Genetics Chapter 19: Gene Mutation and DNA Repair
1/158
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
159 Terms
Mutation
A heritable change in the genetic material, a permanent change in the structure of DNA (genetic material) that can be passed from cell to cell, or if it occurs in reproductive cells, from parents to offspring.
Mutations can be…
Beneficial, neutral or detrimental
DNA repair systems
Reverse DNA damage before it results in a mutation that could potentially have negative consequences.
Homologous recombination
The process whereby identical or similar DNA segments are exchanged between homologous chromosomes.
It occurs when chromosomes cross over during meiosis.
Enhances genetic diversity and helps to repair DNA
Ensures proper segregation of chromosomes.
Ways a gene mutation can occur
Base substitution
Removal of a base pair(s)
Addition of a base pair(s)
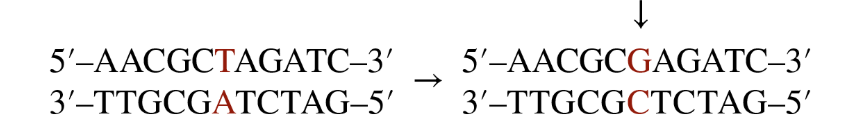
Point Mutations
A change in a single base pair within the DNA. (Base substitution)
Transition - Point Mutation
A point mutation involving a change of a pyrimidine (C) to another pyrimidine (T) OR a purine (A) to another purine (G).
Transversion - Point Mutation
A point mutation in which a purine (A,G) is interchanged with a pyrimidine (C,T) or vice versa.
What point mutation occurs more, transitions or transversions?
Transitions occur more because transversions tends to be readily recognized by DNA polymerase, and the incorrect base is removed by its proofreading function.
Silent Mutation
A mutation that does not alter the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide coded by a gene even though the base sequence has changed.
occur usually at the third base
Missense mutations
A base substitution that does lead to a change in the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide that is coded by a gene.
Nonsense Mutation
A mutation that involves a change from a codon that specifies an amino acid to a stop codon.
Frameshift mutations
A mutation that involves the addition or deletion of a number of nucleotides not divisible by 3, which shifts the reading frame of the codons downstream from the mutation.
Neutral Mutation
A mutation that has no detectable effect on protein function or no detectable effect on the survival of the organism.
Up Promoter Mutation
Mutations in promoters that increase the rate of transcription.
Down Promoter Mutations
Mutations in promoters that decrease the rate of transcription.
Possible consequences of Gene Mutations Outside of a Coding sequence
Promoter - May increase or decrease the rate of transcription
Enhancer/operator site - May disrupt the ability of the gene to be properly regulated.
5′-UTR/3′-UTR - May alter the ability of mRNA to be translated; may alter mRNA stability
Splice recognition sequence - May alter the ability of pre-mRNA to be properly spliced
Wild Type
A relatively prevalent genotype in a natural population.
Mutant Allele
A mutation may change a wild-type genotype by altering the DNA sequence of a gene. When such a mutation is rare in a population, the result is generally referred to as a…
Reversion Mutation
A mutation that changes a mutant allele back to a wild-type allele.
Deleterious Mutations
Mutations that decreases the chances of survival and reproduction.
Lethal mutation
Mutations that result in the death of a cell or organism.
Beneficial Mutation
Mutations that enhance the survival or reproductive success of an organism.
Conditional mutants
A mutant whose phenotype depends on the environmental conditions, such as a temperature-sensitive (ts) mutant.
Suppressor Mutations
A mutation at a second site that suppresses the phenotypic effects of another mutation.
Breakpoint
A region where two chromosome pieces break apart and rejoin with other chromosome pieces.
Position effect
A change in phenotype that occurs when the location of a gene changes from one chromosomal site to a different one.
How do position effects alter gene expression?
A gene may be moved to next regulatory sequences for a different gene
A chromosomal rearrangement may reposition a gene from a less condensed, or euchromatic region of a chromosome, where it is active, to a very highly condensed, or heterochromatic region of a chromosome.
Euchromatic vs Heterochromatin
Euchromatin: Loosely packed, gene-rich, and transcriptionally active chromatin (lightly stained)
Heterochromatin: Densely packed, gene-poor and transcriptionally silent
Key difference is euchromatin is open and accessible for gene expression while heterochromatic is condensed and repressed.
Germ-Line Mutations
A mutation that can occur directly in a sperm or egg cell, or it can occur in a precursor cell that produces the gametes.
If a mutant gamete participates in fertilization, all cells of the resulting offspring will contain the mutation
The effects of germ-line versus somatic mutations.

Somatic Mutation
A mutation in a somatic cell (liver cells, neurons, and skin cells) and can occur within a single embryonic cell.
Spontaneous mutations
A change in DNA structure that results from natural biological or chemical processes.
Induced mutation
A change in DNA structure caused by an environmental agent.
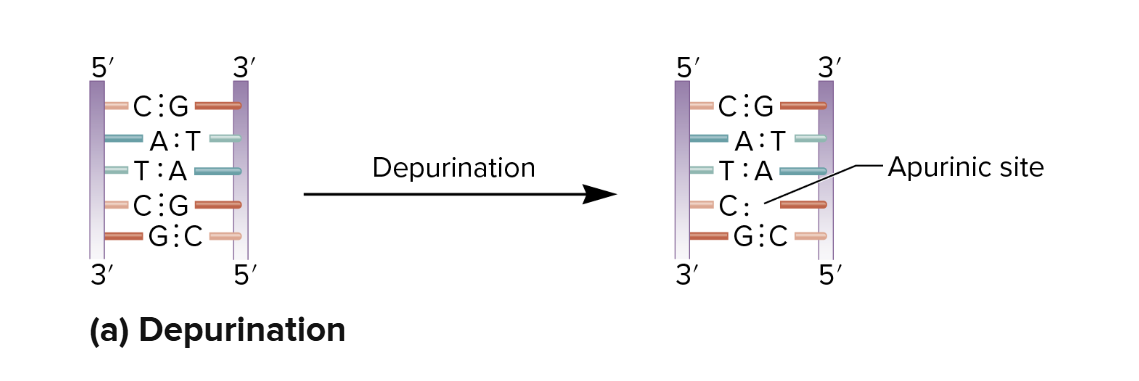
Depurination - Spontaneous Mutation
The removal of a purine base from DNA ( A or G ).
Apurinic Site
A site in DNA that is missing a purine base.
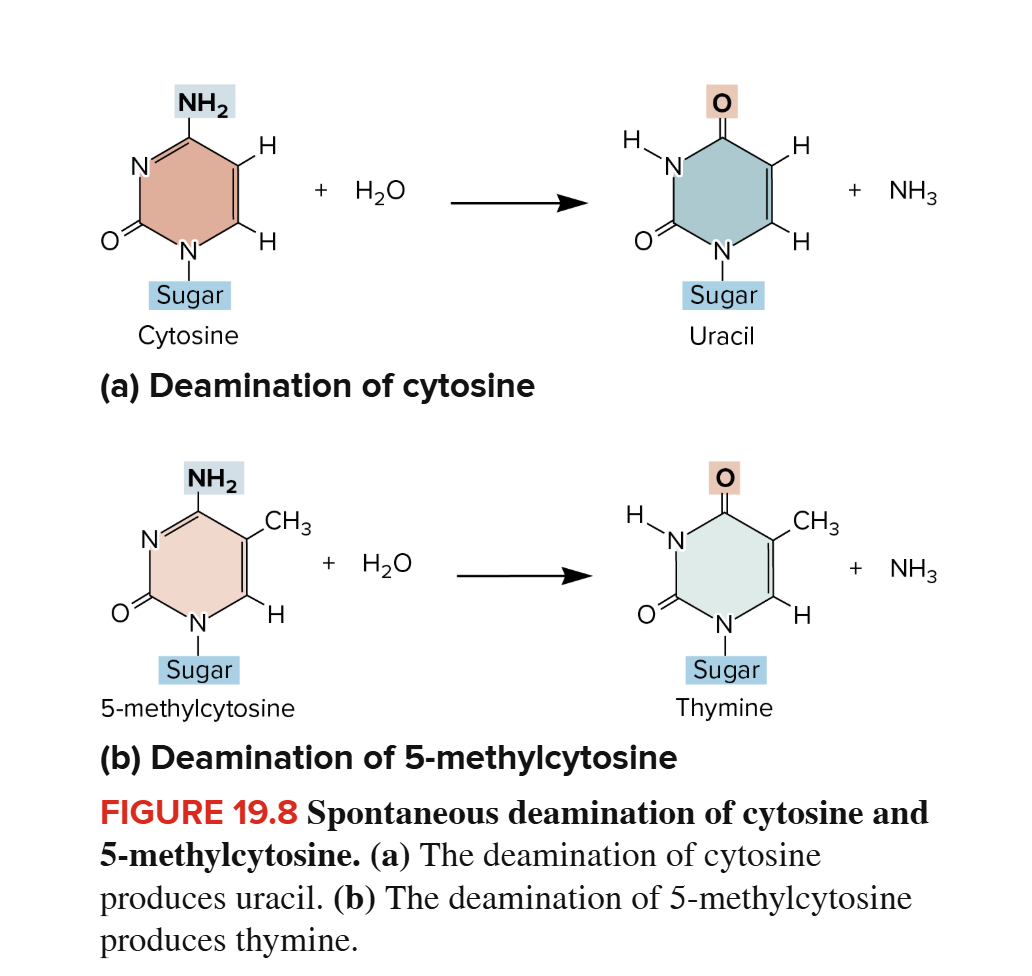
Deamination - Spontaneous Mutation
The removal of an amino group from a molecule.
The removal of an amino group from cytosine produces uracil.
Oxidative DNA damage
Changes in DNA structure that are caused by reactive oxygen specifies (ROS)
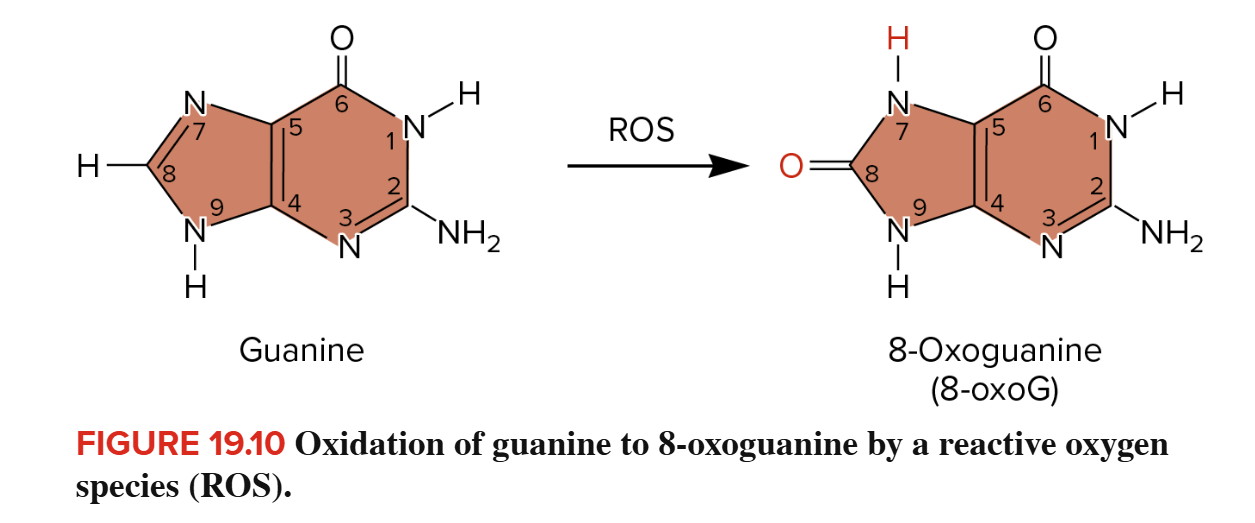
What does oxidative stress do?
Modifies guanine base to 8-oxogianine
Oxidative Stress
An imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and an organism’s ability to break them down.
Mutagen
An agent that can alter the structure of DNA, causing a mutation.
Can be chemical or physical mutagen