COMP 2 FOME
1/264
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
265 Terms
Joint type found in the proximal radioulnar joint
Pivot joint
Differ at one chiral center like D-glucose & D-galactose
Epimers
A surgeon might compress the _____to stop the bleeding from the cystic artery so that you can then ligate that artery.
Hepatic artery
Hepatoduodenal ligament – Contains the
cystic artery, hepatic artery, and bile duct.
Major nitrogen donor for the urea cycle.
Glutamate
Donates a second nitrogen for urea formation.
Aspartate
What are the hallmark laboratory findings of Carbamoyl Phosphate Synthetase I deficiency?
Increased ammonia, decreased citrulline, normal orotic acid.
What laboratory findings are characteristic of Ornithine Transcarbamoylase deficiency?
Increased ammonia, decreased citrulline, increased orotic acid due to excess carbamoyl phosphate entering pyrimidine synthesis.
Why does Ornithine Transcarbamoylase deficiency cause orotic acid in the urine?
Carbamoyl phosphate accumulates and is diverted into pyrimidine synthesis, leading to orotic aciduria.
What laboratory findings are characteristic of Argininosuccinate Synthetase deficiency?
Increased citrulline, decreased argininosuccinate, increased ammonia.
Why does citrulline accumulate in Citrullinemia Type I?
Argininosuccinate cannot be formed, so citrulline builds up in the blood.
What is the treatment for Citrullinemia Type I?
Arginine supplementation to drive the cycle forward, protein restriction, and nitrogen-scavenging medications.
What laboratory findings are characteristic of Argininosuccinate Lyase deficiency?
Increased argininosuccinate, increased citrulline, increased ammonia.
A 2-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department due to severe hypoglycemia, lactic acidosis, and hepatomegaly. His parents report that he becomes irritable and weak several hours after eating, and his symptoms improve with glucose administration. A liver biopsy shows excess glycogen with normal structure but an inability to mobilize it.
Glucose-6-phosphatase
Which enzyme is responsible for transporting acetyl CoA from the mitochondria to the cytosol for fatty acid synthesis?
ATP Citrate Lyase
Which molecule directly activates Acetyl CoA Carboxylase (ACC) to stimulate fatty acid synthesis?
Citrate
Cortex vs paracortex
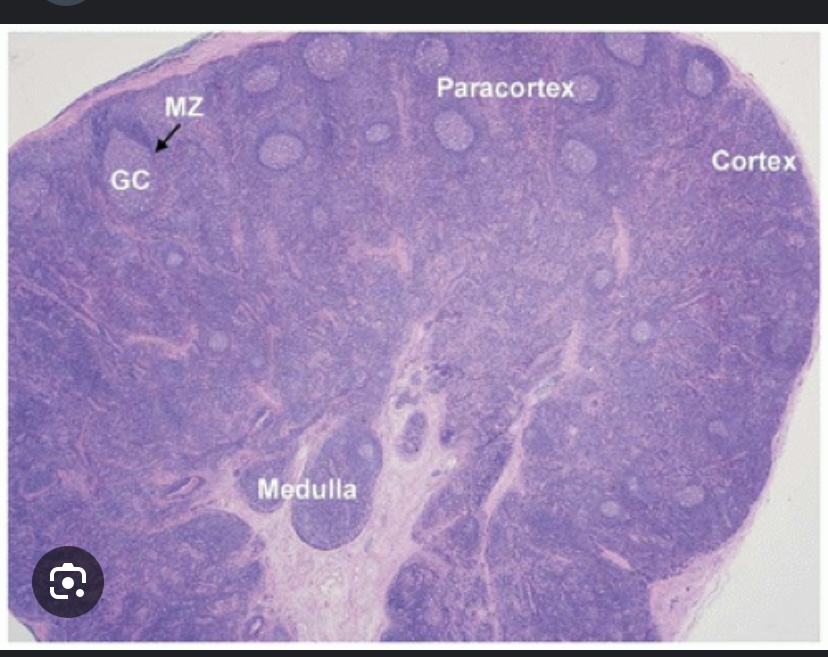
Cortex vs paracortex
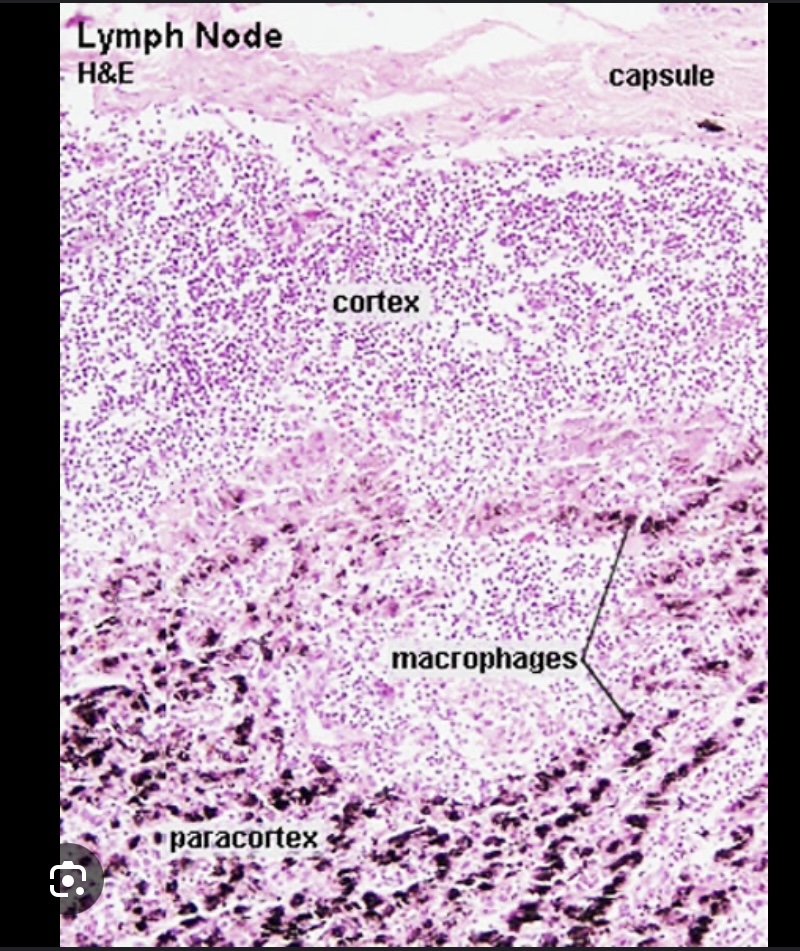
The paracortex contains
T-cells and dendritic cells presenting antigens to T-cells
Primary follicles in the cortex:
Naïve B-cells (not yet exposed to antigens)
Secondary follicles in the cortex
Germinal centers where B-cell proliferation and differentiation occur after antigen exposure.
Homogentisate oxidase
ApoC-II is essential for which of the following processes?
Activation of Lipoprotein Lipase (LPL) for triglyceride hydrolysis
ApoA-I →
Activates LCAT for HDL-mediated cholesterol esterification.
ApoB-48 → Required for
chylomicron secretion from the intestine.
ApoB-100 → Binds
LDL receptors for LDL uptake.
ApoE → Mediates
endocytosis of chylomicron remnants by the liver.
How does the lac operon function in Escherichia coli when lactose is absent?
The lac repressor binds to the operator, preventing transcription of the lac genes, and the operon remains inactive.”
In the Lac operon system, how does the presence of glucose affect the cAMP-CAP complex and the transcription of the lac operon?
High glucose levels decrease cAMP levels, reducing the activation of the Lac operon.
Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding the Lac repressor in the Lac operon?
The Lac repressor binds to the operator region and prevents transcription of the lac genes when lactose is absent.
In the Lac operon system of E. coli, what happens when both glucose and lactose are present in the environment?
The Lac operon is only partially activated due to the presence of glucose.
A patient presents with weakness in shoulder abduction and lateral rotation following a superior scapular injury. Which nerve is most likely affected?
Suprascapular nerve
Weak lateral rotation of the arm Means what’s affected
Infraspinatus
Subclavian artery → Becomes the
axillary artery at the lateral border of the first rib.
The axillary artery continues down the arm and becomes the brachial artery
at the inferior border of the teres major muscle.
The brachial artery bifurcates into the radial and ulnar arteries at the
cubital fossa (near the elbow joint).
Major alternative route if the axilar my is blocked
Dorsal scapular artery (from subclavian artery)
• Suprascapular artery (from thyrocervical trunk)
• Circumflex scapular artery (from subscapular artery)
medullary cords contain
B-cells, plasma cells and macrophages
Medullary sinuses
Channels that allow lymph drainage to the efferent lymphatic vessel.
Primary site for T-cell activation and interaction with antigen-presenting cells
Paracortex (Inner Cortex)
Memorize smooth muscle
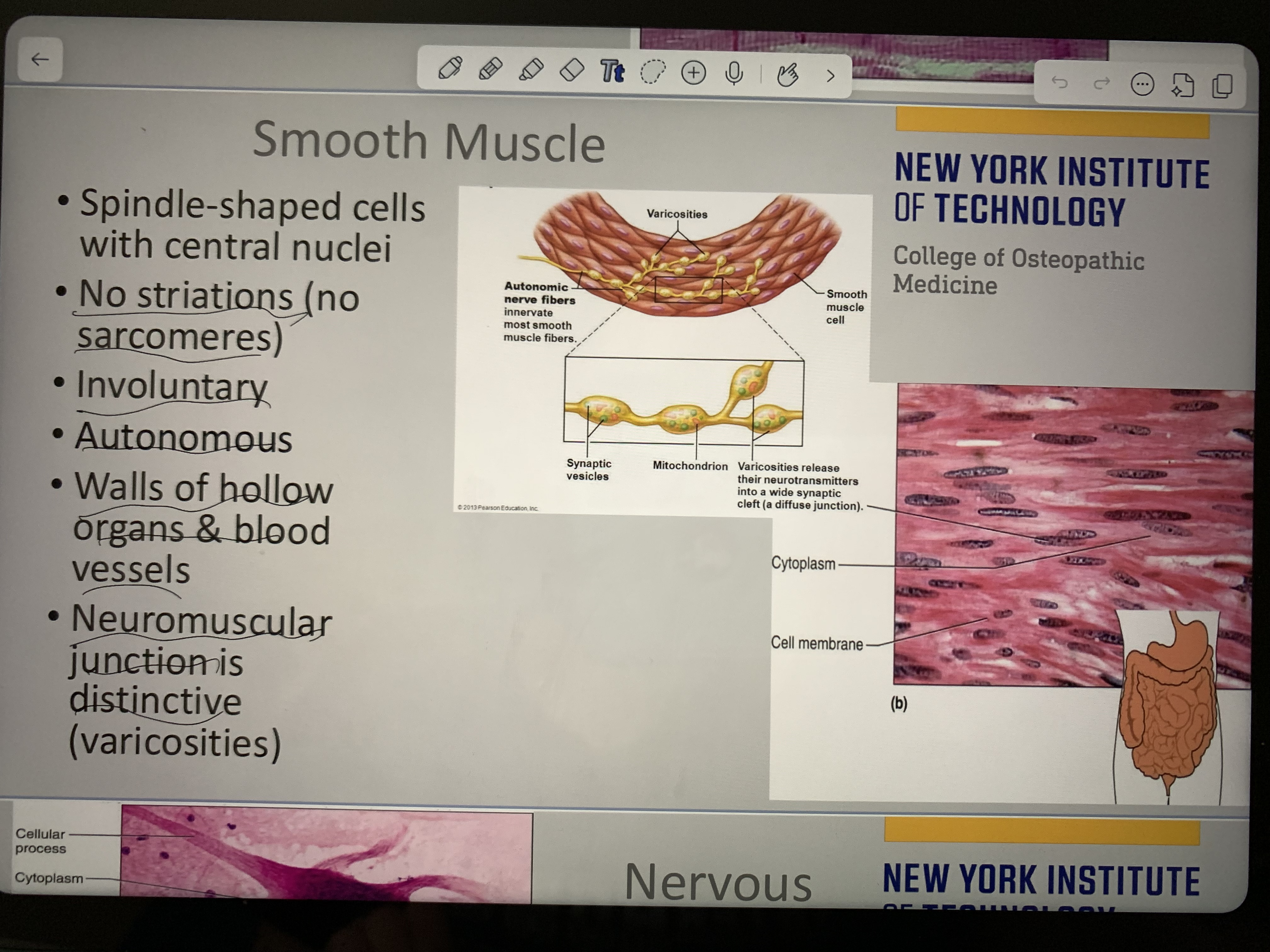
Memorize
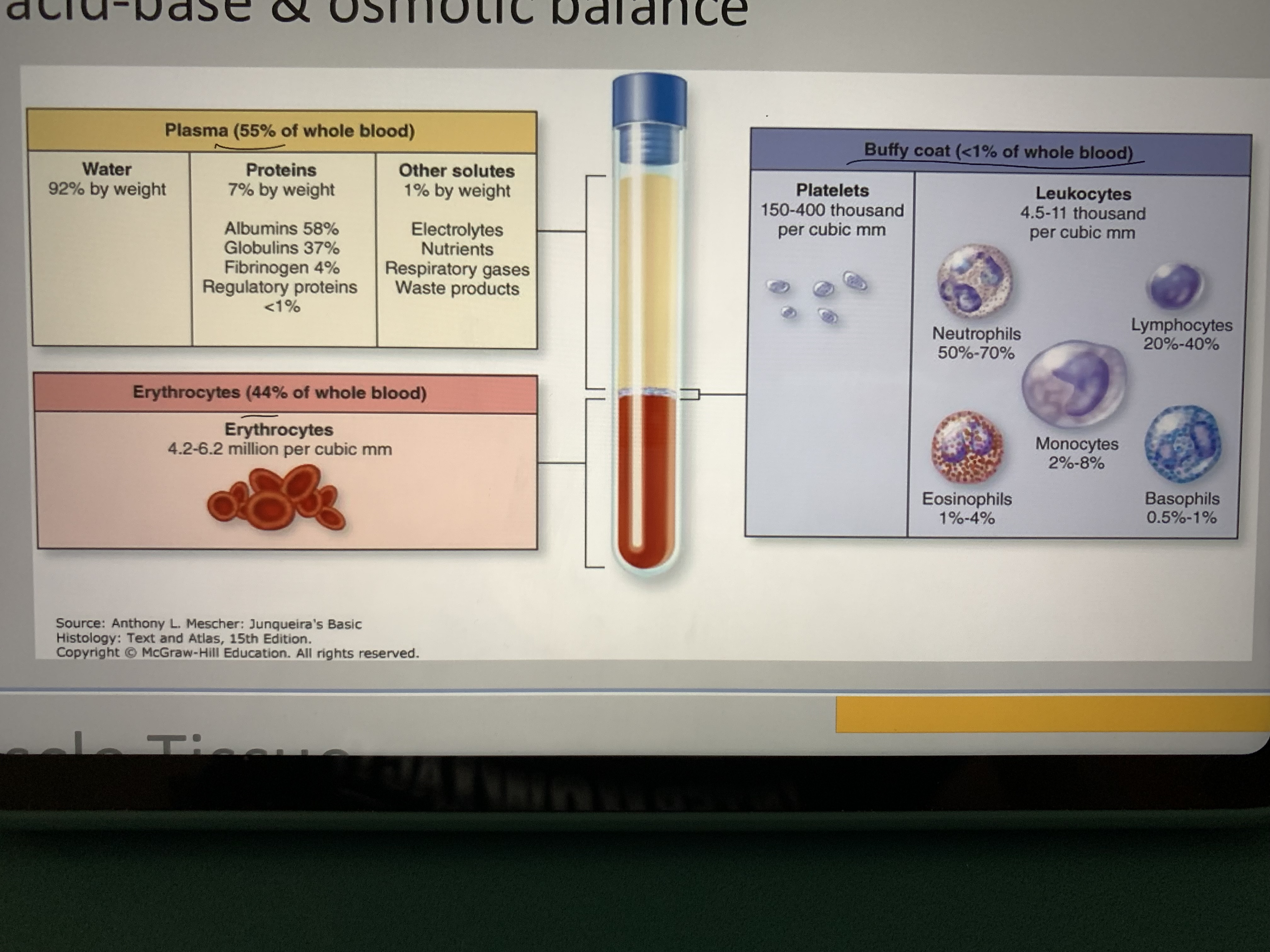
Memorize blood
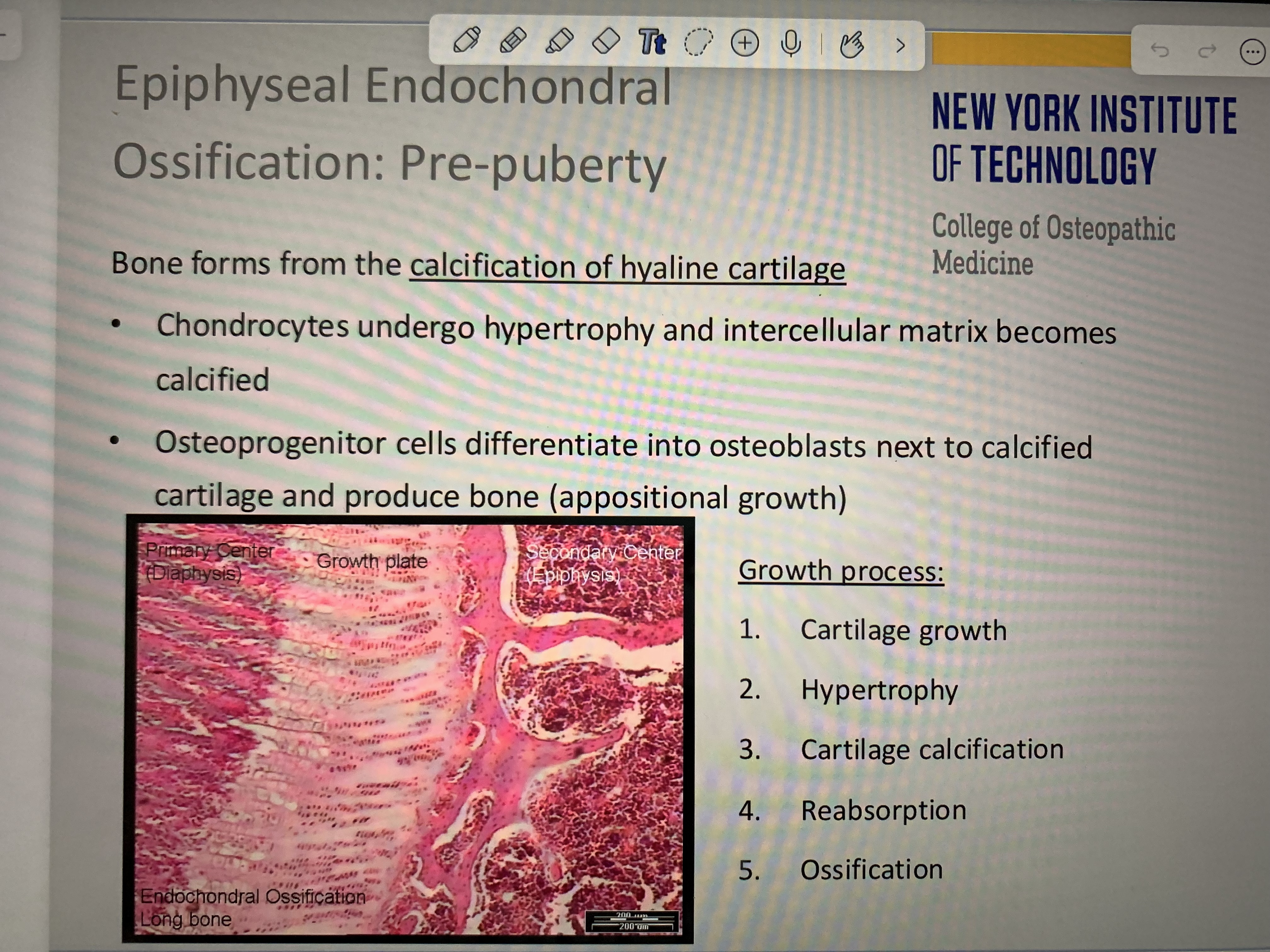
Parts of bone

Memorize
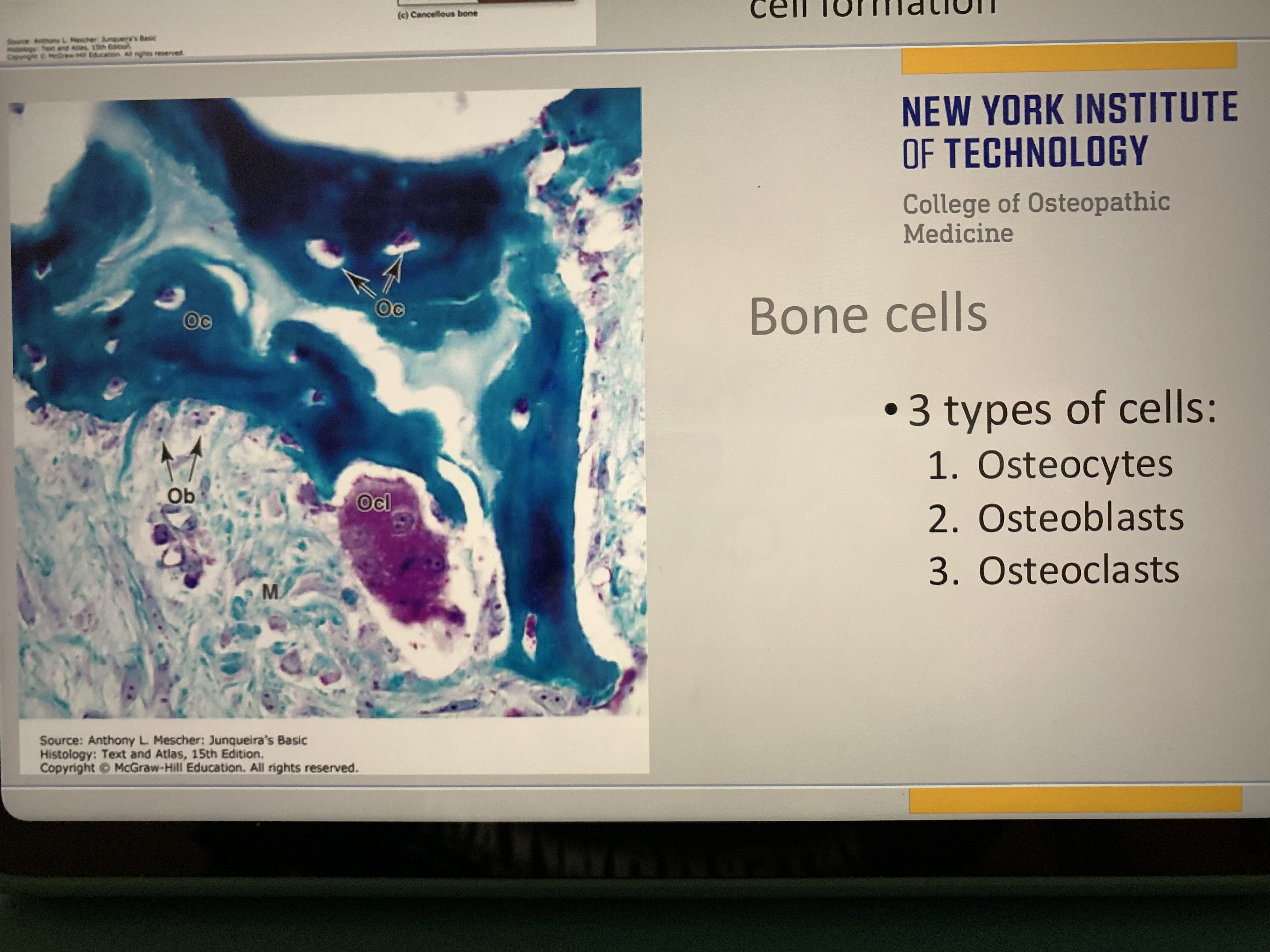
Memorize
Memorize osteoclasts (larger)
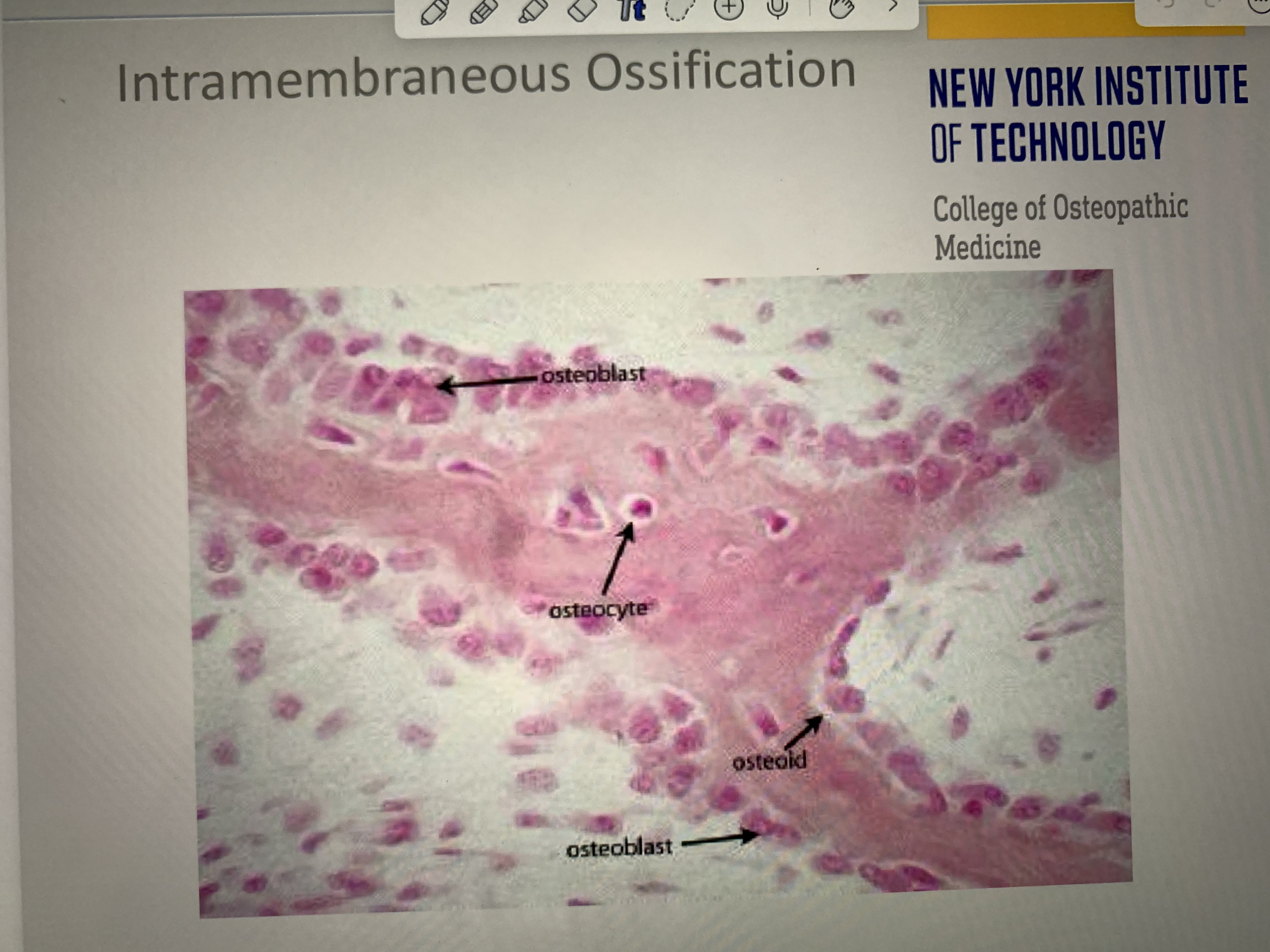
Memorize
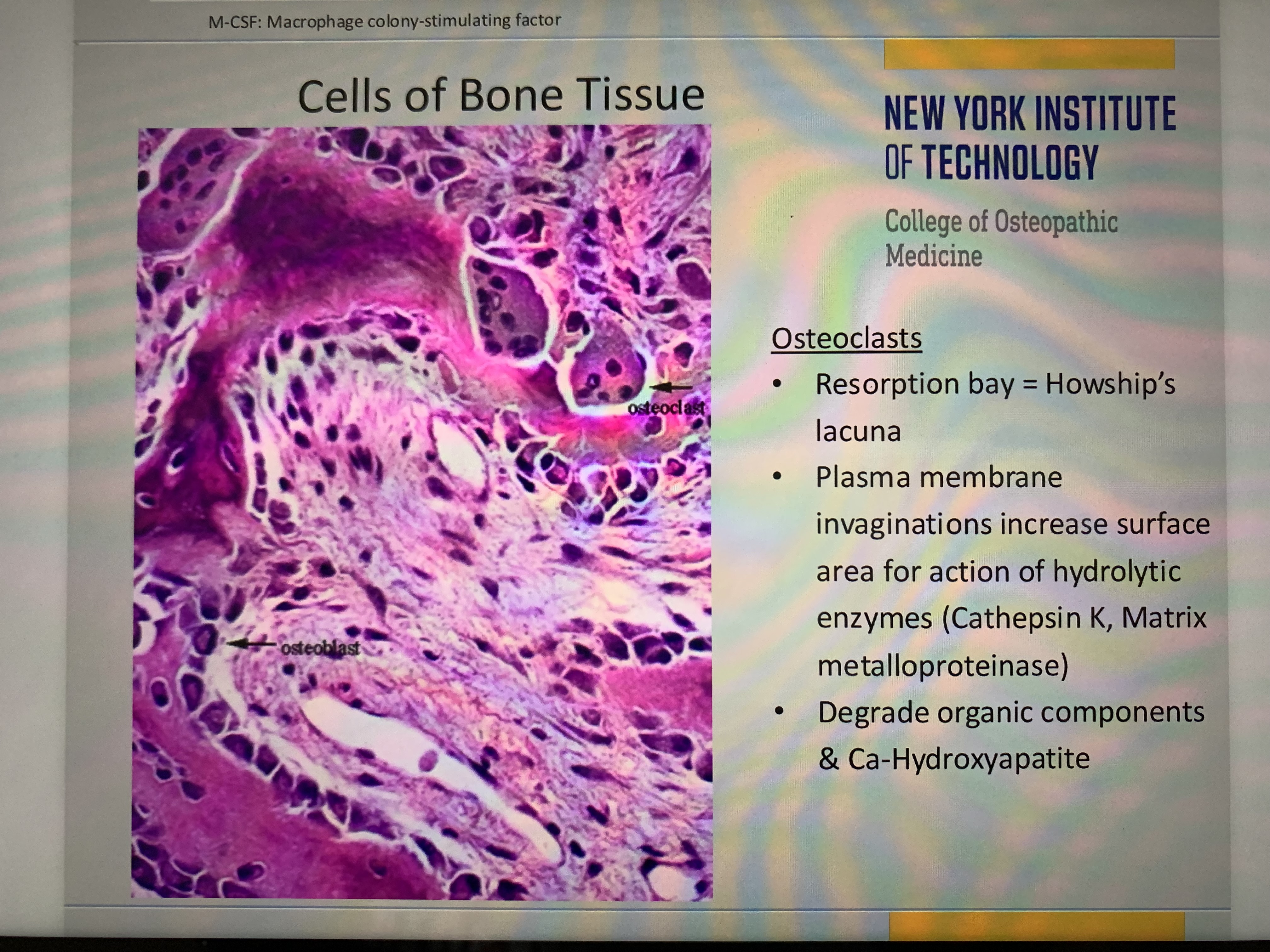
Memorize
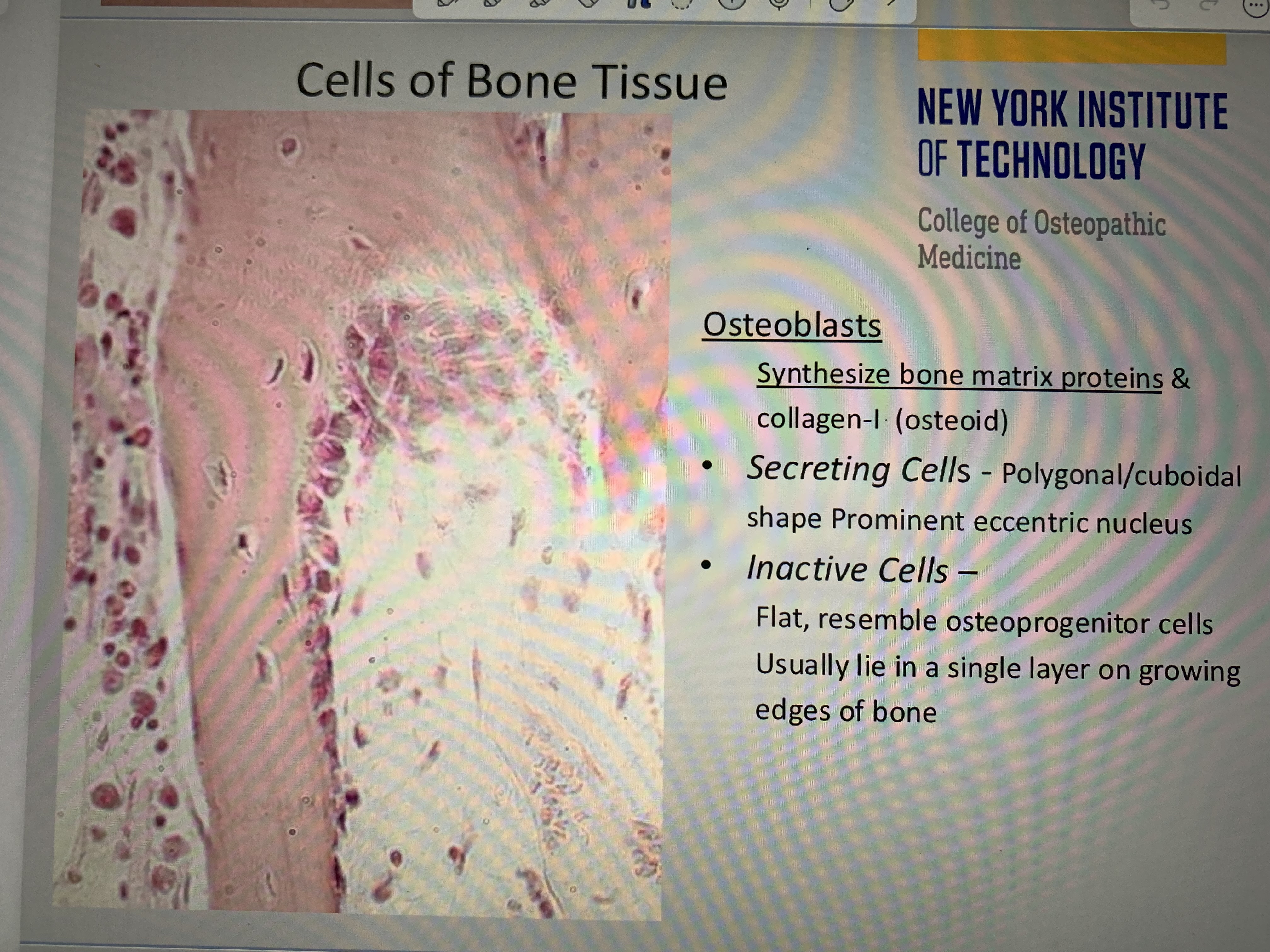
Osteoblasts vs osteoblasts
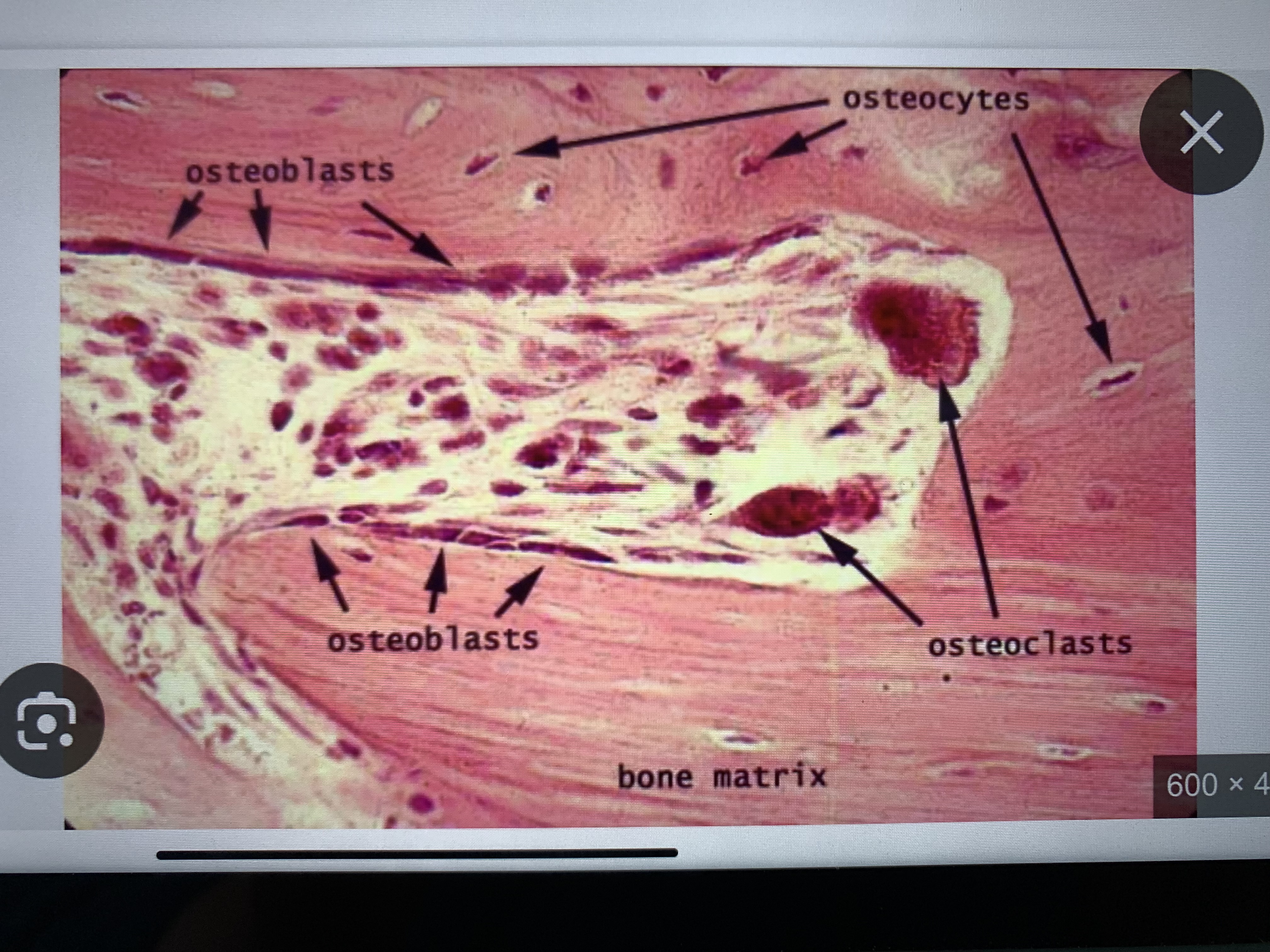
Memorize these parts of bone
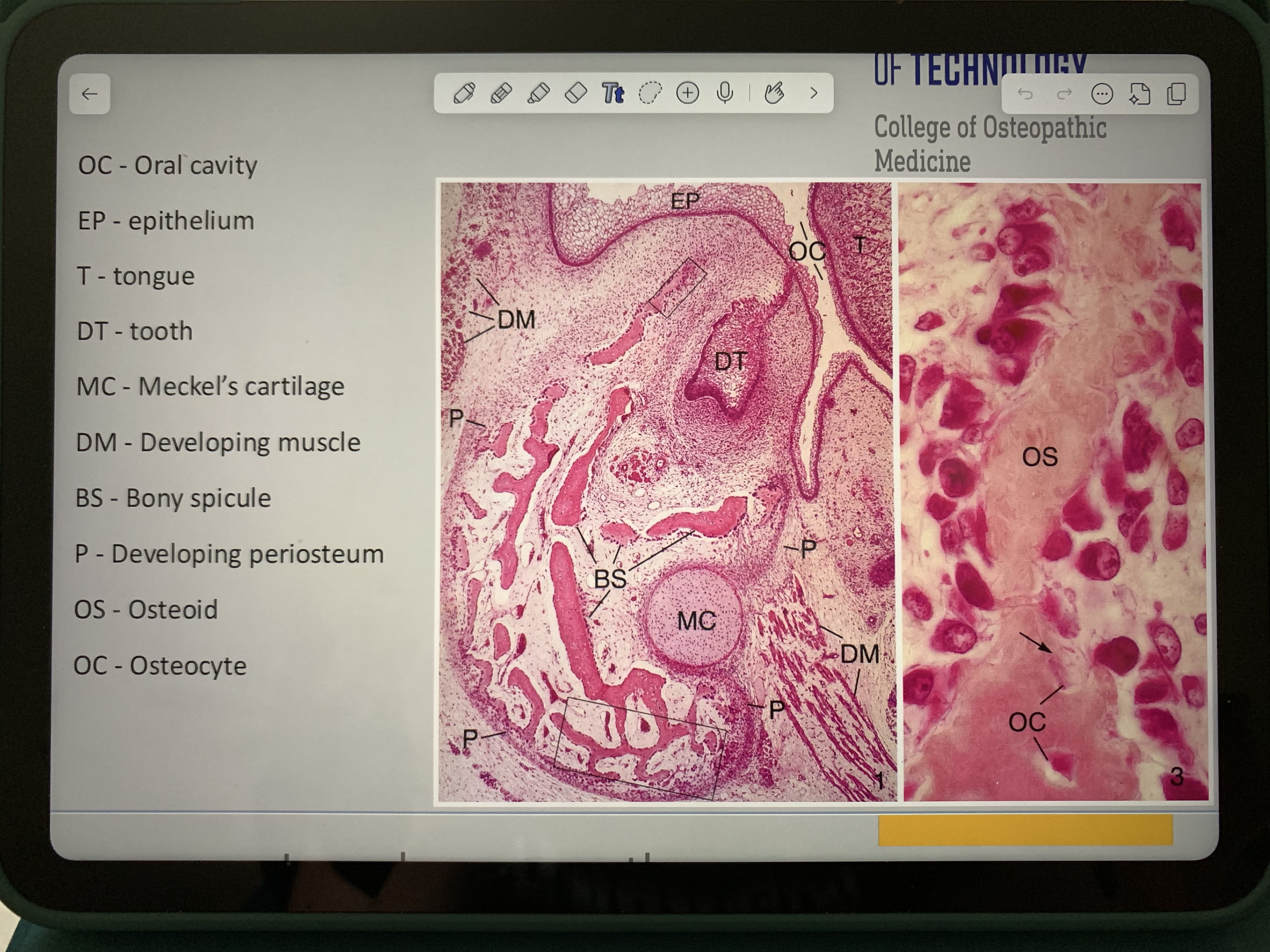
M1
classically activated;
chronic inflammation &
tissue injury
M2
alternatively activated;
resolution of inflammation &
repair
Cytokines
TNF-alpha, ILs, GF, &
prostaglandins
A patient presents with weakness in wrist flexion and pronation, along with numbness over the lateral three and a half fingers. Which nerve is most likely injured?
Median nerve
Which of the following is a key characteristic of fibrocartilage?
Contains both Type I and Type II collagen, but lacks a perichondrium
“Enlarged calves”
Becker’s muscular dystrophy
Lymph nodes are made of
Type 3 collagen
Type 5 collagen
plays a crucial role in organizing and regulating fibrillar collagen (especially Type I collagen) within connective tissues.
A 32-year-old man presents with fatigue, pallor, and recurrent infections. A bone marrow biopsy is performed, and histological analysis reveals a mesh-like network of thin fibers that stain black with a silver stain, supporting a population of developing blood cells. Which of the following collagen types is most abundant in this connective tissue?
Type III
A 45-year-old woman presents with multiple episodes of blistering on her skin and mucous membranes. A biopsy of the affected skin reveals intraepidermal blister formation with acantholysis (loss of cell-to-cell adhesion). Immunofluorescence shows IgG antibodies against desmoglein in the epidermis.
Desmosomes
Pemphigus vulgaris =
Desmosome destruction → Intraepidermal blisters
Bullous pemphigoid
Hemidesmosome destruction → Subepidermal blisters
Kartagener Syndrome
Dynein defect → Immobile cilia
Cilia
Involved in movement (e.g., respiratory epithelium, fallopian tubes), not absorption.
woman presents with progressive muscle weakness, difficulty swallowing, and a rash on her upper eyelids and knuckles. Laboratory tests reveal elevated creatine kinase (CK) and positive anti-Jo-1 antibodies. A muscle biopsy shows perifascicular atrophy and inflammation.
Which of the following epithelial structures is primarily affected in this condition?
Basement membrane
Degeneration of the dystrophin-associated glycoprotein complex
Describes Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophy, which presents with progressive weakness from childhood,
Which of the following is the primary function of the APC protein?
Degradation of β-catenin to prevent excessive cell proliferation
p53 is a key tumor suppressor that regulates the
G1/S checkpoint
The patellar reflex (knee jerk) primarily tests the ____ spinal levels, via the femoral nerve.
L3-L4
loss of sensation over the medial leg but normal motor function. There is no weakness in knee extension or dorsiflexion. Which nerve is most likely affected?
Saphenous nerve
Common fibular nerve → Would cause
foot drop
tibial nerve controls
Plantarflexion, not dorsiflexion
Sural nerve
Provides sensory innervation to the lateral foot, but does not affect dorsiflexion or toe extension.
Superficial fibular nerve → Provides sensation to the
dorsum of the foot (except first web space)
Common fibular nerve injury → Would cause
both dorsiflexion & eversion weakness,
Peyer’s patches (found in the ileum) contain
germinal centers for B-cell activation.
When should you NOT use H&E stain?
Detecting basement membranes, mucins, glycogen, or fungi
• Staining specific cell markers or molecular components
When should you use Periodic Acid-Schiff (PAS) stain?
Detecting glycoproteins, mucins, glycogen, and basement membranes
• Diagnosing diabetic nephropathy (GBM thickening)
• Identifying Tropheryma whipplei (Whipple disease) in macrophages
When should you use Silver stain?
Identifying reticular fibers and basement membranes
• Detecting fungal infections (Pneumocystis jirovecii, Histoplasma)
Identifying reticular fibers and basement membranes
• Detecting fungal infections (Pneumocystis jirovecii, Histoplasma)
Congo Red stain
What stain is best for detecting collagen fibers in fibrosis (e.g., cirrhosis, kidney disease)?
Masson’s Trichrome stain
When should you use Dark Field Microscopy?
Detecting thin, unstained bacteria (e.g., Treponema pallidum – syphilis)
When should you use Confocal Microscopy?
High-resolution 3D imaging of fluorescently labeled tissues
When should you use Phase Contrast Microscopy?
Observing live, unstained cells
• Examining internal organelles without staining
When should you use Fluorescence Microscopy?
Detecting specific proteins using immunofluorescence
• Identifying Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Auramine-Rhodamine stain)
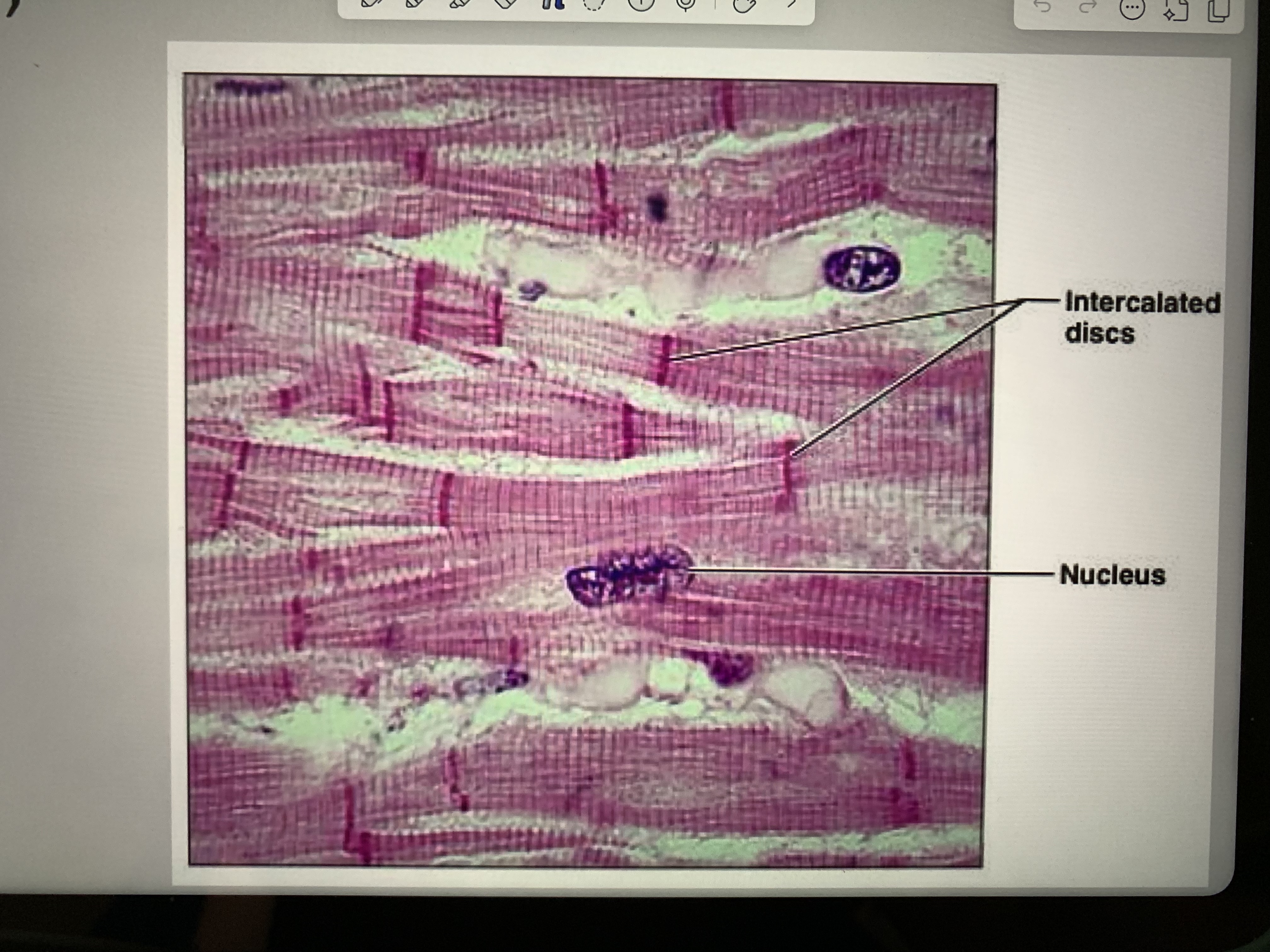
Which of the following correctly describes the function of intercalated discs in cardiac muscle?
in cardiac muscle contain gap junctions for electrical coupling and desmosomes for mechanical stability, allowing for synchronized contraction.
Which of the following best describes the underlying pathophysiology of this patient’s condition of OA?
Loss of proteoglycans and water in hyaline cartilage, leading to decreased resilience and mechanical wear
What is the primary function of follicular dendritic cells (FDCs) in lymph nodes?
retain antigen-antibody complexes to aid B-cell activation in germinal centers.
Contains Type I epithelioreticular cells → form
blood-thymus barrier
Type II and III epithelioreticular cells → facilitate
positive selection (survival of T-cells recognizing MHC)
Type IV and V epithelioreticular cells Is involved in
negative selection (eliminate self-reactive T-cells)
Type VI cells → aid
T-cell maturation
B-cells are found in _____ of lymph nodes, where they proliferate, undergo affinity maturation, and differentiate into plasma cells to produce antibodies (humoral immunity).
Germinal center