Anatomy and Physiology Semester Review
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
Cerebrum
Largest part of the brain; responsible for voluntary muscular activity, vision, speech, taste, hearing, thought, and memory. Outer layer of the brain
Cerebral Cortex
outer region of the cerebrum, containing sheets of nerve cells; gray matter of the brain
Cerebral medulla
white matter between the cortex and nuclei
Frontal lobe
Responsible for planning, personality, judgement, voluntary movement (motor cortex)
Parietal lobe
Responsible for bodily sensations
Occipital lobe
Responsible for visual info
Temporal lobe
responsible for hearing and language
Parts of the brain stem
midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata
Midbrain
A small part of the brain above the pons that integrates sensory information and relays it upward.
Pons
A brain structure that relays information from the cerebellum to the rest of the brain
Medulla oblongata
Part of the brainstem that controls vital life-sustaining functions such as heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure, and digestion.
Dendrite
the part of a neuron that receives information from other neurons and relays it to the cell body
Cell body
the part of a neuron that contains the nucleus; the cell's life-support center
Nodes of Ranvier
part of neuron between myelin sheaths that concentrate the ion channels
Myelin Sheath
Part of the neuron that covers the long nerve fibers
Schwann cell
A type of glial cell that forms insulating myelin sheaths around the axons of neurons in the peripheral nervous system.
Axon
Part of the neuron that connects the cell body to the axon terminal
Axon terminal
Part of the neuron that contains neurotransmitters and sends signals to the next neuron.
Rods
Photoreceptors that provide shades of gray
C
Cones
Photoreceptors responsible for color vision.
Parts of the eye
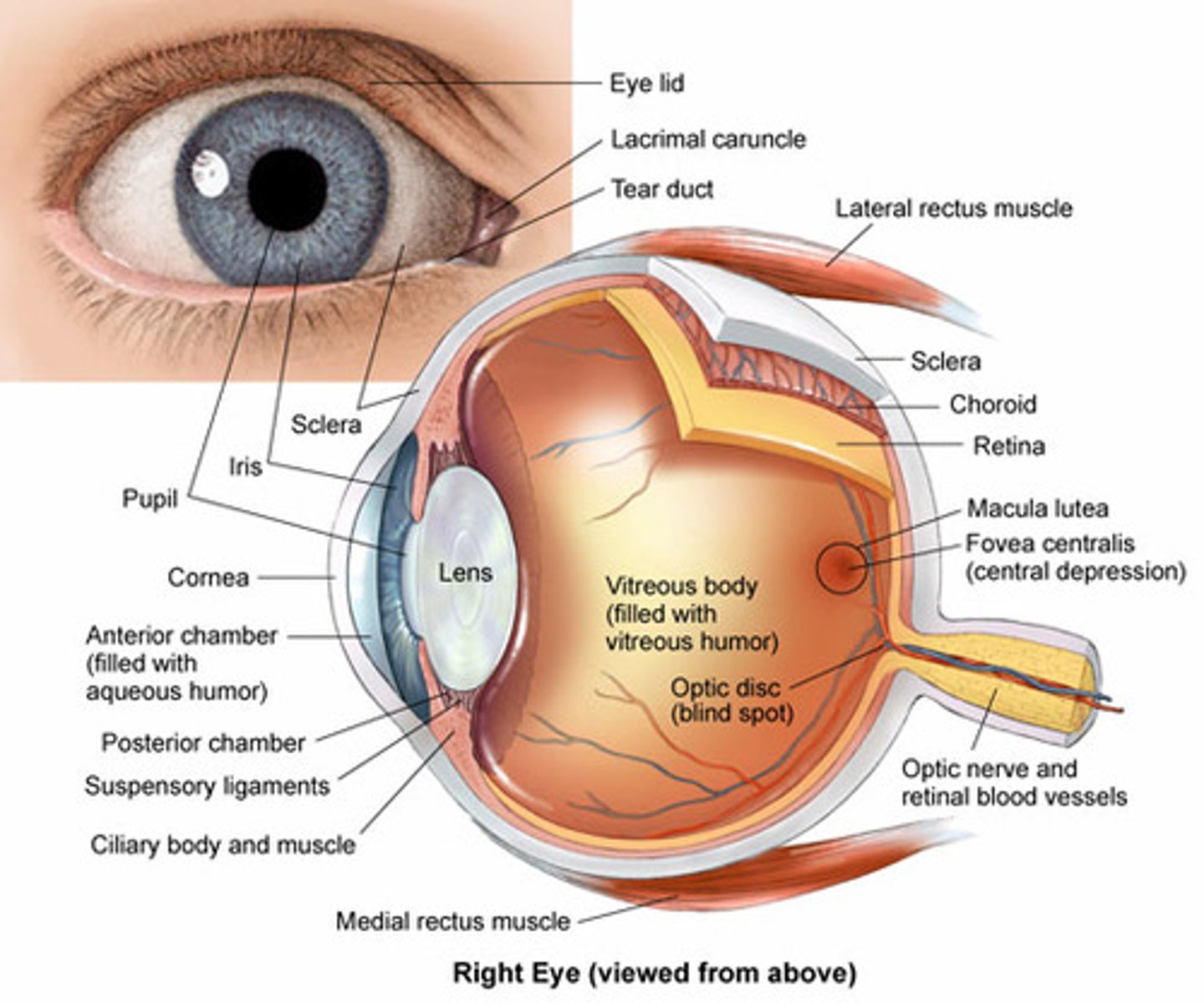
Nearsightedness
a condition in which far objects are hard to see
Farsightedness
a condition in which close objects are hard to see
astigmatism
a condition in which the eye does not focus properly because of uneven curvatures of the cornea
Cataracts
clouding of the lens due to aging
Glaucoma
increased intraocular pressure results in damage to the retina and optic nerve with loss of vision
Colorblindness
inability to see certain color combinations: red-green or blue-yellow; 10% are male and 1% are female
What is a hormone
a chemical messenger carried in the blood that is released by endocrine glands
Insulin
A hormone produced by the pancreas or taken as a medication by many diabetics; lowers blood sugar levels
Glucagon
A protein hormone secreted by pancreatic endocrine cells that raises blood glucose levels; an antagonistic hormone to insulin.
Testosterone
the most important of the male sex hormones. stimulates the growth of the male sex organs and the development of the male sex characteristics during puberty
Epinephrine
Neurotransmitter secreted by the adrenal medulla in response to stress. Also known as adrenaline.
Growth hormone
Anterior pituitary hormone that regulates growth and metabolism.
Melatonin
A hormone manufactured by the pineal gland that produces sleepiness.
E
Estrogen
Responsible for the female reproductive organs and secondary sex characteristics
Diabetes
A condition in which the body is unable to produce enough insulin, the hormone required for the metabolism of sugar
Hypothyroidism
A disorder caused by a thyroid gland that is slower and less productive than normal
Positive feedback loops
a feedback loop in which change in a system is amplified; Ex: childbirth, blood clotting
Negative feedback loop
A feedback loop that causes a system to change in the opposite direction from which it is moving; Ex: body temp regulation
Characteristics of RBC's
no nucleus, biconcave, flexible membrane, life span 120 days, produce hemoglobin (Hgb); act as buffer to maintain acid base balance
Causes of anemia
blood loss, low RBC production, high RBC destruction
Phases of hemostasis
vasoconstriction, platelet plug formation, coagulation
Blood types
A, B, AB, O
Type A blood
Donate to A and AB; receive from A and O
Type B blood
donate to B and AB; receive from B and O
Type AB blood
donate to AB; receive from AB, A, B, and O; universal receiver
Type O blood
Different types of white blood cells
neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, basophils
Most numerous WBC
neutrophil
Platelets
thrombocytes; increase in number in response to bleeding
Largest WBC
monocyte
Transports oxygen
red blood cell
Flow of blood through the heart and body
superior & inferior vena cava → right atrium → tricuspid valve → right ventricle → pulmonary semilunar valve → pulmonary trunk → pulmonary arteries → lungs → pulmonary veins → left atrium → bicuspid valve → left ventricle → aortic semilunar valve → ascending aorta → aortic arch → descending aorta → body
Epicardium
outer layer of the heart
Myocardium
muscular, middle layer of the heart
Endocardium
inner lining of the heart
Systemic circuit
Circuit of blood that carries blood between the heart and the rest of the body.
Pulmonary circuit
carries blood to the lungs for gas exchange and returns it to the heart
Bicuspid valve
valve between the left atrium and the left ventricle; has two flaps; left atrioventricular valve aka mitral valve
Tricuspid valve
right atrioventricular valve separating the right atrium and ventricle; has 3 flaps
Aortic semilunar valve
located between the left ventricle and the aorta
Pulmonary semilunar valve
heart valve opening from the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery
Left Atrium
receives oxygenated blood from the lungs
Left Ventricle
Pumps oxygenated blood into the aorta
Right Atrium
the right upper chamber of the heart that receives blood from the venae cavae and coronary sinus
Right Ventricle
pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs
Lub-Dub sound
Lub- AV valves close
Dub- semilunar valves close
Tachycardia
fast heart rate
Bradycardia
slow heart rate
What does an EKG show
electrical activity of the heart
What is blood pressure
force that keeps blood circulating continuously
Normal blood pressure
120/80
Hypertension
high blood pressure; 140/90
Which artery is commonly used for BP measurement
Carotid artery
Atherosclerosis
condition in which fatty deposits called plaque build up on the inner walls of the arteries
Tunica intima
the innermost layer of a blood vessel; present in all 3 vessels, thin surface
Tunica Media
Smooth middle muscle layer of a blood vessel; bulkiest
Tunica externa
outermost layer of a blood vessel
Arteries
carry oxygenated blood away from the heart
Veins
carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart
Vasoconstriction
the constriction of blood vessels, which increases blood pressure.
Vasodilation
Widening of blood vessels to increase blood flow.
Arterioles
small vessels branching from the arteries
Capillaries
connect arterioles and venules; smallest blood vessel
Venules
small vessels that gather blood from the capillaries into the veins
What does taking your pulse measure
Your blood flowing and your heart pumping; BPM
Systolic blood pressure
the pressure created in the arteries when the left ventricle contracts and forces blood out into circulation; heart is pumping
diastolic blood pressure
the pressure in the arteries when the left ventricle is refilling; heart is relaxing
Gall bladder
An organ that stores bile and releases it as needed into the small intestine
Bile
A substance produced by the liver that breaks up fat particles.
Small intestine function
Absorbs most nutrients; Main absorption organ of the digestive tract
Small intestine parts
duodenum, jejunum, ileum
Large intestine functions (colon)
Absorb water and electrolytes, produce and absorb vitamins, and form and propel feces toward the rectum
Functions of saliva(amylase)
Breaks down complex carbohydrates
What enzyme breaks down starches and carbs
amylase
What enzyme breaks down proteins?
protease
Chyme
Partially digested, semiliquid food mixed with digestive enzymes and acids in the stomach.
Villi
Fingerlike extensions of the intestinal mucosa that increase the surface area for absorption