IGCSE Edexcel Business 3.1 - 3.4
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
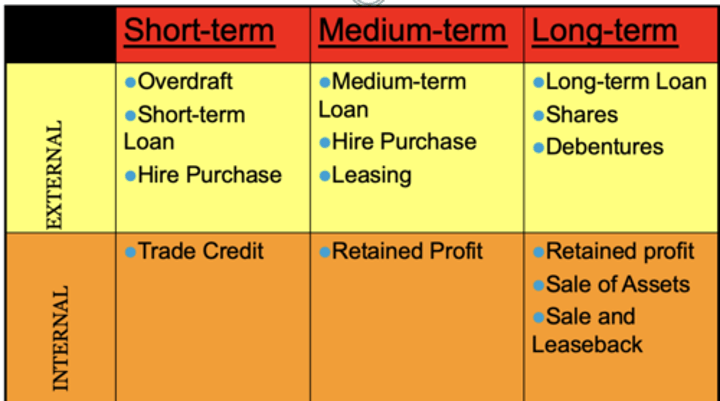
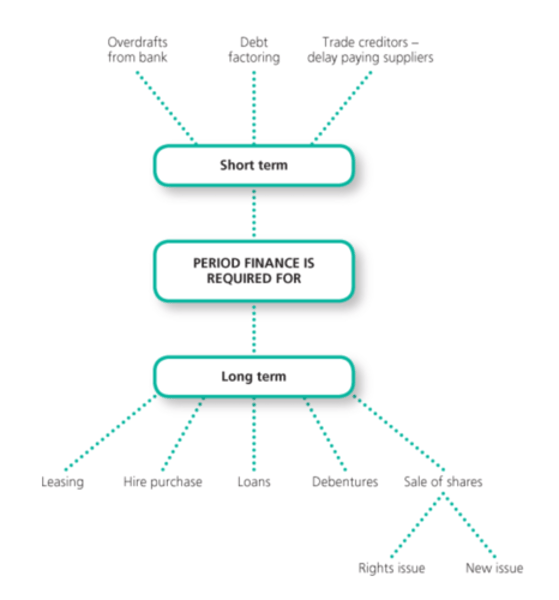
short-term finance
money borrowed for one year or less

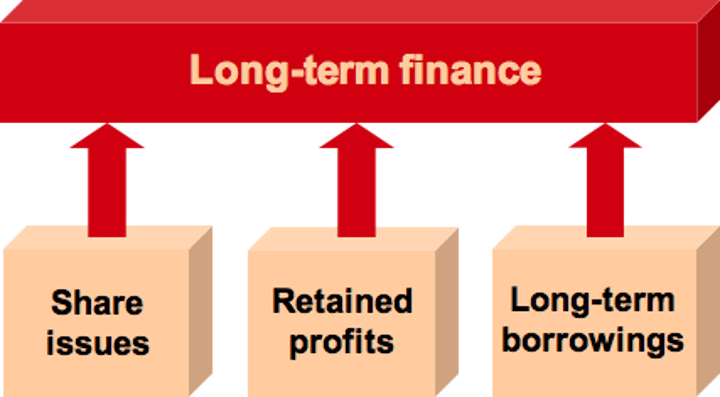
long-term finance
money borrowed for more than one year
examples of short-term finance
bank overdrafts, trade payables
examples of long-term finance
loan capital, venture capital, hire purchase, crowd funding, share capital, leasing

reasons for needing finance
-start-up capital
-operating the business (paying expenses)
-expansion (when established)

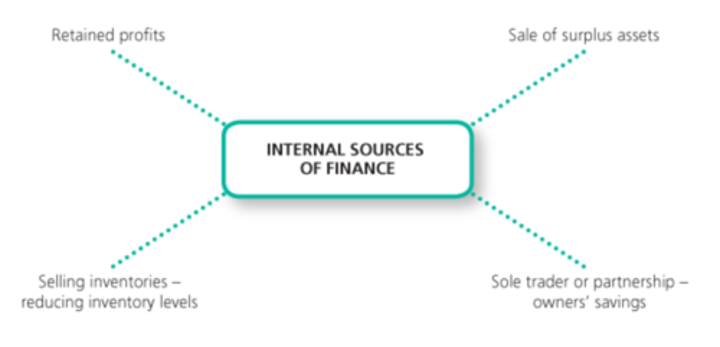
internal sources of finance
come from inside the business and are typically used by established businesses

what are the internal sources of finance?
personal savings, retained profit, selling assets
external sources of finance
come from outside the business. this can help a business pay for short term or long-term transactions

what are the external sources of finance?
loan capital, venture capital, bank overdrafts, hire purchase, crowd funding, trade payables, share capital, leasing, credit cards
personal savings
when an entrepreneur uses personal finance to start / run the business

retained profits
using profit that has not been returned to the owners (established businesses)

selling assets
an established business can sell old assets to raise capital such as old machinery

bank overdraft
means a business can spend more money than is in their bank account

loan capital
a fixed agreement between a business and the bank. normally for a large amount

hire purchasing
a loan for equipment such as machinery and tools. a down payment followed by monthly payments
share capital
limited companies (LTD and PLCs) can sell shares to raise finance

crowdfunding
many investors 'the crowd' who invest in business ventures. normal donation online

venture capital
business people who invest in small to medium businesses with high growth potential

leasing
rental of equipment such as machinery. business never owns the equipment

trade payables
receive stock (raw materials) and pay in 30 to 90 days

advantages of personal savings
no interest payments as an internal source -> reduction in cost of borrowing -> possibility of higher profits as lower costs
disadvantages of personal savings
tends to be a limited source of finance -> will need to use external sources in addition
advantages of retained profits
no interest payments as an internal source -> reduction in cost of borrowing -> possibility of higher profits as lower costs

disadvantages of retained profits
reduces the owner's profit or dividend payment for shareholders -> unhappy -> lose motivation to invest

advantages of selling assets
no interest payments as an internal source -> reduction in cost of borrowing -> possibility of higher profits as lower costs

disadvantages of selling assets
all assets are essential to business functionality -> once sold business not able to use the asset

advantages of bank overdrafts
ability to use cash even if there's none in the account -> able to buy raw materials -> keep the business solvent

disadvantages of bank overdrafts
banks can call overdrafts in at any time - business may not be able to repay - insolvent
advantages of loan capital
large amount of capital at once -> fixed monthly repayments -> business knows exact outgoings each month
disadvantages of loan capital
interest payments -> increase in total costs -> making less likely to make profits as costs are increased
advantages of hire purchasing
able to receive machinery with small upfront payment -> frees working capital for the business -> own the machinery following final payment
disadvantages of hire purchasing
interest rates are high -> which increases costs -> business does not own items until final payment is made -> can be repossessed as a result
advantages of share capital
ability to raise large amounts of capital -> no interest payable -> reduction in operating costs
disadvantages of share capital
loss in stake in the business -> must share profits (dividend payments) -> reduction in profits for founder (dilute current shares)
advantages of crowdfunding
crowdfunding can be a fast source of finance -> from numerous investors -> when traditional borrowing methods are not available

disadvantages of crowd funding
could be difficult to encourage investment -> if business is small -> leads to lack of finance raised
advantages of venture capital
opportunity for large investment (normally £10-100k) and additional skills
disadvantages of venture capital
loss of stake in business -> difficult to make decisions -> conflict -> slow decision making
advantages of leasing
the business acquires new equipment with small investment -> any problems in it replaced -> reduces overall costs

disadvantages of leasing
expensive to lease -> leads to increased costs for the business

advantages of trade payables
no payment for 30-90 days -> frees up capital for other business operation -> such as paying wages or promotion
disadvantages of trade payables
could be a more expensive method of purchasing stock -> increasing cost of sales -> decreasing gross profit
cash flow forecasting
the predicted cash inflows and outflows over a period
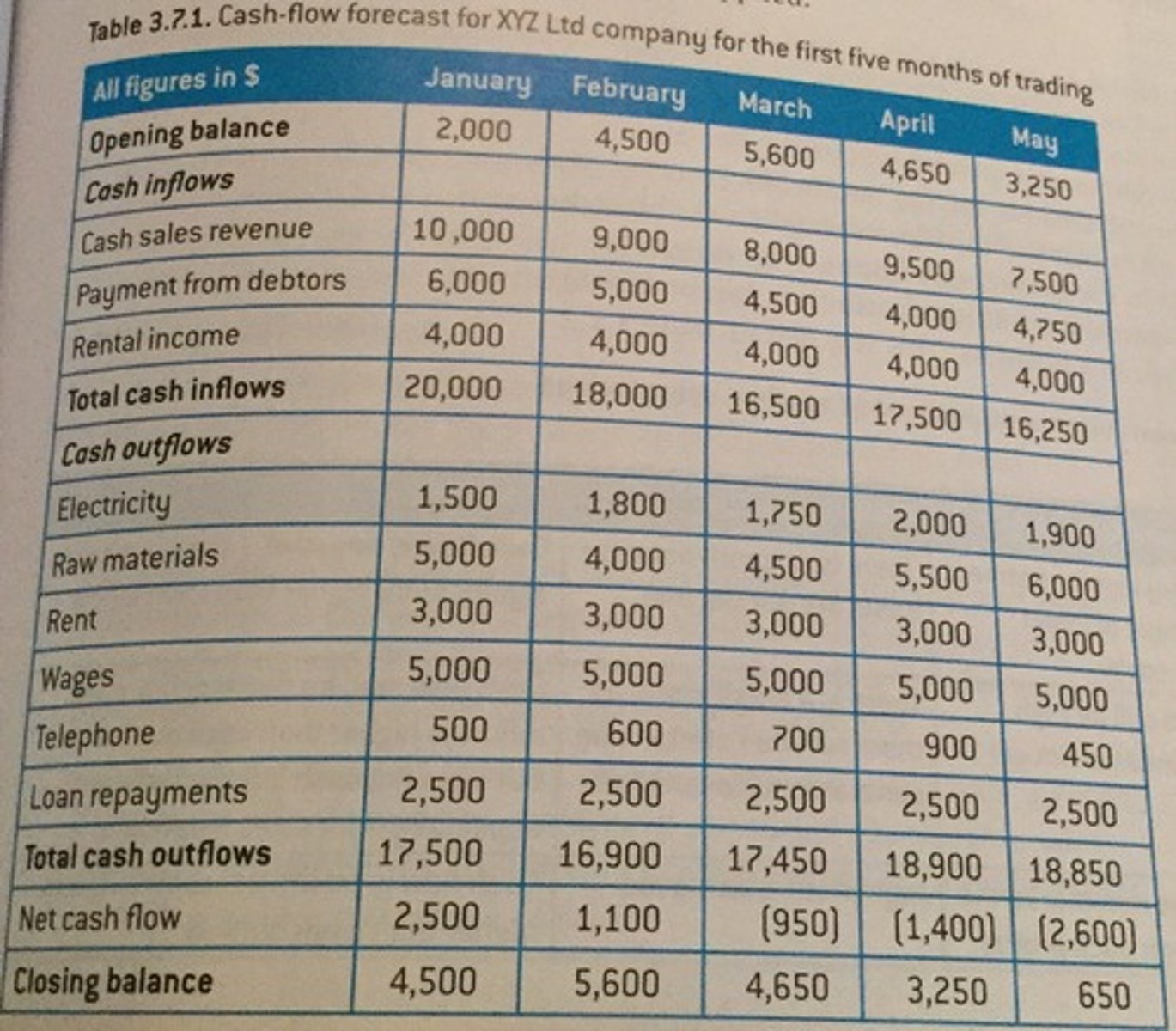
reasons for needing cash
-to pay suppliers (cost of sales)
-to pay overheads and employee wages (expenses)
-to prevent business failure (insolvency)
the difference between cash and profit
businesses can function and stay solvent without making a profit, cash is vital to staying solvent. cash is the inflow and outflow over a period time (cash is not always on hand), it can be tied up in trade credit or owners can give a cash injection. profit is calculated through revenues - total costs, typically at the end of a trading period.
cash inflows
flow of money into a business

cash outflow
flow of money out of a business
net cash inflow
cash inflow - cash outflow
opening balance
the cash the business expects in the account at the start of the month
closing balance
the cash the business expects in the account at the end of the month. becomes opening balance in following month
how can a business improve cash flow?
-decrease prices (possible to increase also)
-increase promotion
-reduce raw material costs (through changing suppliers)
-reduce wages (through making workers redundant)
-reduce rental costs (moving to a cheaper location)
advantages of creating a cash flow forecast
-can help businesses identify cash shortages -> help to plan solutions -> to ensure the business does not become insolvent
-can help a new business apply for funding -> with a cashflow forecast more likely to be accepted -> helps raise capital for expansion / start-up
disadvantages of creating a cash flow forecast
only a prediction -> could be incorrect -> business makes business decision based on the predictions -> could lead to bad decisions
key to calculating cash flow forecasts
A (total cash inflows) - B (total cash outflows) = C (net cash flow)
C (net cash flow) + D (opening balance) = E (closing balance)
revenue
the money that a business recives because of selling a good or service
costs
the expense that a business must meet when setting up and running a business
formula for revenue
price x quantity sold
fixed costs
costs that do not change with the level of output
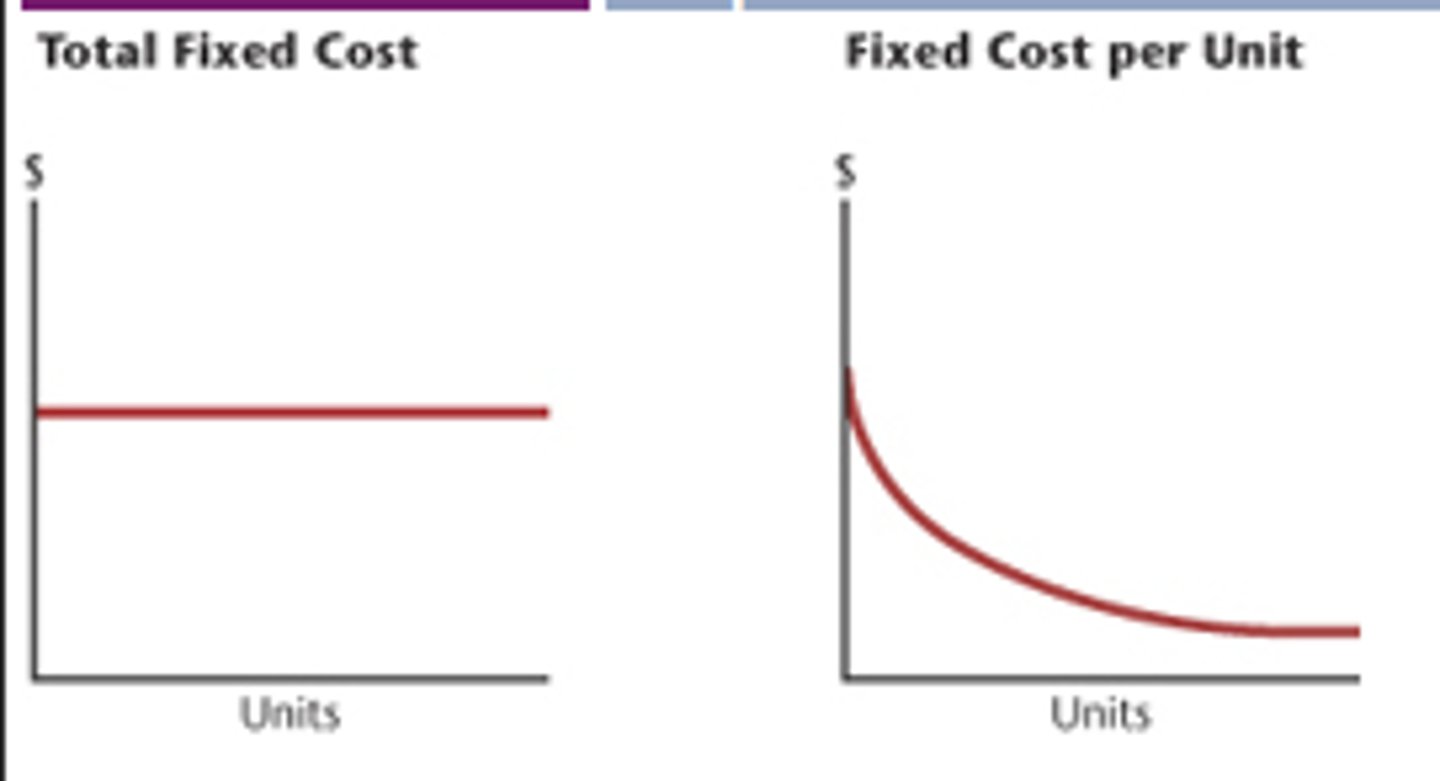
examples of fixed costs
-rent
-business rates
-interest payments
-insurance premiums

variable cost
costs that change when output levels change
examples of variable costs
-raw materials/packaging
-electric
-labour (if paid hourly or overtime)
total costs
all the business costs
formula for total costs
fixed costs + variable costs
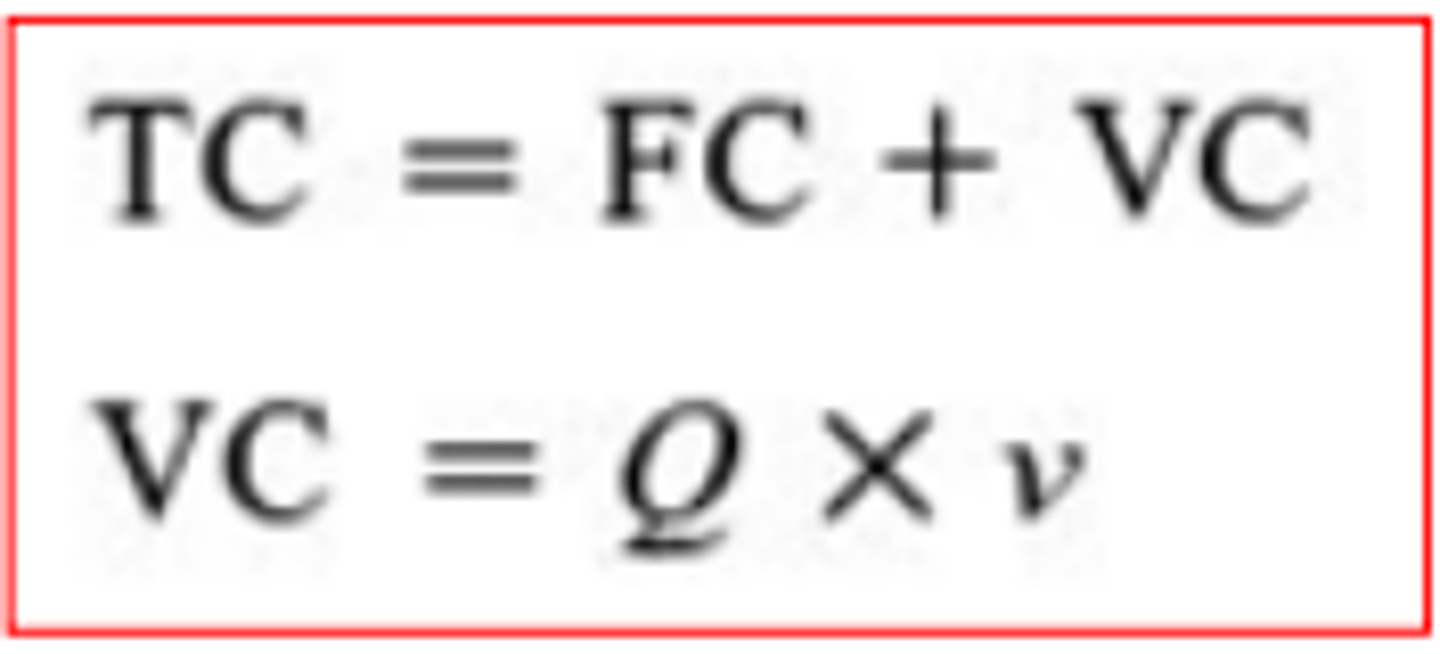
profit
the difference between total revenues and total costs

formula for profit
total revenue - total cost

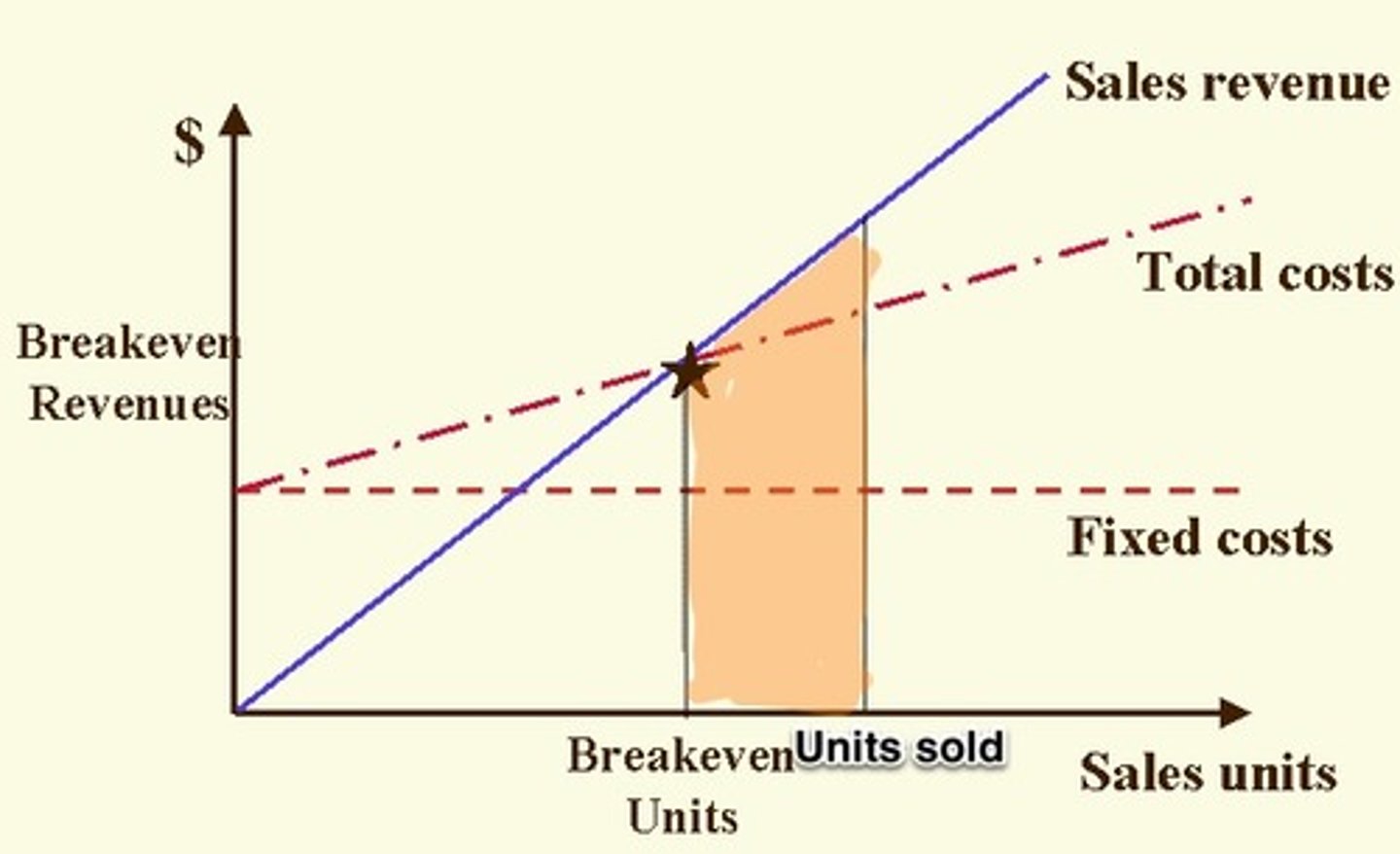
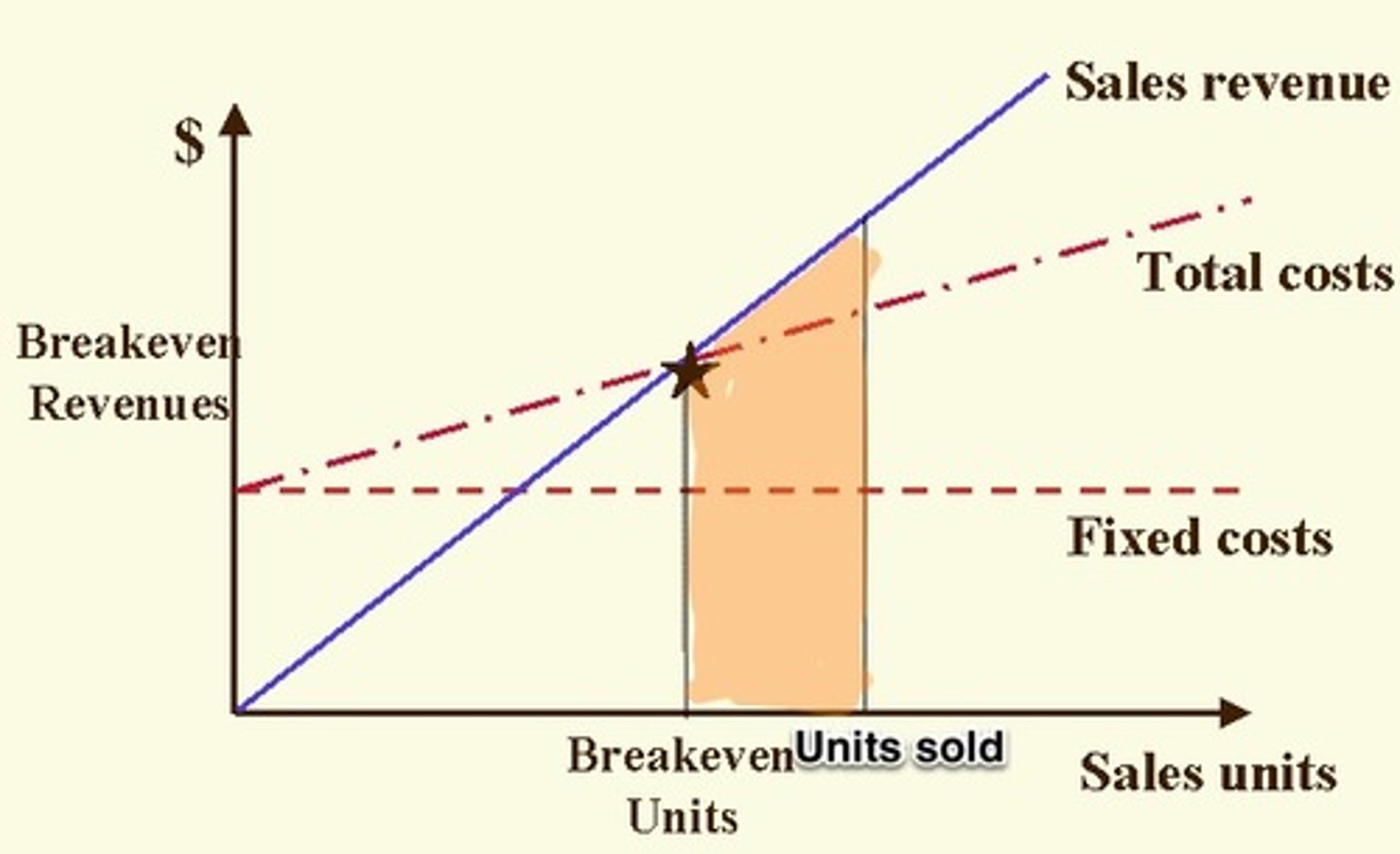
break-even
when total revenues are equal to total costs. therefore, the business does not make a profit or loss
margin of safety
the amount of output available to be sold above the break-even point where the business makes a profit
formula for margin of safety
actual output - break even point
breakeven formula
fixed costs / contribution (selling price per unit - VC per unit)
how does an increase in price impact the break-even chart?
TR becomes steeper -> reduction in break-even point (need to sell less to break-even)
how does a decrease in price impact the break-even chart?
TR becomes flatter -> an increase in break-even point (need to sell more to break-even)
how does an increase in fixed costs or increase in variable costs impact the break-even chart?
TC moves upwards -> the break-even point increasing (need to sell more to break-even)
how does a decrease in fixed costs or decrease in variable costs impact the break-even chart?
TC moves downwards -> the break-even point decreasing (need to sell less to break-even)
advantages of creating a break-even analysis
-it can help a business plan as they can see how many units are needed to be sold to break-even
-business can see the 'margin of safety' -> can create 'what if?' analysis -> what happens if the business increases prices -> can then chose strategy
disadvantages of creating a 'break-even analysis'
-as all lines are straight (TR & TC) it does not factor in if a business does discounts -> therefore is not accurate -> could be misleading -> leading to bad decisions
-if data is incorrect -> due to lack of experience in constructing BE charts -> bad decisions made
statement of comprehensive income
it shows the income and costs of the business and is used to calculate the business profit, at the end of a financial year
keys to calculating the statement of comprehensive income
A (revenue) - B (cost of sales) = C (gross profit)
C (gross profit) - D (expenses) = E (operating profit)
cost of sales
cost of raw materials and/or inventories (stock)
gross profit
revenue - cost of sales (profit before expenses)
expenses
additional overhead costs such as wages and rent. not directly with cost of producing a good or service
operating profit
gross profit - expenses ('bottom line" profit)
finance cost
cost of borrowing money. it's the interest payable to the lender
how can businesses use the statement of comprehensive income?
-investment decisions -> can help a business decide on expansion. if profits are high, expansion may be an option
-cost analysis -> helps a business to identify if costs have risen or fallen and plan a strategy to solve cost issues
-making comparisons -> can be useful for investors to see a comparison of performance and where best to invest their capital
the statement of financial position (balance sheet)
a summary of the business's assets (what the business owns), liabilities (what the business owes) and capital (investment by owners) at a point in time

assets
what the business owns

liabilities
what the business owes

capital
investment by owners

non-current assets
assets that last more than a year
current assets
assets likely to be changed to cash within a year
inventories
this is the stock and raw materials a business is holding
trade receivables
money owed by customers to the company
current liabilities
debts that must be repaid within a year
Trade payables
Money owed to suppliers by the business
non-current liabilities
debts that are payable in more than 12 months
net current assets
current assets - current liabilities
net assets (NCA + CA) - (CL + NCL)
all assets - all liabilities
shareholder equity
all money owed to shareholders (share capital, retained profits and reserves)
capital employed
amount of money invested in a business
examples of current assets
vehicles, property, fixtures & fittings
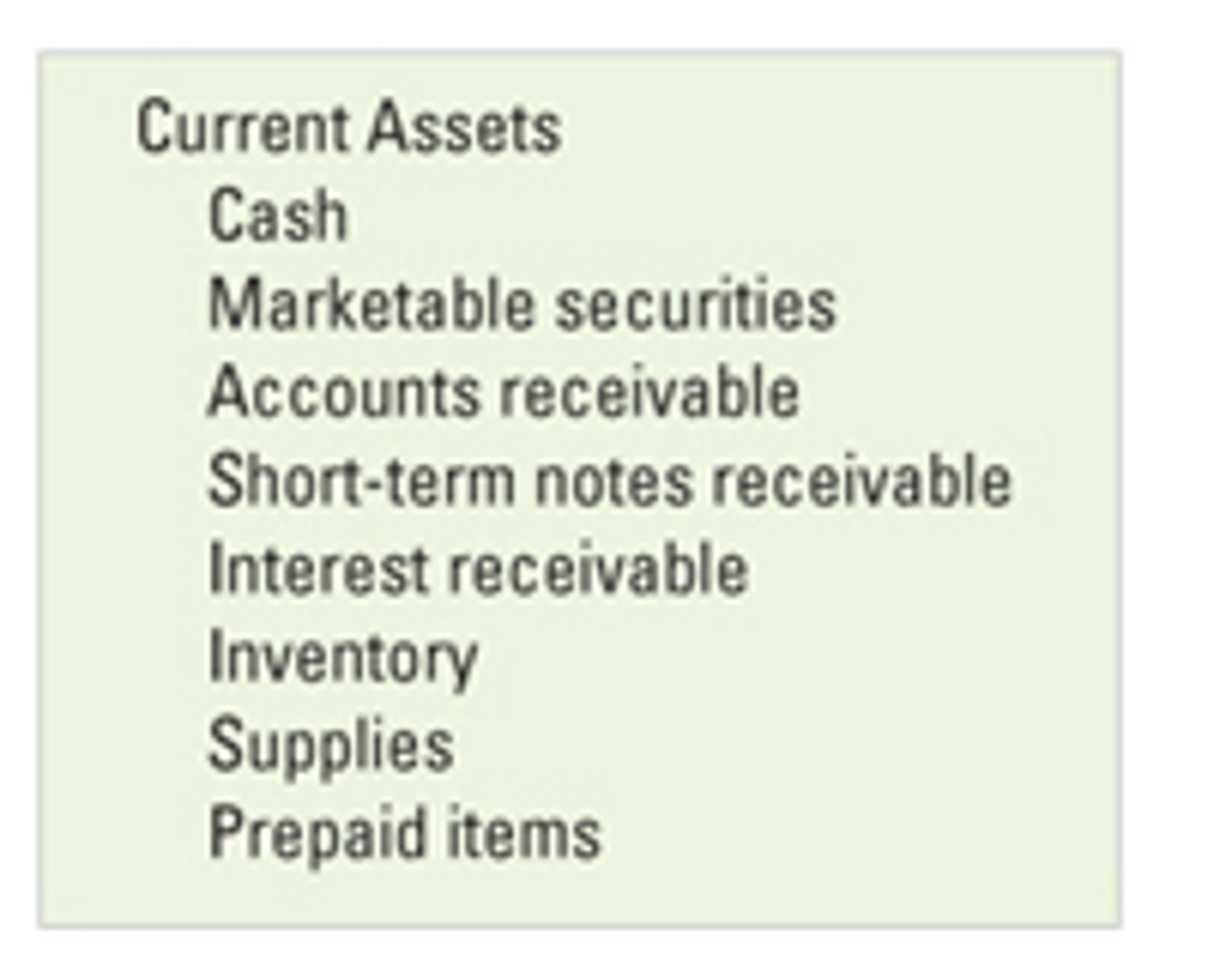
examples of non-current assets
inventories (stock), cash, trade recievables