unit 2 | tides & distances 🌊
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
1
New cards
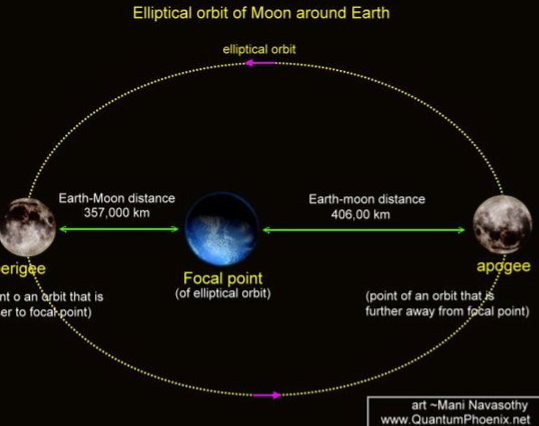
apogee
point of an orbit that is further away from focal point
2
New cards
perigee
point of an orbit that is closer to focal point
3
New cards
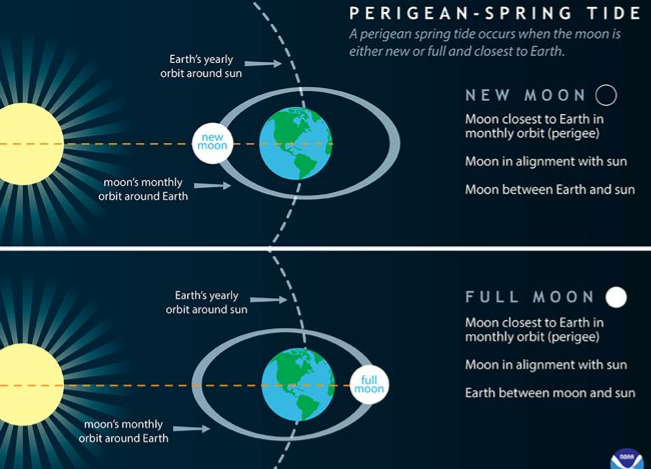
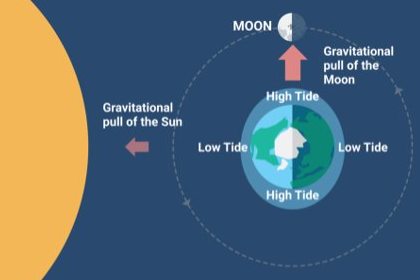
spring tide
* occurs during the full & new moon
* the combined gravity of the sun & moon produces a stronger tide
* higher high tide & lower low tides
* has nothing to do with the season
* occurs twice each lunar month
* moon is aligned with sun
* the combined gravity of the sun & moon produces a stronger tide
* higher high tide & lower low tides
* has nothing to do with the season
* occurs twice each lunar month
* moon is aligned with sun
4
New cards
neap tide
* occurs during the waxing & waning half-moons
* the detracting gravity of the sun and moon produces a weaker tide
* lower high tides & higher low tides
* the detracting gravity of the sun and moon produces a weaker tide
* lower high tides & higher low tides
5
New cards
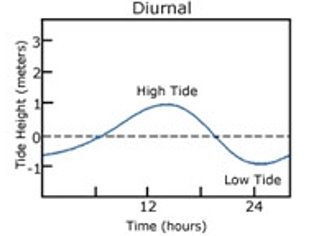
diurnal tide
* 1 episode of high water and 1 episode of low water each day
* occur in locations when the moon is farthest from the equator
* occur in locations when the moon is farthest from the equator
6
New cards
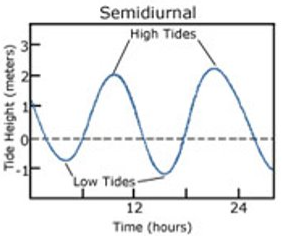
semi-diurnal tide
* 2 episodes of equal high water and 2 episodes of low water each day
* the second high tide rises to the same level it did in the 1st high tide
* the second low tide also matches with the 1st low tide
* occurs when the moon is directly over the equator
* most common type of tidal pattern
* the second high tide rises to the same level it did in the 1st high tide
* the second low tide also matches with the 1st low tide
* occurs when the moon is directly over the equator
* most common type of tidal pattern
7
New cards
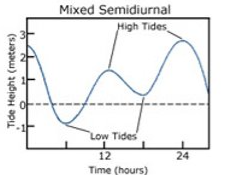
mixed tide
* can have two episodes of high or low water per day
* two high or low tides are unequal
* can either include both sets of unequal high or low waters or only one set of unequal high or low water
* occurs when the moon is extremely far north or extremely far south of the equator
* two high or low tides are unequal
* can either include both sets of unequal high or low waters or only one set of unequal high or low water
* occurs when the moon is extremely far north or extremely far south of the equator
8
New cards
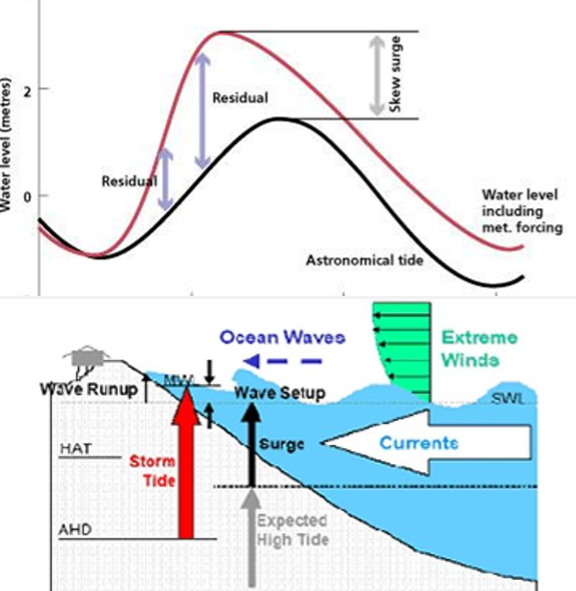
meteorological tides
* tides affected by wind, barometric pressures, rainfall, ice melting, & land drying
* example:
* storm surges: the wind & inverted barometric pressure combine to cause a dramatic increase in sea levels
* example:
* storm surges: the wind & inverted barometric pressure combine to cause a dramatic increase in sea levels
9
New cards
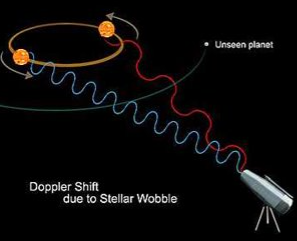
doppler effect
* the apparent change in the frequency of a wave
* with light it’s also called “red shift, blue shift”
* when a star or other luminescent object is moving away from our position then it appears to give off more red light
* when a star or other luminescent object moves closer it appears to give off more blue light
* with light it’s also called “red shift, blue shift”
* when a star or other luminescent object is moving away from our position then it appears to give off more red light
* when a star or other luminescent object moves closer it appears to give off more blue light
10
New cards
cosmological red shifts
* the wavelength at which the radiation is originally emitted is lengthened as it travels through (expanded) space
* cosmological red shift results from the expansion of space itself and not from the motion of an individual body
* cosmological red shift results from the expansion of space itself and not from the motion of an individual body

11
New cards
astronomical units
* major unit used to measure space (AU)
* made from measuring the mean distance from the center of the Earth to the center of the Sun
* 93,000,000 mi
* made from measuring the mean distance from the center of the Earth to the center of the Sun
* 93,000,000 mi

12
New cards
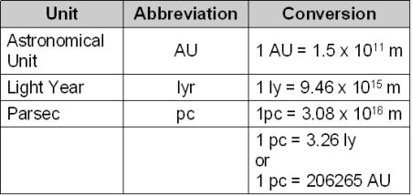
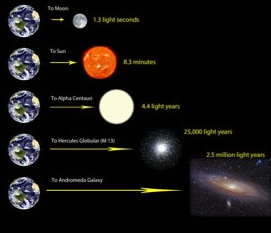
light years
* how long is a light-year in Earth years?
* 5,878,625,370,000 mi (9.5 trillion km)
* 5,878,625,370,000 mi (9.5 trillion km)
13
New cards
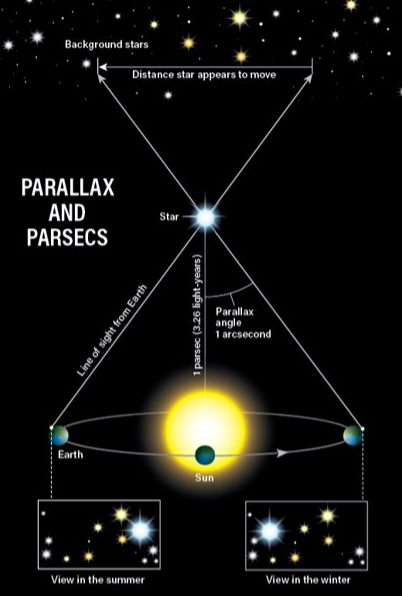
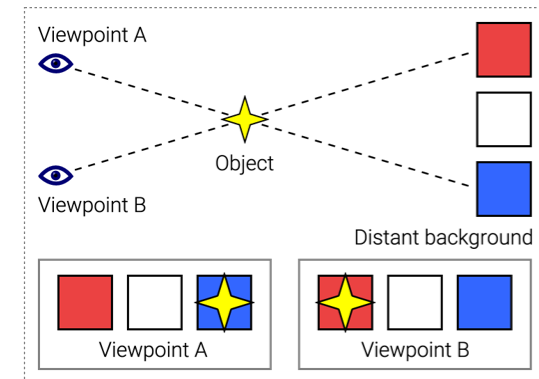
parallax
* the apparent displacement or the difference in apparent direction of an object as seen from two different points not on a straight line with the object especially
**OR**
* the angular difference in direction of a celestial body as measured from two points on Earth’s orbit
**OR**
* the angular difference in direction of a celestial body as measured from two points on Earth’s orbit
14
New cards
parsecs
* a unit of distance used in astronomy, equal to about 3.26 light years (3.086 x 10^13 km)
* one parsec corresponds to the distance at which the mean radius of the Earth’s orbit subtends an angle of one second of arc
* one parsec corresponds to the distance at which the mean radius of the Earth’s orbit subtends an angle of one second of arc