Chemistry, Cells, and Tissues
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Principle parts of a cell
Cytoplasm, nucleus, and cell (plasma) membrane
Nucleus
Contains DNA of cells
Cell Membrane (Plasma Membrane)
Outer covering that defines and encloses each cell. Like the “security guard” of a cell - regulates what substances enter and leave cell
Cytoplasm
Cellular contents between the cell/plasma membrane and the nucleus
2 primary components of cytoplasm
Cytosol - gel-like medium with organic compounds
Organelles - miniature organs that carry out physiological processes that sustain life for the cell (the “organ system” of a cell)
Types of Organelles
Mitochondria
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Golgi Apparatus
Lysosomes
Centrosome
Cytoskeleton
Mitochondria
The powerhouse of the cell - contains enzymes that break down glucose to produce ATP (adenosine triphosphate) which releases energy
Intracellular fluid
Fluid found INSIDE cells make up 2/3 of the total water in a human body
Extracellular fluid
Fluid found OUTSIDE cells - remaining 1/3 makes up the liquid component of blood, lymph, interstitial fluid (fluid that fills the interstitium - small spaces between cells)
Interstitial Fluid
a type of extracellular fluid that fills the Interstitium (small spaces between cells). Constantly circulates around cells providing a medium from which nutrients are extracted and waste is released
Interstitium
The area between cells where the interstitial fluid is located
Transport Mechanisms: 2 categories in which substances move across the cell membrane
Passive transport & Active transport
Passive Transport
A transport mechanism that occurs when the cell does not have to expand energy (no need for ATP) to move a substance through the cell membrane 2 methods:
Diffusion
Filtration
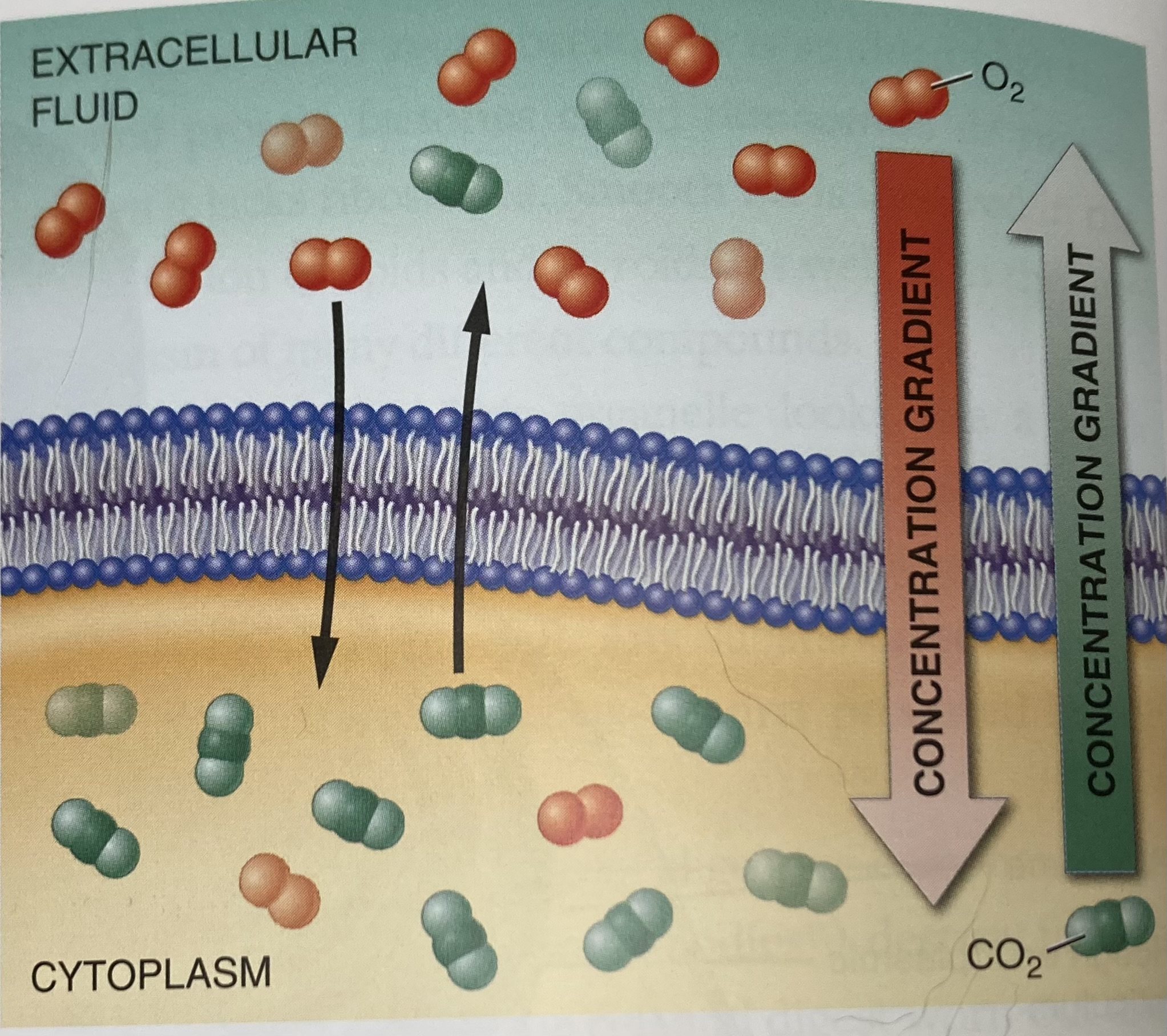
Diffusion
Passive transport mechanism in which atoms/molecules move across the cell membrane from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration (looking for an “open” area to spread out more evenly)
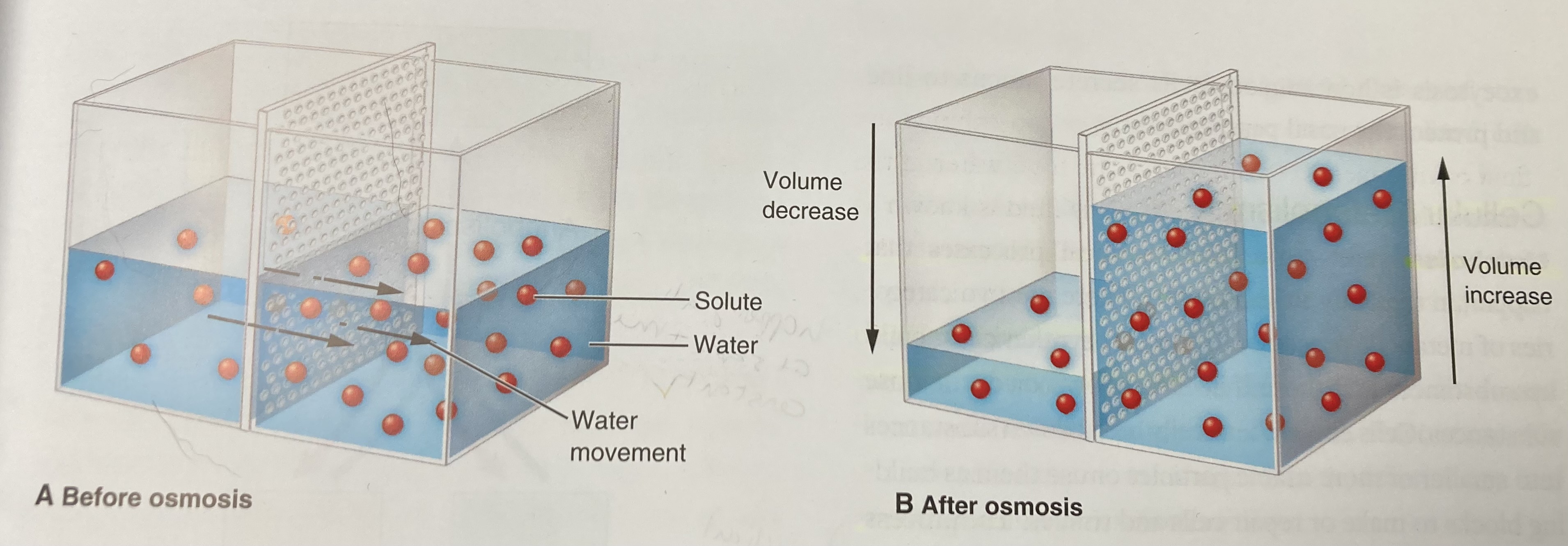
Osmosis - the diffusion of water (not dissolved particles/solutes because they can be too large to cross the cell membrane) from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration
Facilitated diffusion - when a carrier molecule is involved in the diffusion process
Filtration
A passive transport mechanism driven by differences in pressure. When fluid presses against a barrier, they create HYDROSTATIC PRESSURE (fluid pressure) which pushes fluid and small solutes through any opening from an area of high pressure to an area of low pressure
ex) audience at back of rock concert pushes people closer to the front to get a better view, no energy is expended from the people at the front when they are pushed forward
Active Transport
A transport mechanism that requires the cell to use energy (break down ATP molecules) to move substances across the cell membrane. Moving against the concentration gradient (from an area of low to high)
three examples of active transport:
Ion pumps
Phagocytosis
Exocytosis
Phagocytosis
An example of active transport. Literally means “cell eating”. Process is carried out by specialized cells called Phagocytes found in blood, lymph, and connective tissue. Cell membrane of Phagocyte engulfs/“eats” a particle by folding around it and pinching off a portion to form a sac (called a Vesicle) within the Phagocyte. The vesicle is then delivered to a Lysosome for digestion and destruction.
Phagocytes
specialized cells found in blood, lymph, and connective tissue.
Vesicle
A particle-filled sac formed by phagocytes
Pinocytosis
“Cell drinking” - process similar to phagocytosis, but the substance being engulfed by the cell is a liquid instead of a particle