Neonatal and Infant Development: Physical, Cognitive, and Psychosocial Milestones
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
What are the primary developmental tasks of a neonate?
Bonding, growing, developing, eating, sleeping, attaching, and communicating.
What is the average birth weight of a newborn?
7.5 lbs (3400g)
What is the significance of birth weight in infants?
It is the best predictor of infant survival and healthy development.
What percentage of weight can a newborn lose after birth?
Up to 10% of their birth weight.
How long does it typically take for a newborn to return to their birth weight?
By 2 weeks of life.
What risks are associated with a birth weight of less than 3.5 lbs (1500g)?
Increased risk for brain abnormalities, delayed growth, frequent illnesses, sensory or motor impairments, and language or learning delays.
What is the average birth length of a newborn?
20 inches.
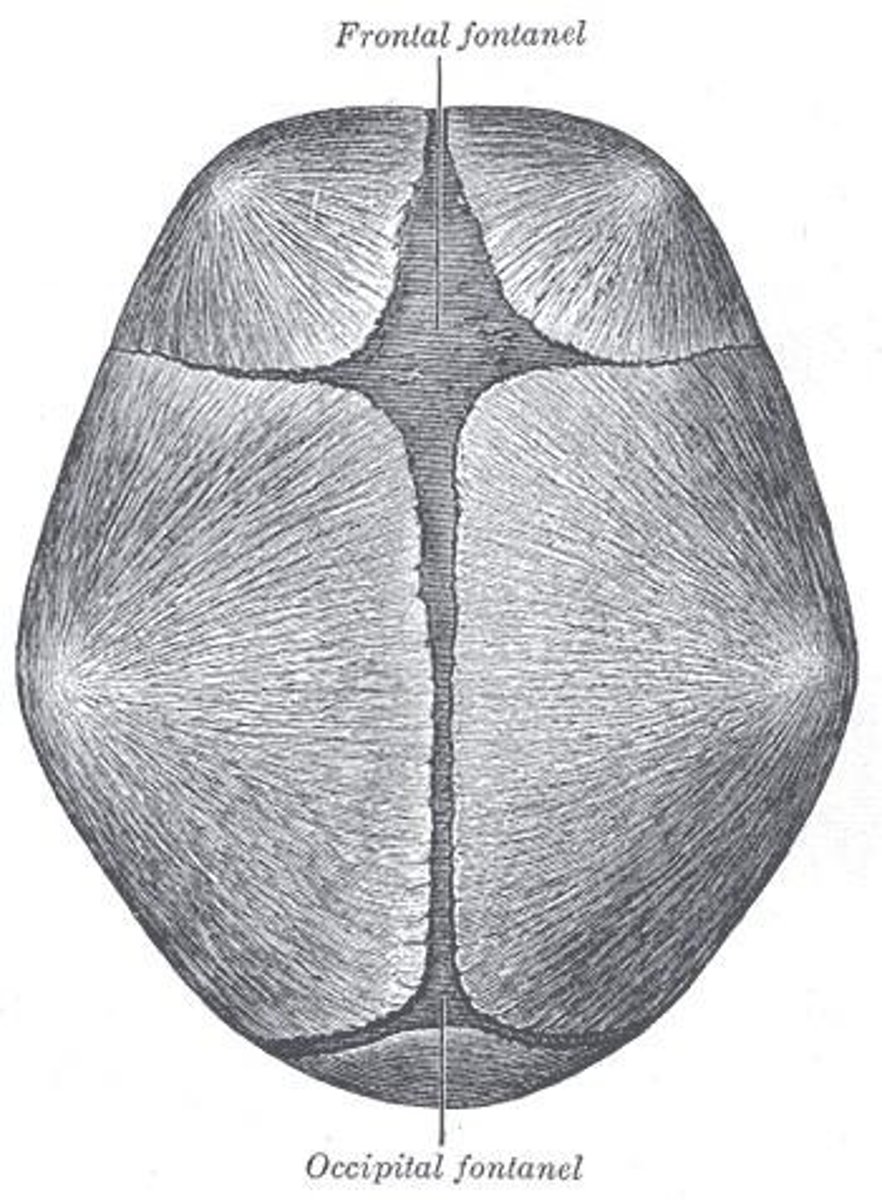
What are some selected physical characteristics of newborns?
Average head circumference of 13-14 inches, presence of anterior and posterior fontanels, and skin conditions like acrocyanosis and lanugo.
What gastrointestinal characteristic affects feeding in newborns?
Delayed gastric emptying and low tone of the esophageal sphincter, leading to increased regurgitation.
What is meconium?
The first stool of a newborn, consisting of products from intrauterine life.
How does a newborn receive immunity?
Through antibodies from the mother during the third trimester and from breast milk postnatally.
What is the risk of infection for newborns?
Newborns are at very high risk for infection, which reduces as they approach 3 months of age.
What is the pattern of myelination in newborns?
It follows a cephalocaudal-proximodistal pattern, developing from head to toe and center to periphery.
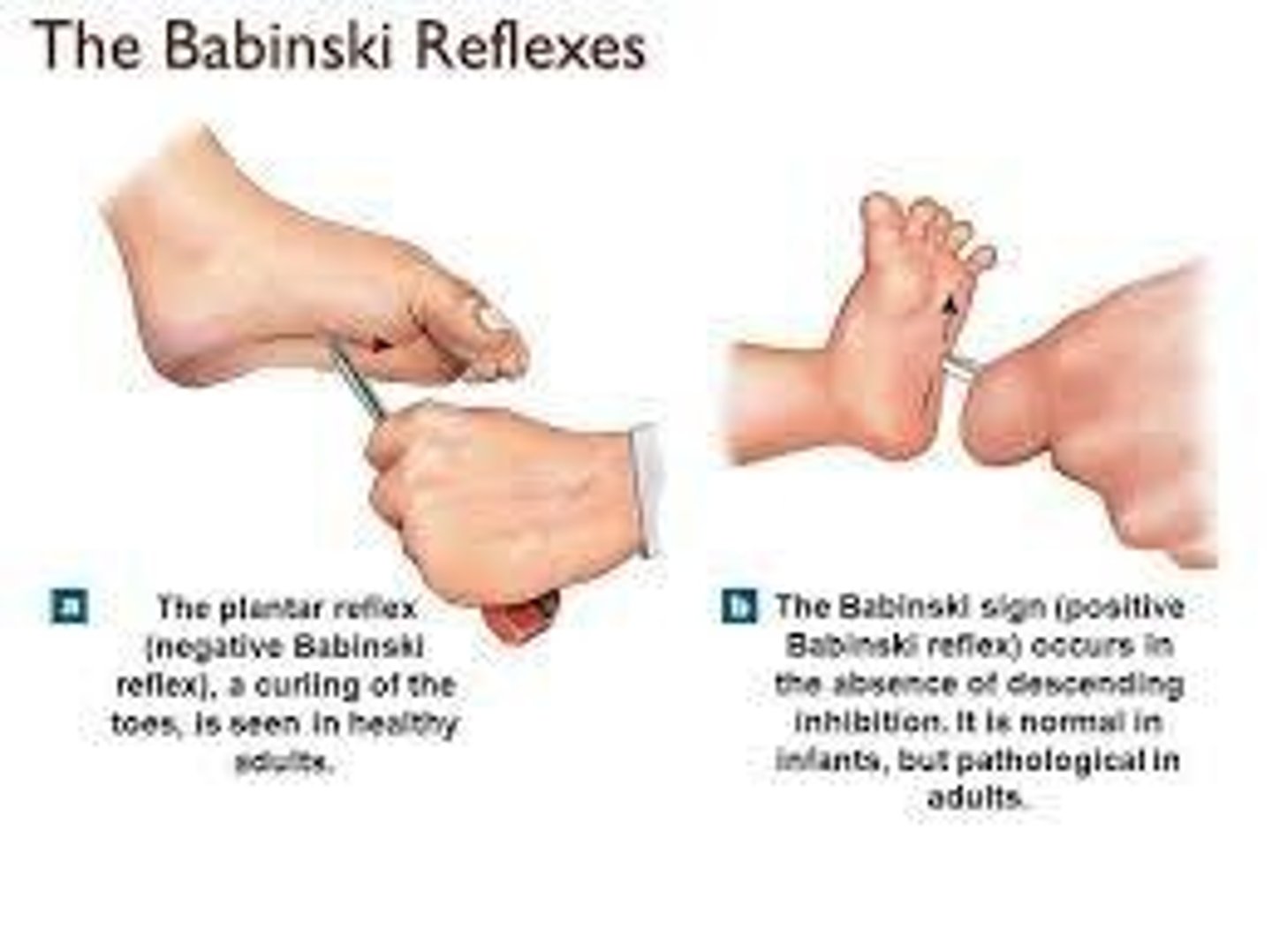
What are some primitive reflexes present at birth?
Moro reflex, tonic neck reflex, rooting reflex, sucking reflex, Babinski reflex, grasp reflex, and stepping reflex.
At what age does the Moro reflex typically disappear?
Around 3 months.
What is the definition of prematurity in newborns?
Birth before 37 weeks of gestation.
What is the difference between low birth weight and preterm infants?
Low birth weight infants weigh less than 2500 grams, while preterm infants are born before 37 weeks gestation.
What are some complications associated with neonatal jaundice?
Impaired ability to rid the body of bilirubin, potentially leading to kernicterus and neurological damage.
What are some implications of attachment and bonding in neonates?
Medical interventions may hinder bonding; special infant stimulation techniques can help improve attachment.
What are some cultural practices related to newborn care?
Practices vary widely; examples include specific rituals, feeding methods, and bonding techniques.
What is kangaroo care?
Skin-to-skin contact between the parent and the infant to promote bonding and warmth.
What are the four sensory capacities of newborns?
Touch, Taste/Smell, Vision, Hearing
How sensitive are newborns to pain?
Newborns are highly sensitive to pain.
What visual preference do newborns have?
Newborns see best close up and prefer geometric shapes with distinct colors.
What is the average sleep duration for newborns?
Newborns sleep 16-20 hours per day.
What are the states of arousal for newborns?
Drowsiness, Quiet Alert, Regular Sleep, Waking Activity
What is one method to soothe a crying baby?
Swaddling, rocking, or non-nutritive sucking.
What is the recommended feeding schedule for breastfed infants?
Breastmilk is best, typically every 2-3 hours.
What is the significance of the 'Trust vs Mistrust' stage in infancy?
Trust develops when basic needs are met; mistrust develops when they are not.
What are the key components of neonatal health promotion?
Nutrition, screenings, immunizations, safe sleep, and accident prevention.
What is the purpose of congenital heart defect screening?
To detect congenital heart defects early.
What is the recommended position for infants in car seats?
Infants should be placed in rear-facing car seats in the back seat.

What is Shaken Baby Syndrome?
A condition caused by shaking a baby, leading to brain injury and potentially death.
What are the physical growth milestones for infants by 1 year?
Weight triples to ~22 lbs and height increases by 50%.
What is the cephalocaudal growth trend?
Developmental trend where growth occurs from head to toe.
What are some gross motor developmental milestones for infants?
Sitting alone steadily by 6 months, standing with support by 8 months, and walking by 12 months.
What fine motor skill develops around 8-9 months?
Emergence of the pincer grasp.
What is the importance of 'en face' interactions?
They are crucial for developing attachment and bonding between parent and infant.
What should never be given to infants as a drink?
Water; only breastmilk or formula is recommended.
What is the role of the 1,000 days campaign in neonatal health?
To encourage breastfeeding and proper nutrition during the critical early days.
What are some signs that a baby might be hungry?
Crying, rooting, and sucking on hands.
What is the average height increase for infants per month?
Approximately 1 inch per month.
What is the purpose of well-child visits?
To monitor growth, development, and vaccinations.
What is the significance of the heel-stick screening?
It identifies serious conditions before symptoms appear.
What are the effects of neglecting a baby's basic needs?
It can lead to mistrust and developmental issues.
What are the main characteristics of Piaget's Sensorimotor Stage?
Infants think with their senses, use organized schemes to make sense of experiences, and adapt schemes through new actions.
What is the significance of schemes in Piaget's theory?
Schemes are action patterns that evolve as infants learn to interact with their environment.
What are the substages of Piaget's Sensorimotor Stage?
1) Reflexive schemes (birth-1 month), 2) Primary circular reactions (1-4 months), 3) Secondary circular reactions (4-8 months), 4) Coordination of secondary circular reactions (8-12 months).
What is object permanence and when does it develop?
Object permanence is the understanding that objects continue to exist even when they cannot be seen, developing around 8-12 months.
How does play contribute to infant development?
Play fosters healthy physical and cognitive growth and strengthens the parent-infant relationship.
What are appropriate play activities for a 4-5 month old infant?
Activities include bouncing in a lap, playing with soft toys, and engaging in interactive games like peek-a-boo.
What are the sensory capacities of infants at 2-4 months?
Infants can focus on objects, locate sounds by turning their head, and prefer familiar voices and faces.
What are the stages of language development in infancy?
Stages include cooing and crying (2 months), babbling (4-6 months), recognizing names (7-8 months), and saying a few words (12 months).
What are signs of a possible communication disorder in infants?
Delayed babbling, lack of response to names, or inability to follow simple directions may indicate a communication disorder.
What is the typical sleep pattern for infants during the first year?
Most infants develop a sleep pattern between 12 am-5 am, with total daily sleep averaging around 15 hours.
How do cultural influences affect infant sleep practices?
Cultural practices vary, with some cultures promoting co-sleeping for bonding, while Western practices often encourage separate sleeping.
What is Erikson's psychosocial crisis of infancy?
The crisis of trust vs. mistrust, where consistent meeting of basic needs fosters trust, while inconsistency leads to mistrust.
What role does attachment play in infant development?
Attachment influences emotional and social development, with infants recognizing and preferring primary caregivers.
What are the behavioral characteristics of infants at 6-9 months?
Infants show stranger anxiety, respond to facial expressions, and look to parents in new situations.
What are appropriate disciplinary strategies for infants?
Distraction for infants under 6 months and firm voice with eye contact for those over 6 months, with consistent limits.
What is the recommended nutrition for infants during the first 6 months?
Exclusive breastfeeding or formula feeding is recommended, with iron supplementation if necessary.
When should solid foods be introduced to an infant's diet?
Solid foods should be introduced after 6 months, when the infant can sit well and the tongue extrusion reflex disappears.
What types of foods should be introduced to infants at 9-10 months?
Finger foods should be introduced, along with meat and eggs by 11 months.
What is the importance of family mealtime for infants?
Eating at the table with family promotes social interaction and healthy eating habits.
At what age do primary teeth typically begin to erupt?
5-7 months
Which primary teeth are the first to erupt?
Lower central incisors
What are common signs of teething discomfort?
Drooling, gnawing, irritability, trouble sleeping, low-grade temperature, decreased appetite
What can be offered to soothe teething discomfort?
Teething rings and cool washcloths
What are nursing caries?
Cavities caused by putting a child to sleep with a bottle containing breastmilk, formula, or juice
What are the recommended ages for well-child visits according to AAP?
1, 2, 4, 6, 9, and 12 months
What is monitored during well-child visits?
Growth, development, and parental education
When does the recommended immunization schedule begin?
Right after birth
What is the safest sleep position for infants?
On their back
What should not be done with bottles during feeding?
Do not prop bottles
What is a key prevention strategy for Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS)?
Creating a safe sleep environment and using a pacifier
What is the safest location for a car seat in a vehicle?
Back seat middle
What should be checked to prevent burns in infants?
Water temperature for baths
What is a common choking hazard for infants?
Small, round foods like grapes and hotdogs
What developmental milestone is indicated by an infant passing a rattle from one hand to the other?
Development of hand coordination
What reflex is positive when an infant's foot is stroked?
Babinski reflex
What should be done to prevent falls in infants?
Constant supervision near bodies of water and securing furniture
What is a recommended activity for infants to promote development?
Supervised tummy time
What is a common behavior of infants when their mother leaves the room?
Crying
What should be avoided when feeding infants to prevent choking?
Foods that are small and odd shapes