AP US History: Imperialism, Spanish-American War, and Early 20th Century Foreign Policy
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
What were the main reasons the U.S. looked outside its borders at the start of the 20th century?
Desire for new economic markets, display of American masculinity, spread of Christianity, Social Darwinism, European imperialism, and strengthening the U.S. navy.
What was the Big Sister policy?
An attempt by the U.S. to take a political and economic leadership role in Latin America.
What diplomatic tensions did the U.S. face with Germany?
A near war regarding the Samoan Islands.
What incident almost led to war between the U.S. and Italy?
The lynching of 11 Italians.
What was the significance of the border dispute with England over Venezuela?
It nearly led to war, but was avoided due to British occupation during the Boer War and mutual fear of Germany. Dispute occurred due to gold being found, both nations wanted the gold-- Monroe Doctrine was involved
What was the outcome of the Great Rapprochement?
It established friendly relations between the U.S. and England that lasted for most of the 20th century.
What led to the American interest in Hawaii in the 19th century?
Economic and religious reasons, along with the decline of the native population due to disease.
What was the McKinley Tariff's impact on Hawaii?
It hurt American sugar owners, leading them to plot for annexation of Hawaii.
What was the result of the U.S. involvement in Cuba during the Spanish-American War?
The U.S. supported Cuban independence, which was integral to business interests and the Panama Canal.
What was the cause of the explosion of the USS Maine?
The cause was debated, but the U.S. believed it was a military attack, leading to war fever.
What was the Teller Amendment?
It promised to give Cuba independence after the war with Spain.
Who commanded the U.S. forces in the Philippines during the Spanish-American War?
Theodore Roosevelt.
What was the Treaty of Paris of 1899?
It granted the U.S. control of Cuba, Guam, Puerto Rico, and the Philippines.
What were the arguments of the Anti-Imperialist League?
They argued that U.S. expansion violated principles of self-determination and freedom.
What was the Insular Cases ruling?
The Supreme Court ruled that people in U.S. territories were under American rule but did not necessarily enjoy all American rights.
What was the Platt Amendment?
It required Cuba to not sign treaties without U.S. approval, limit debt, allow U.S. intervention, and lease military bases.
Why was the Spanish-American War referred to as a 'splendid little war'?
Because its benefits, such as increased respect and military prestige for the U.S., outweighed its costs.
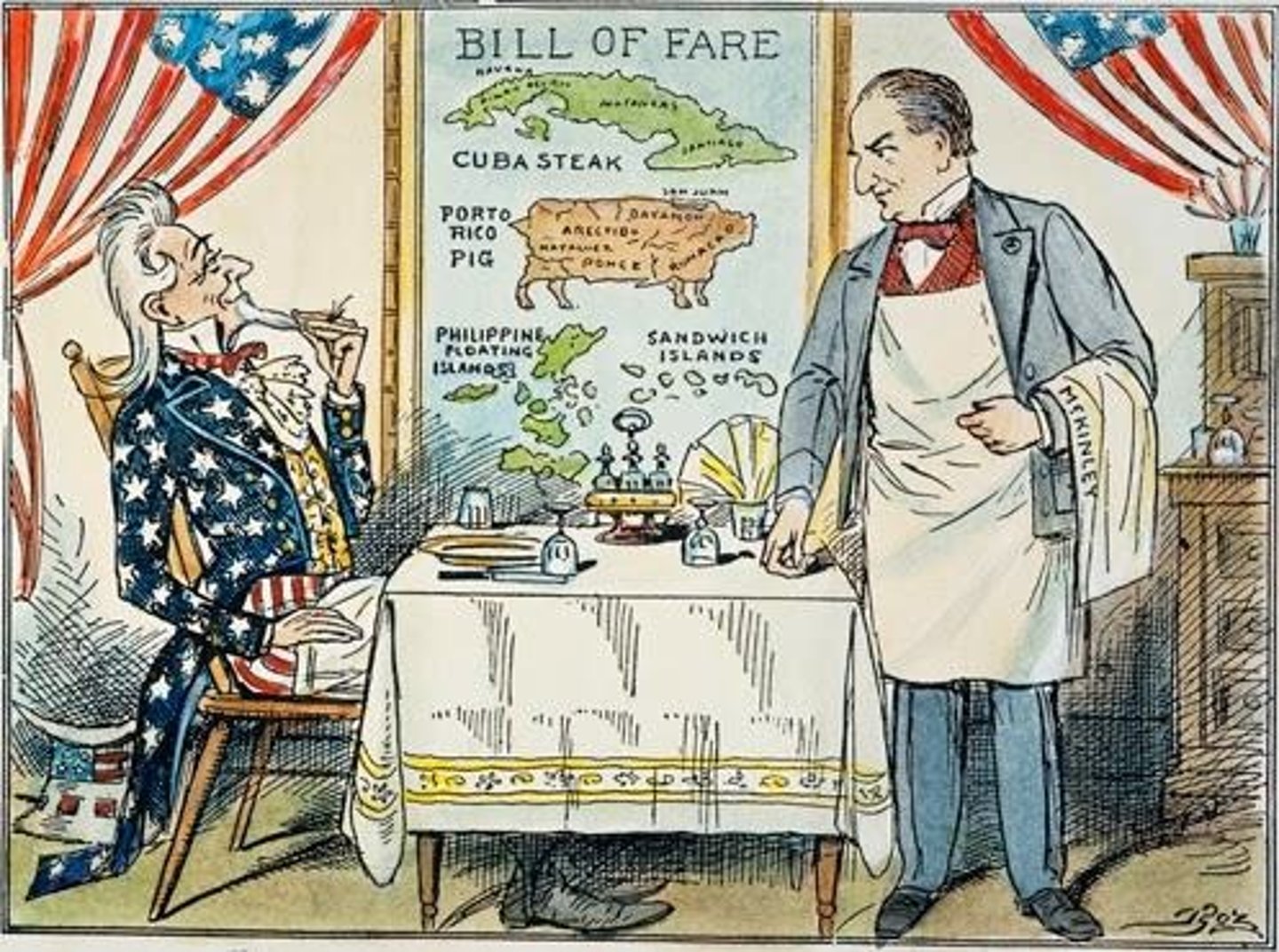
What was the Filipino Insurrection?
It occurred when the U.S. denied the Philippines independence after the Spanish-American War.
What role did General Leonard Wood play in Cuba after the war?
He restructured Cuba, improving agriculture, education, and eradicating yellow fever.
What was the significance of the Rough Riders in the Spanish-American War?
They were a celebrated fighting force led by Theodore Roosevelt, contributing to his national celebrity.
How did disease impact the U.S. military during the Spanish-American War?
Disease nearly devastated the army, affecting their performance.
What was the American view on Puerto Rico's status after the war?
The U.S. believed Puerto Rico would not become a state and established limited self-governance.
What was the impact of the Spanish-American War on U.S. foreign relations?
It marked a shift towards empire-building rather than the acquisition of states.
What event marked the beginning of the Filipino Insurrection?
The U.S. refusal to relinquish control over the Philippines.
How many troops did the U.S. send to the Philippines during the insurrection?
Over 100,000 troops.
What were some atrocities committed by the U.S. during the Filipino Insurrection?
The use of concentration camps and the 'water cure'.
Who became the governor of the Philippines after the insurrection?
William Howard Taft.
What was the purpose of the Open Door Notes issued by John Hay?
To keep China economically open for all nations except for China. Occurred because of their defeat to Japan, they were left weak, Germany and Russia had their eyes on china.
What was the Boxer Rebellion?
A patriotic military group's uprising against foreign influence in China. Was the killing of two hundred foreigners and even more Chinese Christians
What was the outcome of the Boxer Rebellion for China?
China was forced to accept financial punishments and the U.S. promised to protect its territorial integrity.
Who was the Republican candidate in the Election of 1900?
William McKinley.
What was the significance of McKinley's victory in the Election of 1900?
It was largely due to his foreign policy success.
What happened to McKinley shortly after his re-election?
He was assassinated in Buffalo.
How did Theodore Roosevelt view the presidency?
As a 'bully pulpit' to drive national conversation and use the power of the office.
What treaty allowed the U.S. to build a canal in Panama?
The Hay-Pauncefote Treaty.
What was the U.S. response to Colombia's rejection of the canal offer?
TR supported Panama's independence and sent a naval fleet for protection.
What was the Roosevelt Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine?
It asserted that the U.S. would act as the financial arbitrator of the Americas.
What was the impact of TR's big-stick diplomacy?
It created a perception of U.S. aggression in foreign policy.

What role did TR play in the Russo-Japanese War?
He acted as a mediator, leading to a settlement that pleased neither side.
What was the 'Gentlemen's Agreement' between the U.S. and Japan?
An agreement to remove segregation orders in exchange for Japan withholding passports for immigrants.
What was Taft's approach to foreign policy known as?
Dollar diplomacy.
What did Wilson's 'moral diplomacy' emphasize?
Respect for other nations and self-determination.
What was the Jones Act of 1916?
It granted the Philippines territorial status and a promise for independence.
What incident escalated tensions between the U.S. and Mexico during Wilson's presidency?
The Tampico Incident., American sailors were arrested by the Mexican navy, were quickly released, Wilson demanded a military like in haiti-was denied
Who was Pancho Villa?
A Mexican revolutionary leader who opposed the Carranza government.
What actions did Pancho Villa take against the U.S.?
He killed Americans in Mexico and New Mexico.
What was Wilson's response to the actions of Pancho Villa?
He ordered General John J. Pershing to capture Villa.
What was the economic situation in Mexico during this period?
Mexican businessmen were wealthy while most Mexicans were poor.
What was the result of the U.S. intervention in Haiti during Wilson's presidency?
It upheld the Monroe Doctrine but contradicted Wilson's idealism.
What did the U.S. promise to do regarding China's territorial integrity?
To protect it from invaders.
who was appointed governor of the philippines after the filipino insurrection ?
William Howard Taft was governor as improvements of health, roads,and economy were made.