IB Business Quiz Chapter 2
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
private sector
companies and business owned and controlled by individuals and groups of individuals
IPO- privately held to publicly held company
- the process of going from private to public
Social entrepreneur
Charity
Organizations set to raise money to help people in need or to support causes that require funding
Tax exempt in some countries
Not every NGO is eligible for tax exempt status
Charity can operate in the public sector
Economic System
A nation's system for allocating its resources among its citizens, both individuals and organizations
Differences in systems exist by
1. Degree of decentralized use of markets and prices in decision making
2. Degree of centralized government control
Planned Economy
-communism/socialism
- economic resrouces are owned, planned, and controlled by the state
mixed market economy
-in the middle (has some elements of a planned economy and a market economy)
- economic resources are owned and controlled by both private and public sectors
market economy
- economic resources are owned largely by the private sector, with very little state intervention
- capitalism
Public Sector
companies and organizations accountable to and controlled by central or local government (the state)
privatization
the sale of public sector organizations to the private sector
- trend in public sector in many countries toward selling to the private sector
examples of goods and services deemed to be of benefit to society but would be underprovided without the public sector
-infrastructure (roads, waste disposal, etc. )
- public housing
- health care services
- education
- national defense
- renewable energy
- museums
- public parks
- emergency services (police, fire, ambulance)
Sole trader
a for profit organization ; one person who owns a business taking the full risk of getting it up and running
sole trader (con.)
- a business that is exclusively owned by one person who has full control of it and is entitled to all the profit (after tax)
- independence and freedom to make your own business decisions - positive and negative (no one to rely on)
- full benefits no sharing/splitting profits
- liability is all on you
Advantages to being a sole trader
- simple to form
- complete control
- keeps all profits
- close staff relationships
disadvantages to being a sole trader
- unlimited liability
- limited resources -> long hours
- limited fundraising capability
- lack of continuity
partnership
two or more people running the business together; more people so risk and liability is spit up (LP, LLP, General Partnership)
- formed by two or more people to carry out the business together, shared responsibilities, and capital investment
Advantages of partnership
- specialization -> more talent
- more fundraising capability
- shared decision making
- shared business losses
disadvantages of partnerships
- united liability for all partners
- profits are shared
- disagreements among partners
- lack of continuity
limited company : liability
the only liability, only potential loss, a shareholder has if the company fails is the amount invested in the company, not the total wealth of the shareholder - benefit
limited company: legal personality
separate from owners in terms of legal identity
limited company :continuity
exist after death of the owners or exit from the company/partnership
Private limted company/Privately held company
- a small to medium sized business that is owned by shareholders who are often members of the same family: this company cannot sell shared to the general public
- Limited, LTD, PTE
- you cannot buy their shares - they are not listed on the NY Stock exchange
Public limited company (PLC)
- often a large business with the legal right to sell shared ot the general public ; it's share price is quoted on the national stock exchange
- PLC, INC, incorporated
- You can look up on stock exchange ( Inc designator means you will be able to purchase shares from their company)
Share
a certificate confirming part ownership of a company; most types of share entitle shareholders to dividends paid from profits
Initial public offering (IPO)
the process of offering for sale the shares of a private held company to financial institutions and the general public
Shareholders
individuals or institutions that buy/own shares in a limited company
advantages to a private limited company
- limited liability
- separate legal entity
- continuity
- stronger fundrasing capability
disadvantages to a private limited company
- legal formalities
- complicated and expensive to form
- capital cannot be raised by sale of shares to the general public
Advantages to publicly held limited companies
- limited liability
- separate legal entity
- continuity
- stronger fundraising capability
Disadvantages to a publicly held limited company
- legal formalities
- complicated and expensive to form
- fluctuation of share price
- can be taken over against the will of its management
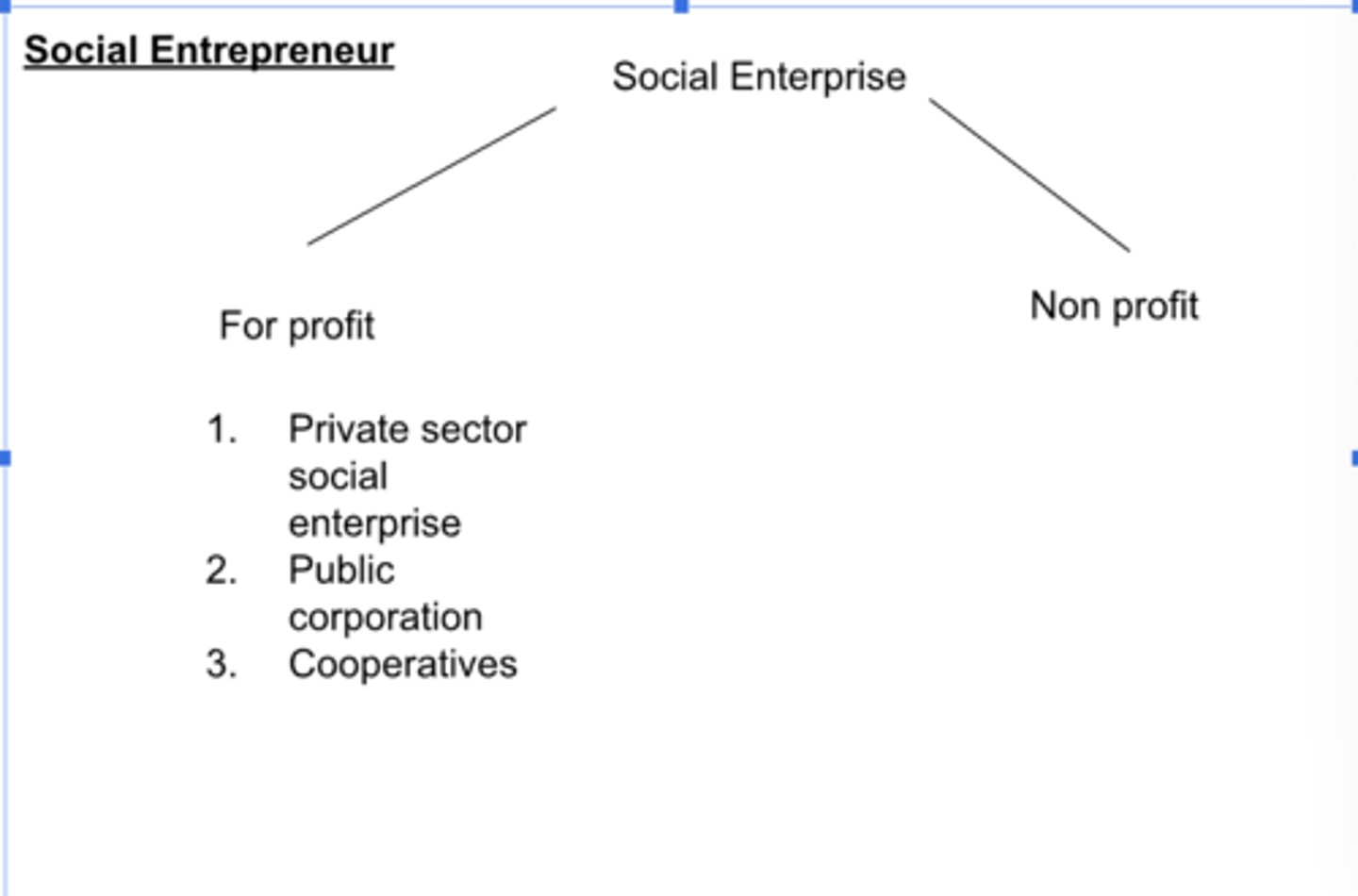
social enterprises
1. for profit
2. non profit
Traditional business
- primary driver is money and profit
traditional charity
- do not rely on profit
-use donations to generate social value
social enterprise
- NOT a legal structure ; a way to classify
- achieve measurable social impact alongside financial return
- Ex. bombas socks on shark tank (every sock you buy, they donate one)
For - profit social enterprises
1. private sector social enterprises
2. public corporation
3. cooperatives
social enterprise
A business with mainly social objectives that reinvests most of its profits into benefiting society rather than maximizing returns to owners
- NOT a charity
Objectives of a social enterprise
the triple bottom line
-1. economic - make a profit
2. social - provide jobs to help local communities
- 3. environmental - protect the environment
Private sector social enterprise
can be set up as a sole trader, partnership, limited companies, or cooperative
Social enterprise is NOT a legal structure
it is a way of doing business
social entrepreneur
anyone who can start either a for/non-profit social enterprise
- a person who establishes an enterprise with the aim of solving social problems or achieving social change
For profit social enterprises (example)
Toms (one for one)
Public corporation
- a business enterprise owned and controlled by the state or government (NOT the same as a publicly held company which is apart of the private sector and the shares are able to be bought by the public)
- also known as nationalize industry or public sector enterprise
are publicly held companies the same as public corporations?
NO: publicly held company ≠ public corporation
For profit social enterprises: examples of public corporations
- brodcasting services (National TV + radio services)
- educational establishments (schools, colleges, universities)
- Housing associations
- national health service providers
- public transport providers (buses and rail transit systems)
- sports and leisure centers (i.e. public swimming pools)
cooperatives
- a group of people acting together to meet the common needs and aspirtions of its members, sharing ownership and making decisions democratically
types of cooperatives
- retail
- agricultural
- worker
- insurance companies (state farm and liberty mutual)
Non - profit social enterprises
1. Non- governmental organizations (NGOs)
2. Charities
Non- profit organization (non- profit social enterprise)
- any organization that has aims other than making and distributing profit is usually governed by a voluntary board
- get money from donations
- purpose of benefiting society
NGO
legal constitute body that functions independently of any government and has a specific aim and purpose- main difference between charity(charity can be governmental, no specific ties to state or countries)
- eg. supporting disadvantaged groups in developing countries or advocating the protection of human rights ; amnesty international, doctors without borders, etc.