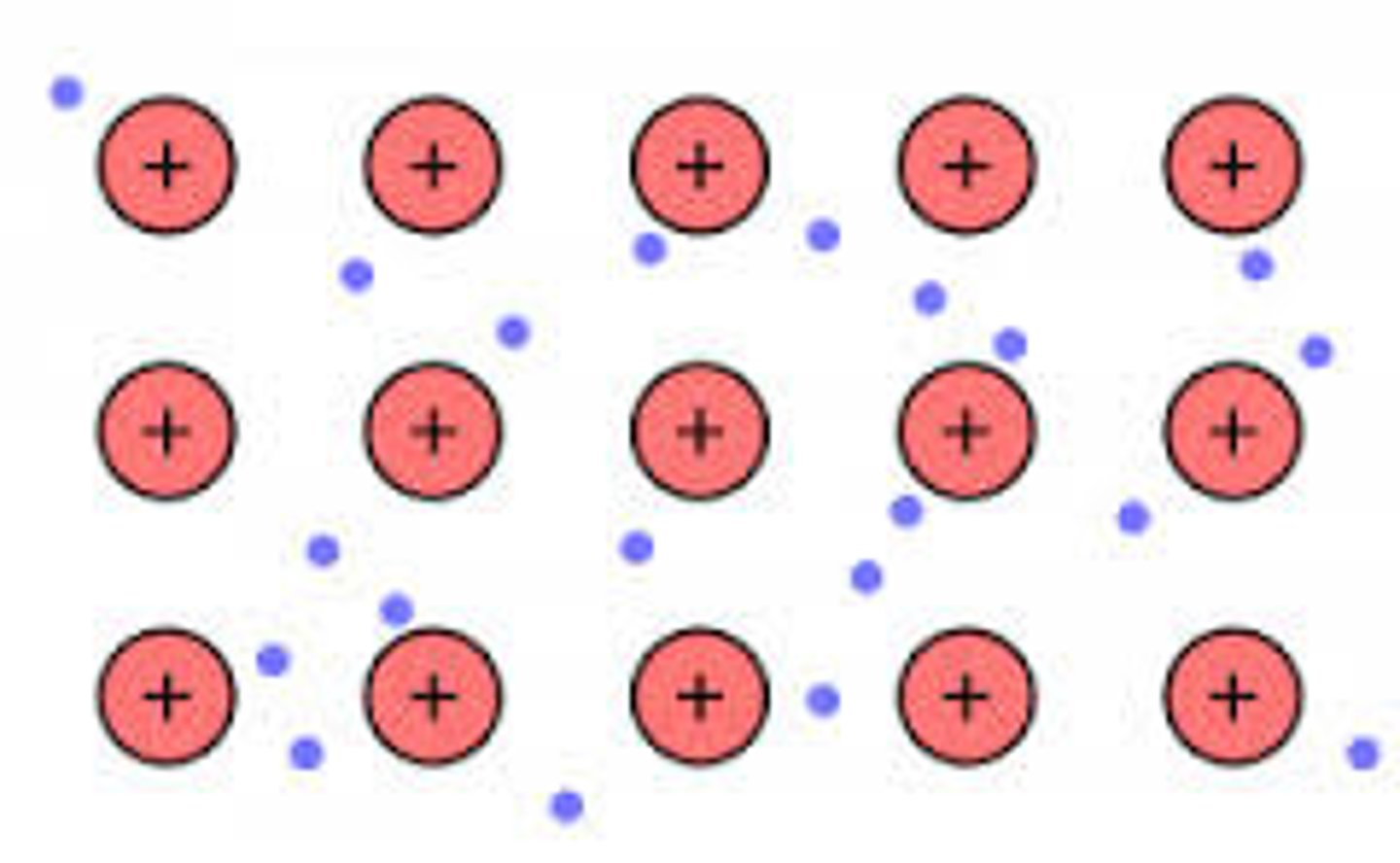
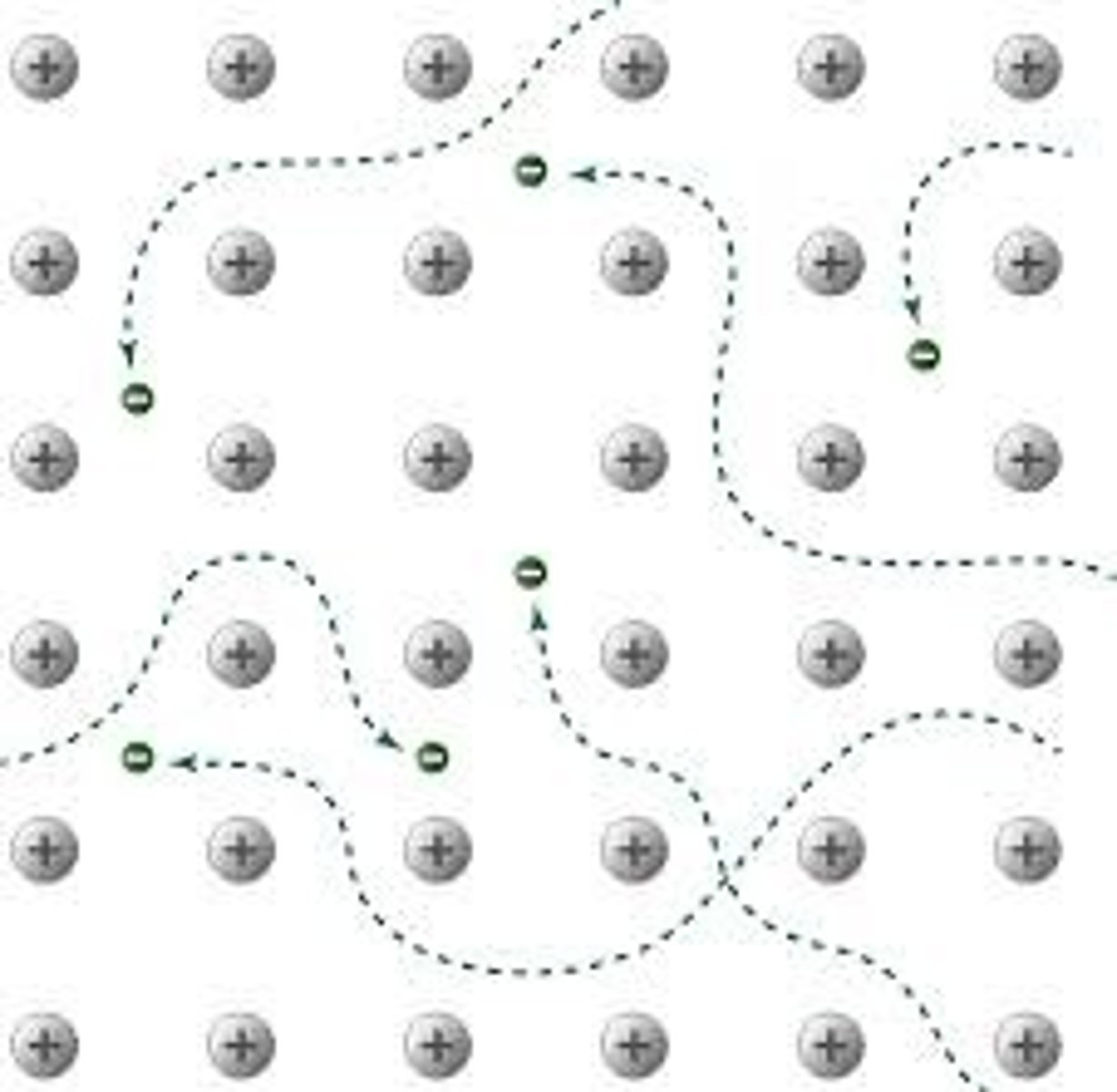
metallic bonding
Chemical bonding that results from the attraction between metal atoms and the surrounding sea of delocalised electrons
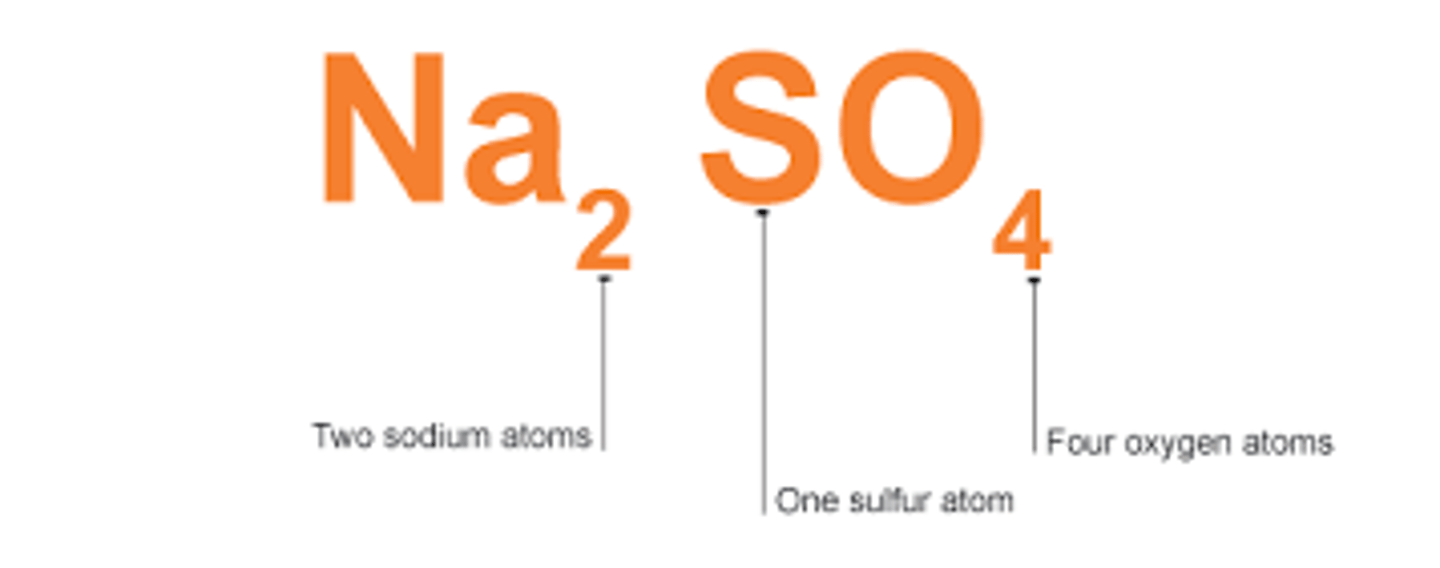
chemical formula
shows the elements in the compound and the ratio of atoms
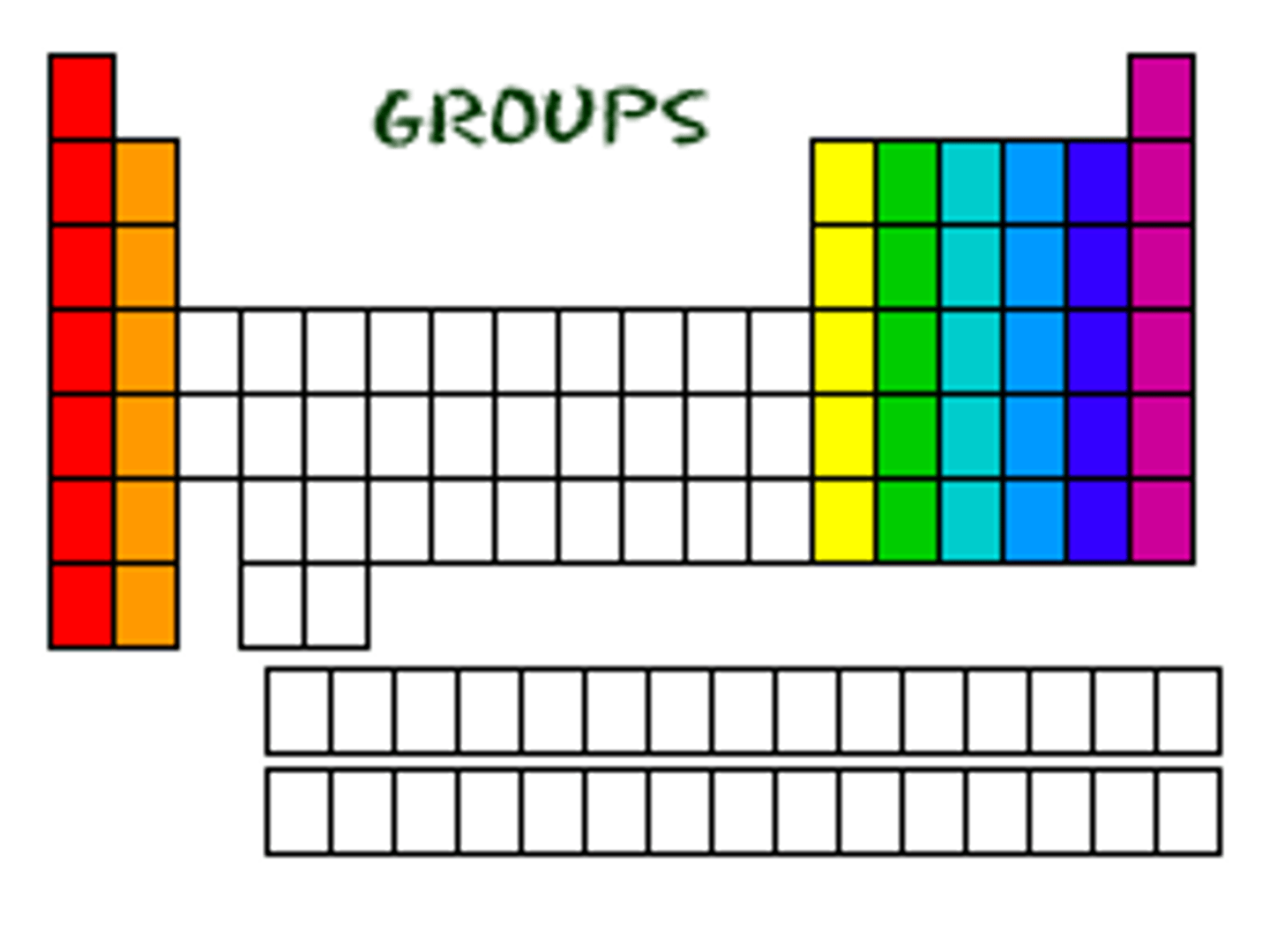
Group
A vertical column on the periodic table
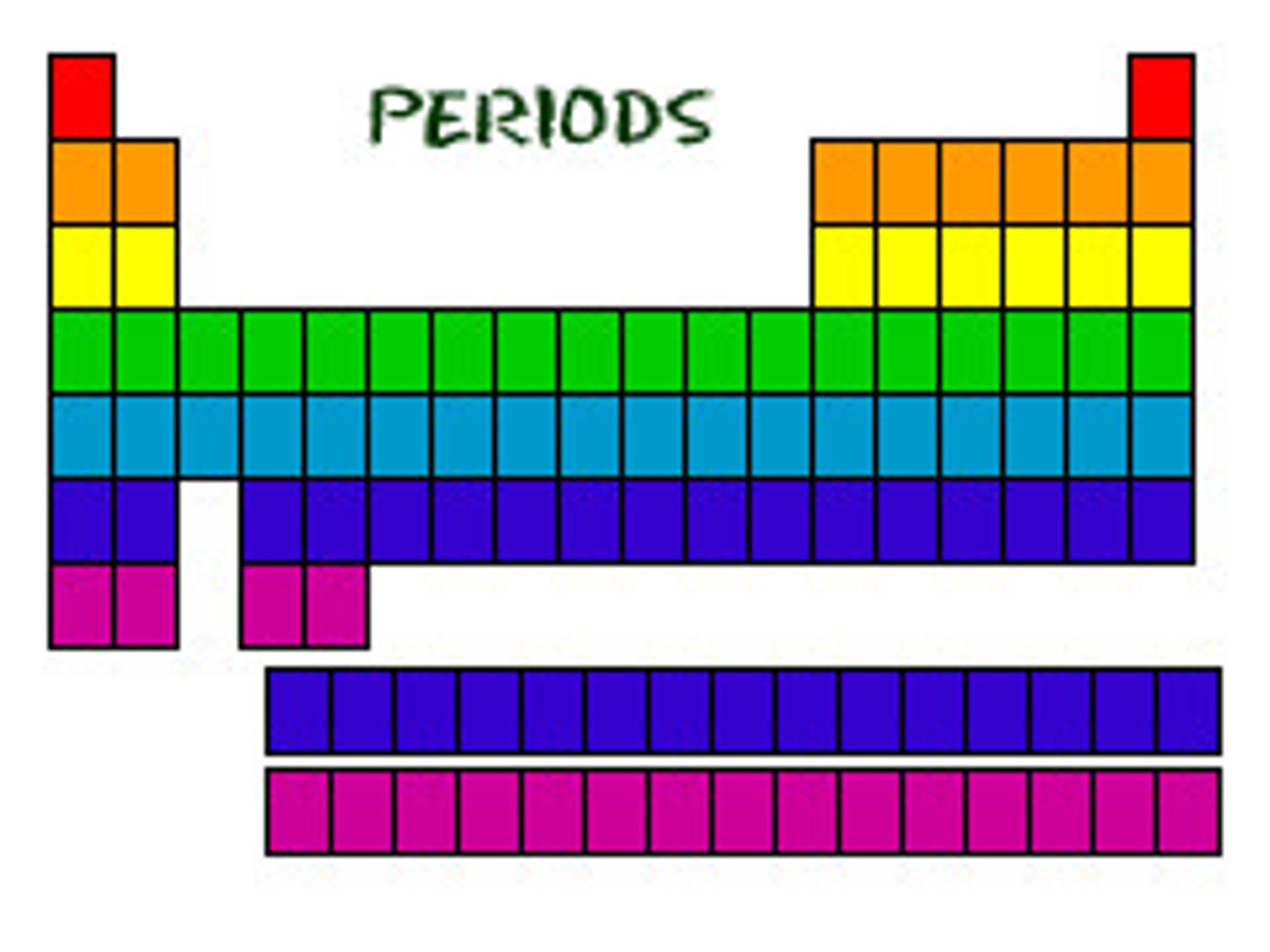
Period
Horizontal rows on the periodic table
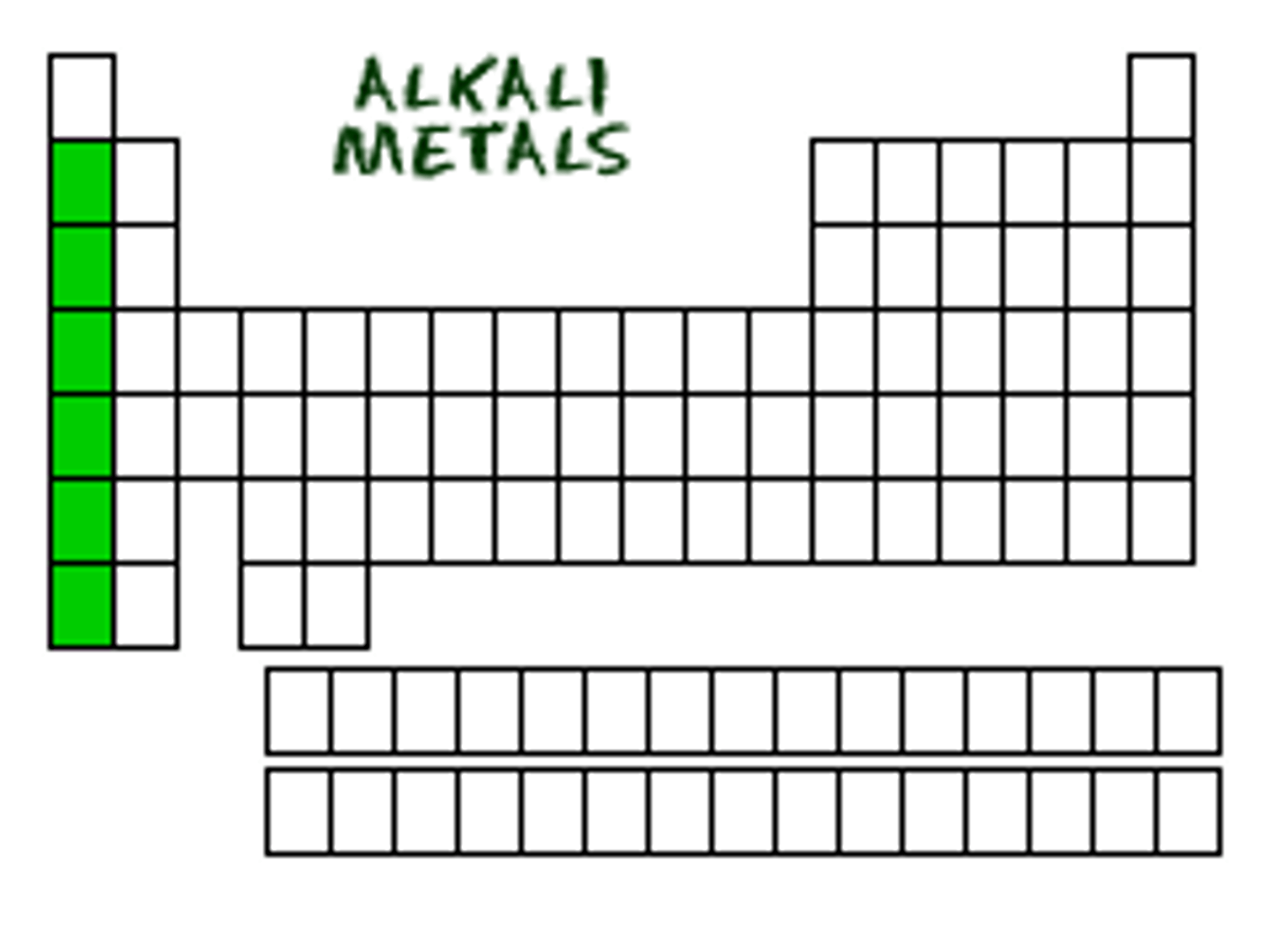
alkali metals
Group 1 elements except for hydrogen, they are highly reactive
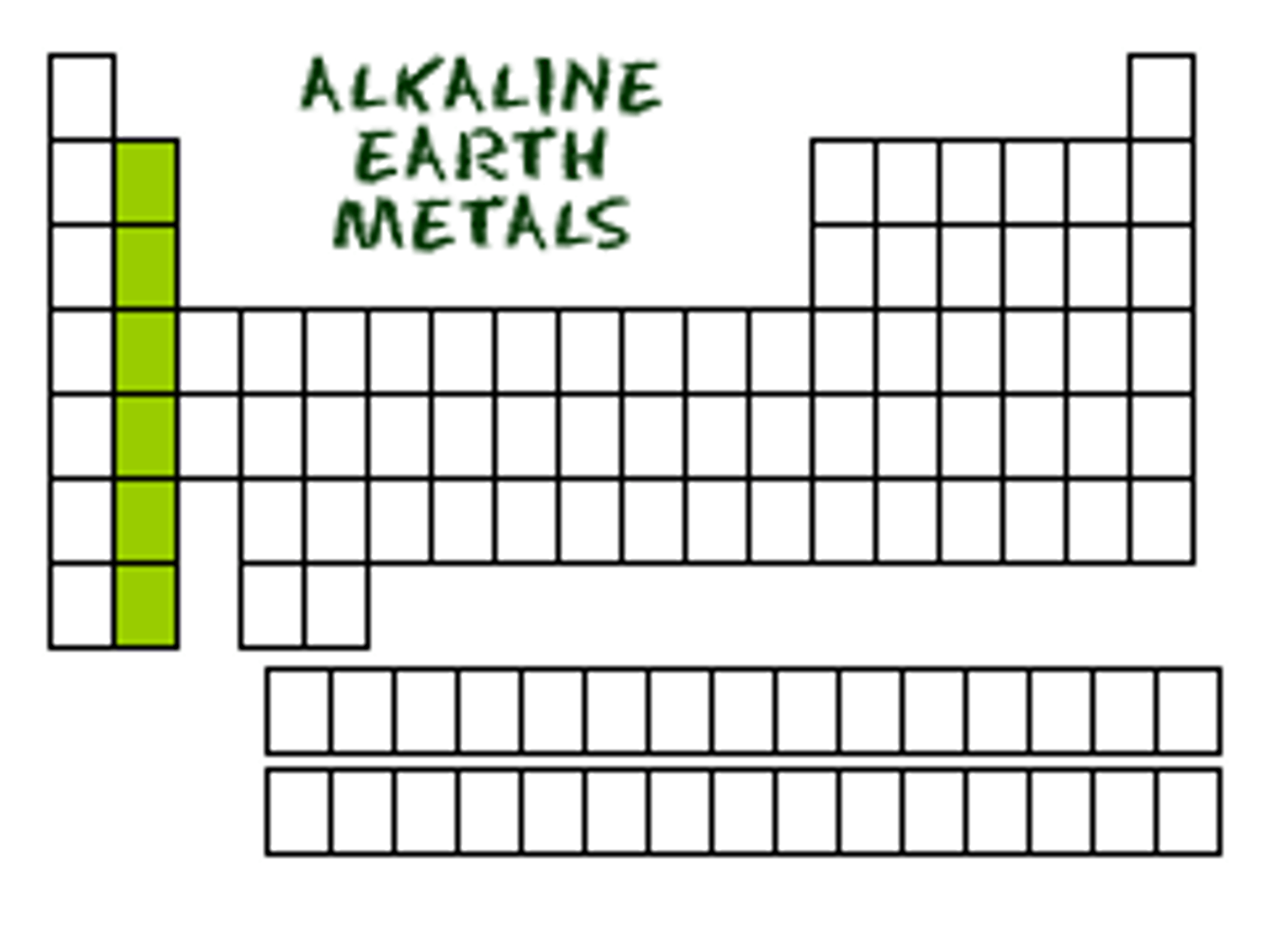
Alkali Earth Metals
Group 2 elements, reactive
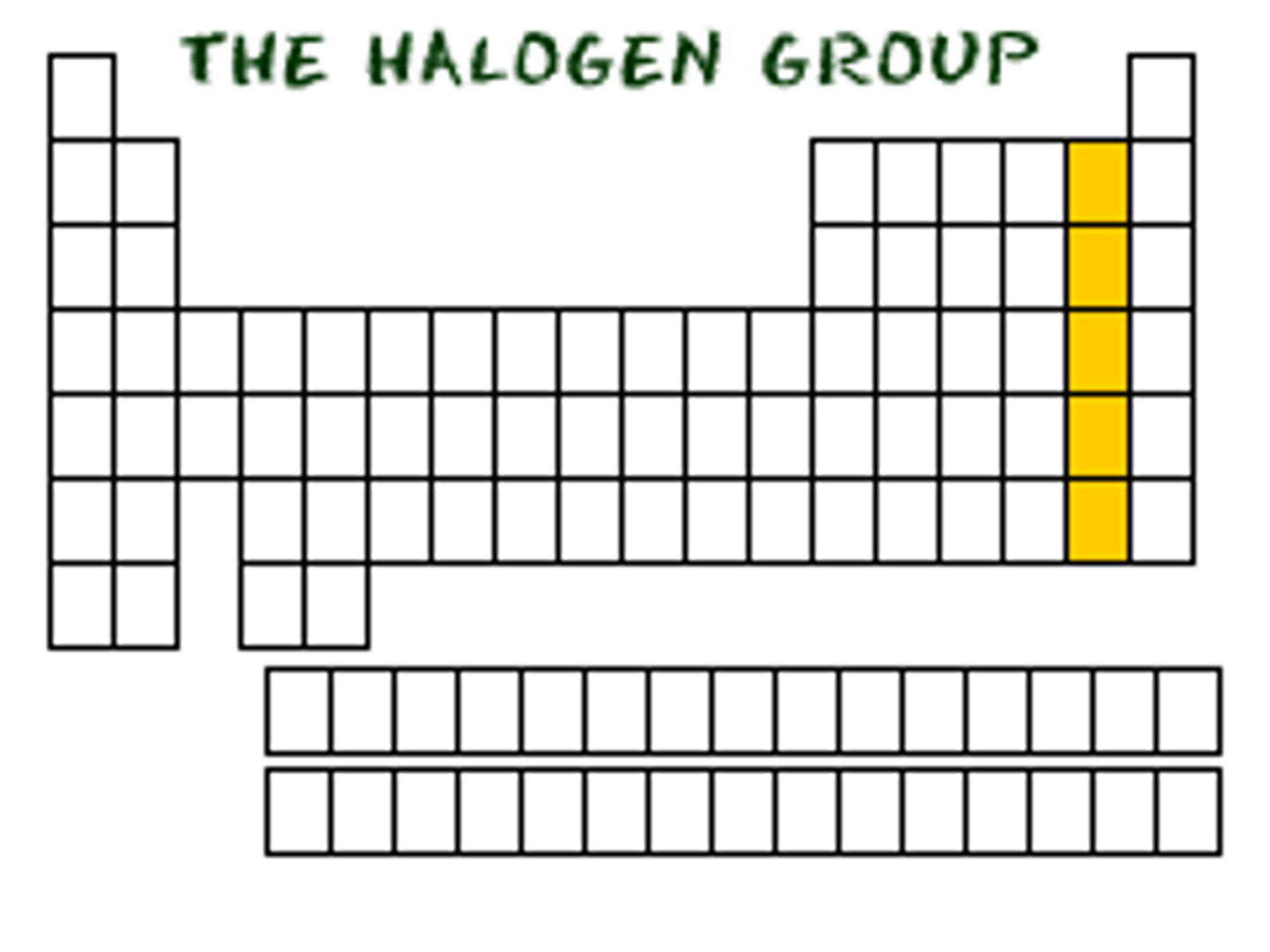
Halogens
Group 7 elements, highly reactive
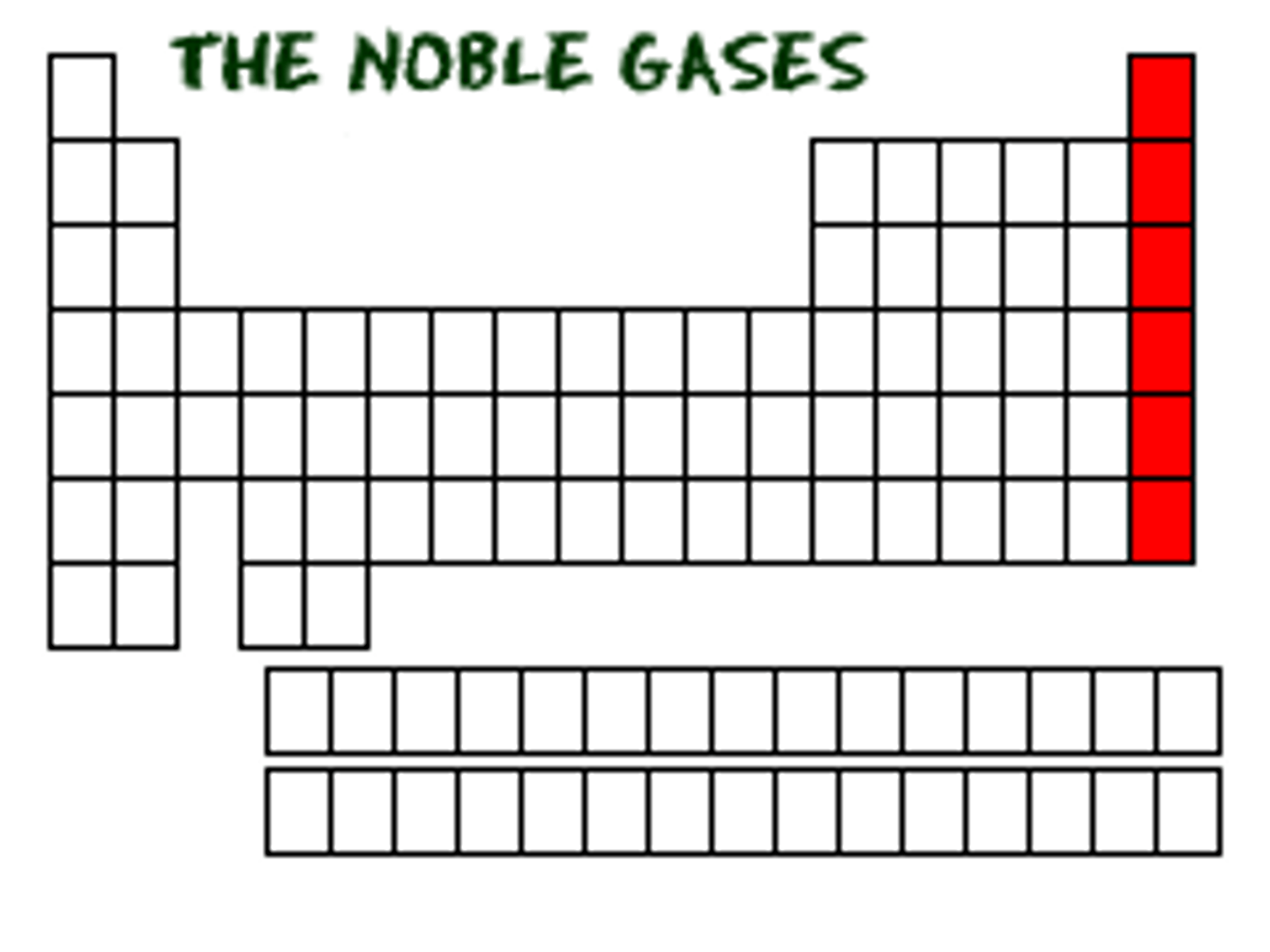
Noble gases
Group 8 elements, not reactive
delocalized
the spreading of electrons over multiple atoms in a molecule or solid, rather than being confined to a single atom or a specific bond between two atoms
flame test
analytical chemistry test used to identify the presence of specific metal cations based on the characteristic color they produce when heated in a flame
hydroxide test
analytical chemistry test that uses sodium hydroxide to identify specific metal cations in an aqueous solution based on the color of the precipitates formed
carbonate test
analytical chemistry test used to identify the presence of the carbonate anion by reacting sample with acid to produce bubbles of carbon dioxide gas
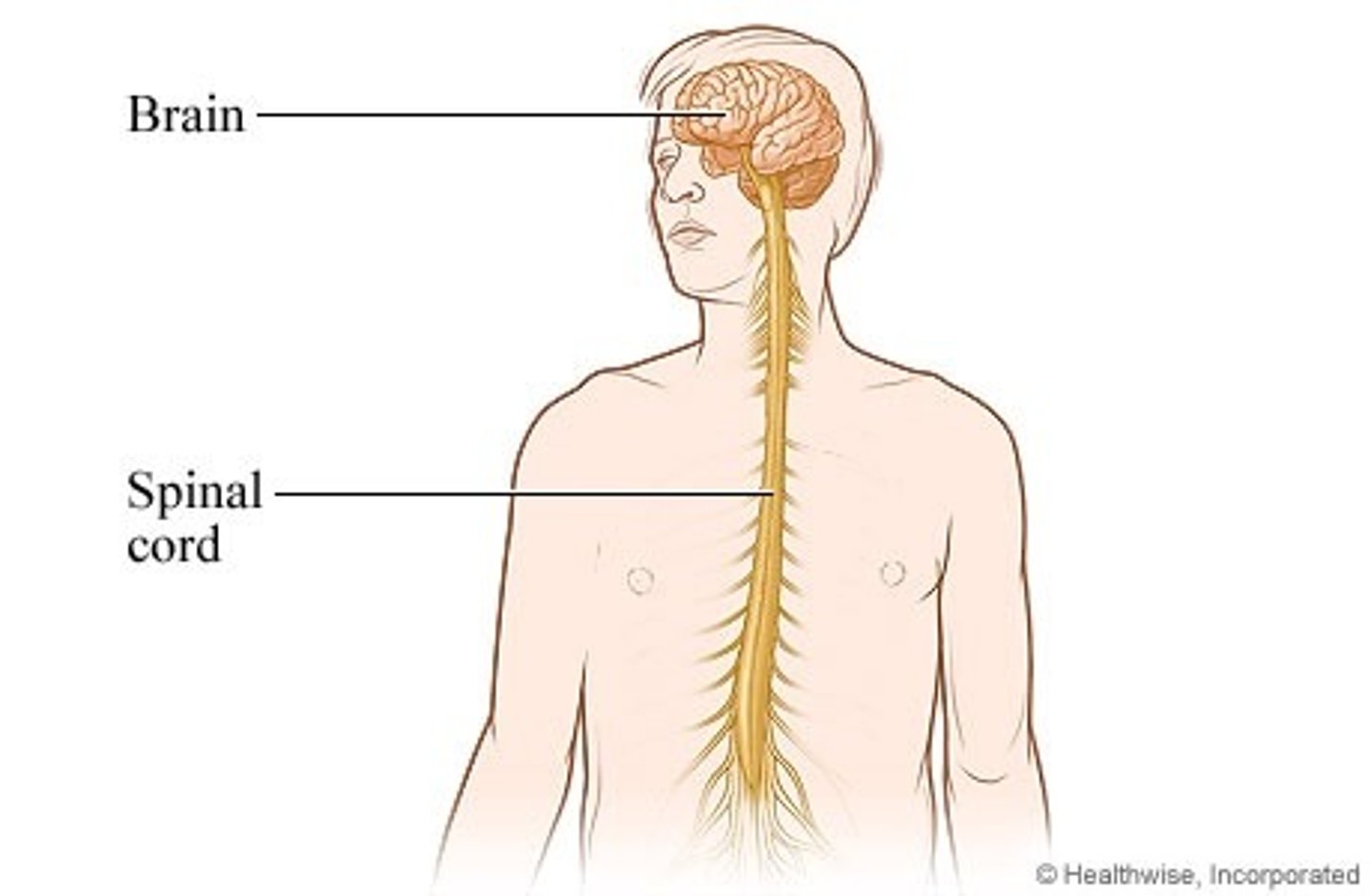
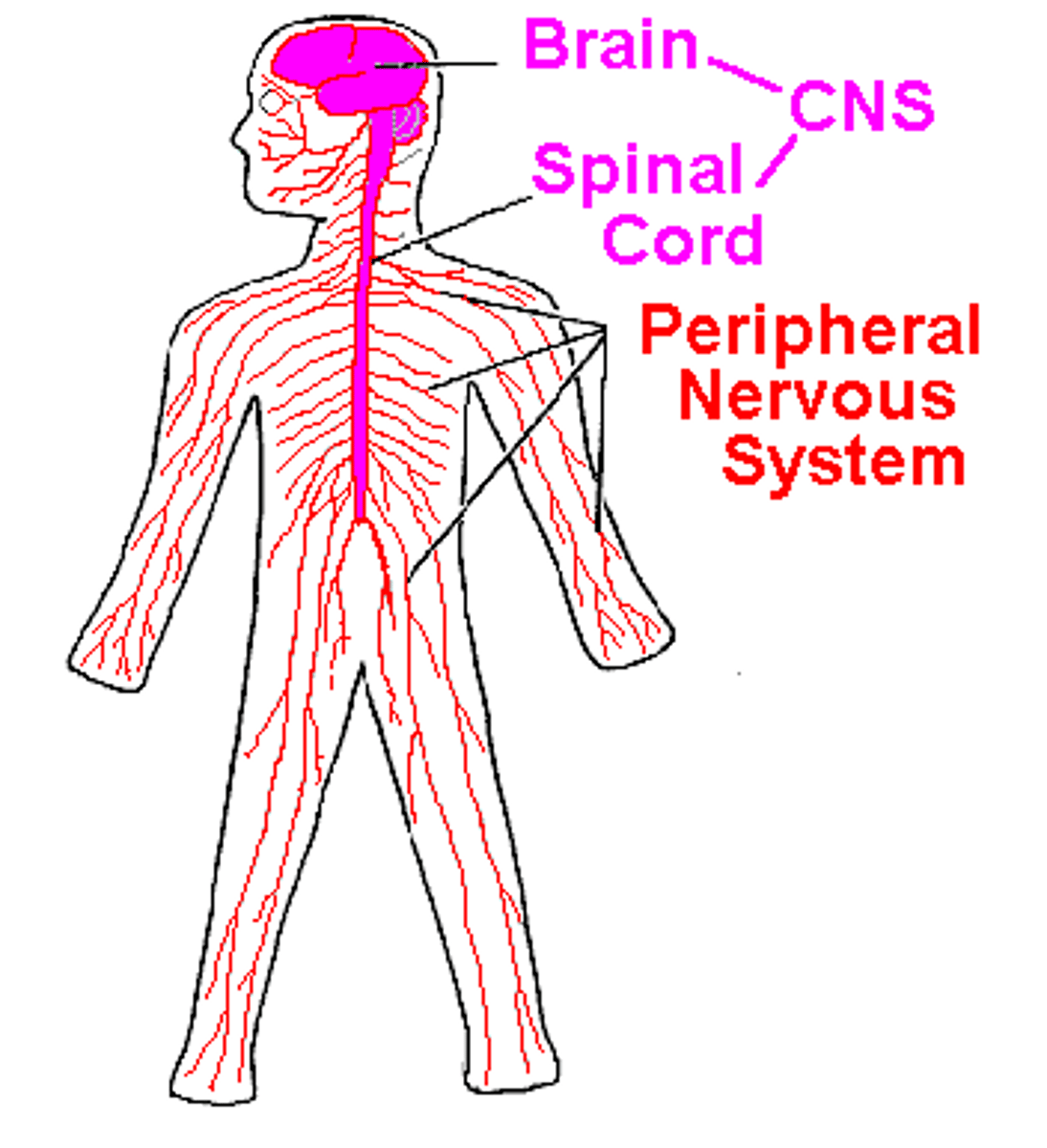
Central Nervous System (CNS)
brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system (CNS) to the rest of the body.
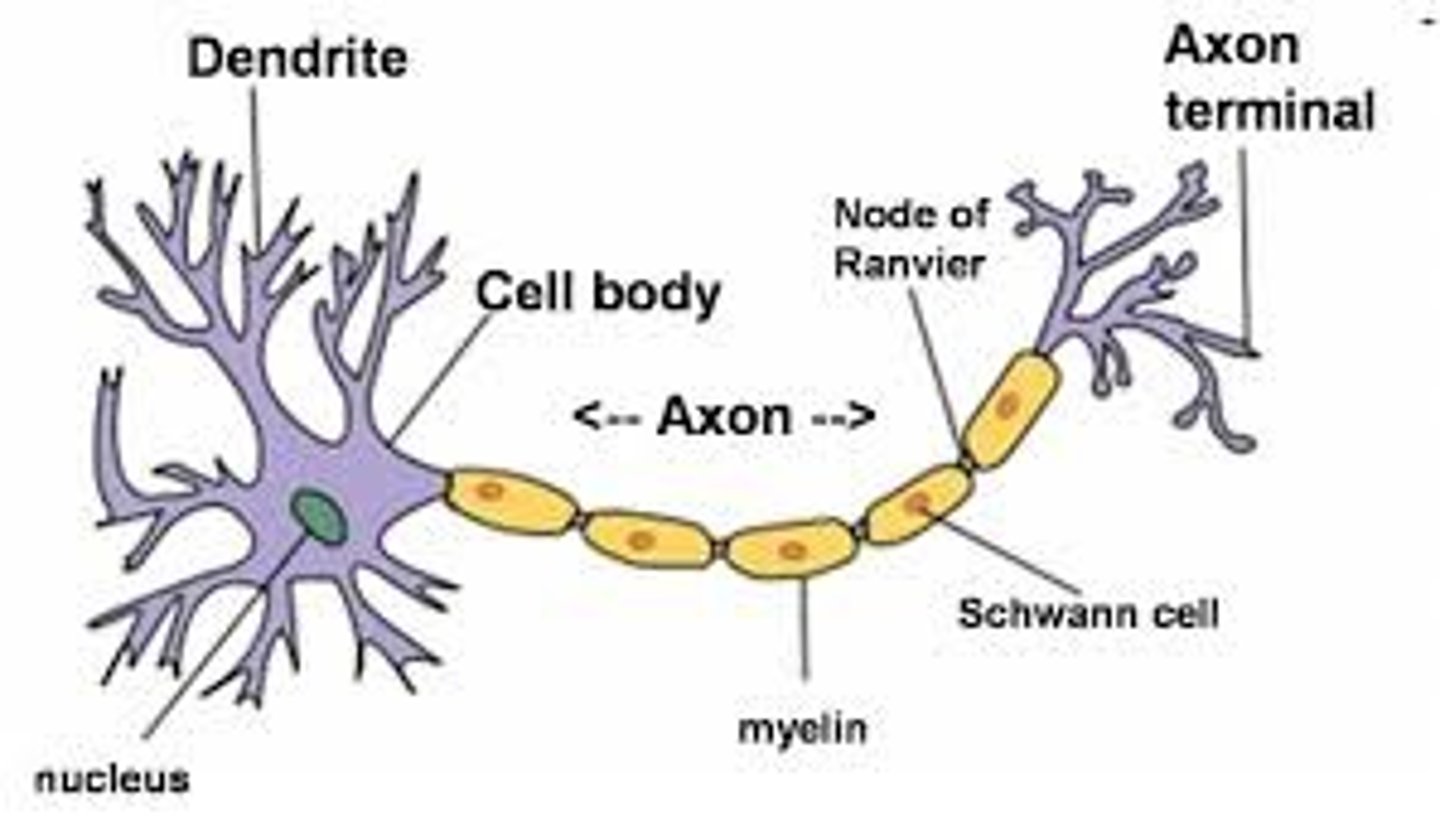
Neurons
specialized nerve cells that transmit electrical signals called nerve impulses around your body
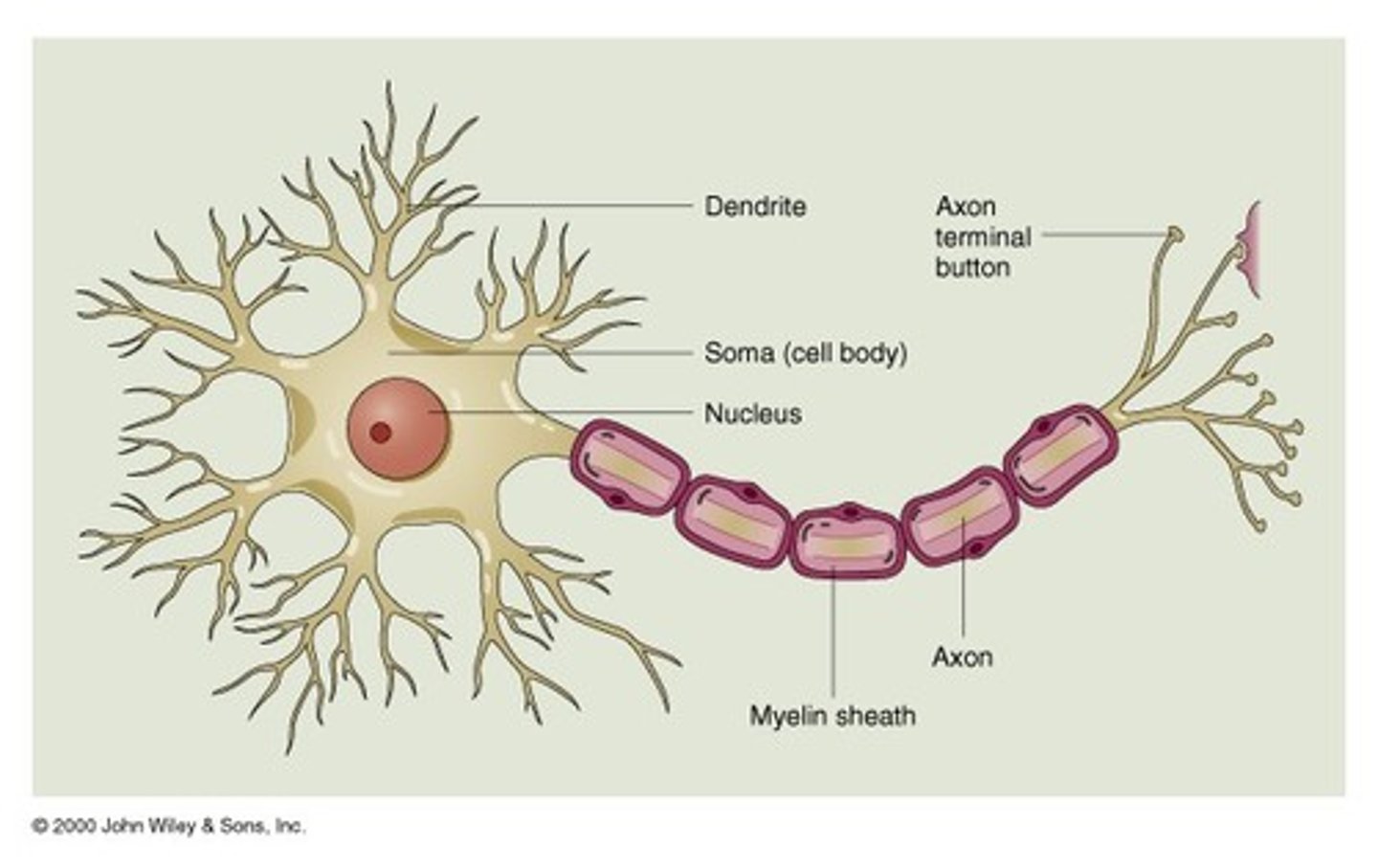
Dendrites
Branchlike parts of a neuron that are specialized to receive information.
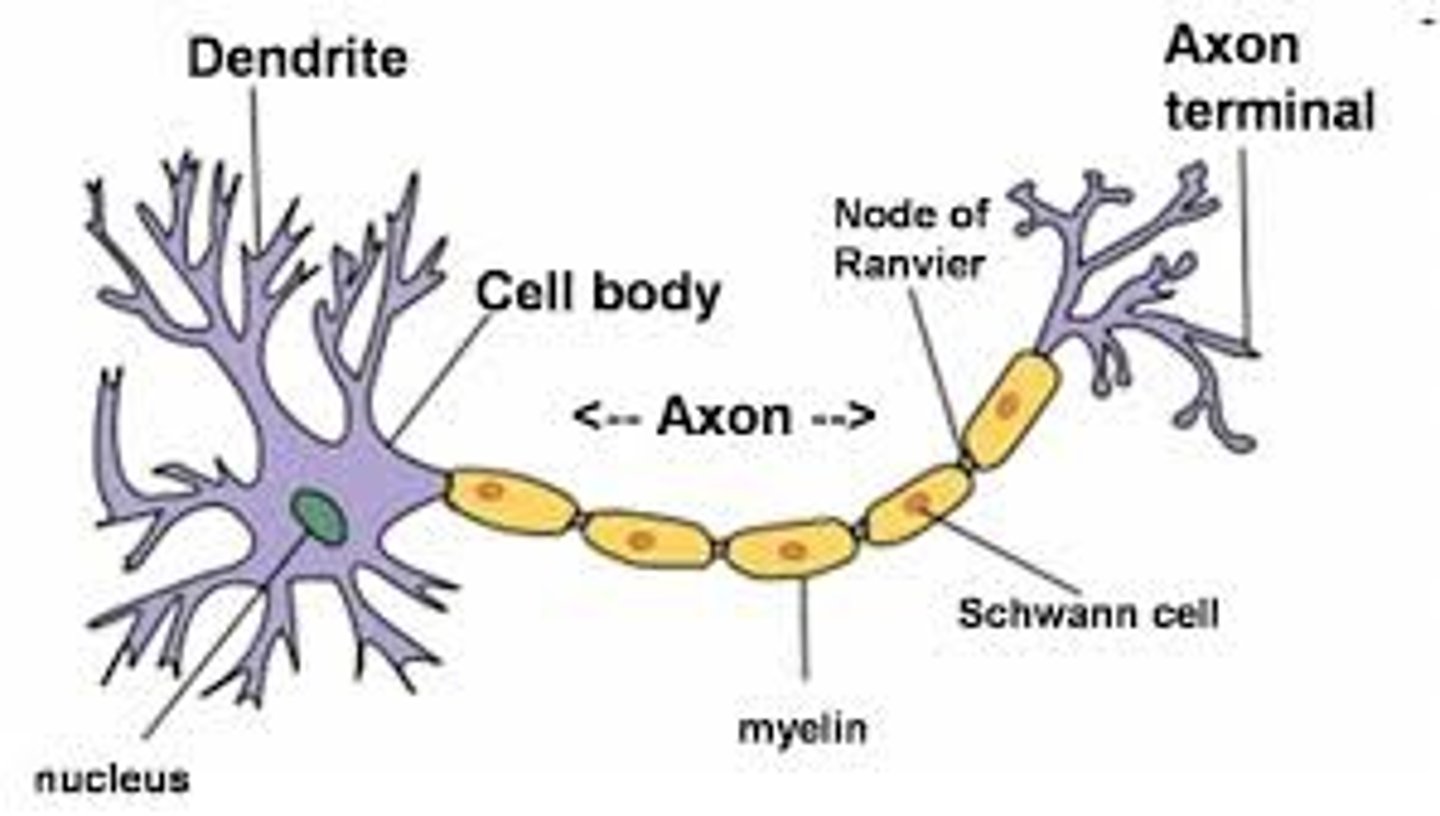
Axon
A threadlike extension of a neuron that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body.
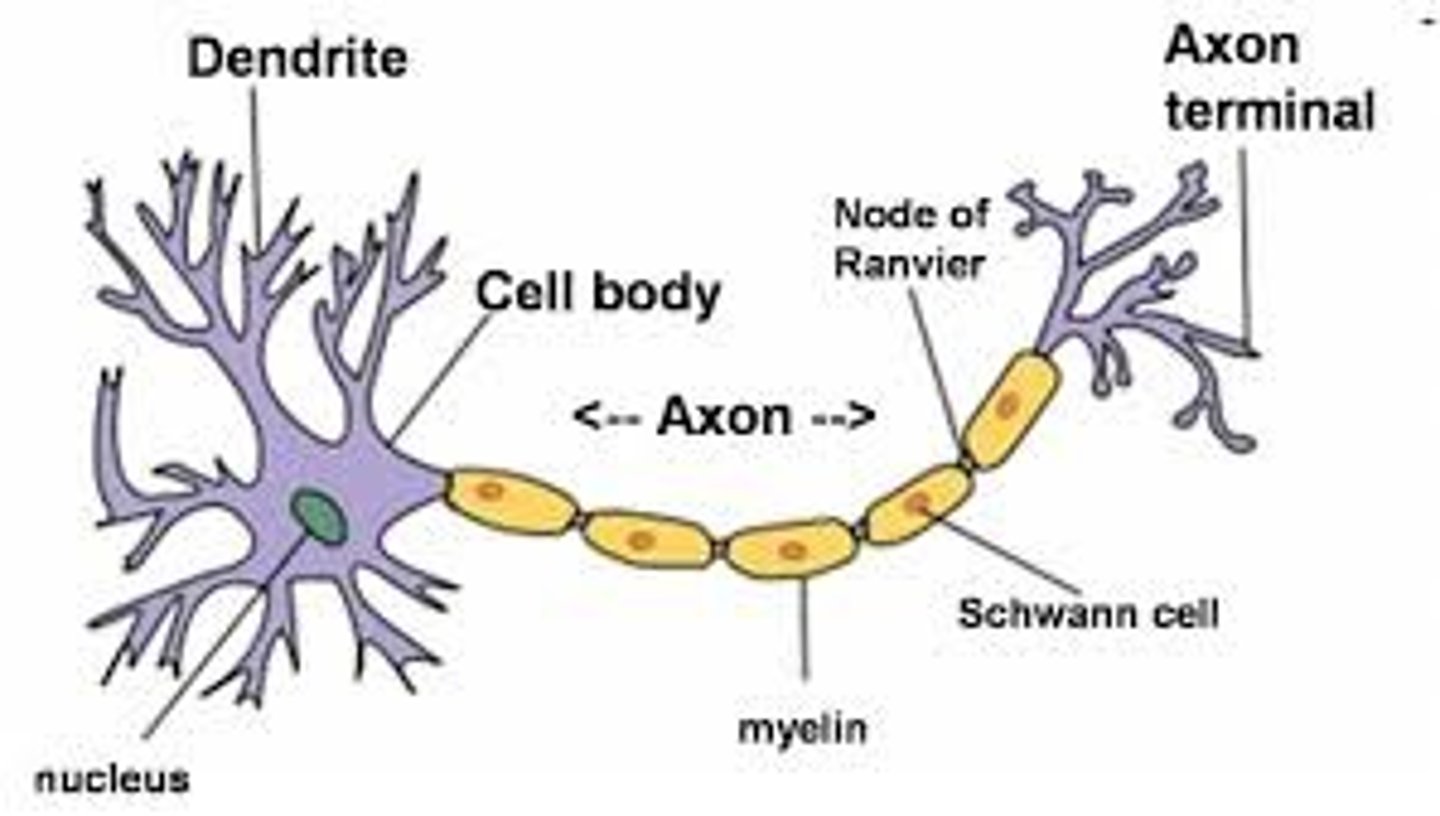
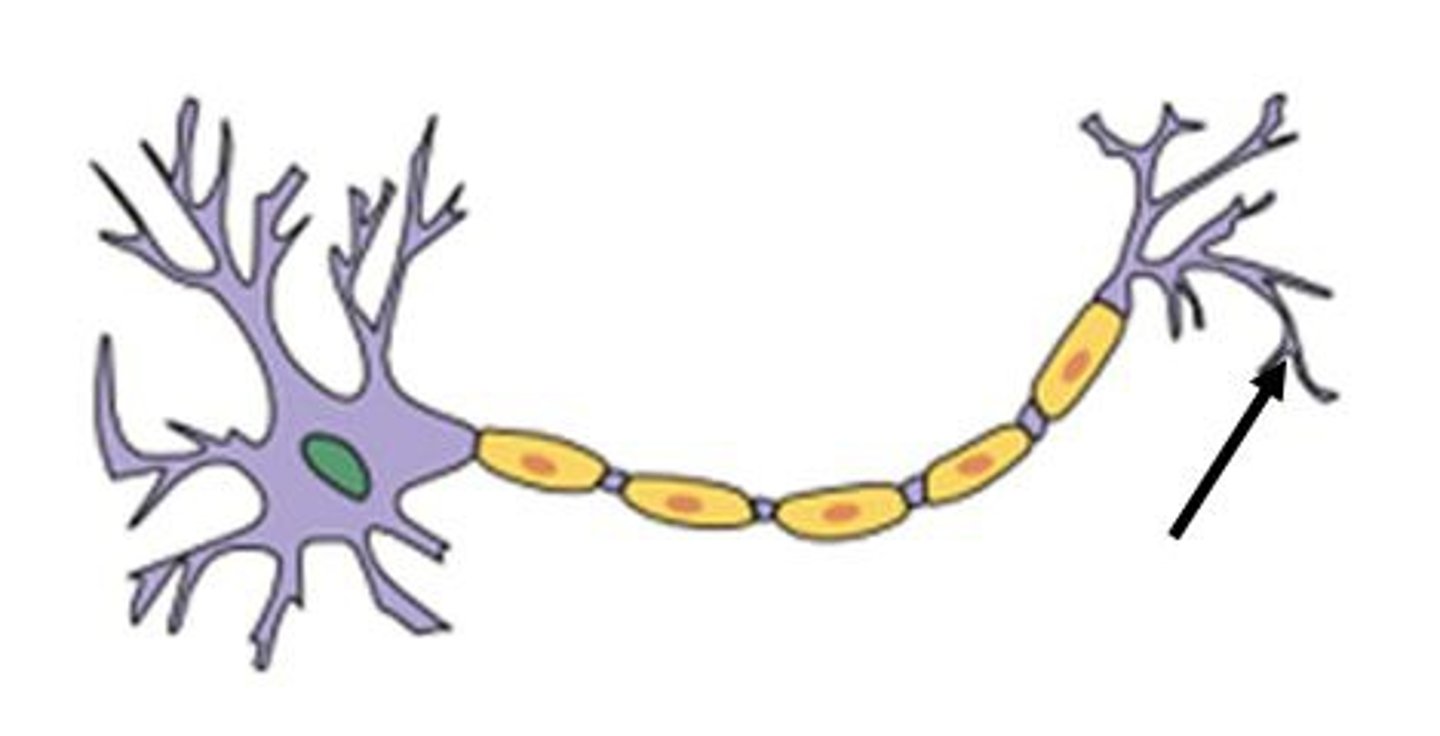
Axon terminal
The endpoint of a neuron where neurotransmitters are stored
Schwann cells
Fatty cells responsible for the formation of myelin.
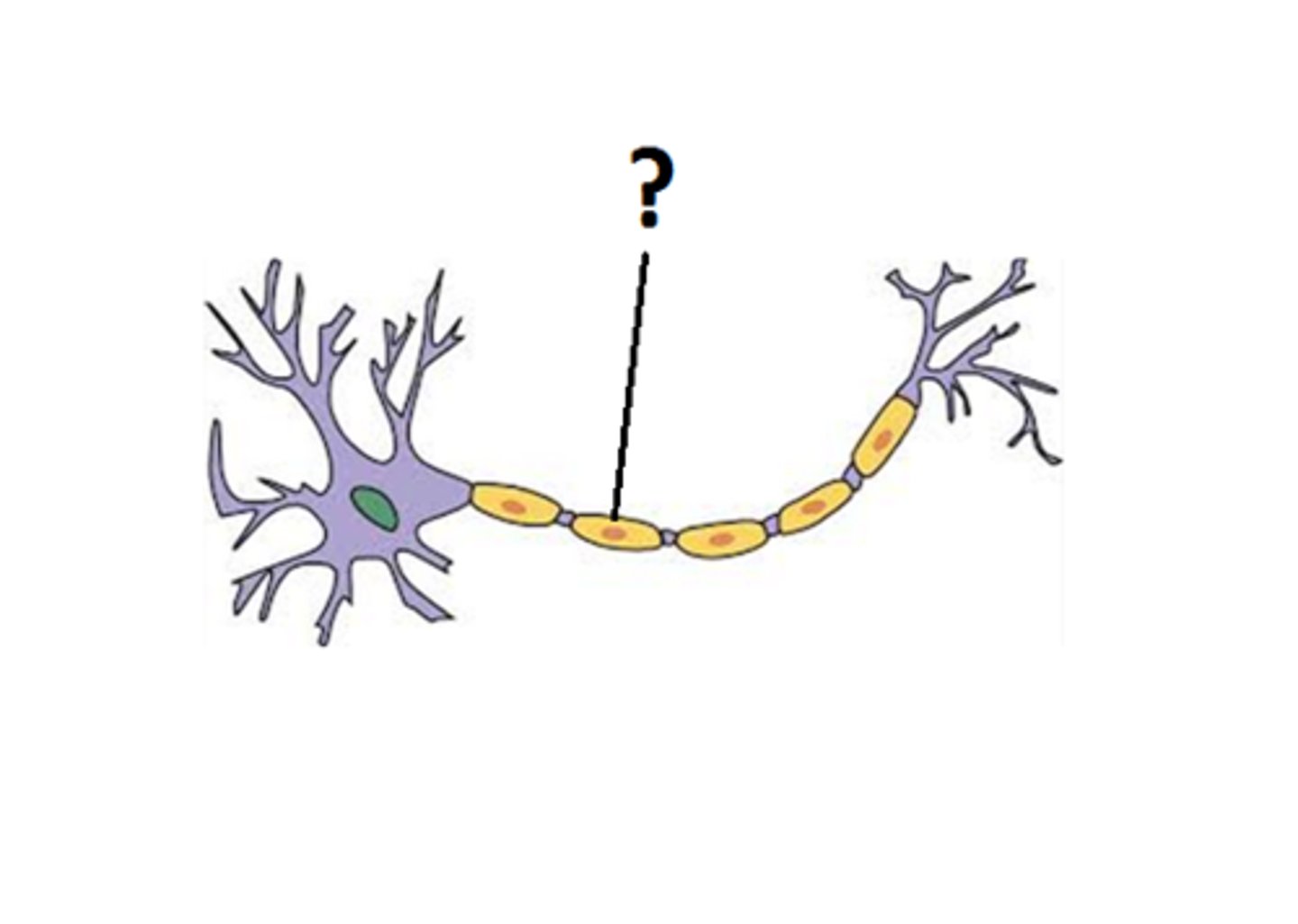
myelin sheath
A fatty layer made up of schwann cells that insulates some axons to allow for faster movement of electrical impulses along the axon
sensory neurons
neurons that receive information from the external world and convey this information to the CNS
relay neurons
These connect the sensory neurons to the motor or other relay neurons. They have short dendrites and short axons.
motor neurons
neurons that carry outgoing information from the CNS to the muscles and glands
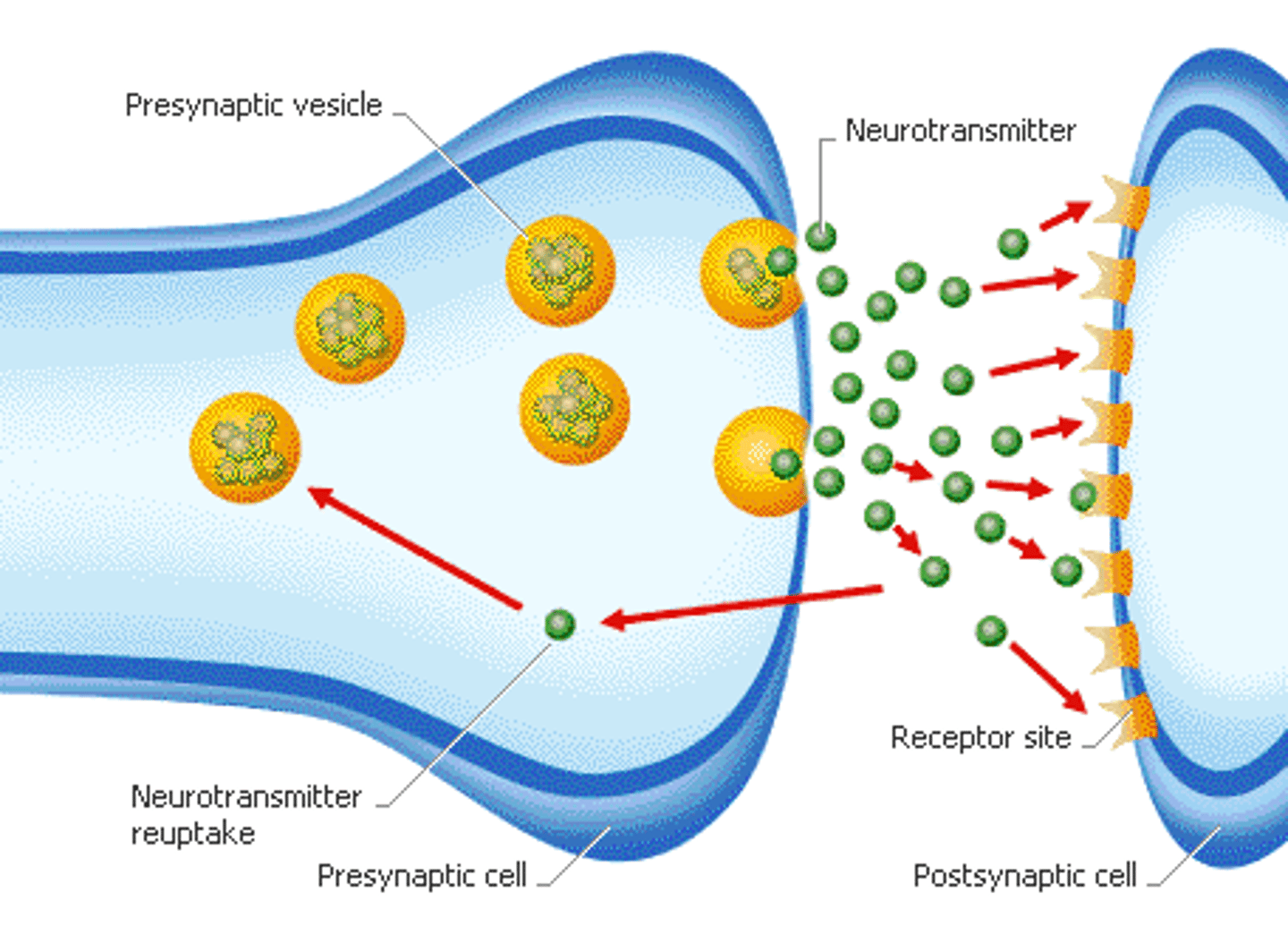
Synapse
Gap between axon terminal of one neuron and the dendrites of the next neuron
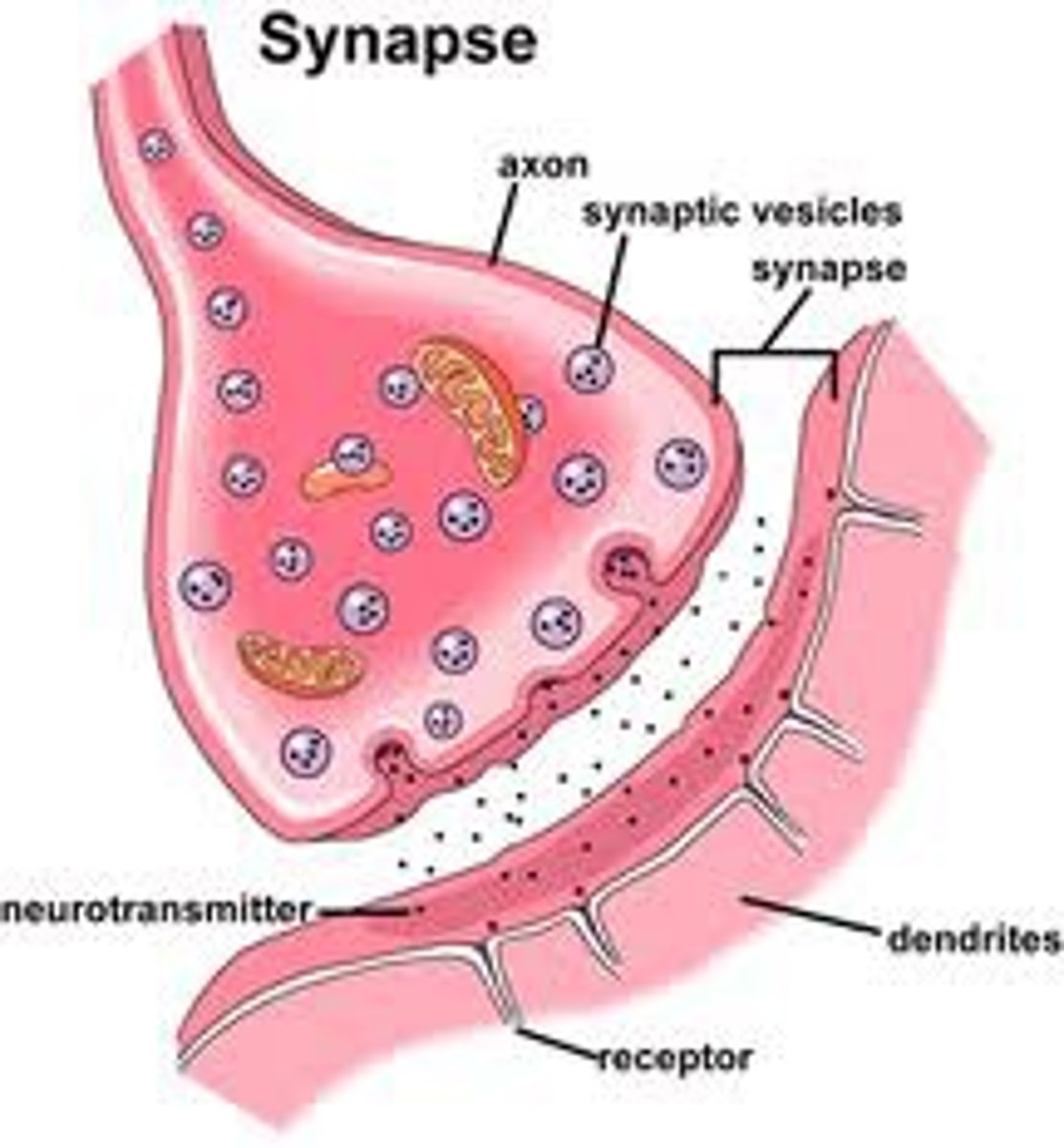
Neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that diffuse across the synaptic gaps between neurons
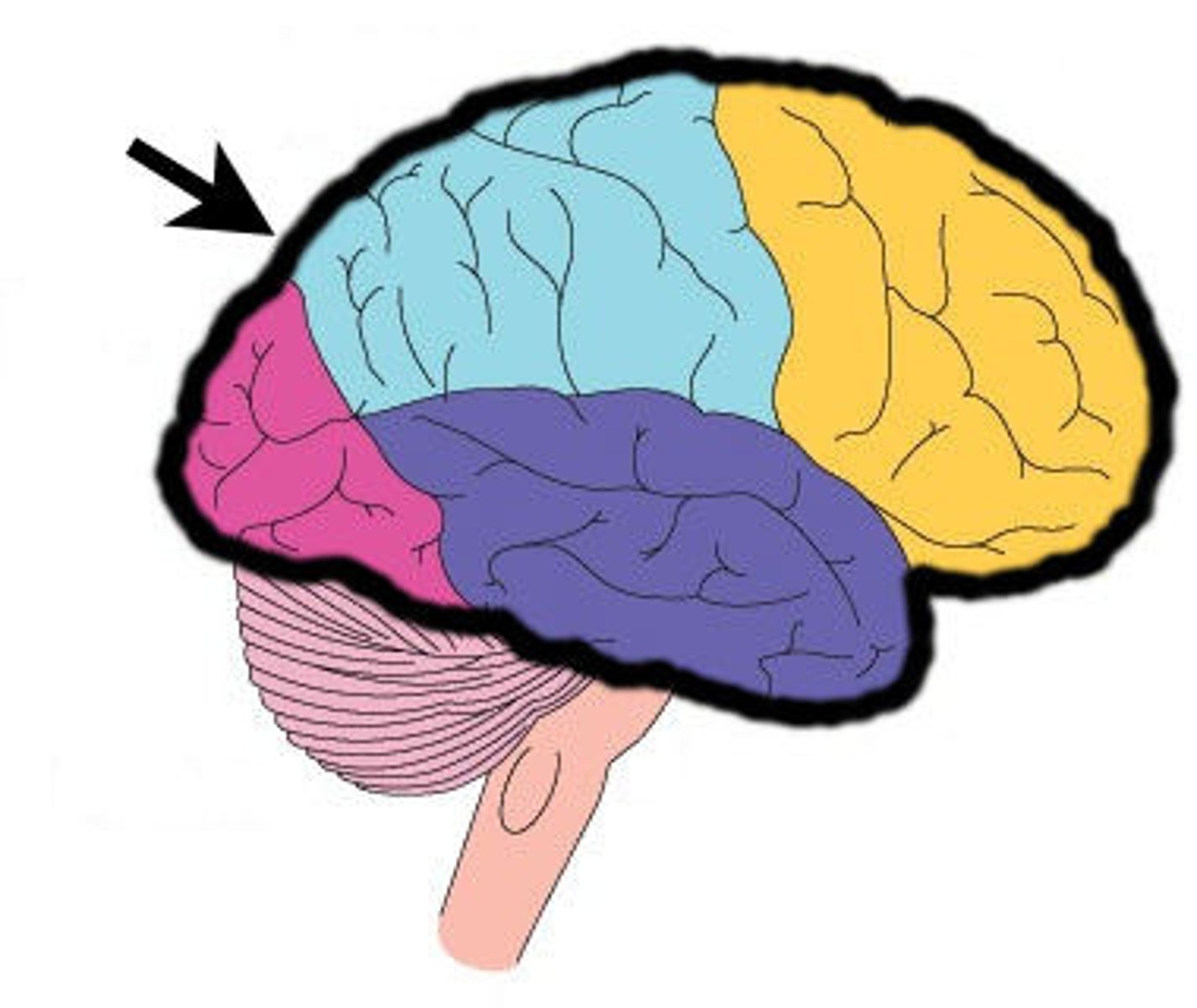
Cerebrum
Largest part of the brain; responsible for voluntary movement, processing sensory information, and complex thought.
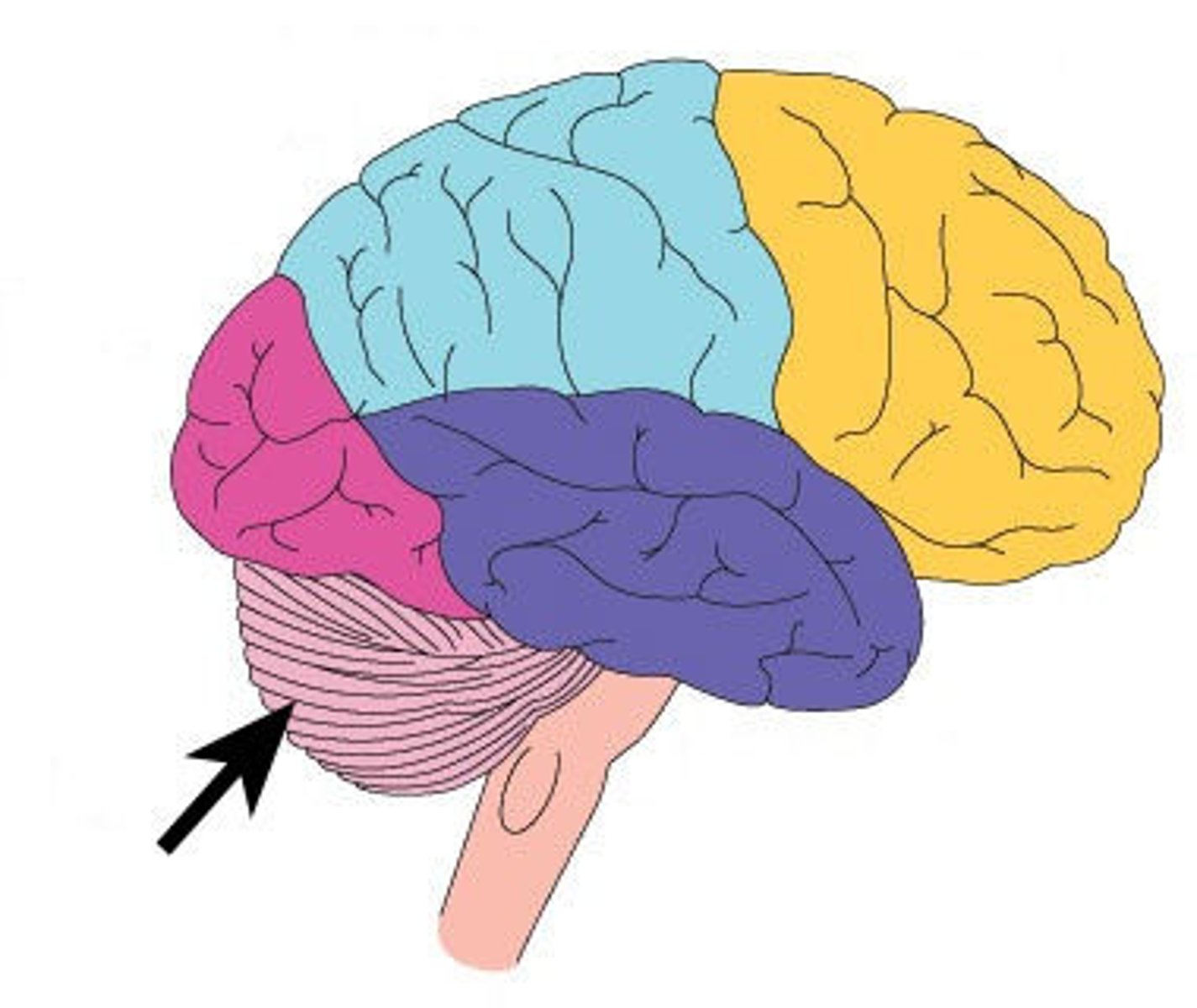
Cerebellum
Balance and coordination
Brainstem / Medulla
responsible for automatic survival functions e.g. breathing, heart rate, blood pressure
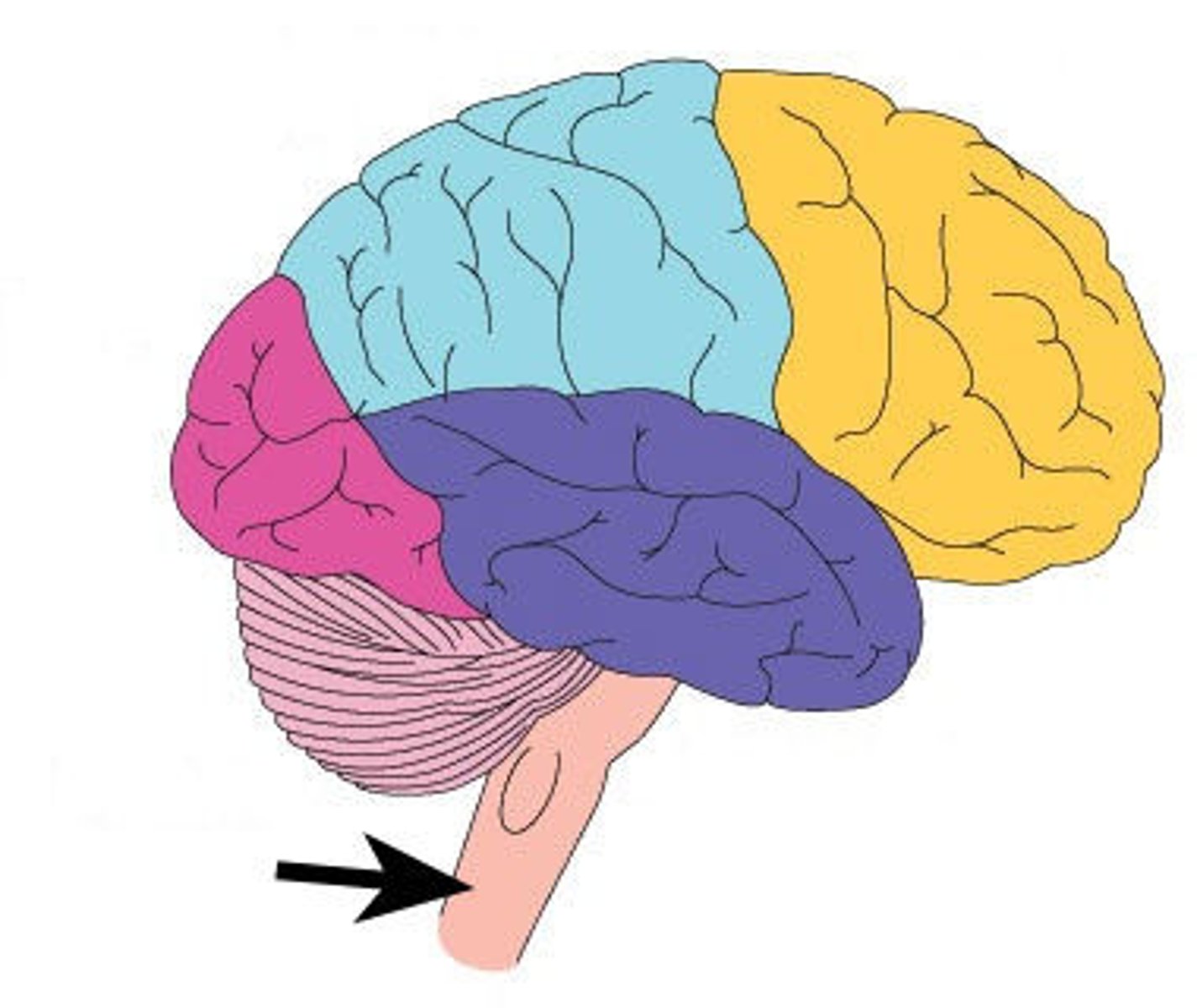
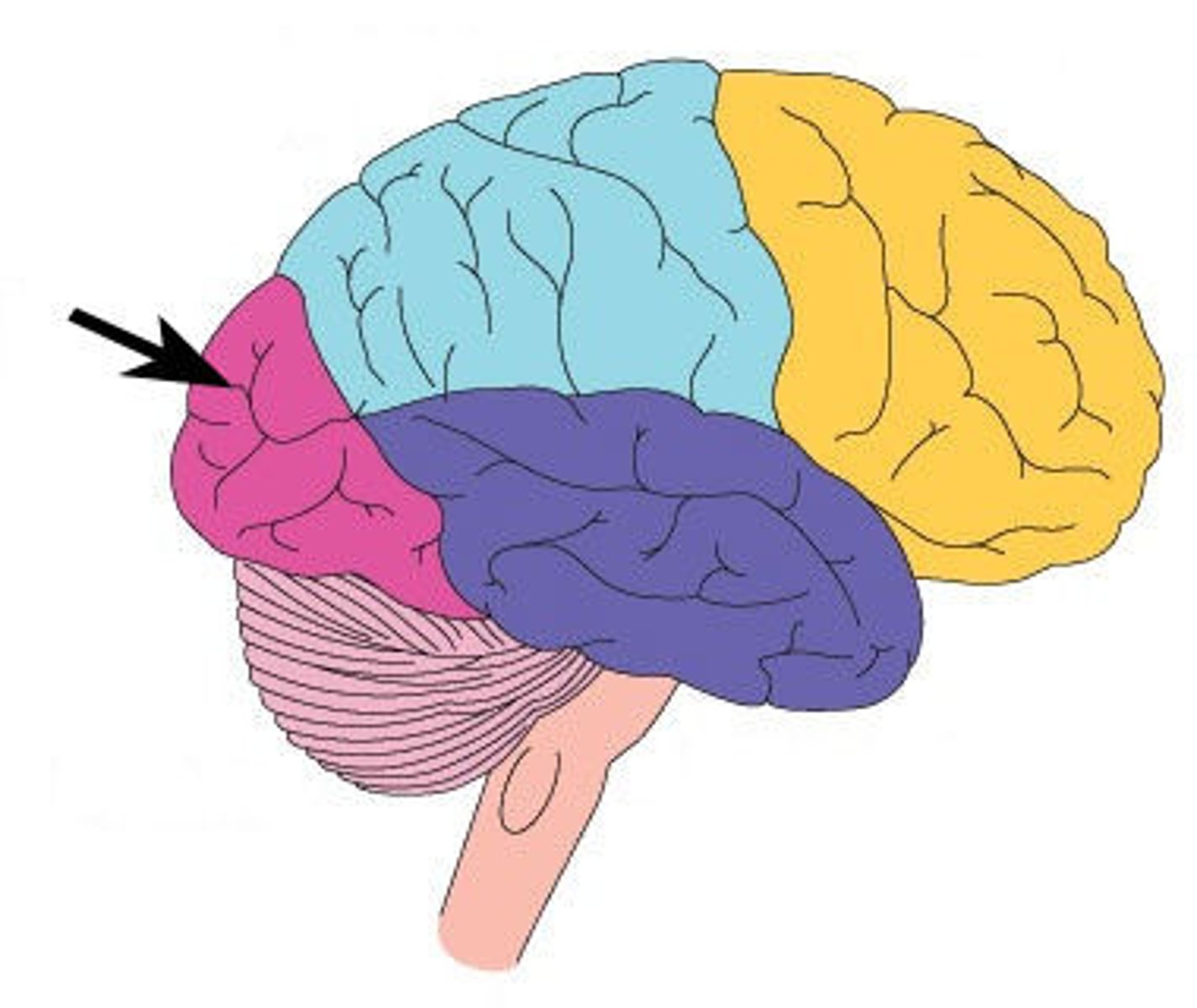
frontal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that controls movement, higher order thinking, problem solving and emotion
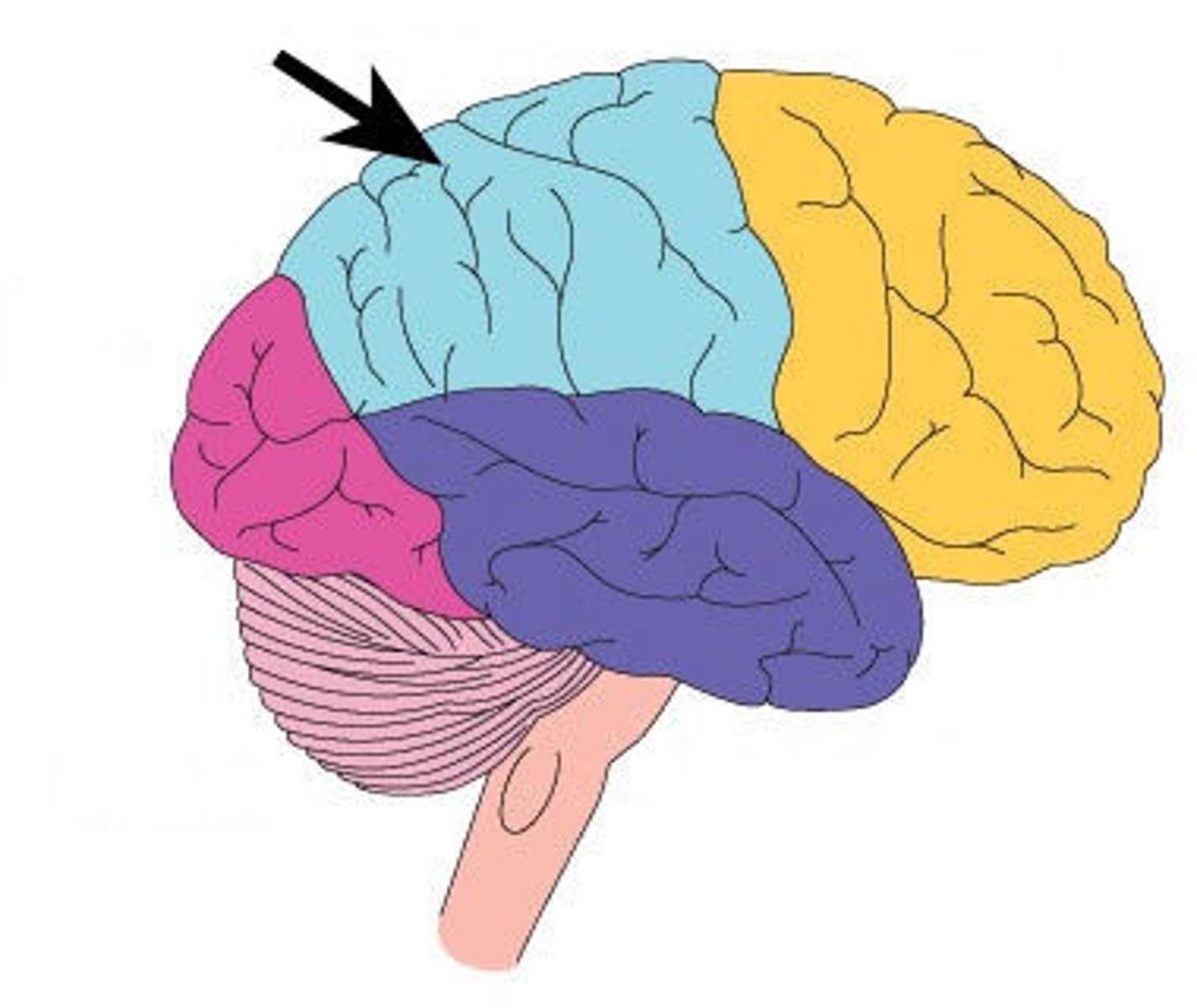
parietal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that receives sensory input for touch and body position
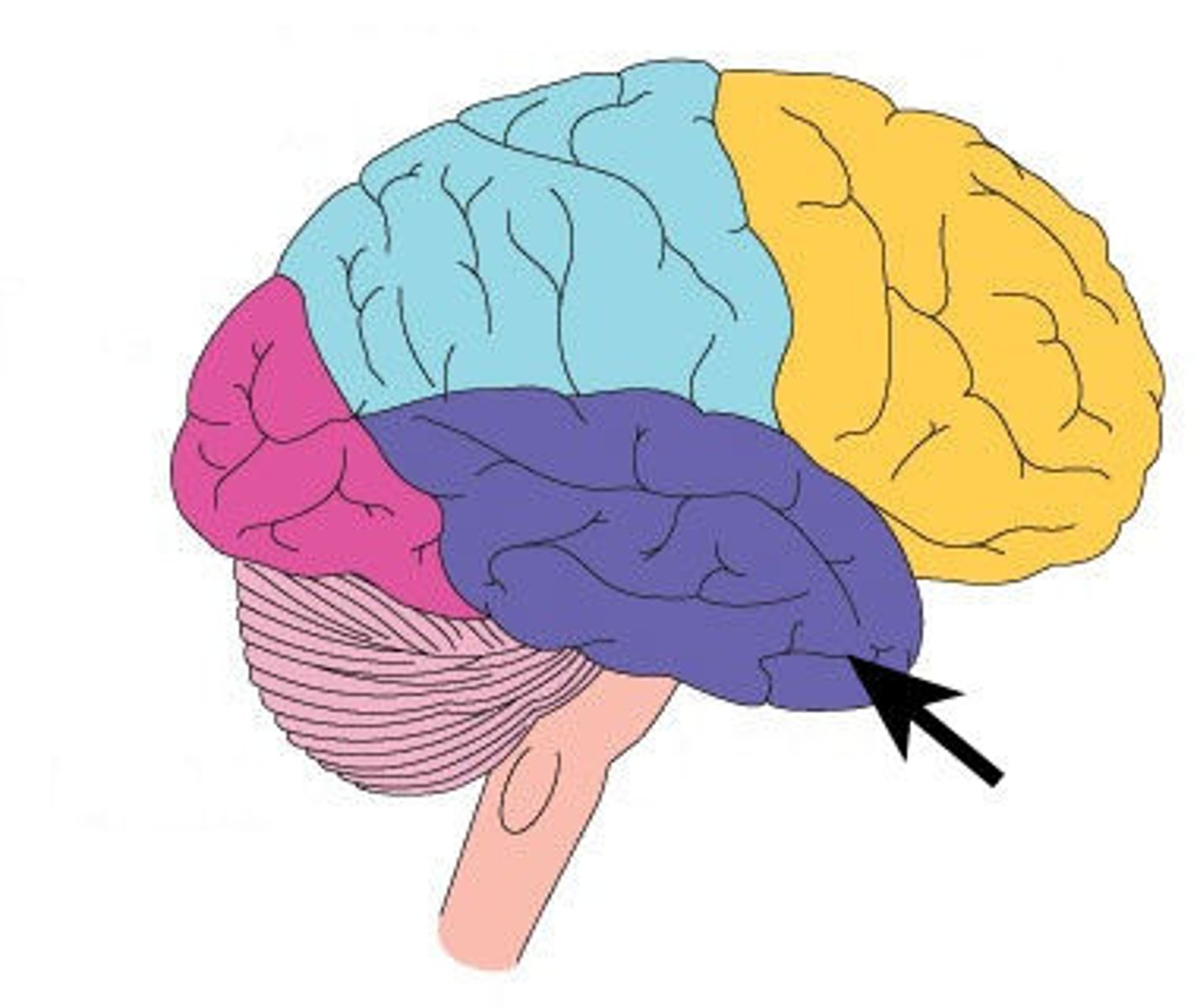
temporal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex responsible for hearing and language.
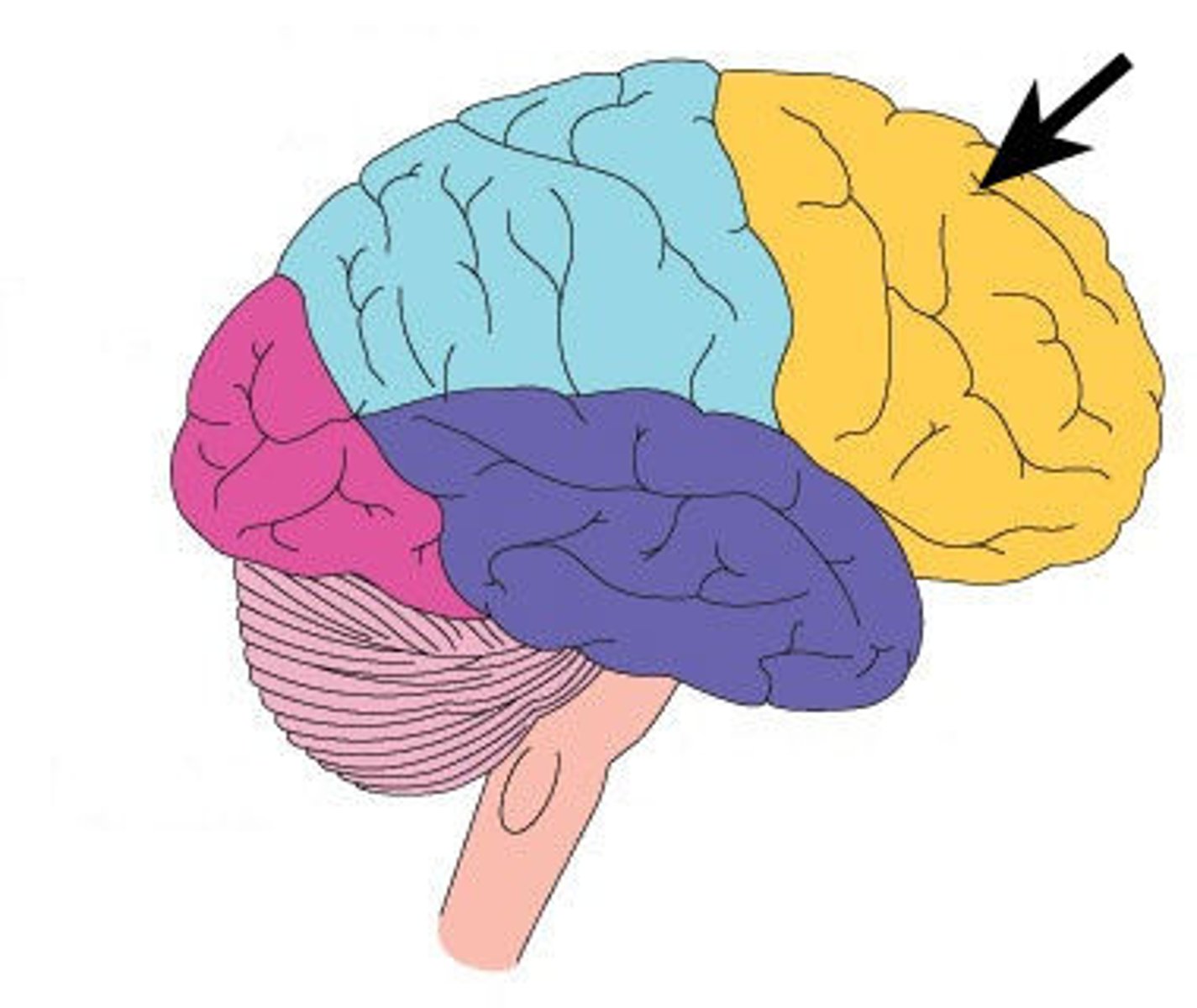
occipital lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information
stimulus response model
Stimulus - receptor - sensory neuron - control centre - motor neuron - effector - response
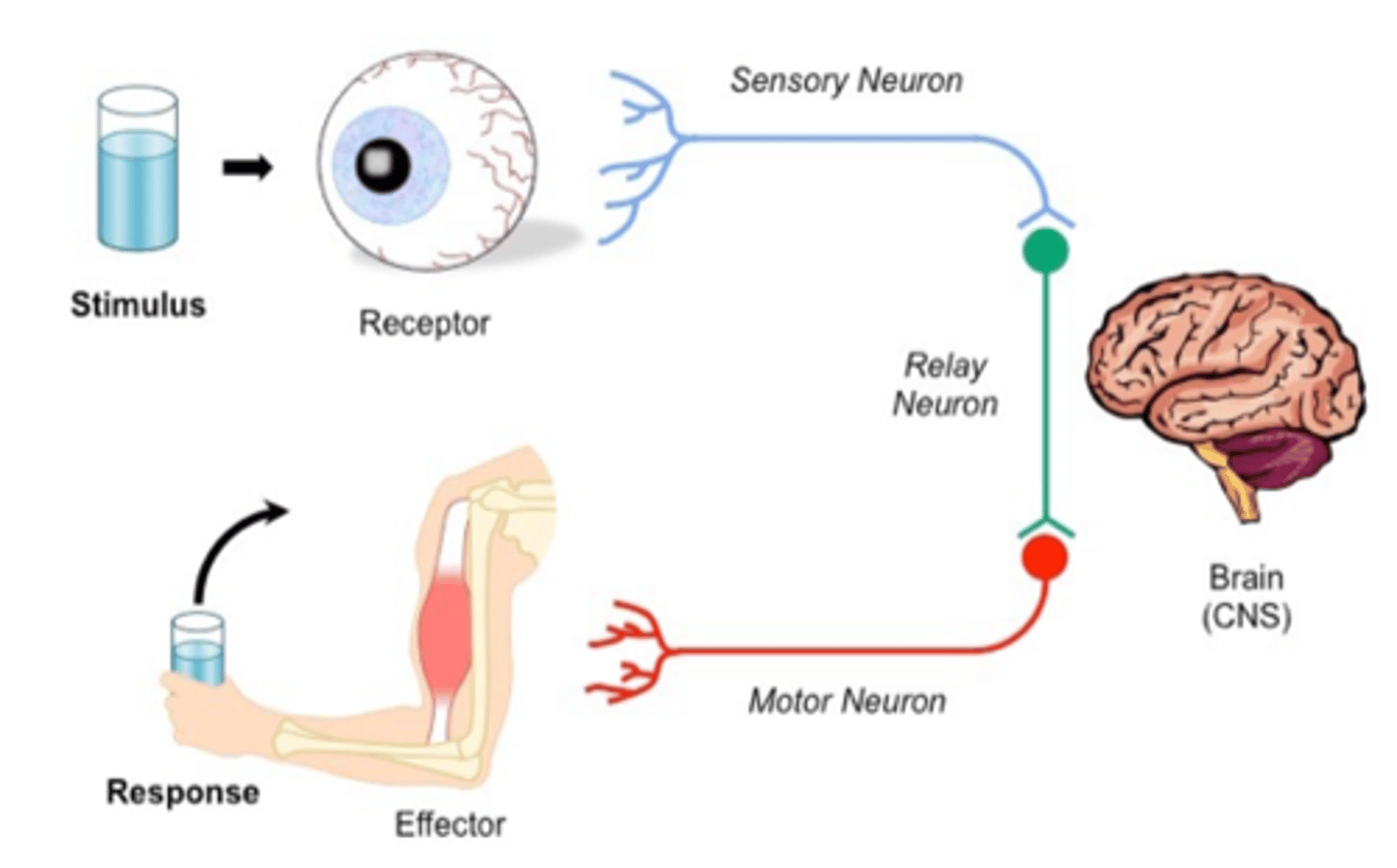
Receptor
special organs or cells that can respond to stimuli and transmit signal to sensory neuron.
photoreceptor - light
chemoreceptor - smell
thermoreceptor - temperature
mechanoreceptor - touch
pain receptor - pain / damaged cells
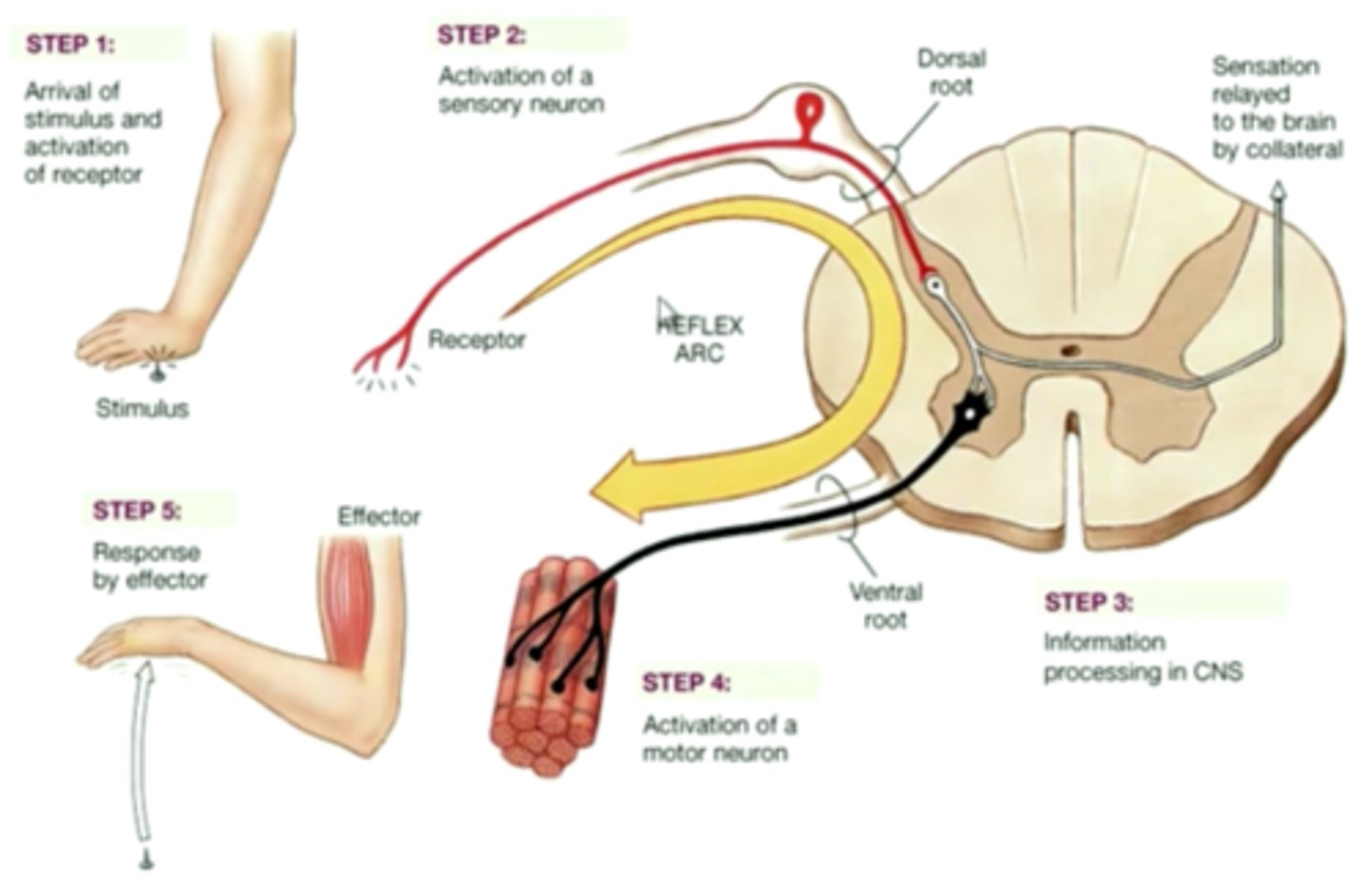
reflex arc
A neural pathway that shortcuts through the spinal cord, resulting in rapid, involuntary action
Metabolism
the chemical processes that occur within a living organism in order to maintain life. catabolic = reactions that break down. anabolic = reactions that build.
cellular respiration
glucose + oxygen --> carbon dioxide + water + energy
Enzymes
Proteins that speed up chemical reactions. Are not used up during reactions.
Homeostasis
process by which organisms maintain a relatively stable internal environment
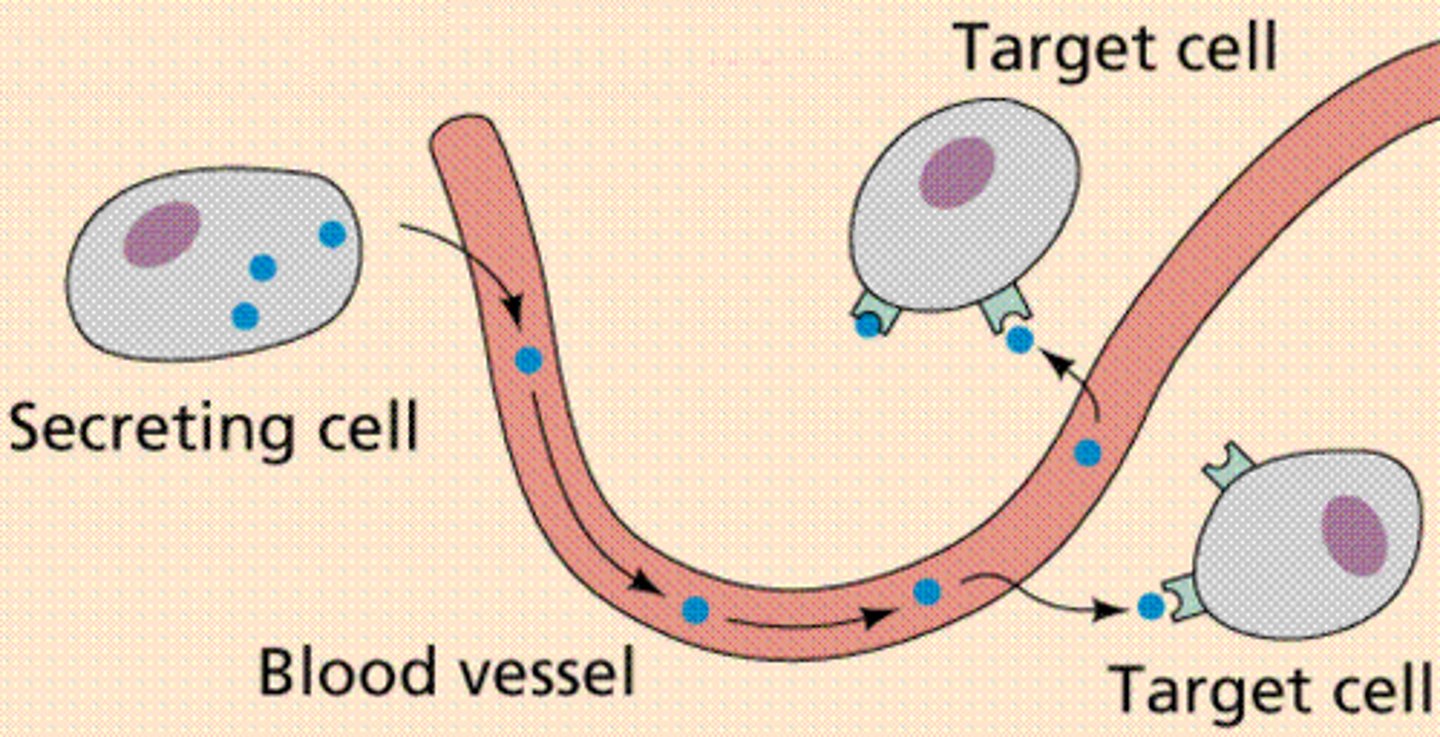
endocrine system
Consists of glands that produce hormones to regulate the body's internal environment
hormones
chemical messengers that travel through the bloodstream, and affect target cells
Hypothalamus
brain region in charge of homeostasis, controls the pituitary gland
pituitary gland
The endocrine system's "master" gland. Controls other endocrine glands.
thyroid gland
produces the hormone thyroxine which increases metabolic heat.
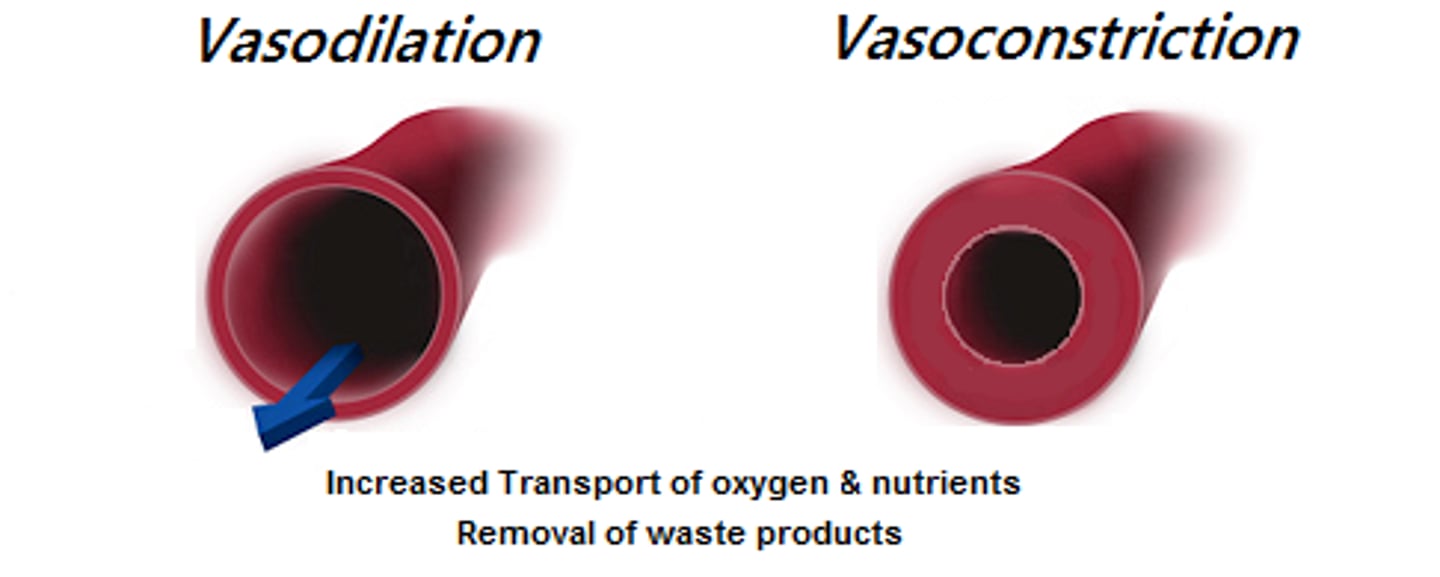
vasoconstriction and vasodilation
narrowing and widening of blood vessels
Sensation vs. Perception
Sensation is arrival of info to brain, perception is interpretation of info in brain
sensory memory
A type of storage that holds sensory information for a few seconds or less.
short-term memory
"working" memory that holds a few items briefly, e.g. seven digits of a phone number while dialing
long-term memory
the relatively permanent storage of information
Rehearsal
the conscious repetition of information, either to maintain it in short-term memory (maintenance) or to encode it for long-term storage (elaborate)
Retrieval
the process of getting information out of long-term memory
Chunking
organizing information into familiar, manageable units; helps improve memory
Contextual Clues
improves memory by situating information in familiar contexts