geology unit 3
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
129 Terms
what is climate?
study of climate is study of how the Sun’s energy is trapped and transported across the Earth
radiative balance
Earth heats up enough so that it emits as much radiation as it absorbs
albedo
reflected solar radiation
when does earth stop warming
when achieves radiative balance with solar and back radiation
main component of Earth’s atmosphere
nitrogen
what does all liquid water do better than air
transports heat
el nino
warm sea surface temperature in eastern equatorial pacific
where is warm water during el nino and why
near south america, NE and SE winds aren’t carrying warm water to indonesia
continents heat up and cool down more than
oceans
do injected particles from volcanism result in heating or cooling and why
cooling because they block the sun’s radiation
plants influence
albedo
what does high eccentricity look like
earth revolves around the sun in a more oval shaped path
what does low eccentricity look like
earth revolves around the sun in a more spherical shaped path
what drives the climate system
heat from the sun
how is heat transferred from the equator to the poles
wind and ocean currents
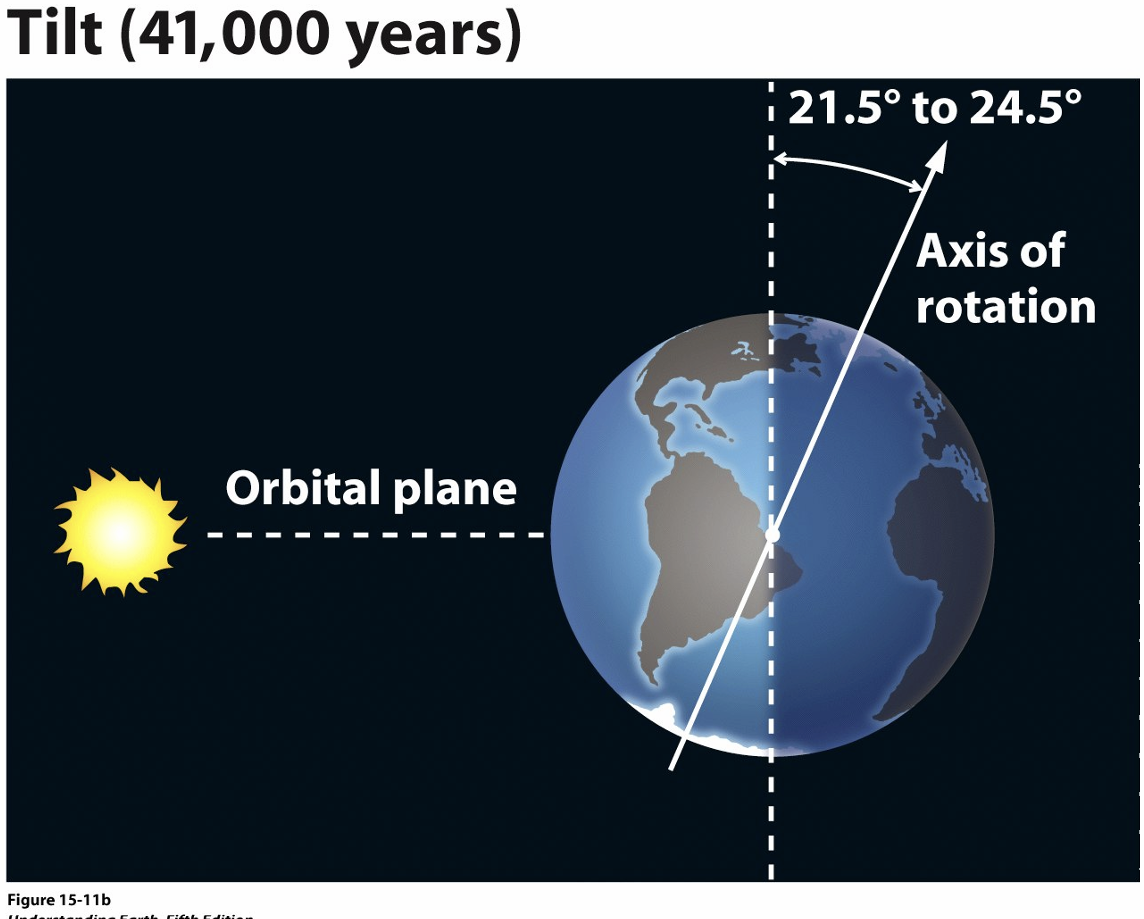
tilt
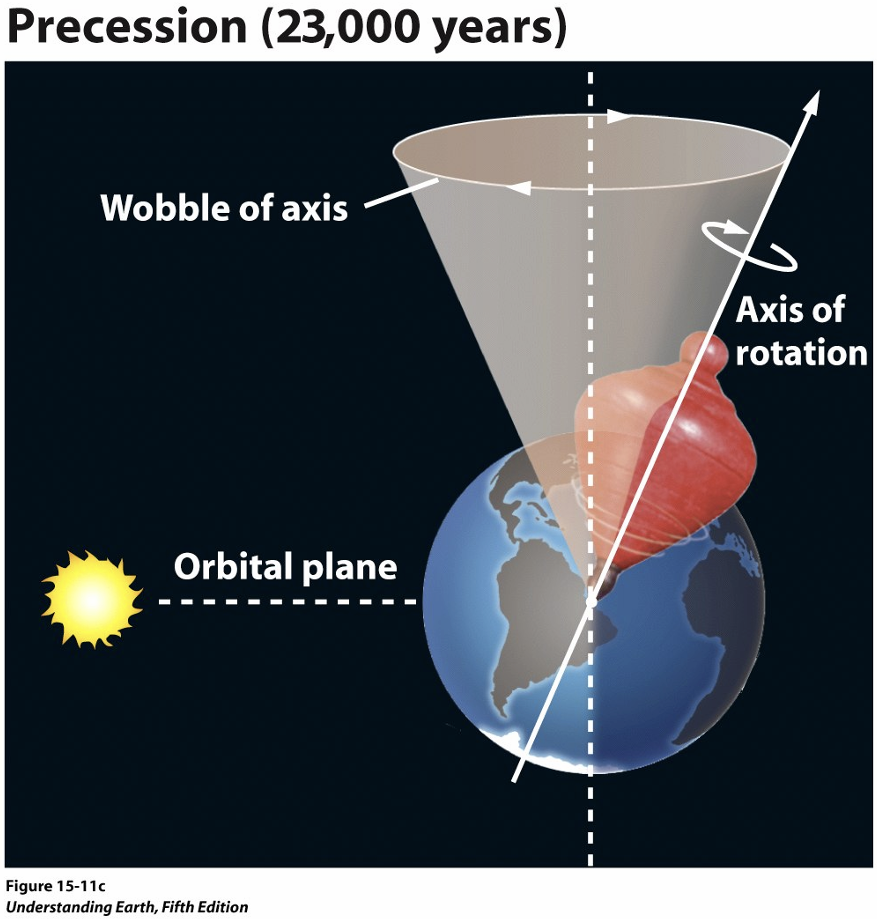
precession
weathering
breakdown and fragmentation of rocks
erosion
removal of weathered material from its source
mass wasting
collapse of hillsides
chemical weathering
minerals in a rock dissolve or undergo chemical alteration in the presence of water and/or air
physical weathering
rocks and the minerals are mechanically fragmented without a change in chemical composition
chemical weathering works faster with
more surface area
what is the influence of silicate weathering on CO2
removes CO2 from the atmosphere and works to form shells (CaCO3)
soils
the residue of chemical weathering
factors that influence soil formation
time, climate, topography, parent material, and organisms
why does most chemical weathering on Earth occur in soils?
soils retain water and remain wet at depth long after surface dries out. plants and microorganisms in the soil produce acids which help chemically weather minerals in the soil
rocks must be broken down before they can
be removed by water, ice, or wind
soils form when
material is removed by chemical weathering
fine sand angle of repose
35
coarse sand angle of repose
40
angular pebbles angle of repose
45
reservoir
storage place for water
hydrologic cycle
models the movement of water from one reservoir to another (means and amount)
relative humidity
amount of water vapor in the air (warm air can hold more than cool air)
when warm air cools, it can become supersaturated and water condenses to form
clouds
most precipitation occurs in louisiana and florida range and progressively decreases as
you go west, with the exception of pacific northwest
runoff map

half the global runoff is carried in 70 largest rivers and half of that is
carried in the Amazon alone
runoff surface storage (reservoirs)
lakes, wetlakes
what do dry periods mean for amount of runoff
low runoff
what do wet periods mean for amount of runoff
high runoff
with high runoff during wet periods, some water is stored and slowly released during
dry periods
water table
boundary between unsaturated zone (vadose zone) and saturated zone (phreatic zone)
groundwater
part of subsurface water that is in the saturated zone
porosity
percent rock volume that is pores - defines the amount of water a volume of rock can hold
porosity increases with
increased sorting
porosity is independent of
grain size
permeability
interconnectedness of pores
permeability decreases with
decreasing grain size, porosity, and sorting
infiltration
surface water infiltrates into the unsaturated zone by gravity and capillary forces and moves into the water table
hydraulic head
elevation of a water table above a particular location-usually sea level
groundwater moves by
gravity and pressure difference along a head gradient
groundwater moves from
high head to low head (not always downhill)
recharge
addition of water that causes the water table to rise (increased evaporation or withdrawal by pumping lowers the water table)
cone of depression
water is pumped faster than it can recharge
aquifer
any permeable, saturated layer that can transport water
aquitard
an impermeable layer that prohibits flow of water
unconfined aquifer
upper boundary defined by the water table
confined aquifer
upper boundary is an aquitard
springs
ground water discharge feature that form wherever the land surface intersects the water table
knowing how the water flows in the aquifer can help
planners protect our water supply and places like Barton Springs
the rate of groundwater use in the U.S. today greatly exceeds
the rate of recharge
laminar flow
flow lines are parallel and do not mix
turbulent flow
flow lines cross and mix chaotically, most rivers and streams
laminar flows have
low velocity, high viscosity, and shallower channels
turbulent flows have
high velocity, low viscosity, deeper channel, and high sediment load
suspended load
fine-grained sediment (typically clay and silt) transported in suspension due to turbulence
bed load
coarser-grained sediment (typically sand and gravel) transported on bottom of stream bed by rolling and sliding
saltation
sediment (typically sand) transported by intermittent jumps - a transitional state between bed load and suspended load
competence
ability to carry material of a given size
capacity
total sediment load
velocity and volume of a flow affect
both competence and capacity
as velocity increases… (dunes and ripples)
flat bed → small ripples → dunes → ripples form on dunes → flat bed (dunes washed away)
ripples and dunes migrate
downstream
stream valley
area between the tops of the slopes on both sides of the river
channel
trough through which the water runs
floodplain
flat area either side of the channel where water overflows during floods
meandering is common in
flat areas
meandering stream
low sediment load, low velocity
max velocity on the outside edge of meandering stream
max erosion
low velocity on inside edge (deposition)
point bar
braided stream
high velocity and high sediment load
braided stream channel patterns depend on
flow velocity and sediment load
drainage basin
area that funnels water into network of interconnected streams
divide
ridge that separates two basins - runoff flows down either side of the divide
antecedent streams
established before a tectonic event uplifts the rock → deeply cut stream channel
superposed stream
erode through resistant rocks after their stream channel has been established on younger flat lying rocks
discharge
volume of water that passes a given point in a given time through a channel of a certain width and depth
discharge formula
width x depth x velocity
discharge generally increases
downstream
increased discharge means
width, depth, or velocity must increases too (velocity generally doesn’t increase downstream)
dynamic equilibrium
balance between erosion of the streambed and sedimentation in the channel and floodplain
dynamic equilibrium balance depends on
topography (slope), climate, streamflow (discharge, velocity), resistance of rock to weathering and erosion, sediment load
longitudinal profile
plot of elevation vs. distance along a stream
profile typically becomes flatter as elevation decreases
the lower level of the profile is controlled by base level (ocean or lake)
floods occur when
the discharge exceeds the capacity of the present channel to accommodate the flow
flooding is
normal and expected event on all rivers when input exceeds the discharge capacity
river engineering (straightening river channels) can make floods worse by
removing natural protective mechanisms
floods are the
leading cause of natural disaster deaths worldwide
floods can cause stream/river to build up
natural levees after many floods