brain and cranial nerves -ANAT
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
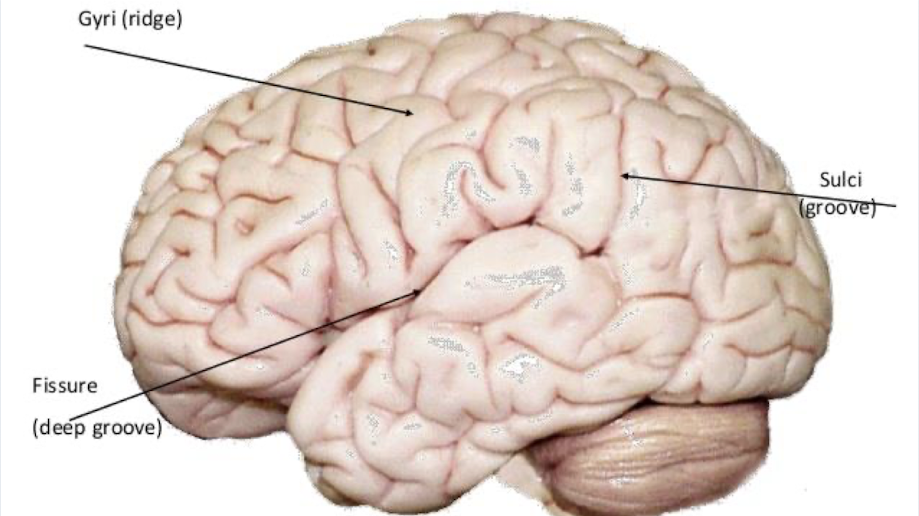
what are the 3 brain surface structures?
gyrus: ridges on brain surface
sulcus: grooves between gyri
fissures: deep sulci between gyri
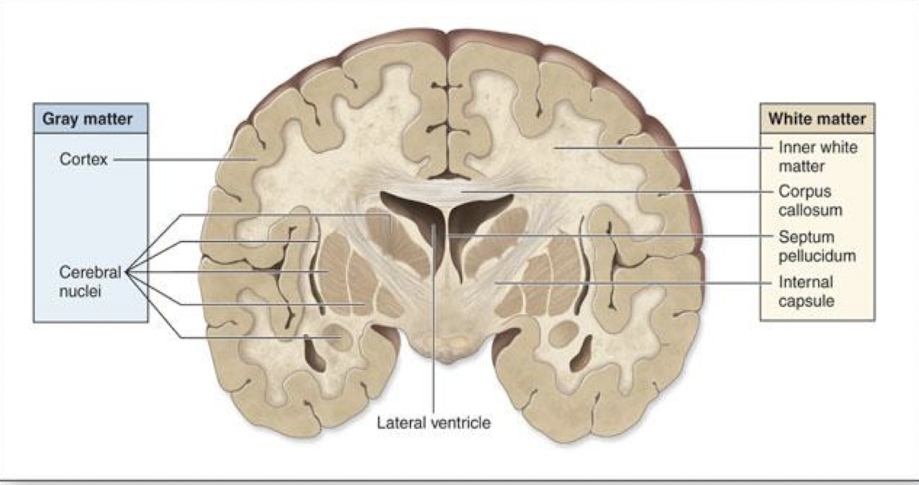
what does gray matter and white matter consist of
gray matter: cell bodies, dendrites, and unmyelinated axons of neurons
white matter: myelinated axons of neurons
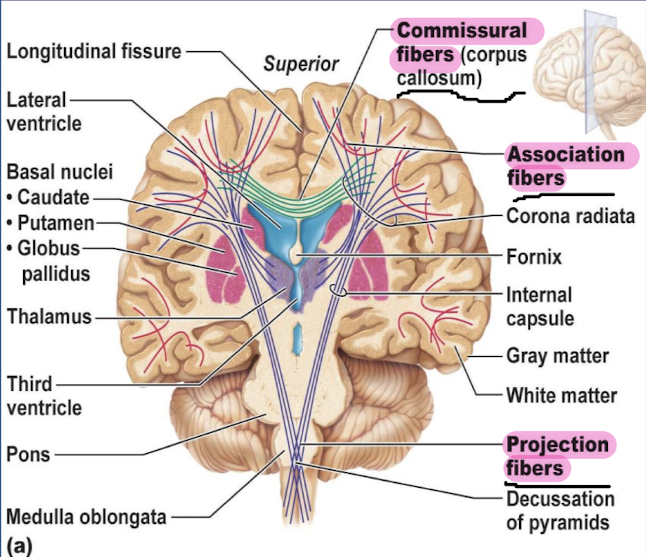
what are the neuronal tracts and what 3 fibers do they contain?
neuronal tracts: axons in the white matter are grouped in bundles/fibers.
association fibers: connect different parts of the same hemisphere
commissural fibers: connect corresponding areas of the two hemispheres
projection fibers: link cerebral cortex to lower brain regions and spinal cord
whats the cerebrum
it is the main part of the brain located in the front area of the skull, it has 2 cerebral hemispheres which are divided by the longitudinal fissure
what are the layers of the cerebrum and what matter does it contain?
Cerebral cortex: superficial layer of the cerebrum which is composed of gray matter
Cerebral Medulla: deep layer of cerebrum, composed of white matter
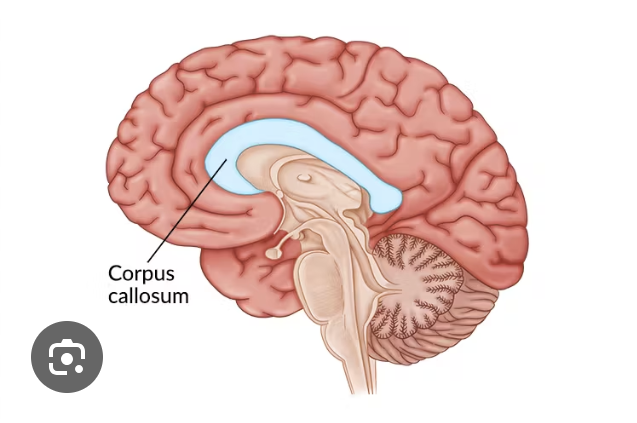
whats the corpus callosum ?
it is a bundle of axons that connect the right and left cerebral hemispheres
what are the 5 lobes and what 2 sulci are there on the cerebrum ?
the 5 lobes are frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal, insula
Central sulcus divides the frontal and parietal lobes
Lateral sulcus divides the frontal/parietal lobes from the temporal lobe
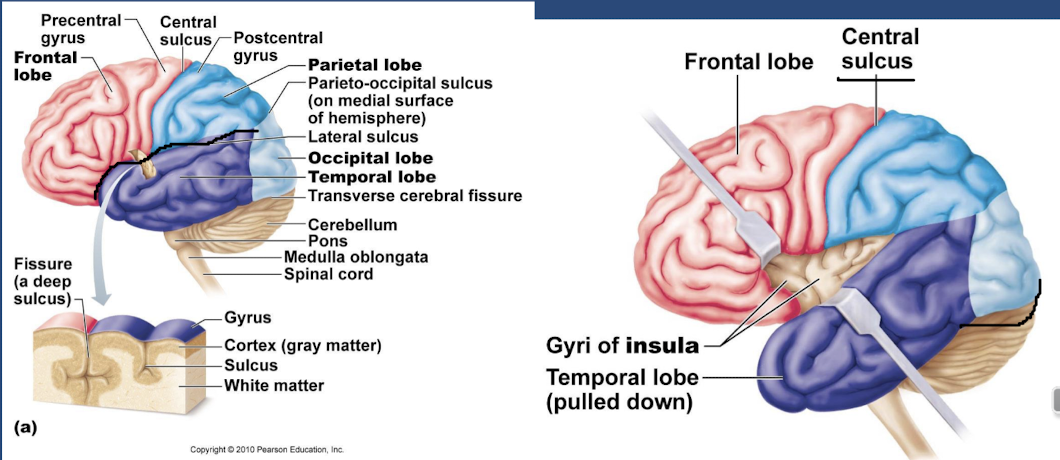
what is the frontal lobe responsible for and where is it?
it is the most anterior lobe of the brain, it gives voluntary motor functions, decision making and planning, as well as personality
what are 2 important areas in the frontal lobe and explain what it is in charge of ?
precentral sulcus: it is the location of the primary motor cortex which controls majority of motor functions
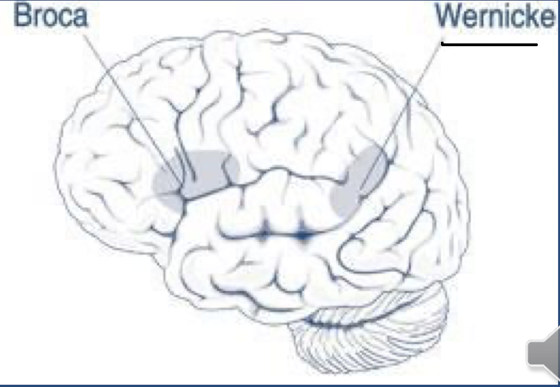
broca’s area: controls muscles used for speech and only present on one side (usually left side)
whats the function and location of the parietal lobe ?
it gives general sensory info for touch, pain, and temperature
what are the 2 important areas for the parietal lobe, and explain them?
postcentral gyrus: contains primary somatosensory cortes, processes touch, pain and temp
wernicke’s area: comprehension of written/spoken language, partially in the temporal lobe
it is after the frontal lobe, before the occipital lobe
whats the function and location of the temporal lobe ?
it functions in giving primary auditory perception, olfaction, and emotional association. It is on the bottom.
whats the functions and location of the occipital lobe
it is the most posterior lobe of the brain. it functions by processing visual info, and stores visual memory
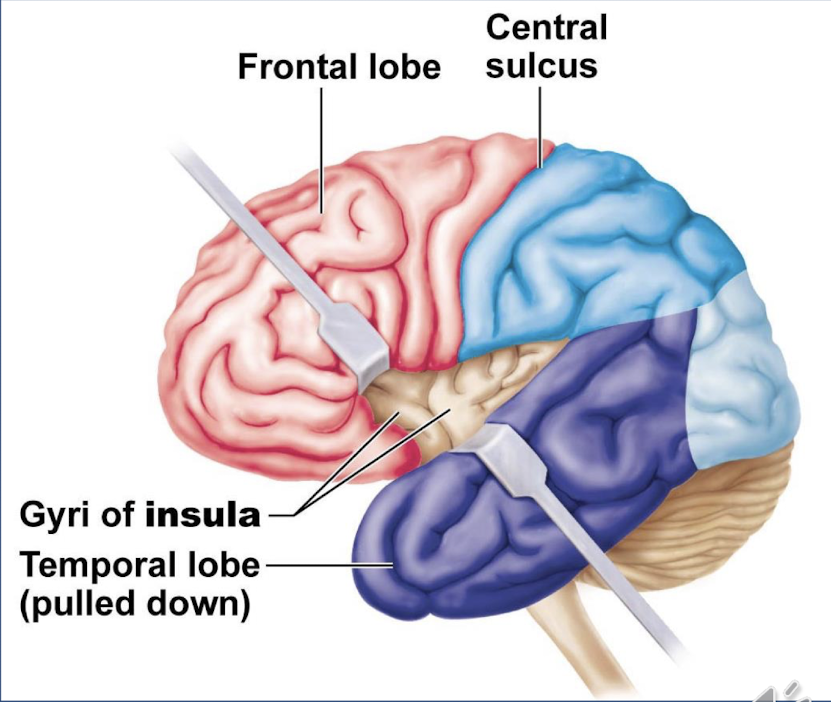
whats the insula and where is it? (hidden one!)
it is located deep the to lateral sulcus, it gives memory and interpretation of taste
what are the 3 regions of diencephalon?
epithalamus, thalamus and hypothalamus
whats the thalamus
it relays both motor and sensory info to and from the cerebrum, it contains specific nuclei from various functions
whats the epithalamus
it is the structure behind the thalamus, contains the pineal gland which secretes melatonin for circadian rhythm (sleep)
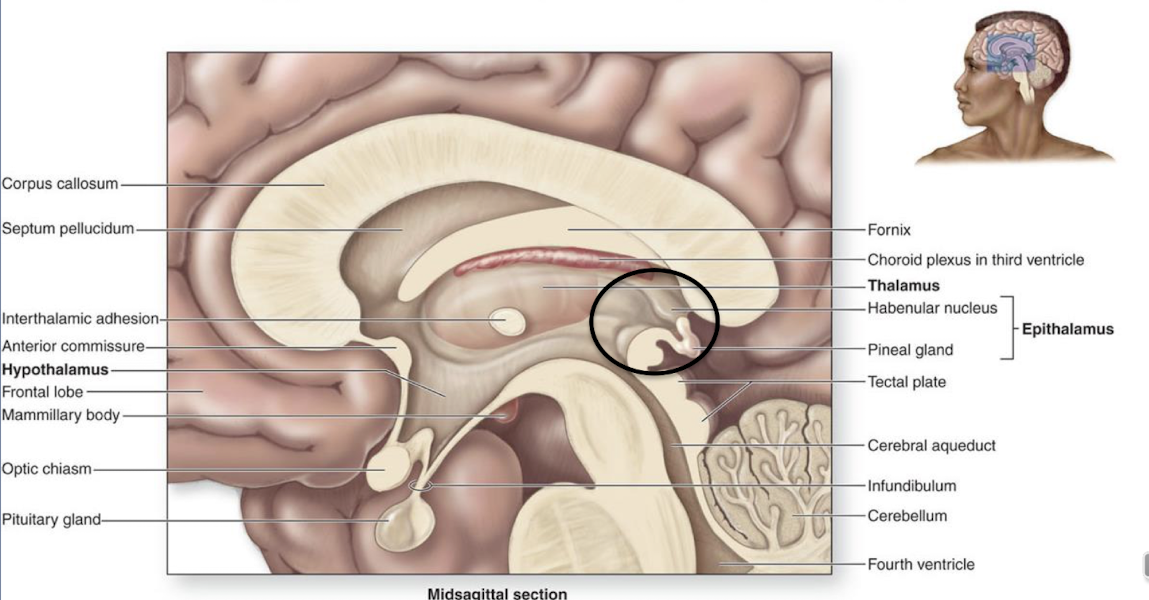
whats the hypothalamus
it contains main nuclei with a variety of functions including appetite, and temperature, it is important for maintaining homeostasis. It connects the nervous system to the endocrine system through the pituitary gland (pituitary hormones control several other hormone glands)
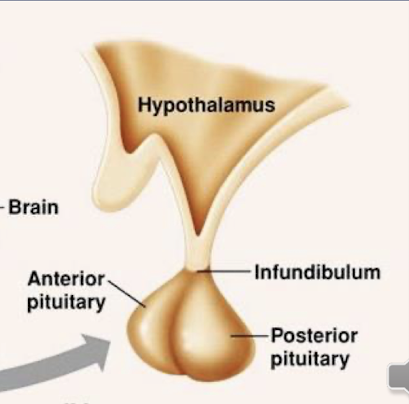
whats the limbic system
it is a group of structures on the cerebrum and diencephalon. It is our “emotional brain”, which allows us to generate emotions, and connects emotions to senses
what 3 regions are in the brainstem
the midbrain, pons and medulla oblongata
what consists of the midbrain ?
midbrain: superior most portion of brainstem
cerebral aqueduct: it essentially the central midbrain
here are some posterior structures…
corpora quadrigemina: consists of the paired superior colliculi and inferior colliculi
superior colliculi: is the visual reflex center, which tracks moving objects, movement of eyes and head in response to visual stimulus
inferior colliculi: auditory reflex center, movement of body in response to sound
what is the pons ?
it is the middle portion of the brainstem, it acts as a respiratory center for the body, controls the skeletal muscles used for breathing, and works with the medulla oblongata
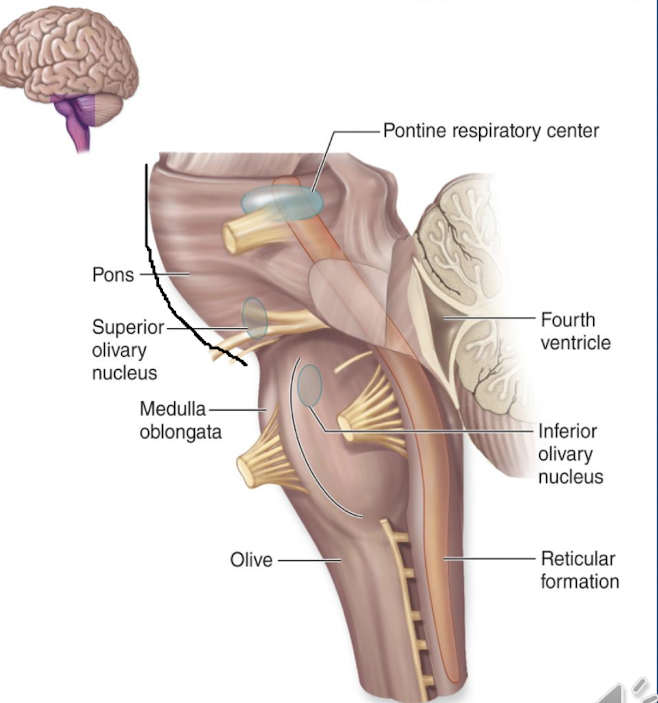
what makes up the medulla oblongata and what are the 3 vital centers?
it is the most inferior portion of the brainstem (continuous with spinal cord), it has multiple vital centers: cardiac center, vasomotor center, and respiratory center
explain the cardiac center, vasomotor center, and respiratory center
cardiac center: regulate heart rate and strength of contraction
vasomotor center:regulate blood vessel diameter
respiratory center: rate of respiration (works with Pons)
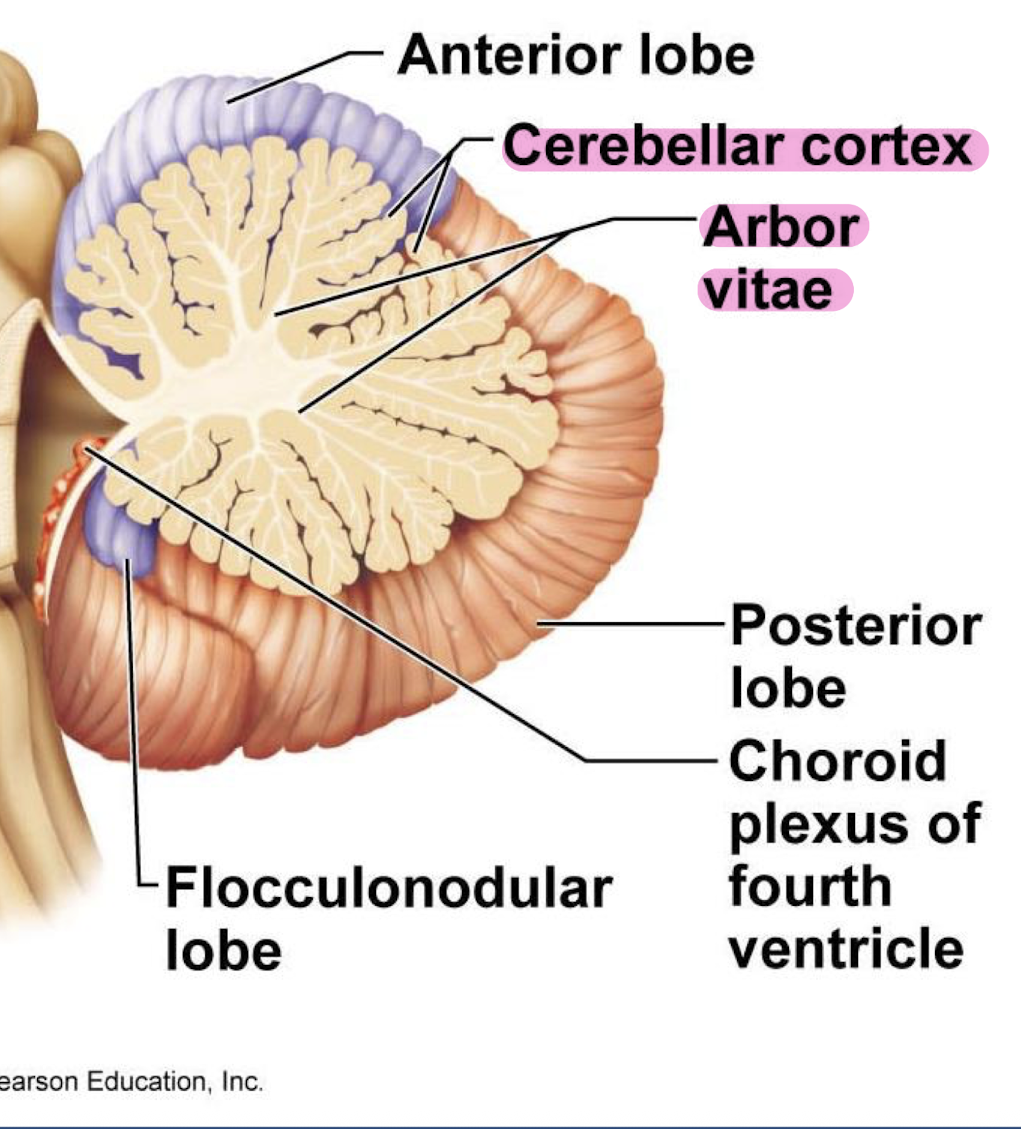
what is the cerebellum?
it is the 2nd largest part of the brain, and contains two cerebellar hemispheres (which are connected by vermis), it functions in fine tune skeletal movements, provides feedback to cerebrum, and maintains equilibrium and posture
what are the effects of alcohol on cerebellum?
loss of gait: cant walk straight or smooth
loss of balance and posture: cant stand on one foot
Inability to detect proprioceptive info: cant close eyes or touch nose
what is the cerebellar cortex and arbor vitae?
cerebellar cortex: outer gray matter
arbor vitae: inner white matter (looks like tree)
what are cranial meninges and what are the 3 layers ?
they are a series of protective coverings on the brain that extend from the brain to the skull. there are 3 layers: pia mater, arachnoid mater and dura mater.
what is meningitis?
it is an infection or inflammation of meninges
whats the pia mater, arachnoid mater and dura mater ?
PIA MATER: “soft mother”, innermost layer which adheres directly to the brain
ARACHNOID MATER: middle layer superficial to pia mater
subarachnoid space: space between arachnoid and pia maters (contains cerebrospinal fluid)
arachnoid trabeculae: web of elastic fibers that extend into subarachnoid space
DURA MATER: tough, superficial-most layer
periosteal layer: next to skull
meningeal layer: lies deep to periosteal layer
subdural space: between dura and arachnoid maters
subdural hematoma: blood accumulates in subdural space
what are dural venous sinuses?
Within the dura mater there are separations between the periosteal and meningeal layers that drain blood and CSF from the brain
whats the cranial dura septa? and what are the 2 structures of it?
they are just extensions of the dura mater and meningeal dura mater, that leads into the cranial cavity
falx cerebri: extends into the longitudinal fissure, separating the right and left hemispheres of the brain
tentorium cerebelli: between the cerebrum and cerebellum
whats the ventricular system and what are the 4 types
the ventricular system is a series of cavities in the brain that hold cerebrospinal fluid
There are 2 lateral ventricles )one in each hemisphere)
Third ventricle: located between the two thalami
Cerebral aqueduct: located in the midbrain
Fourth ventricle: located between the pons and cerebellum
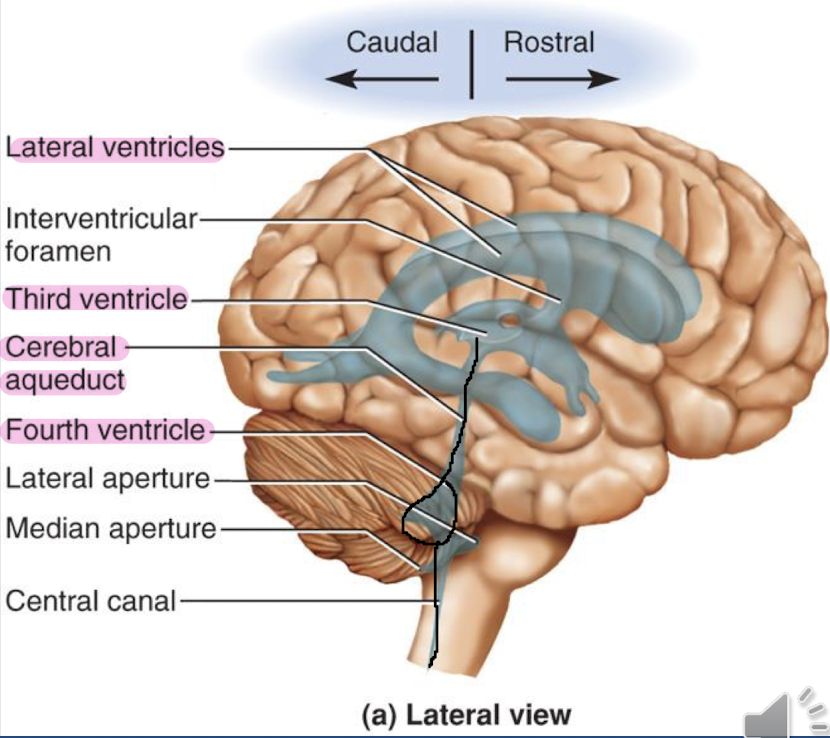
what is the central canal
it starts in the medulla oblongata and runs through the spinal cord (small hole in middle of spinal cord and long canal in the brainstem).
what is the cerebrospinal fluid and its functions?
it is a clear filtrate that circulates in ventricles and subarachnoid space, complete volume is replaced approximately every 8 hours.
functions
buoyancy: keeps brain afloat
reduces brain weight by 97%
protection: slows movement of skull
* similar to tofu being in a liquid *
how is CSF produced ?
it is produces by the choroid plexus:
capillaries located in each ventricle that filters plasma from the blood to form CSF
plasma is retrieved by arachnoid villi that extend into the superior sagittal sinus
what is CSF circulation?
1) CSF produced in ventricles and flows through ventricles
2) flows form fourth ventricle into central canal
3) CSF returned to the blood through arachnoid villi into dural venous sinus
fill in this chart
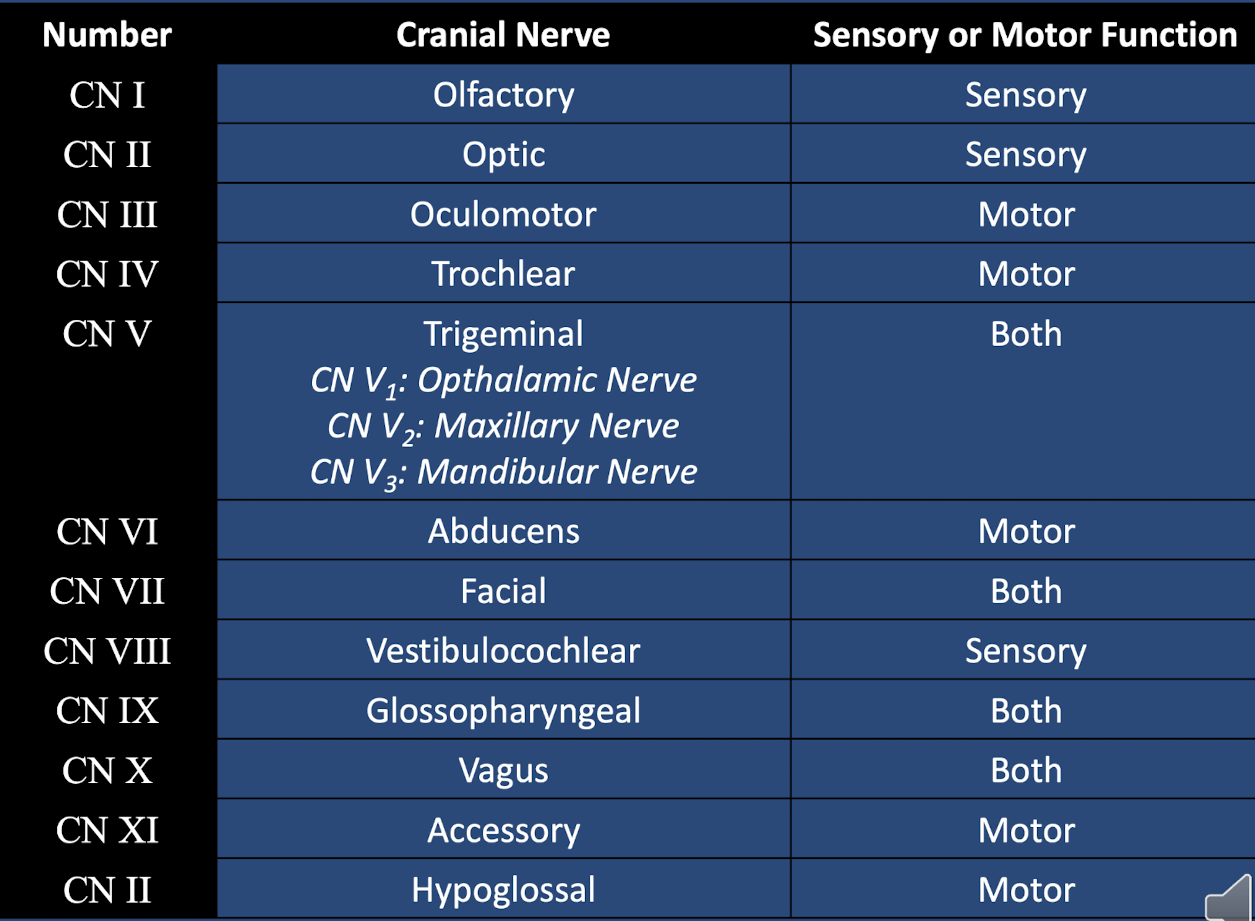
what is the olfactory CN I ?
sensory: smell
entrance/exit: olfactory foramina in cribriform plate of ethmoid bone
whats optic CN II?
sensory: vision
origin: retina
entrance/exit: optic canal of sphenoid bone
whats the oculomotor CN III?
motor: controls eye movement, eyelid raising, and pupil construction
innervates medial rectus, superior/inferior rectus, inferior oblique
entrance/exit: superior orbital fissure of sphenoid bone
whats the trochlear CN IV?
motor: innervates superior oblique eye muscle
entrance/exit: superior orbital fissure of sphenoid bone
whats the trigeminal CN V ?
motor: jaw movement/innervates muscles of mastication
sensory: touch, temp and pain
opthalamic divison V1: cornea, nose, forehead, scalp (forehead region)
maxillary division V2: nasal mucosa, palate, gums and cheek (maxillary region)
Mandibular division V3: sensation to face at mandible region
origin: level of the pons
entrance/exit:
opthalamic V1-superior orbital fissure of the sphenoid bone
V2 maxillary branch- foramen rotundum of the sphenoid bone
V3 mandibular branch- foramen ovale of the sphenoid bone
what is abducens CN VI?
motor: innervates lateral rectus eye muscle
origin: pons
entrance/exit: superior orbital fissure of sphenoid bone
whats facial CN VII?
sensory: taste to anterior 2/3 of tongue
motor:
innervates muscle of facial expression
secretions of lacrimal and salivary glands
entrance/exit: internal acoustic meatus of the temporal bone to the stylomastoid foramen of the temporal bone
whats vestibulocochlear CN VIII?
sensory: hearing and equilibrium
origin: vestibule and cochlea of inner ear
entrance/exit: internal acoustic meatus of temporal bone to pons
glossopharyngeal CN IX?
origin: medulla oblongata
sensory: taste to posterior 1/3 of tongue, monitor oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in blood
motor: innervates pharynx muscle, regulate secretions of parotid gland
whats vagus CN X? (LV BUFFET!!)
Entrance/exit: jugular foramen
sensory: taste
motor: helps with swallowing
what is the accessory CN XI?
entrance/exit
spinal root enters through foramen magnum of occipital bone
entire nerve exits through jugular foramen of the skull
motor:
cranial root: muscles of pharynx
spinal root: sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles
whats the hypoglossal CN XII ?
entrance/exit: hypoglossal canal of the occipital bone
motor: innervates intrinsic and extrinsic tongue muscles