brain bee full set
1/368
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
369 Terms
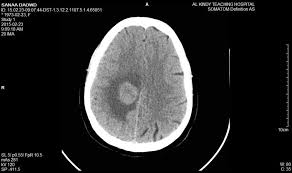
CT scan(cat scan) pros
3d X-RAY
Diagnostic of changes over time
Noninvasive and quick
CT scan(cat scan) clinical uses
See hemphorages( internal bleeding)
See tumor
See fractures and such
Damage to the meniges(increase contrast on picture)
DTI( diffusion tensor imaging) pros
See the movement of water in white matter
Helps see which parts of the brian are connected
noninvasive
DTI( diffusion tensor imaging) clinical uses
Helps see MS and tumors
Pre surgical planning
EEG(Electroencephalography) pros
Non invasive
See electrical acitivty of the regions of the brain by attaching electrodes to the head
Captures millisecond changes important for diagnosing
EEG(Electroencephalography) clinical uses
Diagnosing epilepsy and seizure disorders
Sleep disorders
PET scan pros
Help see if certain parts of the brain are functioning correctly(based on metabolic activity)
Sensitive to early changes in diseases
PET scan clinical uses
Diagnosing alzheimers(dementia)
Differentiate harmful and nonharmful tumors
Diagnosing cognitive decline
MRI pros
High detailed imagery of brian tissue allowing to easily see abnormalities
3d
Sensitive to changes
MRI clinical uses
Spotting tumors
Diagnosing MS
FMRI BOLD
Detect changes in blood oxygenation(BOLD)
BOLD(detects the decrease of deoxyhemoglobin,less oxygenated blood, as oxyhemoglobin floods the area)
Blood oxygenation level dependent
FMRI clincal uses
surgical planning and mapping brain area functions
Alcohol
Dampen excitatory signals and increase inhibitory signals
Antagonist to exictarory receptors and agonist to inhibitor receptors
relaxtion
Rohypnol
Date rape drug
Causes relaxtion and causes sedation
allosteric modulator that increases the binding of GABA to its receptors
Ketamine
Dissociative anesthetic
Sedation, hallucinations, etc
Depressants drugs
alcohol, rohypnol, ketamine
depresses the nervous system
Nicotine
Acts on the acetylcholine receptor( function: natural alerting mechanisms
Increase alertness and arousal
Methamphetamine/meth
Overuse causes free radicals to destroy the body
Causes an abnormal release of dopamine from neurons, causing euphoria
Amphetamines
Release huge amounts of dopamine(pleasure) and serotonin(hallucinations)
euphoria
Cocaine
Prevents dopamine and serotonin reuptake, causing it to stay in the synaptic cleft for longer
euphoria
Heroin and morphine
Binds to opioid receptors
Relief,euphoria, pain relief
marijuana(cannibis)
Acts on the neurotransmitters that affect control of muscle and pain sensitivity
Artificial endorphins\
relaxation
Ventral tegmental area
The VTA,located in the midbrain, has dopamine-producing neurons and innervates to the mesolimbic tract
Mesolimbic tract
Filled with dopamine producing neurons which release dopamine in to the nucleus accumbens in the basal ganglia when we do something we enjoy
Mesocortical tract
The 2nd place VTA innervates to is the PFC
Changes in the dopamine projections causes changes in the PFC which may lead poor decision-making making like most addicts have
Heminglect syndrome Causes
Stroke or damage to the right side of the brain, usually in the right parietal cortex(important for involuntary attention)
Heminglect syndrome symptoms
1. The patient is unaware of the left side of his body
2. May eat food from one side
3. Write from one side
4. May ignore the other side of their visual(cant notice stimuli from left side)
ADHD symptoms
Unable to focus'
Hyperactivity
Impulsive behavior
ADHD treatments
Methylphenidate(improve attention by increasing dopamine and norepinephrine)
Schizophrenia symptoms
Hallucinations
Delusions
Hard to make decisions
Loss of motivation and pleasure
attention issues
Prospronogia causes and symptoms
The inability to identify a familar face (family members, friends)
Caused by the damage to the FFA and PPA
HAND(HIV associated neurological disorder) symptoms
Mainly affects processing speed and motor skills
causes of epilepsy
Stroke, Brain tumor, Traumatic brain injury, Central nervous system infection,
Generalized seizure
a seizure that affects both sides of the brain
Absence (Petitmal) Seizures
Causes rapid blinking or staring spells
tonic-clonic seizure
Tonic phase: muscles stiffening
clonic phase: muscle spasms and convulsion
secondary generalized seizure
Partial seizure that transitions to generalized seizure activity
focal seizure
A simple focal seizure can cause twitching or a change in sensation, triggering strange smells or tastes.
a big one can cause loss of conciousness or confusion
Cerebral palsy causes
Head injury to brain areas related with movement
Bleeding in the brain
infection
Cerebral palsy symptoms
Damage to motor areas, stiffness in muscles and involuntary movements may occur
Ischemic stroke causes
a blockage in the blood vessels(usually because of a blood clot)
athersclerosis(build up of fatty plaques in vessels)
Ischemic stroke treatment
Tissue plasmogen activator(tPA) dissolves clots and opens up the blood stream
hemorrhagic strokes causes
burst of blood vessel in the brain is caused by
1. Caused by high blood pressures
2. Aneurysm(weak blood vessel walls)
3. Amyloid buildup in blood vessels
what is Peripheral neuropathy(a symptom of diseases)
Damage to the peripheral nerves in the peripheral nervous system
Peripheral neuropathy
Tingling and numbness
Muscle weaknessBurning or shooting pain
quadriplegic cause and symptoms
damage to the spine
paralysis of limbs
strabimus
Causes
Damage to ocular nerves
Symptoms
Eye deviations
Middle sightness
Outward deviation
fragile X syndrome Causes
genetically mutation of FMR1 gene in the chromosome X
fragile X syndrome symptoms
1. Autism
2. Delay in learning basic skill(language, crawling, walking)
3. Flat feet, low muscle tone
Autism symptoms
1. Bad social skills(bad at social cues, sharing emotions)
2. Could have no speech at all
3. Intense focus on one thing
4. Unusual sensitivity to sensory inputs
Megalencephaly and microcephaly Causes
Too much proliferation of neurons
Genetical mutation
Megalencephaly and microcephaly Symptoms
Bigger head for mega and smaller head for micro
Intellectual disabilities
Delayed motor development
Delayed speech development
Seizures
Migraines causes
Changes in the brain stem and interactions with the trigemial nerve
Increase activity in the cerebral blood vessels
migraines symptoms
1. Throbbing head pain
2. Hypersensitivity to light
3. Migranous aura(flashing lights and lines)
Migraines treatments
triptan(activates specific serotonin receptors prevent migraine)
Congenital insensitivity to pain
the condition of being born without the ability to perceive pain
Brocas aphasia(non fluent) Symptoms
1.Person can only say short phrases and words
2. Reading and comprehension is fine though
3. Can't write
Wernickes aphasia(fluent) symptoms
1. Fluent speech but the words are arranged wrongly
2. Comprehension, reading, writing, are all impaired
Global aphasia definition and where the damage is
Cant read, write, comprehend, and speak
damage to both brocas and wernickes area
Conduction aphasia causes
1. Damage to the connection between the brocas area and wernickes area
2. Damage specifically to the arcuate fasciculus which is a white matter tract
Conduction aphasia Symptoms
1. Speech and comprehension are good
2. Word finding and repeating words is bad
Dyslexia symptoms
Difficulty of pronouncing phonemes ( letter sounds)
Difficulty pronouncing new words
Abnormal signaling of the language parts of the brain to memory
Conductive hearing loss causes
Caused by a ear tumor or changes in middle ear pressure
damage up to the oval window
Sensorineural hearing loss causes
Damage to areas of the inner ear
Caused hair cell damage, brain tumor
Narcolepsy causes
Low levels of orexin(arousal NT)
Narcolepsy Symptoms
1. Random sleep attacks
2. Cataplexy attacks(paralysis of the muscles)
3. Sleep paralysis(cant move body waking up or starting to sleep)
4. Hallucinations of getting attacked
5. Hypnagonic hallucinations as you go to bed
Obstructive sleep apnea Causes
Obesity
Genetically inherited enlarged tonsil and other throat or mouth characteristics
Obstructive sleep apnea symptoms
Terrible sleep
Wake up in the middle of the night to breath
Snoring - gasping for air- cycle repeats
3 types of insomnia and definition
Onset insomnia, Maintenance insomnia, Fatal familial insomnia
insomnia, REM sleep disorder treatments
Benzodiazepines(induces sleep because it enhances the effects of GABA inhibitory NT)
Restless leg syndrome causes
Iron deficiency
Incorrect dopamine signaling
Restless leg syndrome symptoms
Tingling or buzzing in someones limbs causing them to voluntarily move them
Isnt classified as a sleeping disorder but it can deter sleep
Periodic limb movement disorder
Involuntary kicking or swinging of the legs and arms
Bipolar disease Symptoms
Mania symptoms
-Recklessness
-Easily distracted
Depression symptoms
-Hopelessness
-loss of pleasure and interest
Bipolar Disease Treatment
Lithium drugs(antipsychotics that help decrease mania symptoms)
Antidepressants for depression symptoms
Major depression Treatments
SSRI's (seratonin reuptake inhibitors, more serotonin in the brain)
SAD(seasonal affective disorder)
a type of depression that is related to changes in seasons and begins and ends about the same time every year
PTSD symptoms
1. Reliving the traumatic event(flashbacks)
2. Avoidance of things that remind you of the traumatic event
3. hyperarousal(very wary of your surroundings)
4. Dizziness, fainting,
PTSD treatment
Prazosin and beta blockers which decrease norepinephrine(flight or fight NT)
Borderline personality disorder symptoms
condition marked by extreme instability in mood, identity, and impulse control, Intense fear of abandoment, Views of others can suddenly change
, Fear of being alone
Korsakoff's syndrome symptoms
1. Inability to form new memories after the onset of the disease
2. Short-term memory is cooked
3. Gaps in long-term memory
4. confabulation(filling in memory with false info)
No behavioral or personality changes
Korsakoff's syndrome causes
1. Both are caused by vitamin B1 deficiency(thiamine)
2. B1 deficiency caused by alcohol abuse or malabsorption(inability to absorb the vitamin)
Alzheimers disease Causes
1. Amyloid beta plaques(Neuritic plaques)
tau(tangles within neurons)(Neurofibrillary tangles)
Shrinked brain
2. Mutation of the PSEN gene, which cleaves the amyloid precursor protein(producer of amyloid beta peptides)
3. TOMM40 mutation, which causes a change in the length of the intron, causes Alzheimer's
4. Loss of function Mutation in the TREM2 allow the amyloid beta protein to build without restraint
Alzheimers disease Symptoms
Early: Memory problems, Difficulty calculating and concentrating
Mild: Personality and behavioral changes, Taking longer to complete certain tasks, getting lost
Moderate: Forget who family are, Hallucinations, Can't learn new things
Severe: Bedridden,Weight loss,Bowel issues
Frontotemporal dementia causes
Tau protein tangles
Mutation of C9ORF72
Frontotemporal dementia Symptoms
1. Behavioral and personality changes
2. difficulty in social settings
3. Language difficulties (loss of speech)
4. Memory loss like Alzheimer's
Alzheimers treatments
1. memantine(NMDA antagonist that prevent exocitoxicity by calcium)
2. donepezil,Rivastigmine, (aceythcholinerase inhibitor that increases aceythcholine in the brain)
3. Donepezil and memantine is combined to help relieve symptoms in moderate and severe stages
Botulism causes
Toxin cleaves the SNARE protein, preventing the SNARE protein from helping neurotransimitter filled vesicles from expelling NT's in the synaptic cleft
botulism symptoms
Muscle spasms
muscles and face
localization theory
The theory that all brain parts have different, unique functions
Reticular theory
All parts of the nervous system are physically connected and work together as a network(replaced with the neuron doctrine, which founded synapses)
Convergence projection theory
States the reason why people feel pain in one area when the damage is in a internal organ(referred pain), is that the nerves of the body areas both converge at the same secondary neuron in the spinothalamic tract
Central sensitization theory
Internal organ damage sends persistent pain signals, which then activate long-term potentiation, causing a hyper-sensitivity to pain signals even if the stimuli is non-noxious
NREM 1
Muscles still somewhat active
Brain waves get lower and lower frequencies
Alpha waves(8-13) to theta waves(4-8)
NREM 2 characteristics
Theta waves(4-8hz)
Research suggest that the k complex and the sleep spindles may happen because of memory processing and also minimizing perception of distracting sounds
NREM 3(SWS)
Delta waves(0.5-4hz)
Called deep sleep
Heart rate, respiration and blood pressure drop to the lowest point
Slow wave sleep
Large amplitudes , low frequency
Suprachiasmatic neurons
The suprachiasmatic neuron is in the hypothalamus
Excites the pineal gland to release melatonin
Uses visual information about light to either inhibit or excite the pineal gland
Retinohypothalamic tract
An alternate pathway that turns light into signals that go to the Suprachiasmatic neurons
More activity(more light) causes the SCN to inhibit the pineal gland more
VLPO(ventrolateral preoptic neuron)
Produces GABA which inhibits arousal(mainly in NREM)
Declarative/explicit memory definition and types
conscious recollection of facts, events, etc
includes semantic memory, episodic memory, and prospective memory, and spatial memory