Economics Elasticity
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Price Elasticity of Demand
The responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in price of a product. It is a measure of how sensitive buyers are to a change in price.
PED = 0
- Perfectly INELASTIC
- Change in P will not change Qd
- Usually necessary for survival
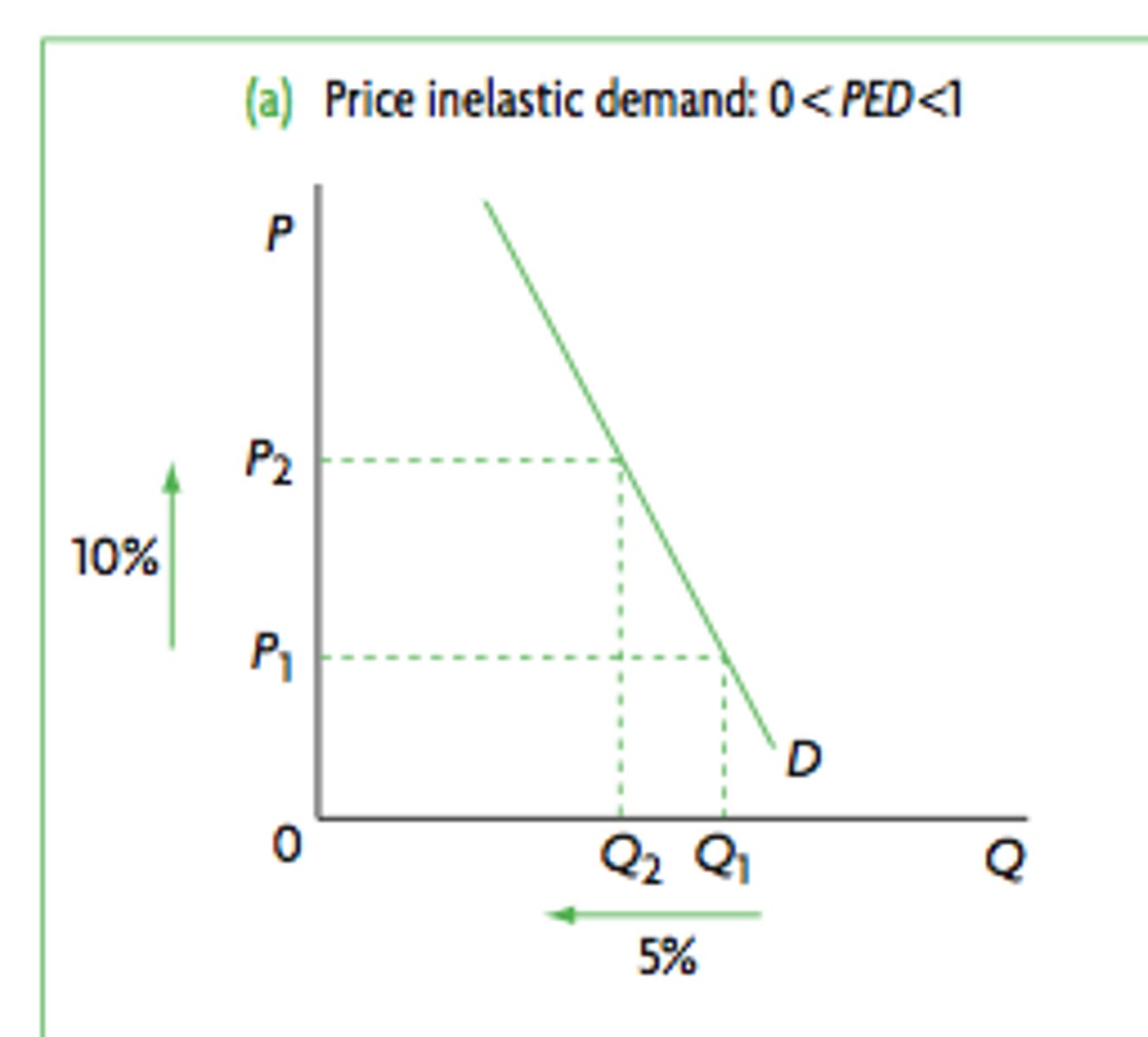
PED < 1
- Relatively INELASTIC
- If P⬆️ by 1% Qd will ⬇️ by <1%
- Less sensitive to change in P
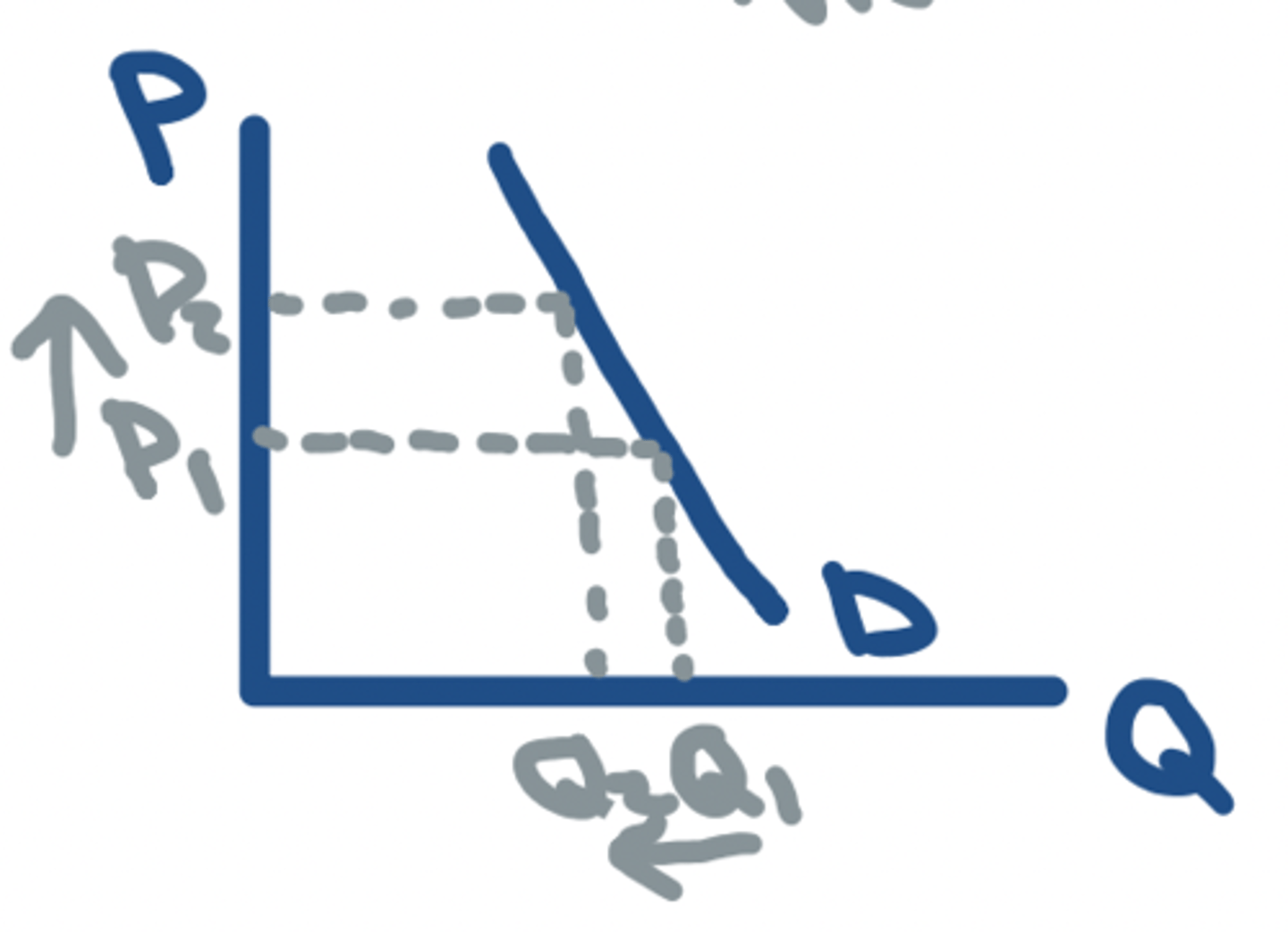
PED = 1
- Unitary ELASTIC
- The same change will occur on both axis
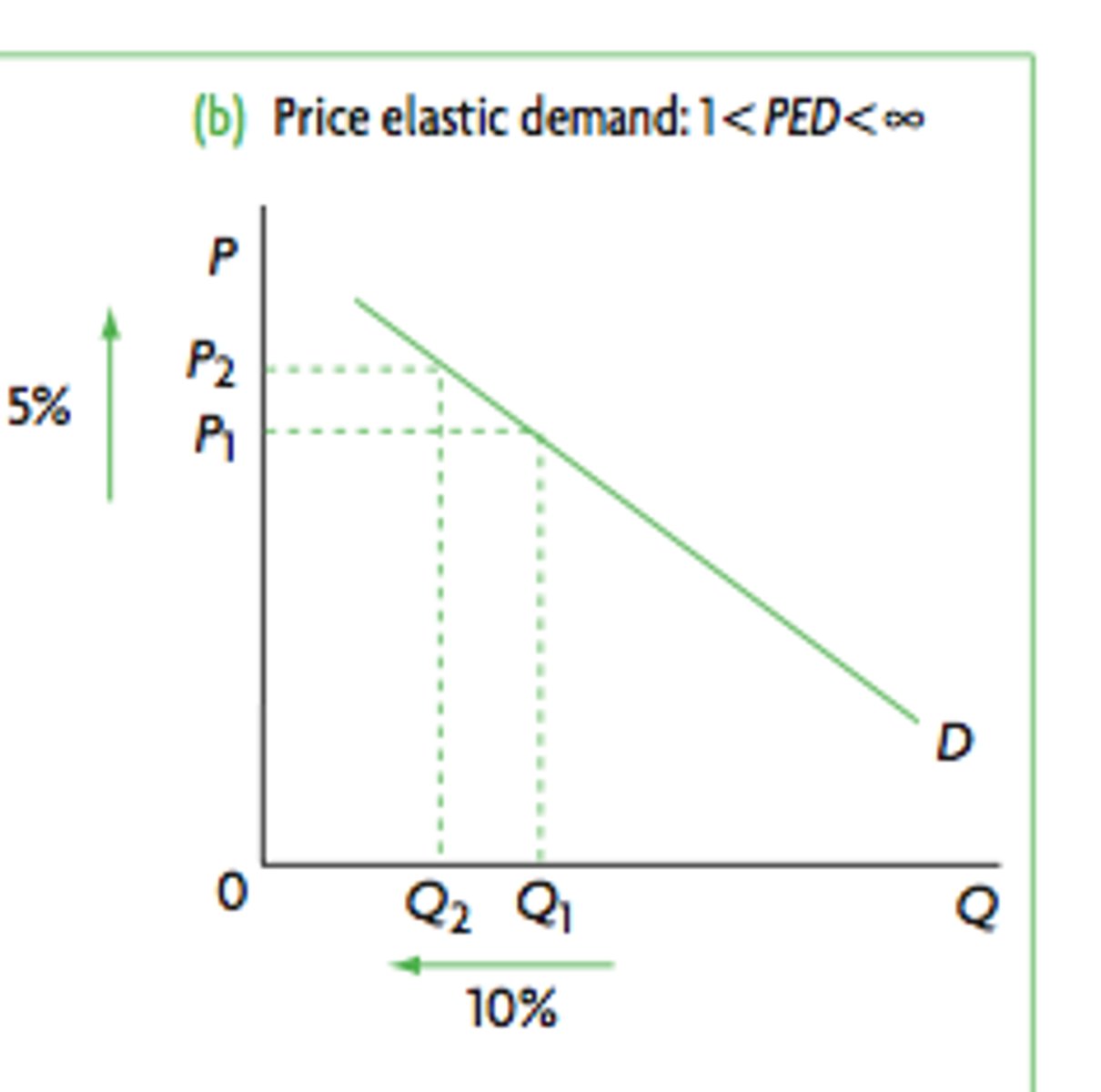
PED > 1
- Relatively ELASTIC
- If ⬆️ in P by 1% Qd will ⬇️ by > 1%
- More sensitive to ⬆️ in P
PED = Infinity
- Perfectly ELASTIC
- Any ⬆️ in P consumers will stop buying
- Usually goods with perfect substitues
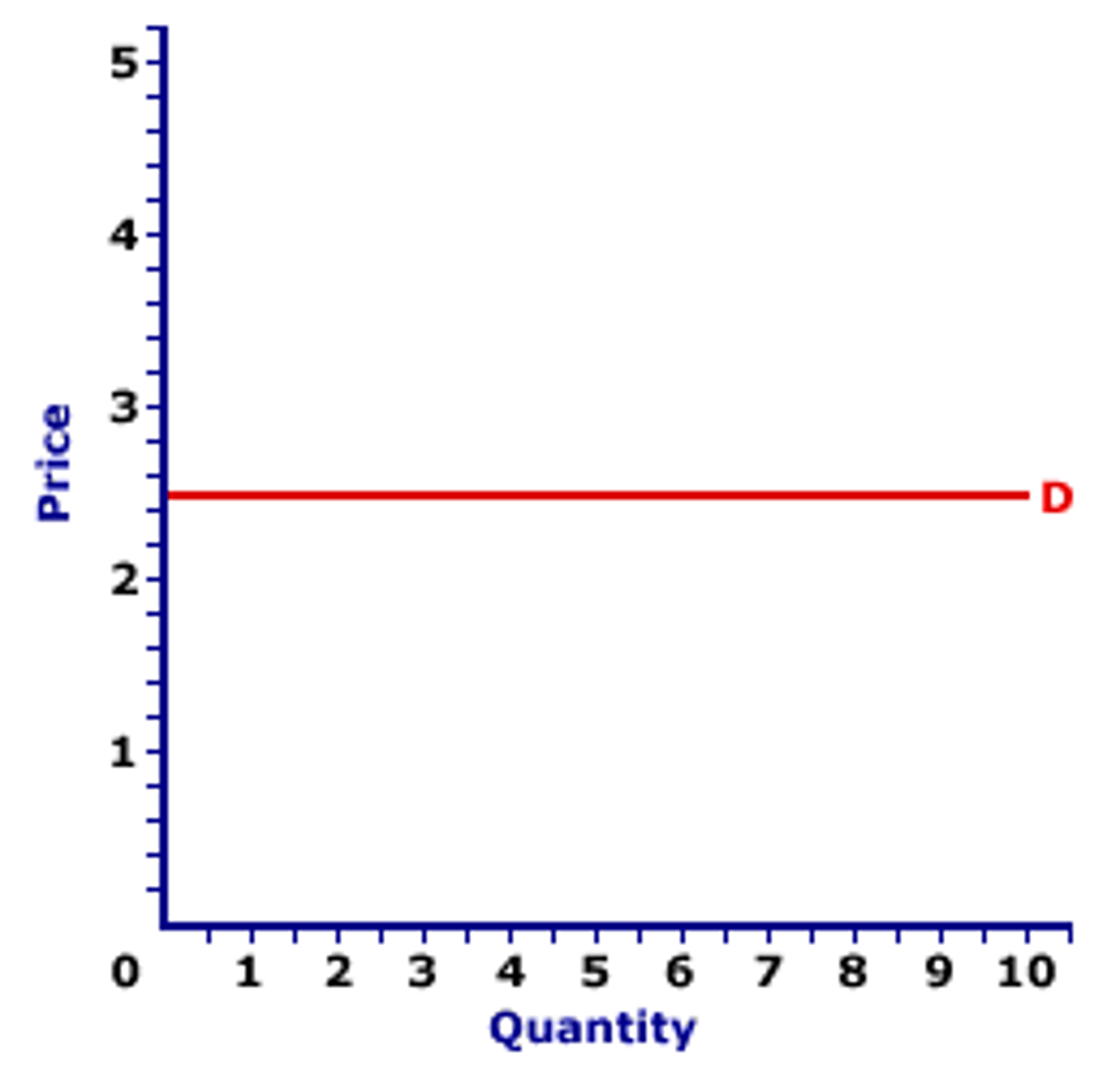
Determinants of PED
- Availability of substitutes
- Proportion of income spent
- Necessity or luxury?
- Time
- Definition of a market
PED Determinant - Availability of Substitutes
- The greater teh substitute the more elastic
- Demand for good that have few substitutes are inelastic
- More sensitive to change in price (can switch to other products)
PED Determinant - Proportion of income spent
- Little of our income = more inelastic
- Lots of income = more elastic
PED Determinant - Necessity or Luxury?
- If necessity = inelastic
- If luxury = more elastic
PED Determinant - Time
- How long consumers have to shop around / delay purchase
- More time = more elastic
PED Determinant - Definition of a Market
- Broadly defined market = more inelastic
- Narrowly defined market = more elastic
TR: P⬆️ - ELASTIC
⬆️ in P = ⬇️ in TR
- P and TR move in opposite directions
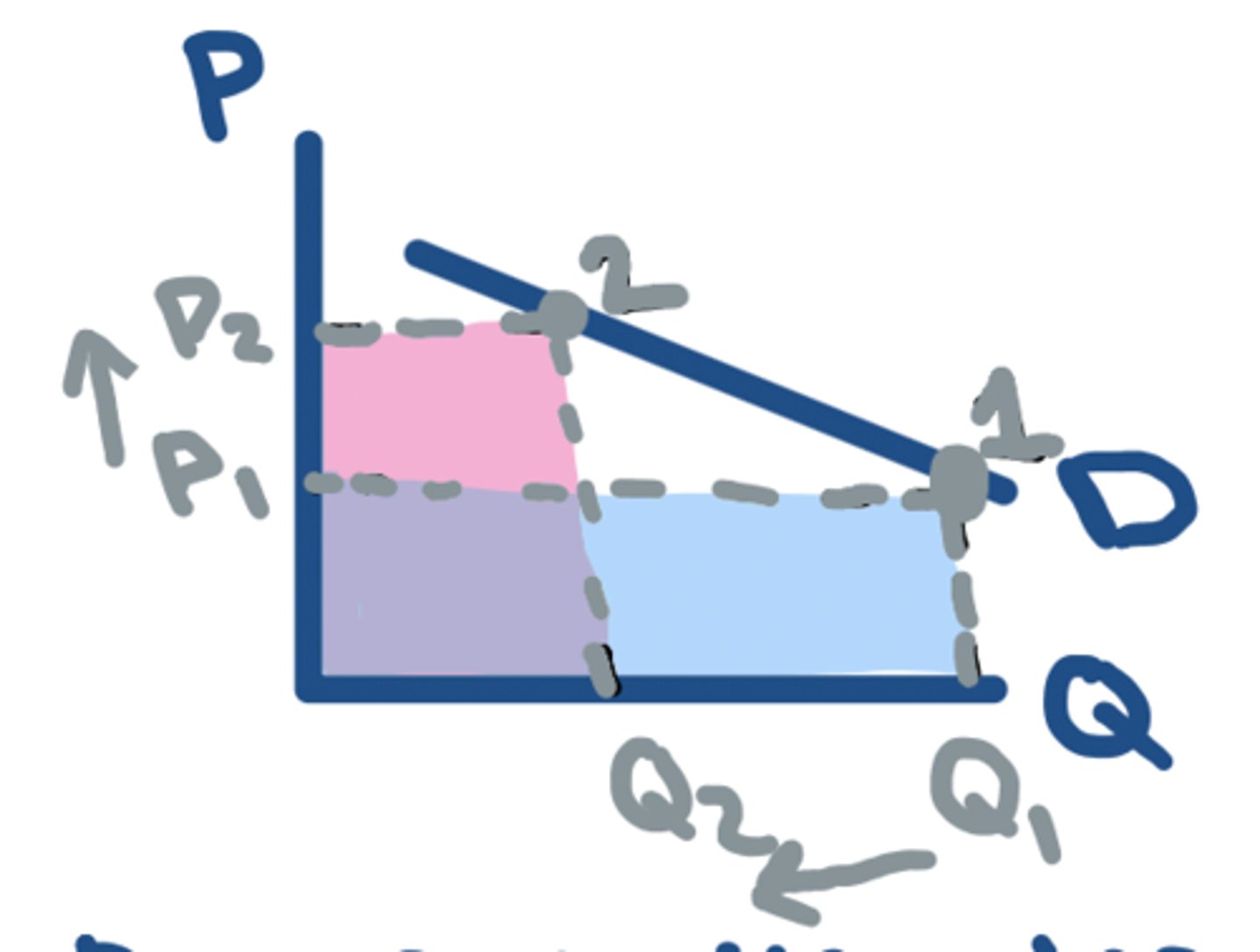
TR: P⬇️ - ELASTIC
⬇️ in P = ⬆️ in TR
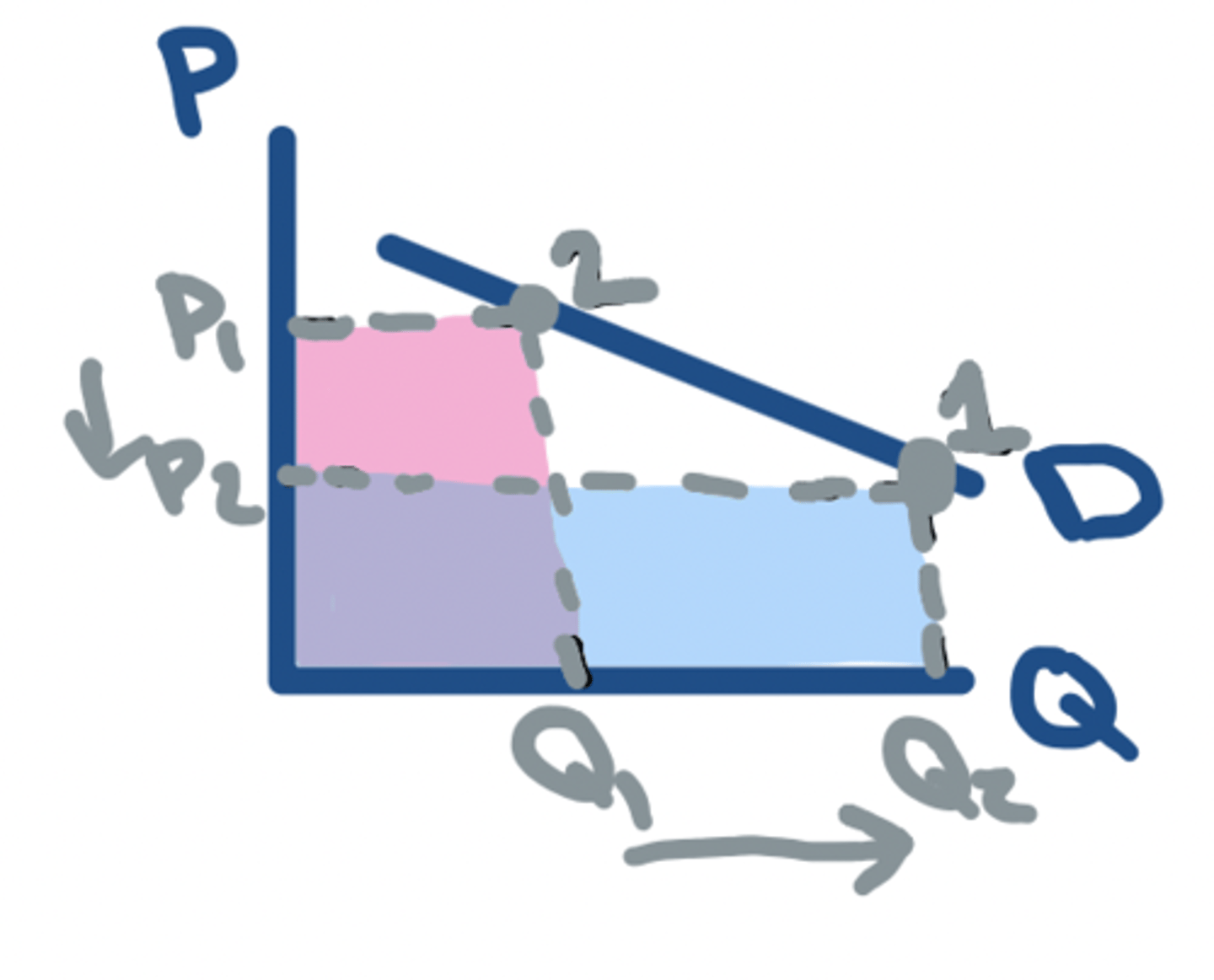
TR: P⬆️ - INELASTIC
⬆️ in P = ⬆️ in TR
TR: P⬇️ - INELASTIC
⬇️ in P = ⬇️ in TR
Price Elasticity of Supply
A measure of the responsiveness of quantity supplied of a good to a change in the price of that good.
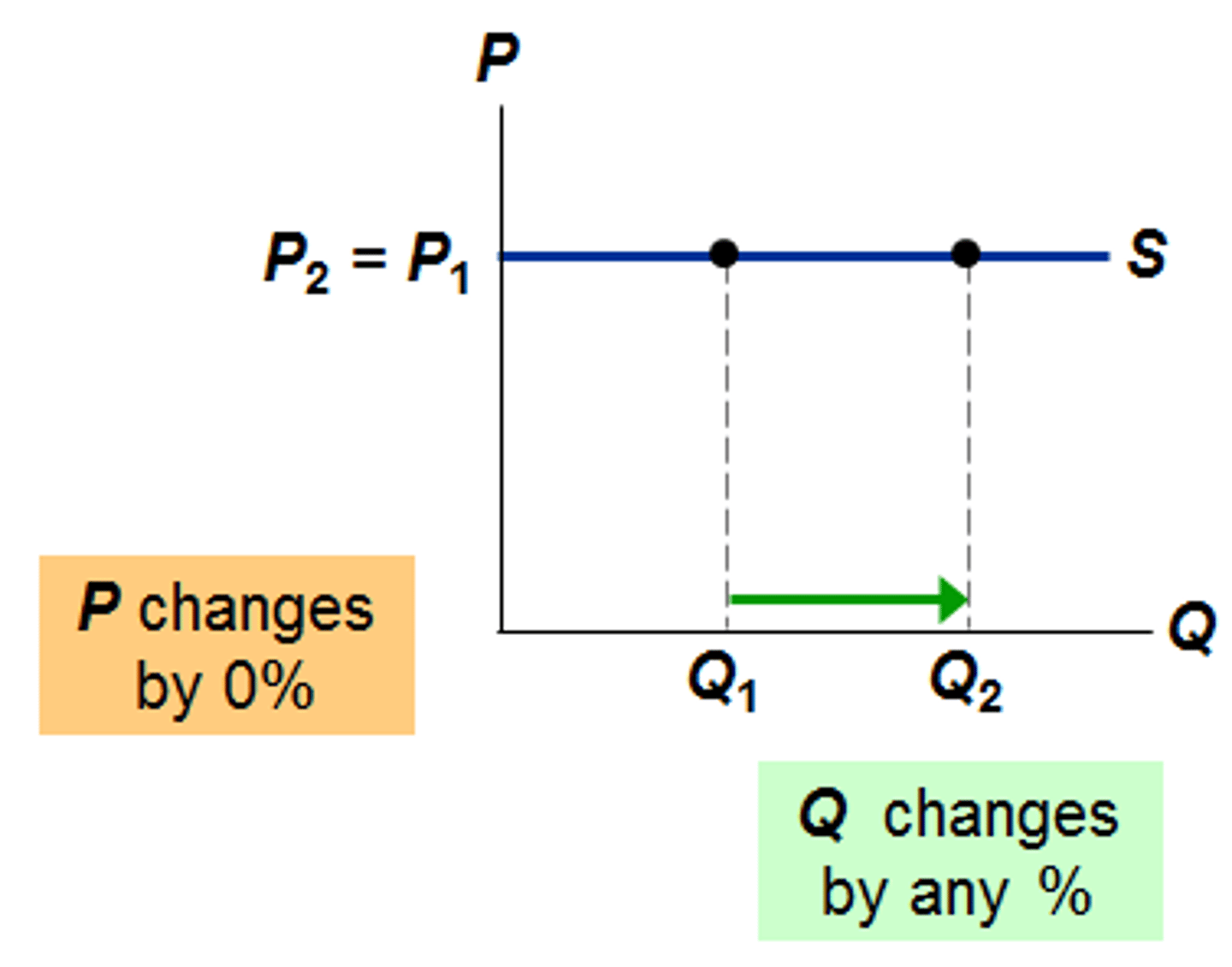
PES = 0
- Perfectly INELASTIC
- A change in P will not change Qs
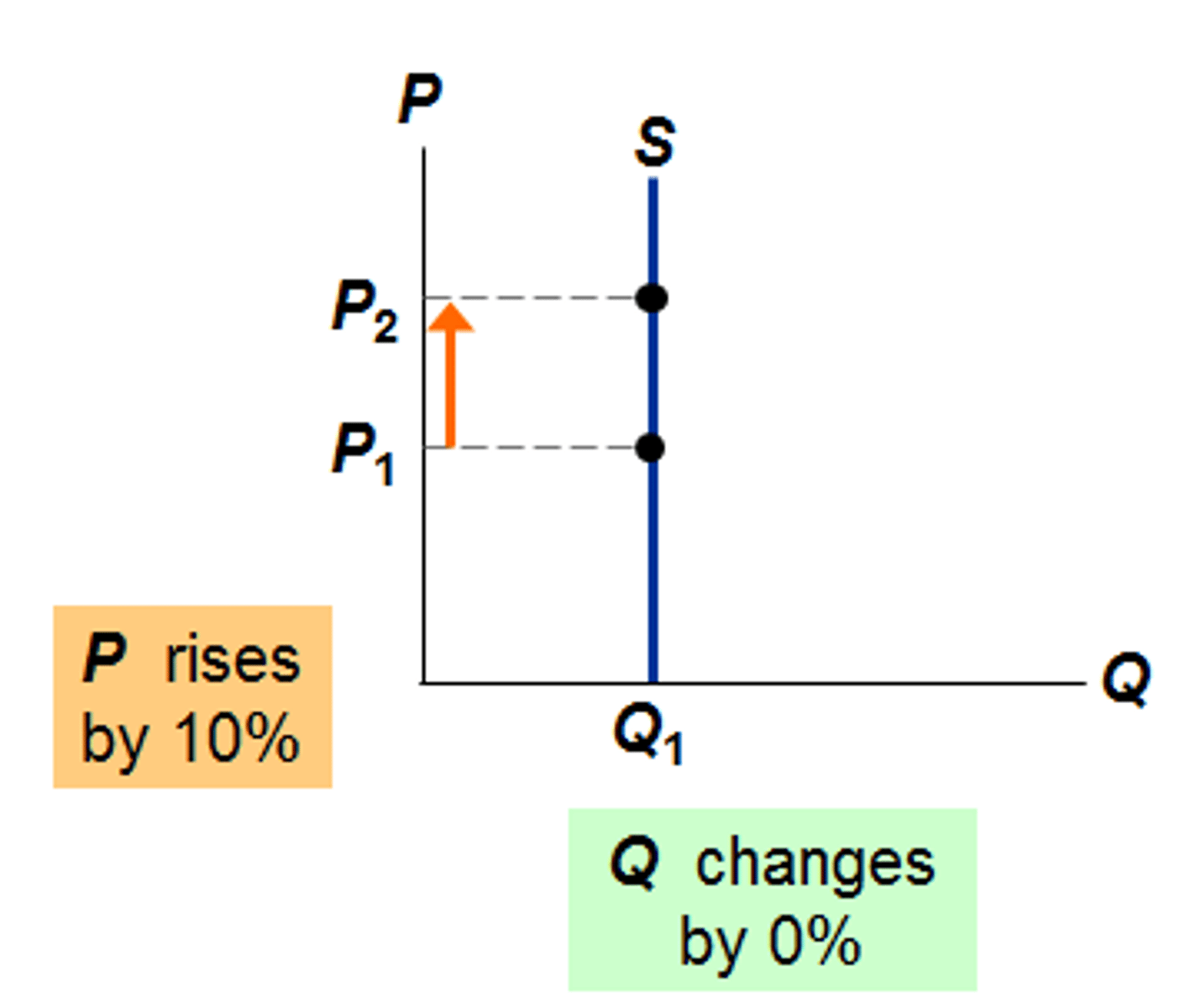
PES < 1
- Relatively INELASTIC
- A ⬆️ in P of 1% will result in < 1% ⬆️ in Qs
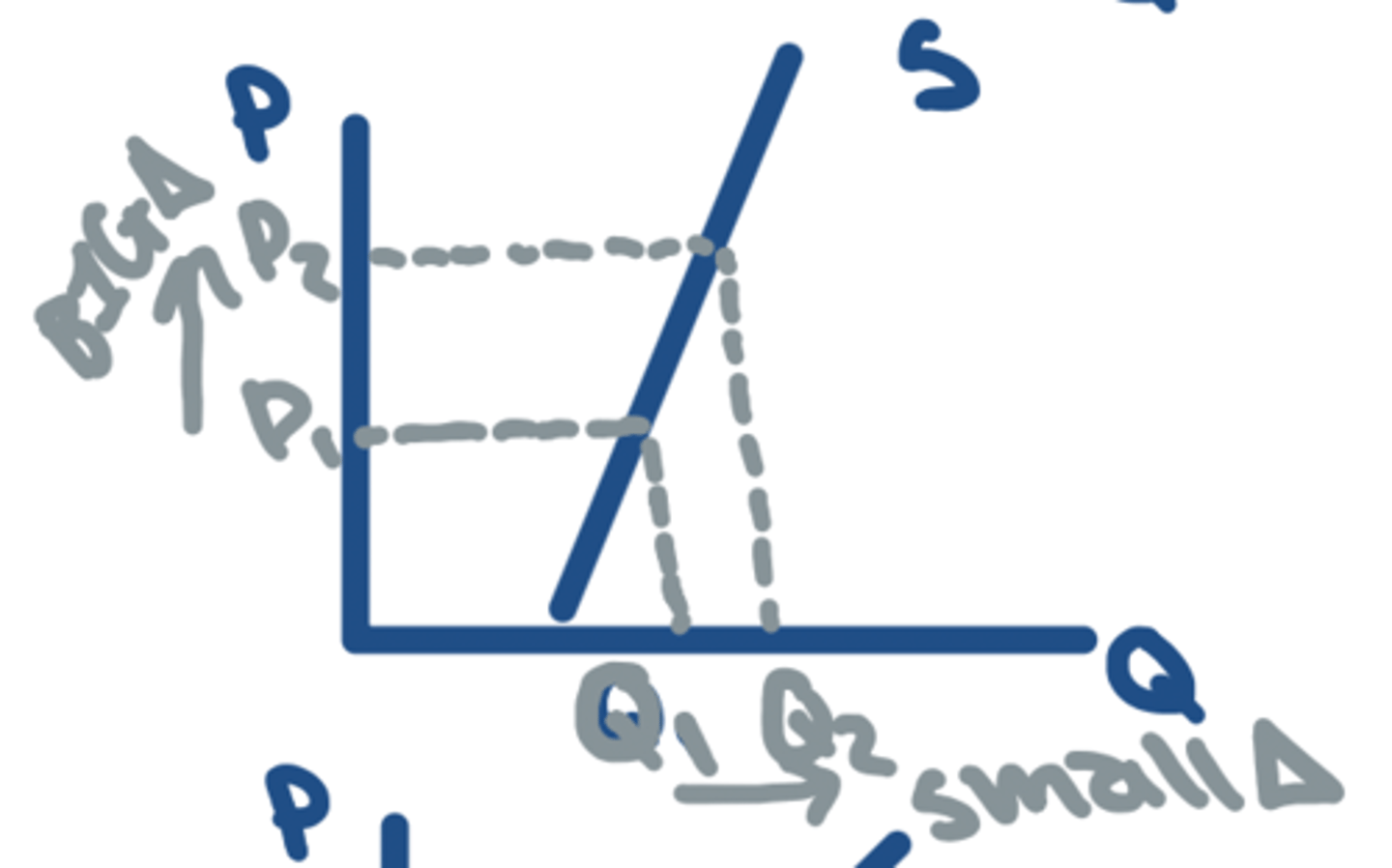
PES = 1
- Unitary ELASTIC
- P change = Qs change
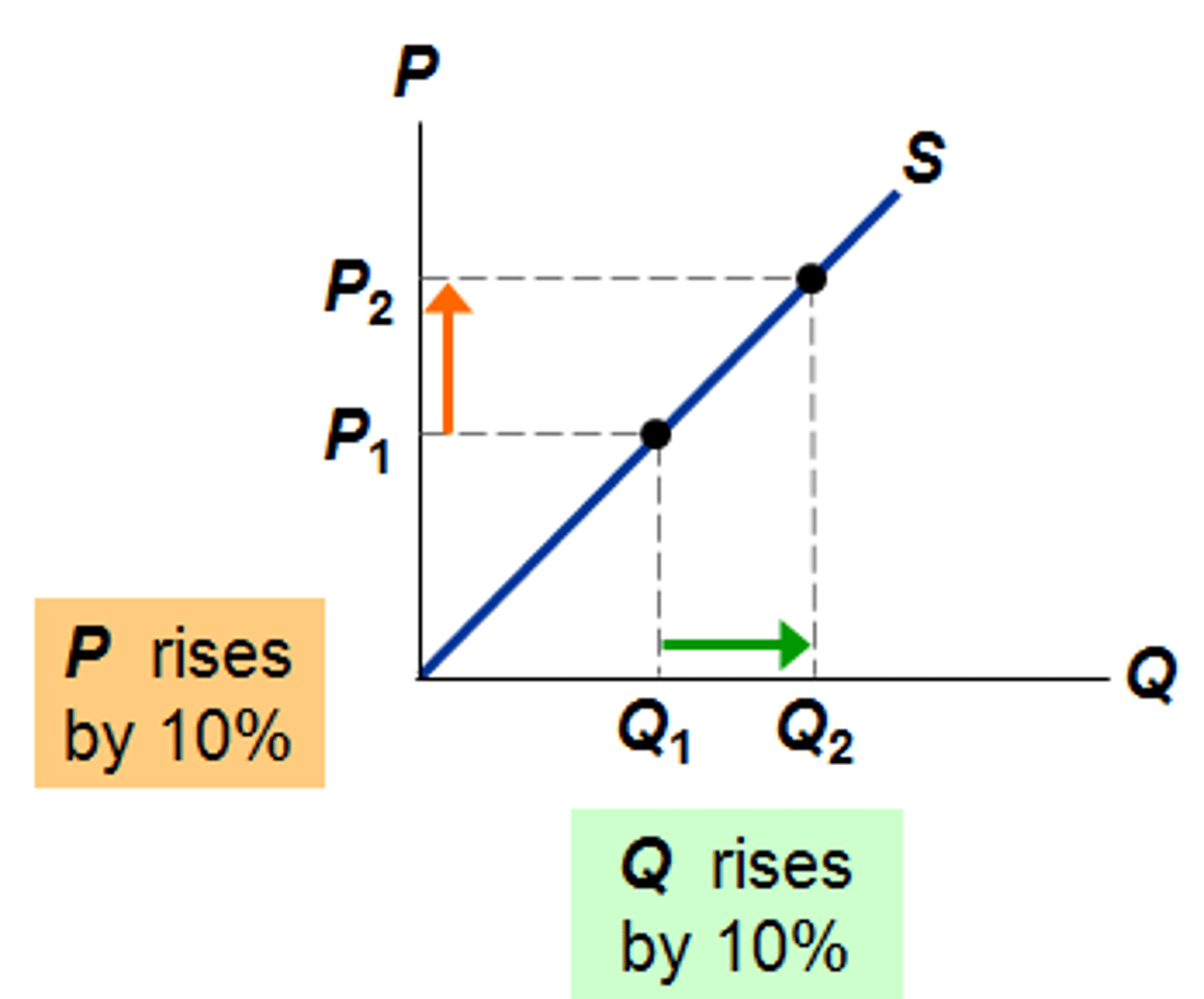
PES > 1
- Relatively ELASTIC
- a ⬆️ in P of 1% will result in > 1% change is Qs
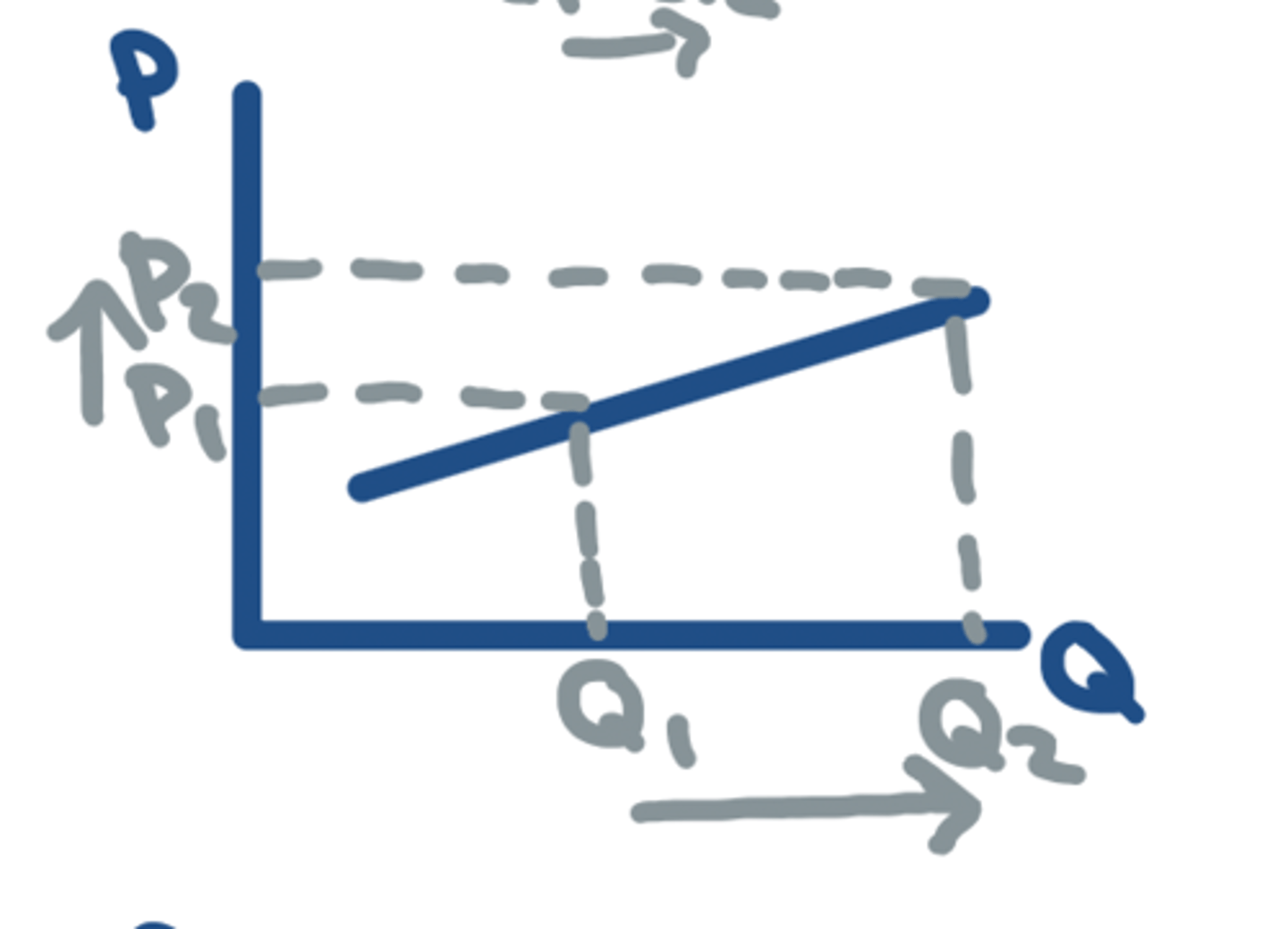
PES = Infinity
- Perfectly ELASTIC
- Eg. minimum wage
Price ELASTIC goods in SUPPLY
Sellers can easily and quickly expand supply in response to a change in P. Eg. manufactured goods
Price INELASTIC goods in SUPPLY
Sellers can not quickly and easily expand supply. Eg. Agricultural goods
Determinants of PES
- Time
- Ability to store inventory
- Nature of industry
PES Determinant - Time
- If producers can respond quickly to change in P, elastic
- If goods take a long time to produce, inelastic
PES Determinant - Ability to store inventory
- Goods that can be stored are more elastic than perishable goods
- Producers of storable goods can be flexible with their supply
PES Determinant - Nature of industry
- Agricultural goods are inelastic, manufactured is elastic
- Farmers need to wait until next growing season, manufactured goods supply can be easily adjusted depending on the market