IB History Paper 1: Apartheid South Africa
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
DF Malan
Afrikaner nationalist Prime Minister, advocate of fascism, racial purity, and designer of much of Apartheid
National Party (NP)
The now-defunct party that created apartheid and dominated politics during the apartheid era
Petty Apartheid
The first stage of the Apartheid era from 1948 - 1959; also called "baaskap" ("boss rule"); it's main purpose was, through a series of laws and actions, to ensure the complete domination of the white ethnic minority and the subjugation of the Black majority.

Grand Apartheid
The second stage of the Apartheid era, beginning with the government of HF Verwoerd in 1959; its main goal was the complete territorial segregation of South Africa. It tried to establish moral legitimacy behind the apartheid system
Population Registration Act of 1950
required that each inhabitant of South Africa be classified and registered in accordance with his or her racial characteristics as part of the system of apartheid.

Race Classification Board
Board charged with deciding which race a person belonged to

Prohibition of Mixed Marriages Act (1949)
Banned marriages between white people and black people.

Immorality Act (1950)
Prohibited all sexual relations between whites & non-whites.
Most couples found guilty were sent to prison!
Non-whites were given harsher sentences than whites.

Reservation of Separate Amenities Act (1953)
Ensured signs were put up in public places saying 'Europeans Only' in the white areas and 'Non-Europeans Only' in the areas designated for black people or coloureds. These signs were put up everywhere, including train stations, post offices, parks, and beaches. The best facilities and services were reserved for white people.

Group Areas Act (1950)
Relegated non-whites to designated residential areas in South Africa
Pass Laws Act (1952)
-"Passbooks" would be required to be carried at all times
-Not having your passbook was a crime
-Passbooks were used by the white government to harass and criminalize blacks

Sophiatown
Johannesburg township, center of black cultural life, cleared out by authorities because of its proximity to white suburbs

Bantu Education Act (1953)
-Schools were segregated
-Non-white schools had fewer resources than white schools and were in worse conditions
-Students were taught about tribal identity and culture
-poor education was justified by the mentality that "non-whites are only meant to be menial workers anyway"

Extension of University Education Act
An apartheid policy that stopped non-Europeans from entering English speaking universities
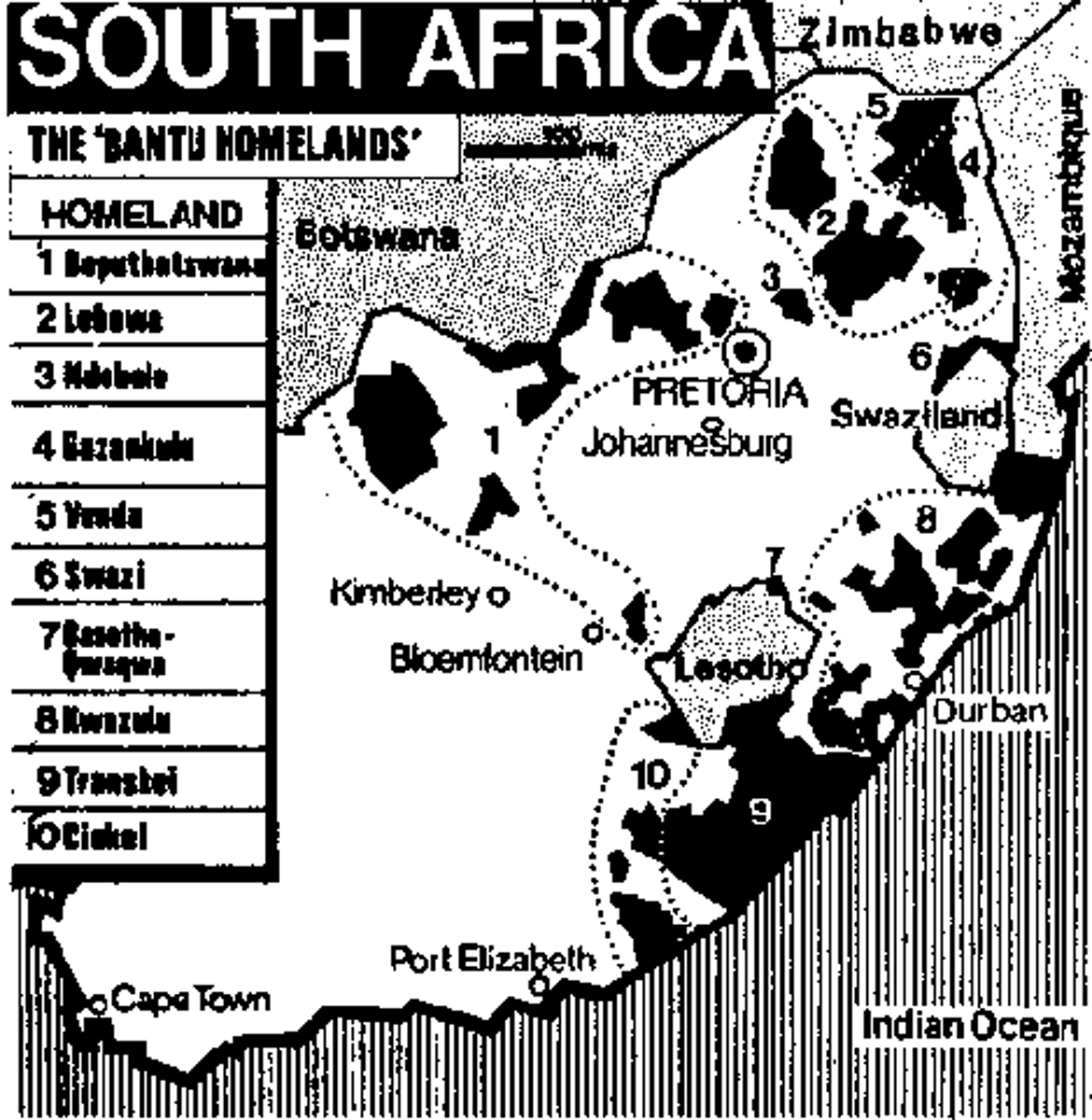
Bantustan system
also known as "homelands" system, apartheid policy where black inhabitants were forced to live on territories set aside by government (part of grand apartheid)
Verwoerd
SA's prime minister from 1958-1966. He came up with and implemented apartheid. "Father of Apartheid." He was a member of the National Party and was assassinated in '66.

Defiance Campaign
1952; launched by the ANC, SAIC, and FAC against the new laws regarding passbooks; wanted to fill the courts and prisons with people arrested for not having the proper passbooks and overwhelm the system; protesters were extremely peaceful ---> hard for the government to justify using force against them and increased support for the movement; ended after a series of government provoked riots (killed 26 Africans and 6 whites)

Civil Disobedience
A form of political participation that reflects a conscious decision to break a law believed to be immoral and to suffer the consequences.
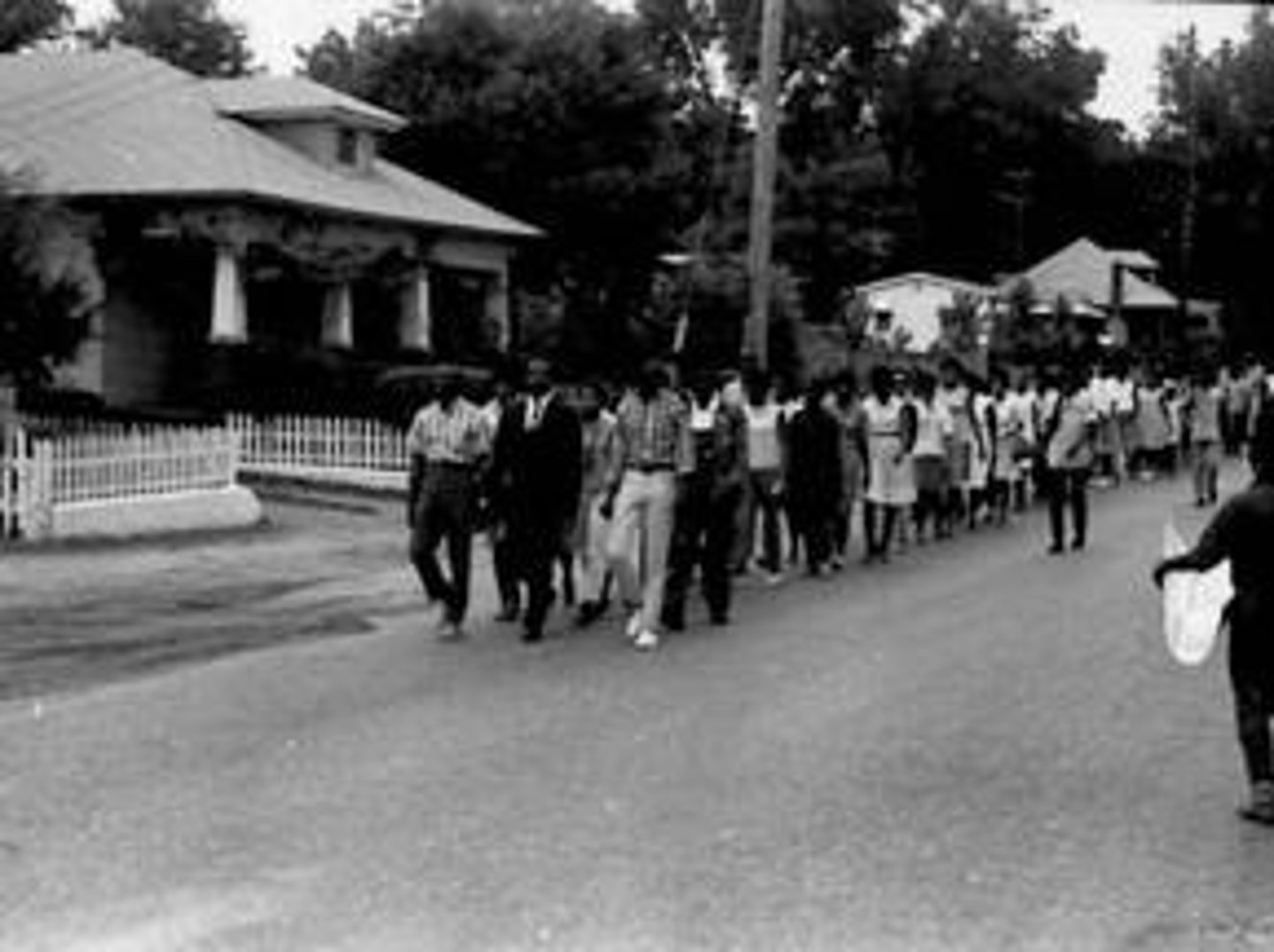

Freedom Charter
Declaration of principles issued by ANC in 1956; advocated racial equality, free education and medical care, public ownership of mines, banks and big industry

Alexandra Boycott
a protest undertaken against the Public Utility Transport Corporation (PUTCO) by the people of Alexandra in Johannesburg, South Africa.
It is generally recognized as being one of the few successful political campaigns of the Apartheid era

Sharpesville Massacre
1960; peaceful protest against apartheid; police shoot down 69 people, declares state of emergency- suspends rights until problem is solved; turning point in decision to use armed violence
Rivonia Trial
Trial that took place in South Africa between 1963 and 1964 in which leaders of the ANC were tried. This trial sent Nelson Mandela to prison.
African National Congress (ANC)
the main organization that opposed apartheid and pushed for majority rule in South Africa; later a political party

South African Communist Party (SACP)
Marxist organisation closely tied to the ANC; the organised workers' strikes in an effort to pressure the Apartheid government and were accused of treason by the South African government after socialist principles were included in the Freedom Charter.

Umkhonto we Sizwe (Spear of the Nation)
a.k.a the MK
- in 1961 nelson mandela and others from the ANC formed this group
- the underground movement began a campaign of sabotage against the government
Albert Luthuli
Zulu chief who became the president of the ANC in 1952 known for his commitment to non-violence. Repeatedly banned by the South African government, he opposed the adoption of armed struggle and was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 1960.

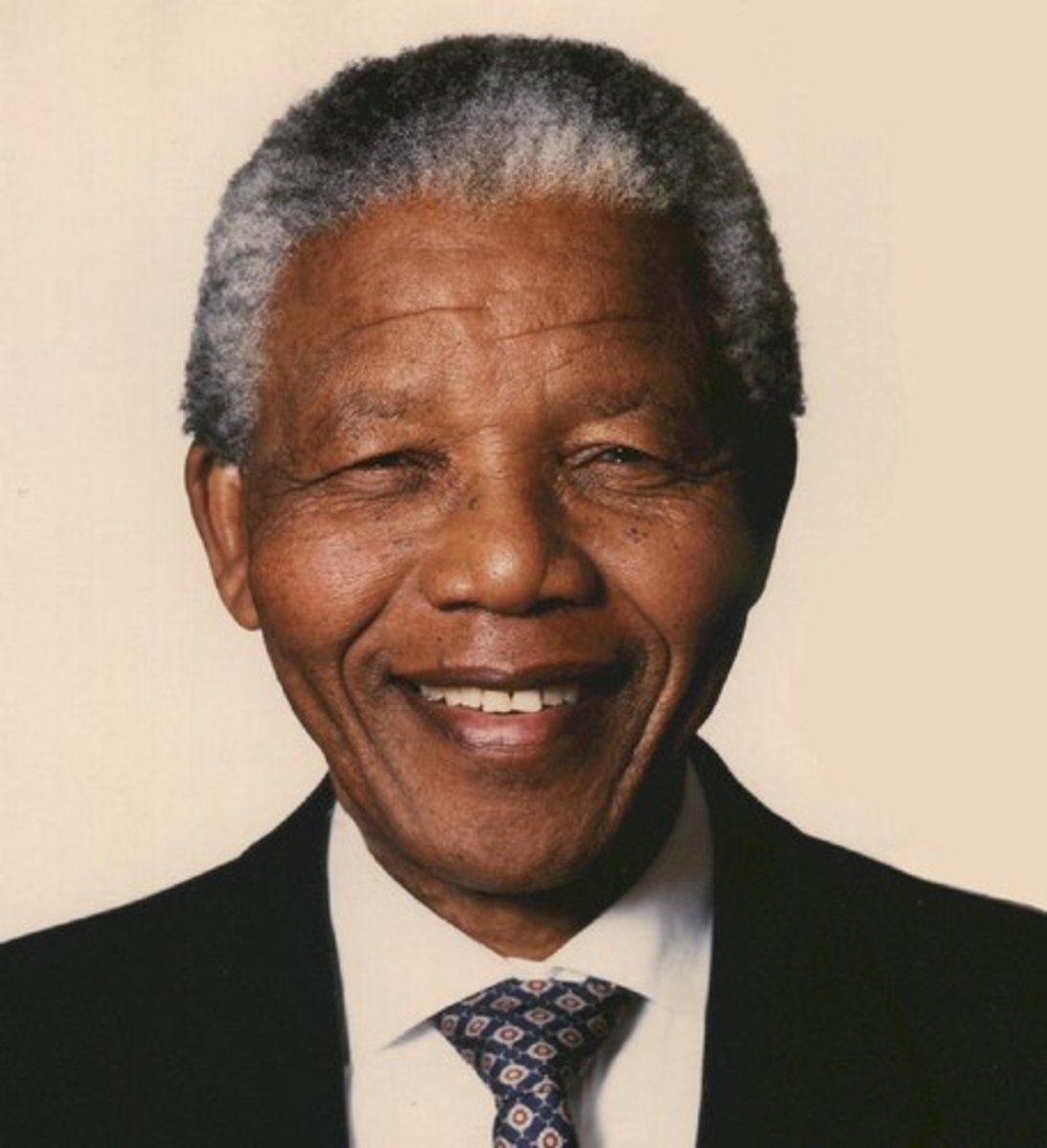
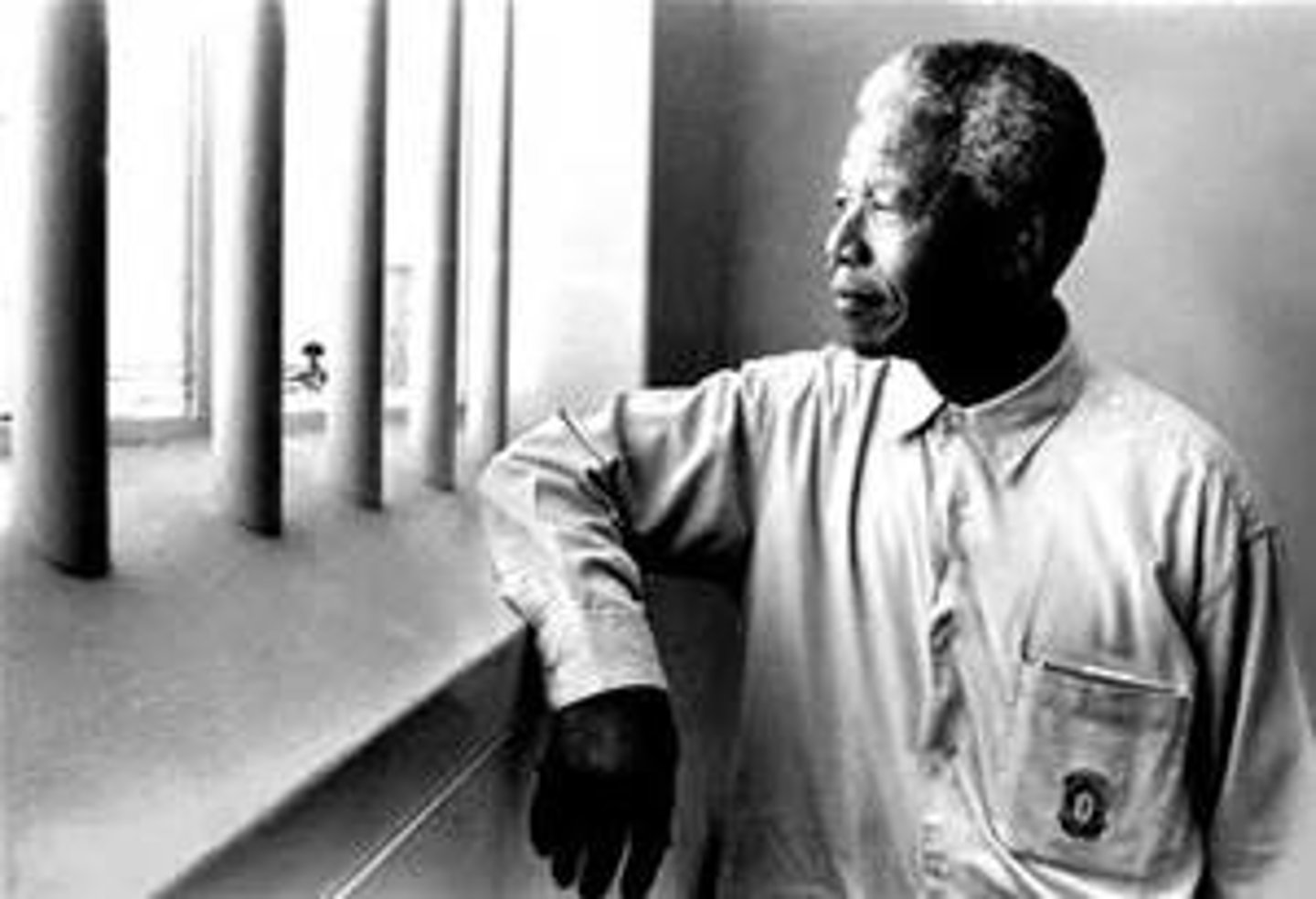
Nelson Mandela
ANC leader imprisoned by Afrikaner regime; released in 1990 and elected as president of South Africa in 1994.
