Psychology winter exam 2023
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
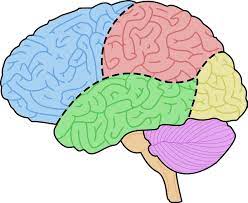
Lobes of the brain
Frontal
Parietal
Occipital
Temporal
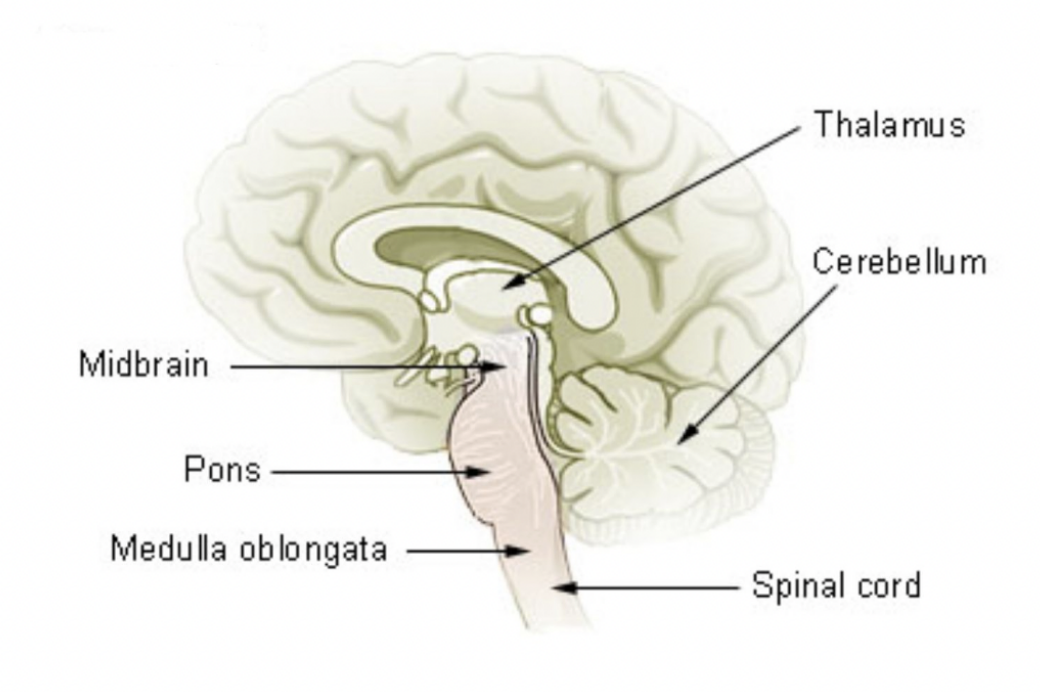
Brainstem - Primal brain
Ensures survival and controls our self-preserving behaviour.
The 4 “f’s” of the primal brain
Feeding, Fighting, Fleeing, Reproducing
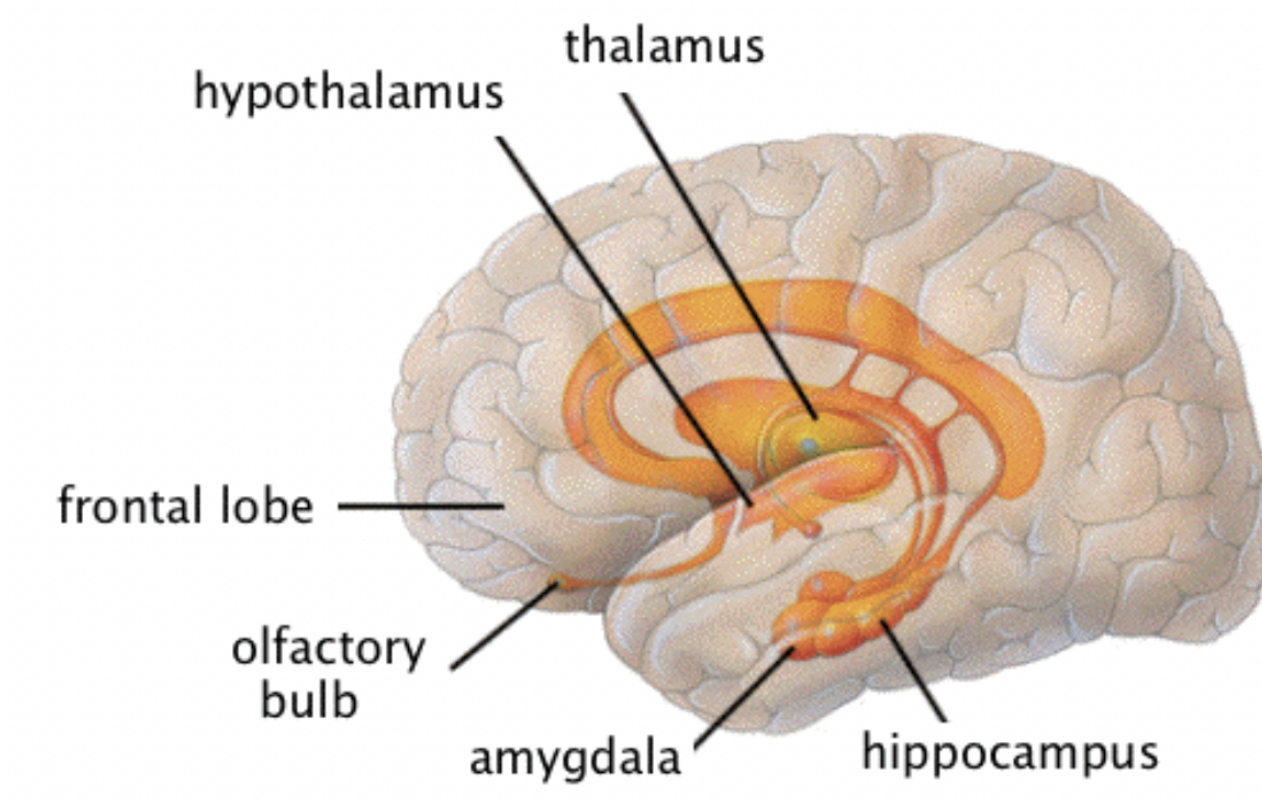
Limbic system - Emotional brain
Emotions, learning and memory.
Cortex - Thinking brain
Analysis, learning, memory, decision making, problem solving.
Techniques to study the brain
Case studies
Animal research
Brain imaging technologies
Studies in neuroplasticity
Localization of functions
Different parts of the brain have different functions which play a role in human behaviour.
Interactionist approach
Uses biological, cognitive, and sociocultural to get a richer understanding of behaviour.
Reductionist approach
Analyses a complex behaviour through basic mechanisms.
Data triangulation
When more than one source of data is used.
Method triangulation
When more than one research method is used.
Researcher triangulation
When more than one researcher studies a case.
Theory triangulation
When we look at a case from more than one theoretical perspective - ex. biological, cognitive, and/or sociocultural.
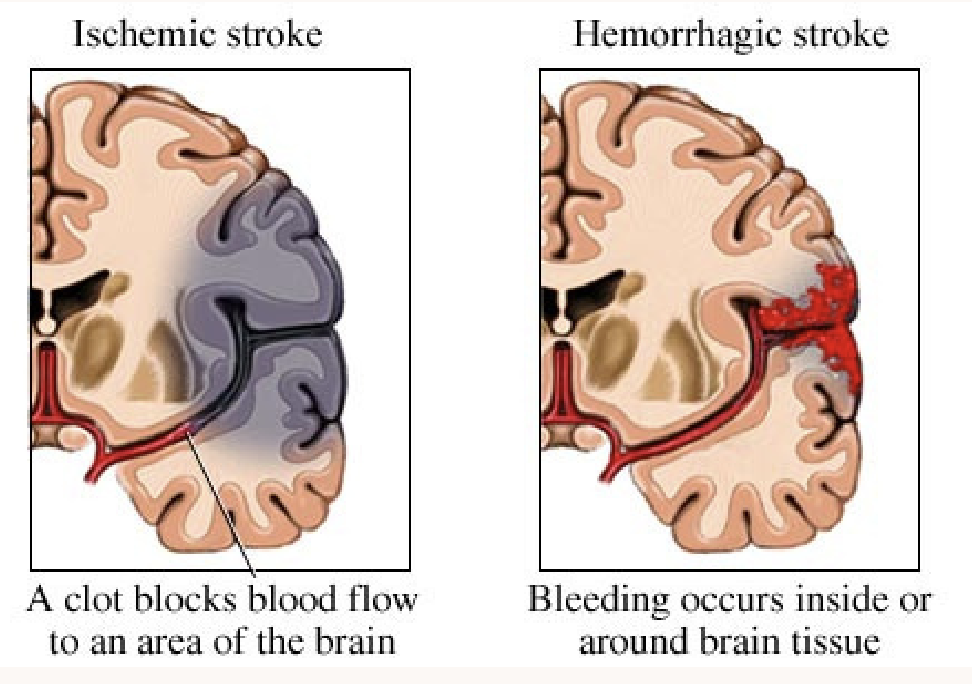
Strokes
Brain attacks. Occurs when something blocks the blood supply.
Brain imaging techniques
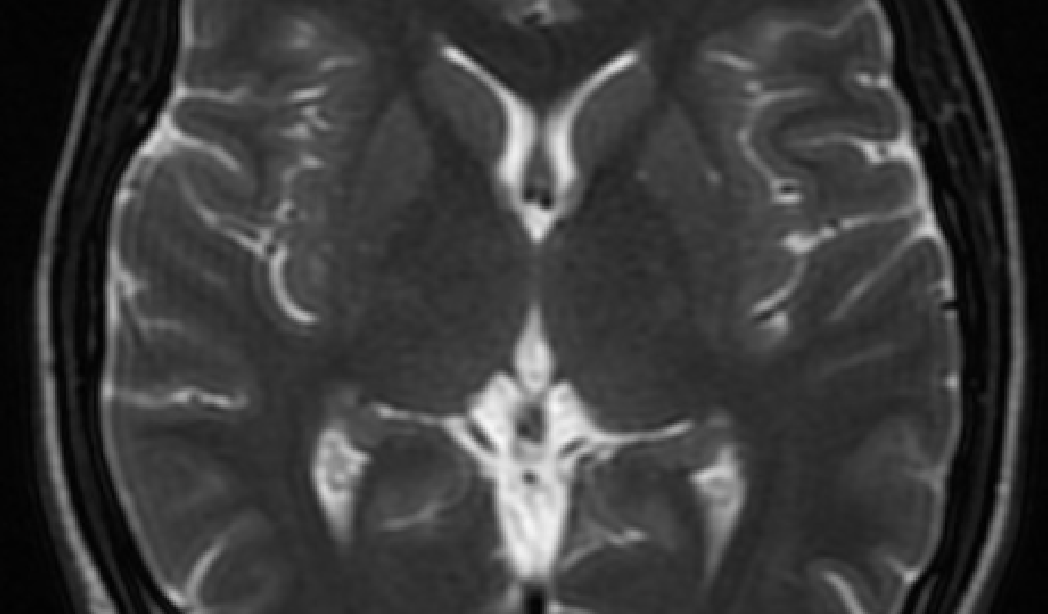
MRI
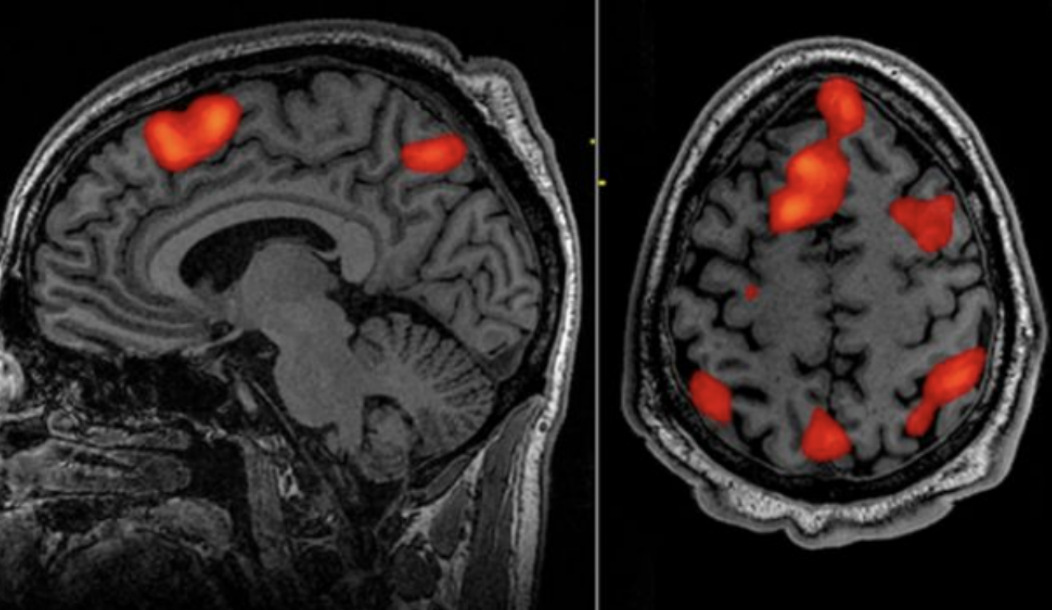
fMRI
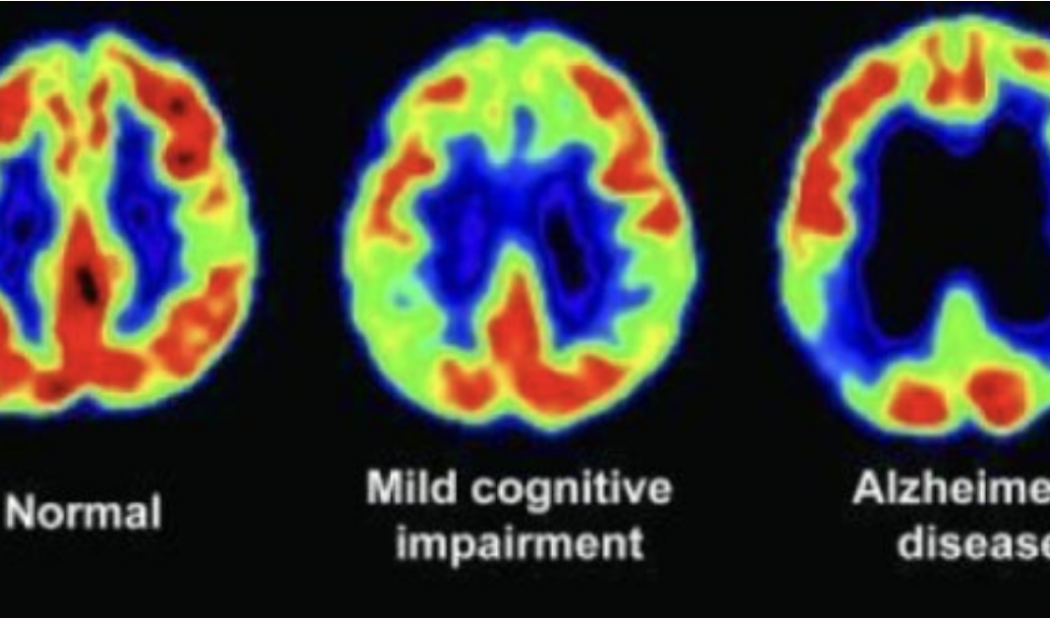
PET
MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging: uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to generate detailed images of the inside of the body.
fMRI
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: measures and maps brain activity by detecting changes in blood flow to produce images showing which parts of the brain are activated during specific tasks or in response to stimuli.
PET
Positron Emission Tomography: Observes metabolic processes in the brain by detecting the gamma rays.
Neurotransmitters
Chemical messengers that transmit signals across synapses, the gaps between neurons (nerve cells), allowing communication within the nervous system.
Neuron
They are cells responsible for transmitting information by electrical and chemical signalling.
Synapse
A connection between two neurons or between a neuron and a target cell that allows cells to communicate with each other.
Agonist
They hold on to synaptic receptors and increase the effect of the neurotransmitters.
Antagonist
They hold on to synaptic receptors but they decrease the effect of the neurotransmitter.
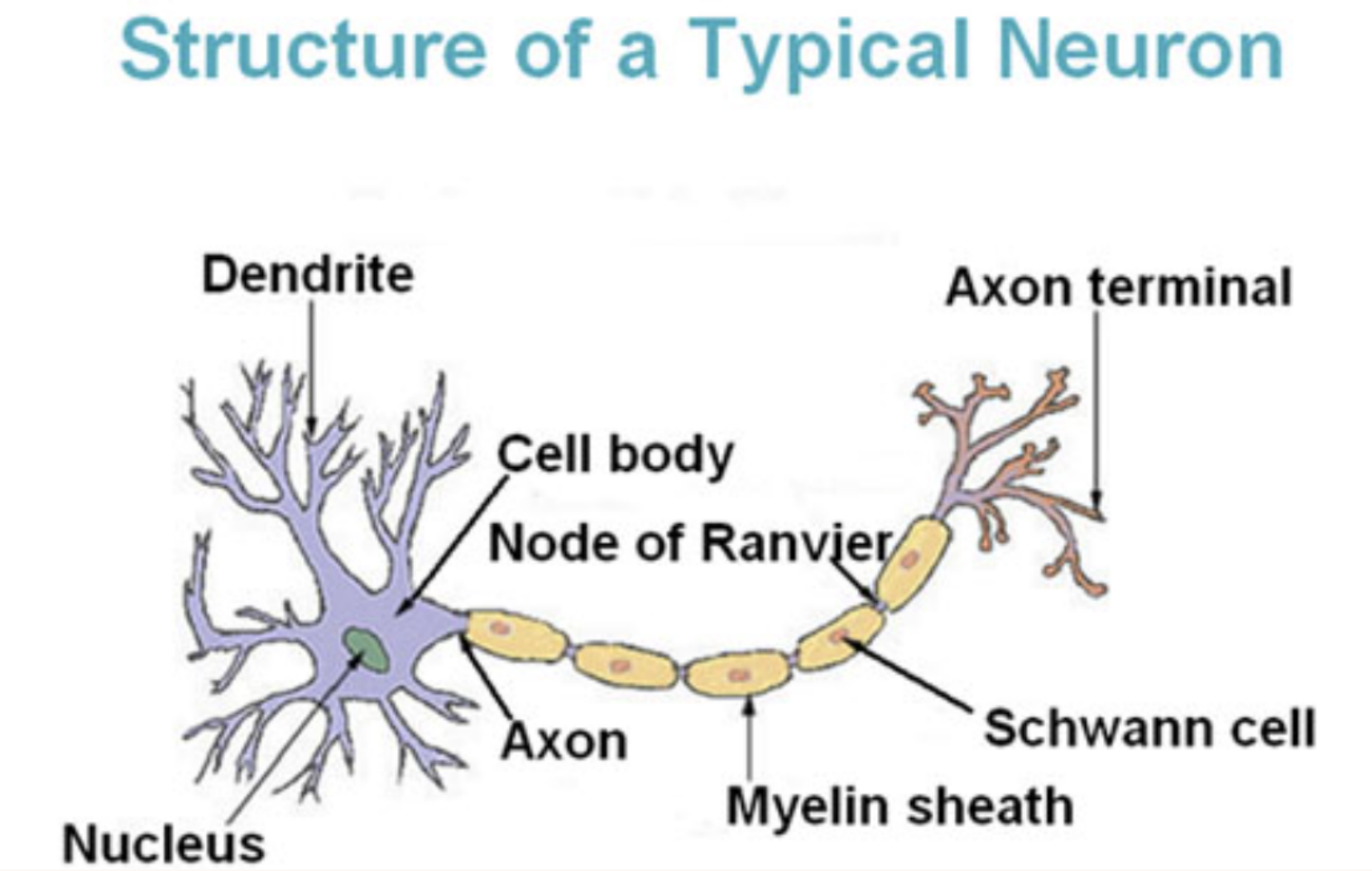
Structure of a typical neuron
Dendrite
Cell body
Nucleus
Node of Ranvier
Axon
Myelin sheath
Schwann cell
Axon terminal
Excitatory neurotransmitters
They allow the impulse of a neuron to cross the synapse and then produce stimulating effects on the brain.
Inhibitory neurotransmitters
They stop the impulse of a neuron, preventing it from crossing the synapse
Drugs that function as agonists
Opioids
SSRIs
Drugs that function as antagonists
caffeine
beta blockers
Hormone
A chemical that is secreted by glands in the endocrine system to regulate changes in the body.
Cortisol
It is produced in the adrenal glands. It increase the amount of glucose (sugar) in the blood and provides energy for the “fight or flight response”.
Adrenaline
A hormone and neurotransmitter that the adrenal glands release in response to stress or excitement. It prepares the body for the "fight or flight response”.
Effects of adrenaline
Increase in heart rate
Dilating airways
Redirecting blood flow to vital organs
Providing a boost of energy
Flashbulb memories
A highly vivid and detailed ‘snapshot’ of a moment in which a consequential, surprising, and emotionally arousing piece of news was learned.
Dopamine
A feel-good neurotransmitter. It is responsible for motivation.
Testosterone
A hormone that increases sexual desire toward your new partner and increases feelings of aggression.
Noradrenaline
A neurotransmitter and hormone that helps control emotions and stress. It provides a rush of excitement and stimulates the production of adrenaline, which makes our heart race, and our palms sweat.
Serotonin
A neurotransmitter and hormone to which levels drop when we fall in love. These low levels cause the obsessive thinking and heightened mood extremes
Oxytocin
A hormone linked to human attachment and levels of trust and is secreted as a result of touch and sexual activity.
Sexual selection
A process in evolution that involves traits that help an individual secure a mate and reproduce successfully.
Intrasexual selection
A type of sexual selection where members of the same sex (usually males) compete with each other for access to mates (usually females).
Natural selection
How organisms better adapted to their environment tend to survive and reproduce more successfully than those less adapted, leading to the propagation of advantageous traits within a population over time.
Parental investment theory
How parents invest time, effort, and resources into raising their offspring. It suggests that because reproduction demands more from females (like carrying and nurturing the young), they often invest more in their offspring compared to males.
Internal validity
How well an experiment is done.
Extraneous variables
Factors or conditions, apart from the ones being studied, that could affect the results of an experiment.
Construct validity
How well a test or experiment measures the theoretical construct or idea it's supposed to measure.
External validity
The extent to which the results of a study can be generalized to other situations
Population validity
A type of external validity that describes how well the sample used can be generalized to a population as a whole.
Ecological validity
A type of external validity that looks at the experimental environment and determines how much it influences behavior.
Frontal lobe
Reasoning
Planning
Thinking
Decision making
Parietal lobe
Movement, orientation, perception
Occipital lobe
Visual processing
Temporal lobe
Processing auditory information, memory and speech
Major parts of the human brain
Cortex
Cerebellum
Limbic system
Brain stem
Limbic system
thalamus
hypothalamus
amygdala
hippocampus
CAM (casual animal model)
Biological functions and resulting behaviour in mammal that are similar to human.
[animal] → [human]
HAM (hypothetical analogical model)
Use of animal research to create hypothesis regarding humans (and their physiology and behaviour).
[animal] → [hypothesis] → [humans?]