developmental psychology ch2
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What are the important debates in developmental psychology?
Nature-nurture
Activity-Passivity
Continuity-Discontinuity
Universality-Context Specificity
Nature-nurture interactions:
Truth lies in between:
Gene environment interactions
Gene environment correlations
Epigenetics
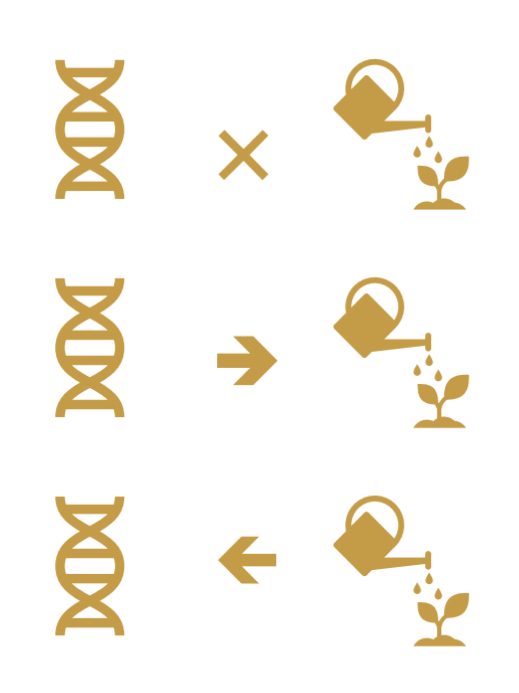
Gene environment interactions:
People with different genes are affected differently by environmental factors.
Gene environment correlations:
Passive genotype environment fit: Association between the inherited genotype of a child and the environment its raised in.
Evocative genotype environment fit: Association between genetically programmed behaviour and others’ reactions to that behaviour.
Active genotype environment fit
Association between an individual’s genetic tendencies and the environmental niches that they actively select.
Epigenetics:
Environment sensitive genes - gene expression can be changed by environmental influences across the lifespan.
Activity vs Passivity:
Does the person have an active or passive role in their development?
Ex. Identity developing in emerging adulthood - is it because the environment demands or the person?
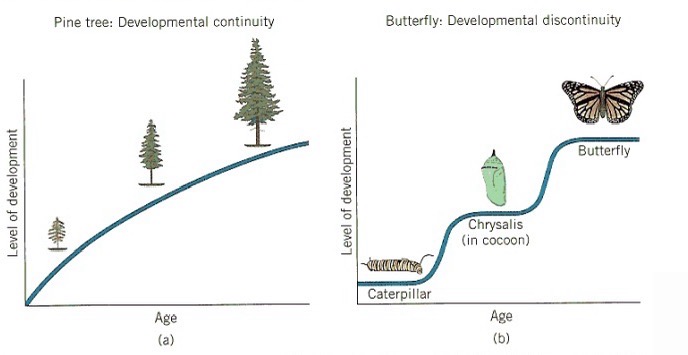
Continuity vs Discontinuity: How does development take place?
In a continuous way - Do individuals become quantitatively more/better/faster?
In a discontinuous way - Do individuals develop qualitatively different abilities at different times?
Universality vs Context specificity:
How universal or context specific is development? What is the role of culture, social context, etc for development?
What are some important theories in developmental psychology?
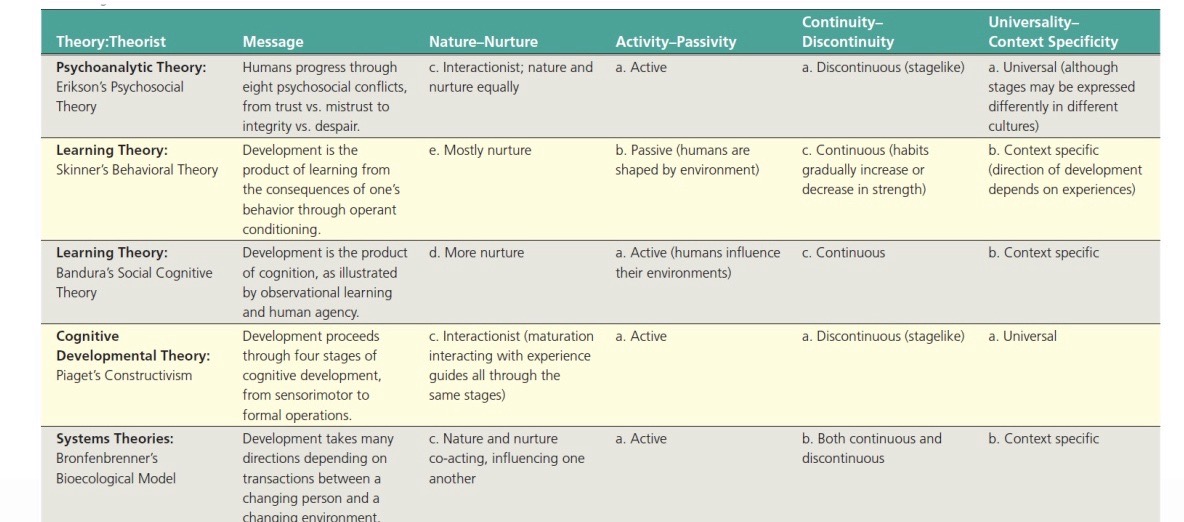
Erikson’s Psychosocial Development Theory
Learning theories: Behaviourism
Social-cognitive learning theory - Bandura
Ecological model by Bronfenbrenner
Cognitive Development by Piaget
Socio-cultural theory by Vygotsky
Social clock model
Selection, optimisation, compensation
Socio-emotional selectivity Theory
Erikson’s Psychosocial Development Theory
Personality develops throughout the lifespan, it’s influenced by culture, society, and history.
Development of personality is divided into 8 stages, where each includes a conflict.
If one stage was dealt with in maladaptive manner, the following ones could not be adequately attended = maladaptive individual.
Successful solution = virtues
Erikson’s stages of development:
Trust vs mistrust: Birth to 1 year - Can I trust others? Virtue - Hope
Autonomy vs shame and doubt: 1-3 years - Can I act on my own? Virtue - Will
Initiative vs guilt: 3-6 years - Can I carry out my plans successfully? Virtue - Purpose
Industry vs inferiority: 6-12 years - Am I competent compared to others? Virtue - Competence
Identity vs role confusion: 12-20 years - Who am I and where am I going? Virtue - Fidelity
Intimacy vs isolation: 20-40 years - Am I ready for a committed relationship? Virtue - Love
Generativity vs stagnation: 40-65 years - Have I given something to future generations? Virtue - Care
Integrity vs despair: 65 years and older - Has my life been meaningful? Virtue - Wisdom
Traditional Behaviourism:
Watson: Classical Conditioning. Development = learning associations. Love for parents due to good associations.
Skinner: Operant Conditioning. Development = individual’s learning experiences. Behaviour becomes more or less probable.
→ Reinforcement strengthens behaviour
→ Punishment weakens behaviour
Social-cognitive learning theory of Bandura
Humans learn through observational learning → Modeling (watching and imitating others)
Role of cognition: anticipation of consequences likely to follow behaviour.
Learners pay attention, construct and remember mental representations of what they saw. Active, cognitive role of learner.
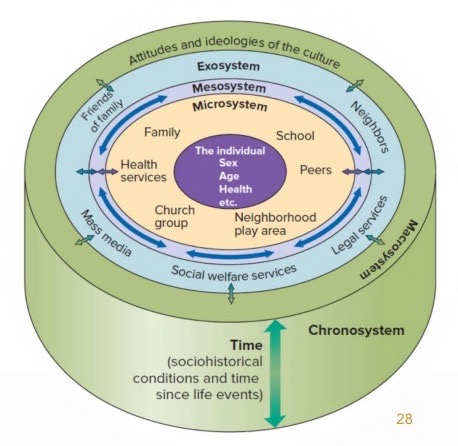
Ecological model by Bronfenbrenner
Identifies five environmental systems:
Microsystem – Immediate environments (e.g., family, school)
Mesosystem – Interactions between microsystems (e.g., parent-teacher interactions)
Exosystem – Indirect environments (e.g., parent’s workplace, media)
Macrosystem – Cultural values, laws, ideologies
Chronosystem – Time-related changes (e.g., historical events, life transitions)
What are the contributions of the Ecological Model?
Systematic examination of micro and macro dimensions of environmental systems.
Attention to connections between environmental systems.
Emphasis on other social contexts than family.
Critic of the Ecological Model
Influence of biological and cognitive factors underestimated → addition of biological influences in later versions
Theories specific to different periods of the lifespan:
Childhood: Cognitive Development by Piaget, Socio-cultural theory of Vygotsky
Middle age: Social clock model
Older age: Selection optimisation compensation, Socio-emotional selectivity
How does cognition develop according to Piaget?
Universally fixed order of phases → discontinuous development
Each phase qualitatively different
Child actively contributes to own knowledge formation (little scientist)
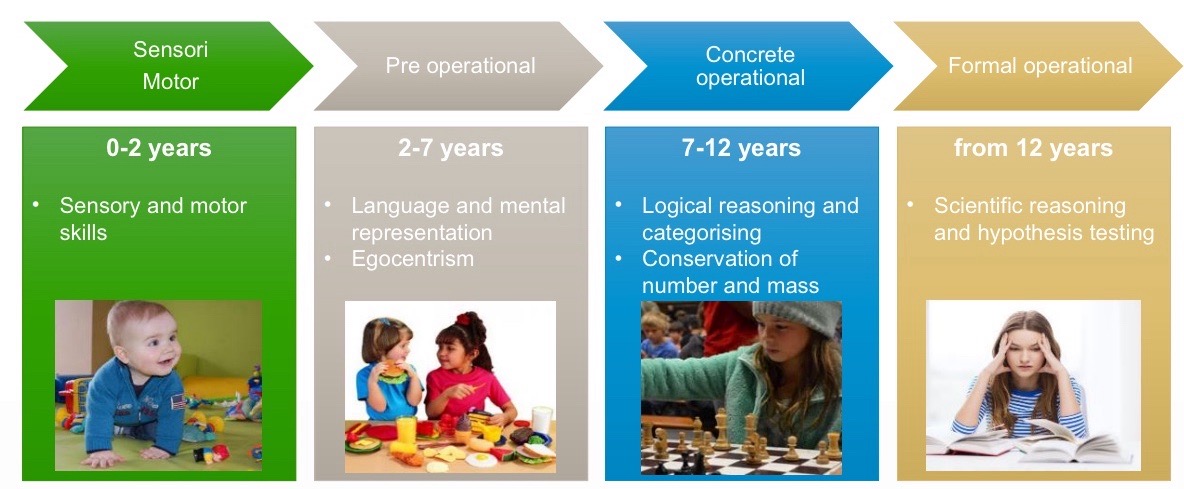
Impact of Piaget - Education:
School age (6-7 yr old): Start concrete operational phase: learning to read, write, and calculate.
Start high-school (12-13 yr old): Start formal operational phase: scientific reasoning
Boosted research on cognitive development.
Socio-cultural theory of Vygotsky:
Educator that was inspired by socialism
Children actively develop intellectually by interacting with their sociocultural environment
Development is a shared process (of the one who learns + the environment)
People around us enable our cognitive growth: adults make children mentally advance
Zone of proximal development (Vygotsky)
Gap between the child’s ability to solve a problem on its own and the potential development that they can make with the help of someone else.
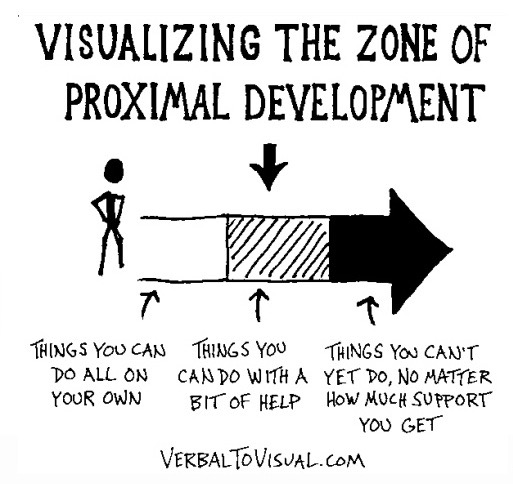
Scaffolding (Vygotsky):
Degree of support adapted to child’s level of ability and degree of support is reduced gredually.
Language use by parents stimulates cognitive development, children learn via “inner speech”: words migrate inwards.
Social clock model by Neugarten
Shared societal expectations which tasks should be fulfilled in which age = Normative time schedule.
Persons compare themselves with others and the normative time schedule.
Violations of the normative time schedule = social disappointment
Fitting with normative time schedule = social support
Developmental tasks as social expectations:
Adulthood is determined by biological and external regulations compared to childhood.
Adults have more freedom to create their development and adjust to it.
Social norms and expectations can set the frame for these decisions.
Theories on aging:
Aging is accompanied by age-related losses - theories focus on psychological and behavioural processed in adapting to and maintaining performance on functional tasks.
Selection, Optimisation, Compensation Model
Psychological and behavioural processes in adapting to age-related losses and disabilities, maintaining performance on functional tasks.

Socio-emotional selectivity theory - Carstensen
The approach of ending, due to aging, makes us change our priorities and motivations.
Emotionally meaningful goals are prioritised over exploration.
→ Effects on preferences, social networks, and emotional experience
→ Positivity effect in cognitive processing of older adults: Pay more attention to, better remember, and place more priority on positive information.
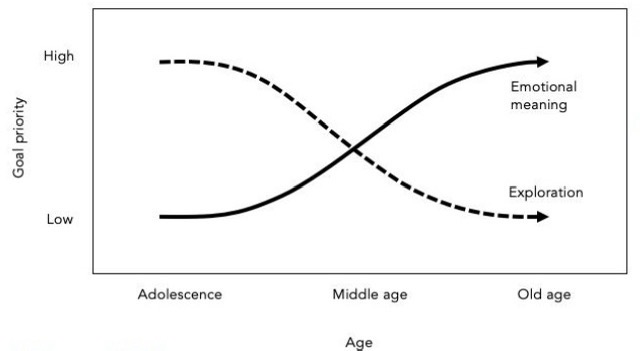
Table on theories