AP Psych Unit 1 CED
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
126 Terms
Heredity, or “nature,”
refers to genetic or predisposed characteristics that influence physical, behavioral, and mental traits and processes.
Environmental factors, or “nurture,”
refers to the external factors that one experiences, such as family interactions or education.
The evolutionary perspective
explores how natural selection affects the expression of behavior and mental processes to increase survival and reproductive success. Some theorists have sought to apply principles of the evolutionary perspective in ways that discriminate against others (eugenics)
Types of research on the effects of genes on individual behavior and mental processes
twin studies, family studies, and adoption studies.
central nervous system (CNS)
includes the brain and the spinal cord and interacts with all processes in the body
peripheral nervous system (PNS)
relays messages from the central nervous system to the rest of the body and includes the autonomic and somatic nervous systems
autonomic nervous system
governs processes that are involuntary and includes the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems.
Somatic nervous system
governs processes that are voluntary
Parasympathetic nervous system (in autonomic nervous system)
Slows down body - “rest and digest”
Sympathetic nervous system (in autonomic nervous system)
“Fight or flight” - Heartrate increase, pupils dilate
neurons
neural cells that transmit information
glial cells
cells that provide structure, insulation, communication, and waste transport
Purpose of neural cells
form the basis of the nervous system and are the building blocks of all behavior and mental processes
Purpose of Heredity and environmental factors
interact to shape behavior and mental processes
(In the spinal cord) the reflex arc
demonstrates how neurons within the central and peripheral nervous systems work together to respond to stimuli
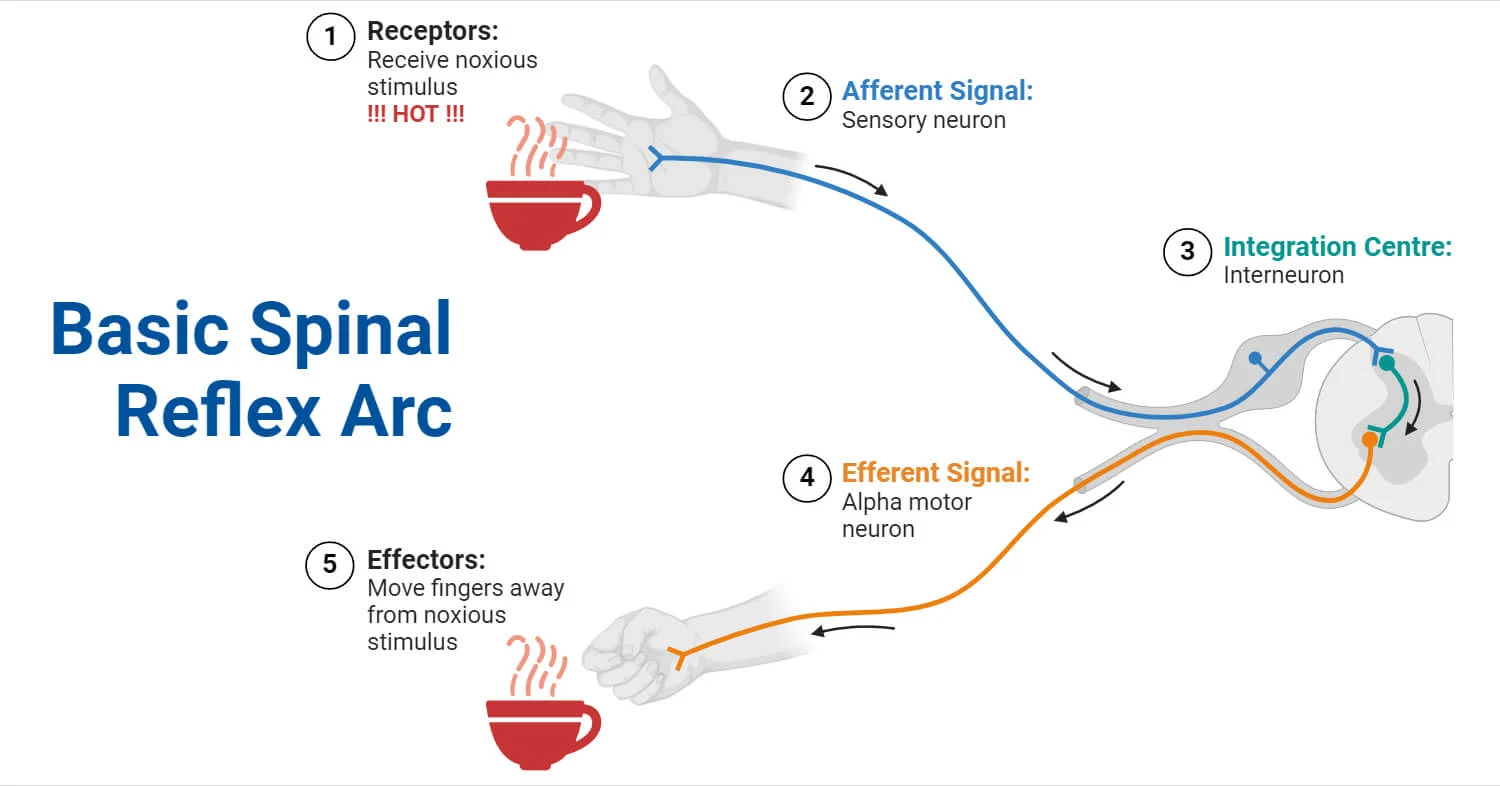
sensory neurons (afferent)
Transmits signal from receptor to Central Nervous System
motor neurons (efferent)
Transmits signals from the Central Nervous System to muscles
interneurons (inner)
Neuron that receives information and relays it to other neurons
All-or-none principle
a neuron must receive enough signal to either fire or not
Systematic firing
how neurons typically fire
Depolarization
When the neuron fires
Refractory Period
Brief amount of time where a neuron cannot fire
Resting Potential
Stable state of a neuron (needing stimuli to fire)
Reuptake
When neurotransmitters are reabsorbed by the axon terminals (after firing)
Threshold
Amount of stimulus for a neuron to fire
Disruptions to neural firing could result in
disorders such as multiple sclerosis or myasthenia gravis.
multiple sclerosis
Immune system attacks myelin sheath leading to disruption of the central nervous system
myasthenia gravis
Immune system creates antibodies that block acetylcholine receptors in nerve muscle connections leading to muscle weakness
neurotransmitter specific function(s) depend on
the neurotransmitter’s location in the nervous system.
Neurotransmitters communication (excitatory)
making an action potential more likely
Neurotransmitters communication (inhibitory)
making an action potential less likely
dopamine (neurotransmitter)
reward, motivation, movement (low parkinsons) (high schizophrenia)
serotonin (neurotransmitter)
mood, sleep, appetite(low linked to depression)
norepinephrine (neurotransmitter)
alertness, arousal, flight-or fight
glutamate (neurotransmitter)
major excitor, memory (too much seizures/migranes)
GABA (neurotransmitter)
major inhibator (slows nervous system linked to anxiety/insomnia)
endorphins (neurotransmitter)
pain relief, pleasure
substance p (neurotransmitter)
transmits pain, anxiety and stress
acetylcholine (neurotransmitter)
muscle action, learning (low alzheimers)
adrenaline (hormone)
leptin (hormone)
signals fullness
ghrelin (hormone)
signals hunger
melatonin (hormone)
sleep-wake cycle (penial gland)
oxytocin (hormone)
promotes social bonding, love, and trust
agonists
encourage neural firing
antagonists
discourage neural firing
reuptake inhibitors
block the reabsorption of neurotransmitters back into the cell
Stimulants
Ex. caffeine and cocaine, typically cause increased neural activity
Depressants
Ex. alcohol, typically cause decreased neural activity
Hallucinogens
Ex. marijuana, typically cause distortions in perception and/or cognition
Opioids
Ex. heroin, typically act as pain relievers.
Psychoactive drug use can lead to
tolerance and/or addiction. Addiction can create significant withdrawal symptoms if the psychoactive drugs are no longer consumed
The brain stem (including the medulla)
generally controls basic functioning such as breathing and heart rate
reticular activating system and the brain’s reward center
generally control alertness, some voluntary movement, eye movement, and some types of learning, cognition, and emotion
cerebellum
generally controls coordination of muscle movement, balance, and some forms of procedural learning
cerebral cortex is divided into two hemispheres and includes
the limbic system (thalamus, hypothalamus, pituitary gland, hippocampus, amygdala), corpus callosum, and the lobes of the cortex.
thalamus
brain’s sensory relay station
hypothalamus
Homeostasis, hormone regulation
pituitary gland
“master gland” of the endocrine system
hippocampus
memory formation (not storage) (long-term and short)
amygdala
Processes emotion
corpus callosum
nerve fibers connecting the right and left hemispheres of the brain
occipital lobes
generally control visual information processing and are located in the rear of the brain.
temporal lobes
generally control auditory and linguistic processing and are located on the sides of the brain.
parietal lobes
generally control association areas, which process and organize information, and the somatosensory cortex, which processes touch sensitivity. These lobes are located near the back crown of the brain.
frontal lobes
located just behind the forehead, generally control linguistic processing, higher-order thinking, and executive functioning, especially in the prefrontal cortex. The motor cortex is located at the rear of the frontal lobes and controls most types of skeletal movement.
Split brain research
achieved by severing the corpus callosum (often a treatment for severe epilepsy), reveals that the right and left hemispheres of the brain may specialize in different activities and functions
left hemisphere
Areas of the brain that affect language are typically located here
Broca’s area
responsible for speech production
Wernicke’s area
responsible for speech comprehension
Testing cortex specialization
showing information in each visual field, taking advantage of the brain’s contralateral hemispheric organization to see where the brain specializes
Brain plasticity
the ability of the brain to rewire itself or modify or create new connections throughout development and generally allows for the function of a damaged part of the brain to be assumed by a different part of the brain.
EEG
records brain’s electrical activities in waves (when something happens) Stages of sleep are identified here
Research on the brain is done
to promote understanding of how the different structures of the brain work and how the brain functions together as a whole
fMRI
maps brain’s activities (where something happens)
Consciousness
has varying levels of awareness of thoughts, feelings, behavior, and events in individuals’ internal and external worlds
circadian rhythm
The sleep/wake cycle, which in humans is about a 24-hour cycle. Jet lag and shift work are disruptions of the circadian rhythm.
NREM sleep
occurs in Stages 1 through 3 and decreases in duration throughout the cycle. Stage 3 the deepest
Hypnagogic sensations
occur as one enters Initial Stage 1 sleep
REM sleep
Produces waves similar to waking, but the body is at its most relaxed. Dreaming occurs during REM sleep. The frequency of REM sleep typically increases as the cycle progresses.
REM rebound
When deprived of sleep, you spend more time in REM stage
activation-synthesis theory
dreams aren’t meaningful but the brain’s attempt to make sense from random nerve signals. Proposed by Hobson & McCarley in 1977
consolidation theory
dreaming helps the brain to transform short-term memories into long-term ones
Narcolepsy
sudden uncontrollable sleep attacks into REM, can be triggered by high emotions
REM sleep behavior disorder
lack of REM atonia (muscle paralysis) causing people to act out dreams
sleep apnea
breathing suddenly stops during night causing person to stay in light sleep
somnambulism
sleep walking during deep stage 3 NREM
Insomnia
difficulty falling/ staying asleep
Sensation
the process of detecting information from the environment that meets a certain threshold and transducing stimuli into neurochemical messages for processing (perception) in the brain.
Absolute threshold
occurs when a stimulus can be detected at least 50% of the time.
Just-noticeable difference
smallest change in stimulus that can be detected
Sensory adaption
diminished sensitivity to stimuli due to being used to constant stimulus
sensory interaction
The sensory systems constantly work together
Synesthesia
experience of sensation in which one system of sensation is experienced through another.
Retina
photosensitive surface at the back of the eye. Cells in the retina capture visual information that is transduced to the brain for processing
blind spot
known due to incomplete images, the visual nerve exits the eye here, but brain fills in gaps in incomplete images
accommodation
Visual stimuli are focused onto the retina by the lens via a process called
When accommodation of the retina is altered
nearsightedness or farsightedness can result
rods
Cells that lie in the periphery of the eye and detect shapes and movement, but not color. These cells are mainly activated in low-light environments. These cells play a role in light and dark adaptation.