CD3: Traumatic injuries to permanent teeth
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
30%
how many percent of children/teens in the USA will have tooth injuries?
maxillary central incisors
Which teeth are the most commonly injured?
unexpectedly
One feature common to all patients presenting with acute dental trauma is the fact that they come to us ....
WHEN did the injury occur
The answer to this question will imply a time factor, which could influence the choice of treatment
wash the patients face
The first step in the examination procedure, is to ...
pulp testing
done to serve as baseline, but not always accurate immediately following trauma
3 months
When will pulp testing be considered accurate?
CBCT
which radiograph should be considered the imaging modality of choice for diagnosis and management of limited dento-alveolar trauma, root fractures, luxation, and/or displacement of teeth and localized alveolar fractures, in the absence of other maxillofacial or soft tissue injury that may require other advanced imaging modalities
crown fracture, crown-root, root fracture (7%), alveolar fracture
types of tooth fractures
crown fracture
the vast majority (75%) of traumatic injuries is...
uncomplicated crown fracture
Enamel fracture or enamel-dentin fracture that does not involve the pulp
Diagnosis:
•PA radiograph(s)
•Evaluate size of pulp chamber and stage of root development
•Pulp test
maintain pulp vitality, restore normal esthetic and function
What are the goals for an uncomplicated crown fracture
repaire, no NS-RCT needed
Treatments for an uncomplicated crown fracture
complicated crown fracture
Enamel-dentin fracture with pulp exposure
positive vitality tests, exposed pulp, normal mobility, percussion test, one occlusal and 2 PA, radiographs of lip (if tooth fragment not found)
Clinical assessments and findings for complicated crown fracture
size, hemostasis possible, growth stage/apical development
Factors determining treatment of pulp exposure
short exposure period after trauma, not associated with PDL injury, small exposure
pulp capping indications (Cover the pulp with Ca(OH)2/ MTA)
maintain vitality, pulp cap/partial pulpotomy
Treatment for a complicated crown fracture with an open immature apex
crown root fracture
Fracture involves enamel, cementum and dentin, May or may not expose the pulp
Diagnosis:
•2+ PA radiographs
•Pulp test
coronal fragment
for a crown root fracture treatment, what may be stabilized to adjacent teeth for emergency treatment?
Gingivectomy, ortho or surgical extrusion
crown root fracture treatment necessary to restore the tooth
Pulp capping or Pulpotomy, NS-RCT (for mature)
In a crown root fracture, what treatment do we use on an immature tooth? For a mature tooth?
Root fracture
Fracture involving dentin, cementum, and the pulp
•The coronal fragment is usually mobile and sometimes displaced
•The apical segment is usually not displaced
Prognosis:
•Apical 1/3>Middle 1/3> Cervical 1/3
Diagnosis:
•2+ PA radiographs taken at different angles
•(Or CBCT scan…)
Root fracture
Which fracture does not involve the enamel?
reduction of fractured segments, immobilization of coronal segment, splint 3-4 weeks, endo tx (if pulp necrosis occurs)
root fracture treatment
25%
What is the prognosis percentage for pulp necrosis in a horizontal root fracture
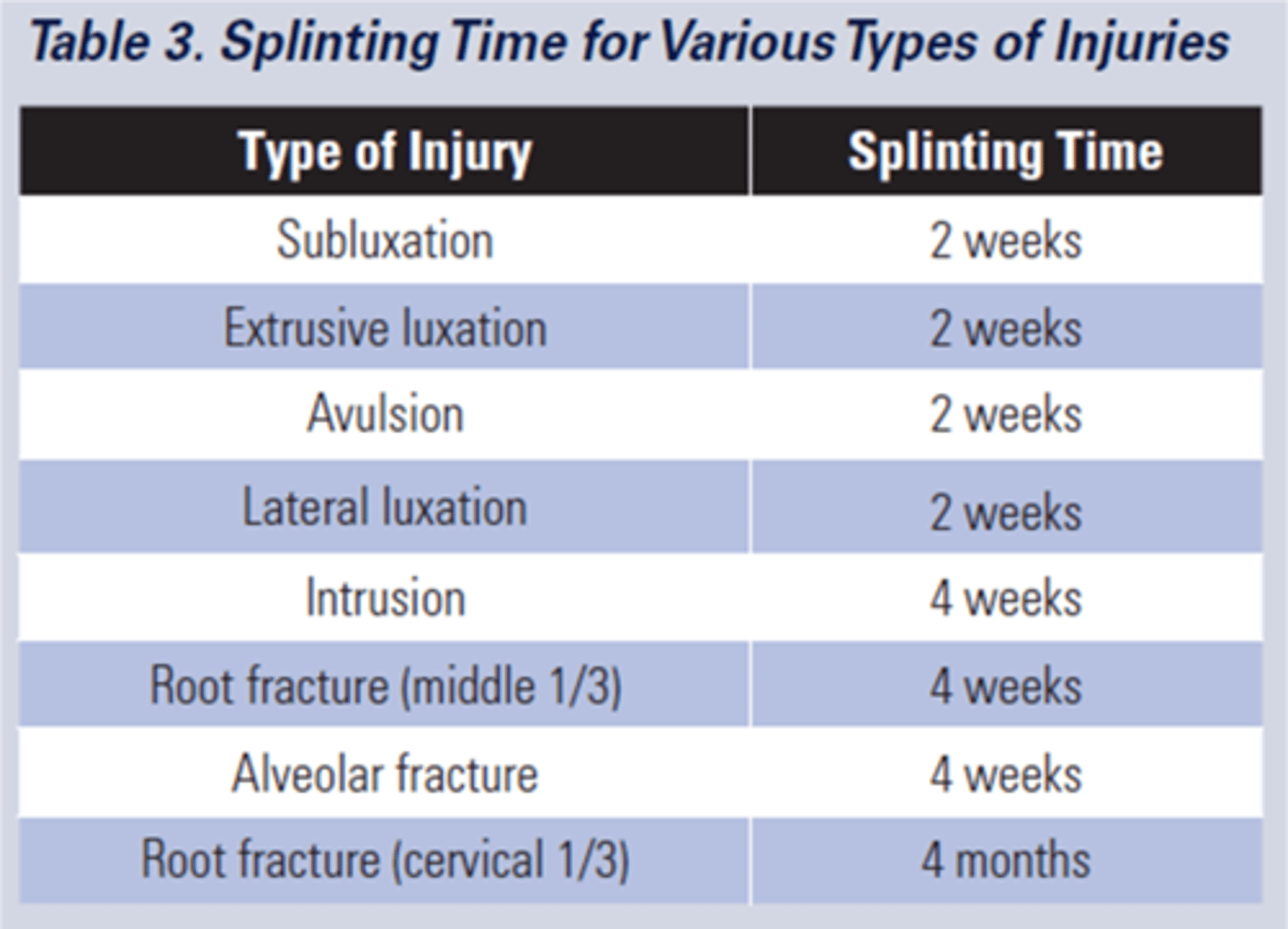
4 weeks
Follow up time for splint removal in the apical third and mid root
4 months
follow up time for splint removal with a root fracture near the cervical area
usually not
Are alveolar fractures usually treated by general dentists/endodontists?
alveolar fracture
Diagnosis:
When the mobility of one tooth is tested, several teeth move
•Hematoma in the adjacent attached gingiva or mucosa
•Pano radiograph/CBCT
Treatment:
•Reposition
•Splint
Concussion
Definition:
•No displacement
•No mobility
•Usually sensitive to percussion and/or tender to touch
Flexible splint ( is optional - can be used for the comfort of the patient for 7-10 days)
Treatment for tooth concussion
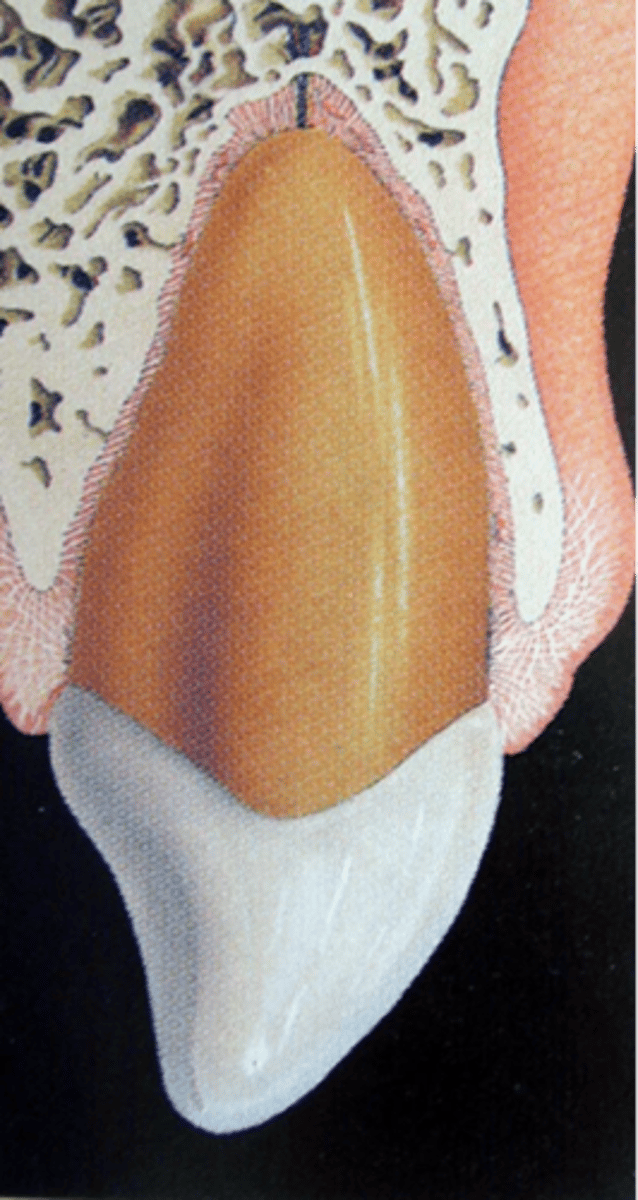
Subluxation ("loosening")
Definition:
•Tooth is tender to touch and mobile, but not displaced
•Hemorrhage from gingival sulcus possible
Diagnosis:
•2+ PA radiographs
•No radiographic abnormalities
Treatment:
•Flexible splint is optional – 7-10 days
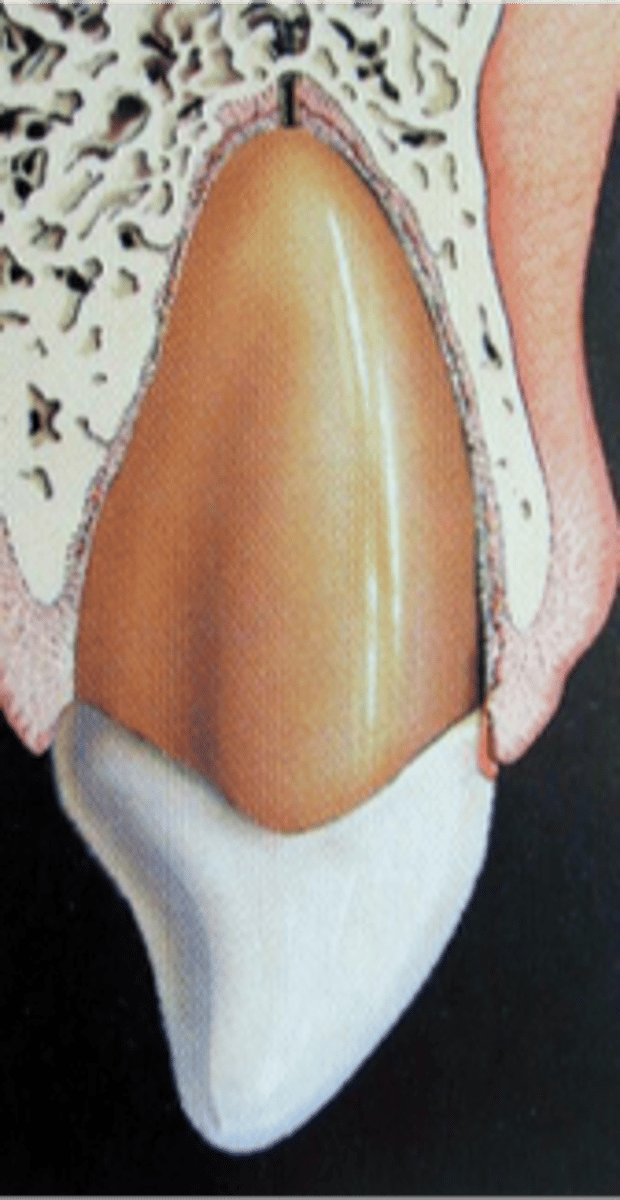
Extrusion ("partial avulsion")
Definition:
•Elongated, mobile tooth
•Partial displacement of the tooth out of socket.
•Angulated radiograph: increased PDL space apically
Treatment:
•Reposition
•Stabilize tooth with flexible splint for 1-2 weeks
•if pulp necrosis for complete root formation-> endo
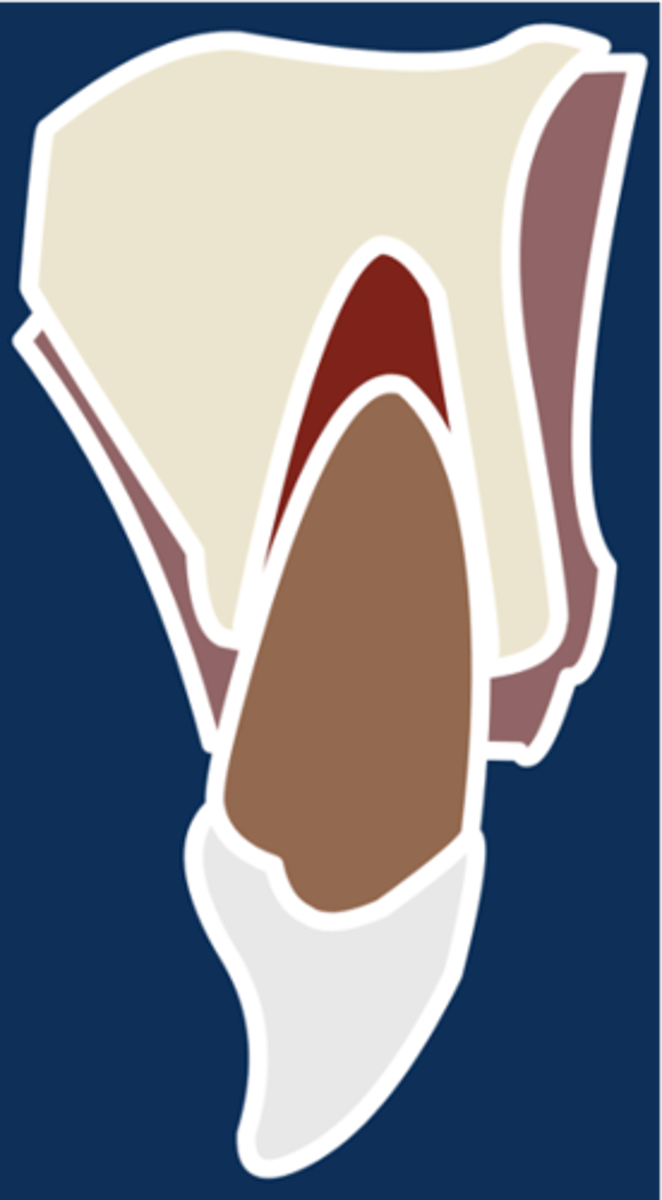
Lateral Luxation
Definition:
•Displacement of a tooth buccally or lingually
•Usually accompanied by fracture of socket
•Usually locked into bone
•Not tender to touch, not mobile
Diagnosis:
•2+ angulated PA radiographs
•(CBCT?)
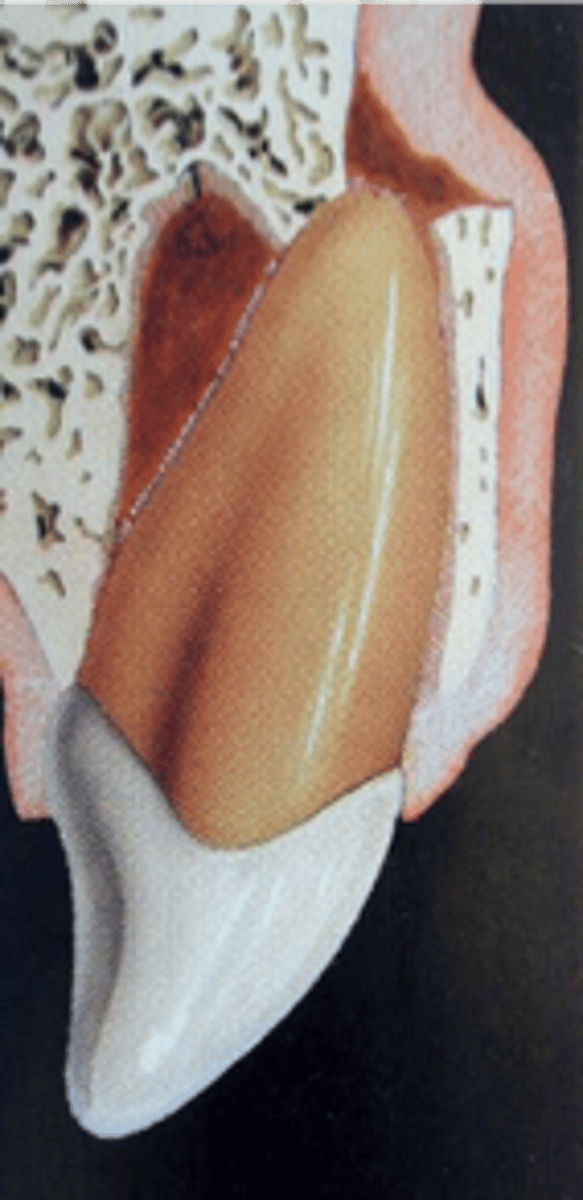
reposition tooth, radiograph, stabilize tooth splint 1-2 weeks
lateral luxation treatment
Intrusion
Definition:
•Apical displacement of tooth into the alveolar bone
•Tooth is driven into the socket, compressing the PDL
•Tooth appear to be shortened or missing
•Severe type of luxation injury
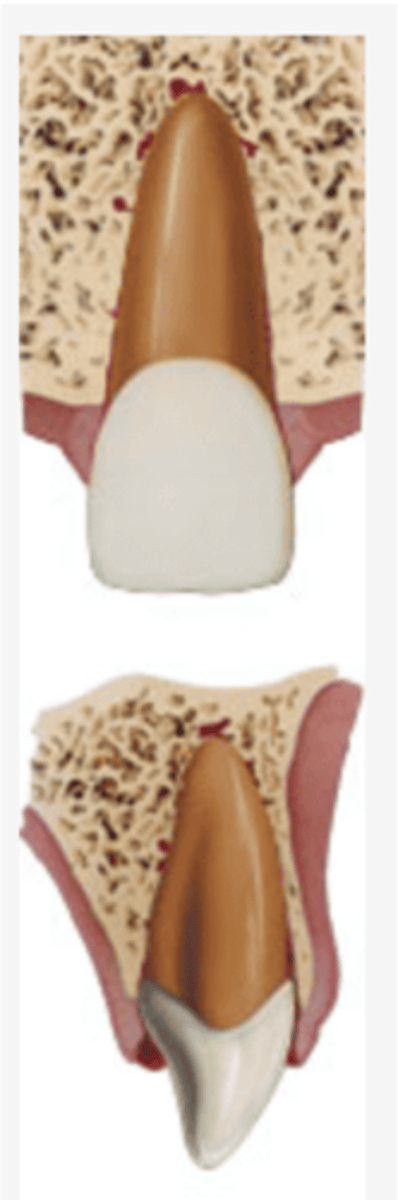
Spontaneous reposition/re-eruption
treatment for intrusion in teeth with immature root formation
reposition, endo in the first 2 weeks, prognosis is poor
treatment for intrusion in teeth with mature root formation
soft food for 1 week, chlorhexadine rinse for 2 weeks
For intrusion, what is an important instruction you need to give to your patient
Follow-up procedures
Avulsion
Definition:
•The tooth is separated from socket completely
•PDL torn
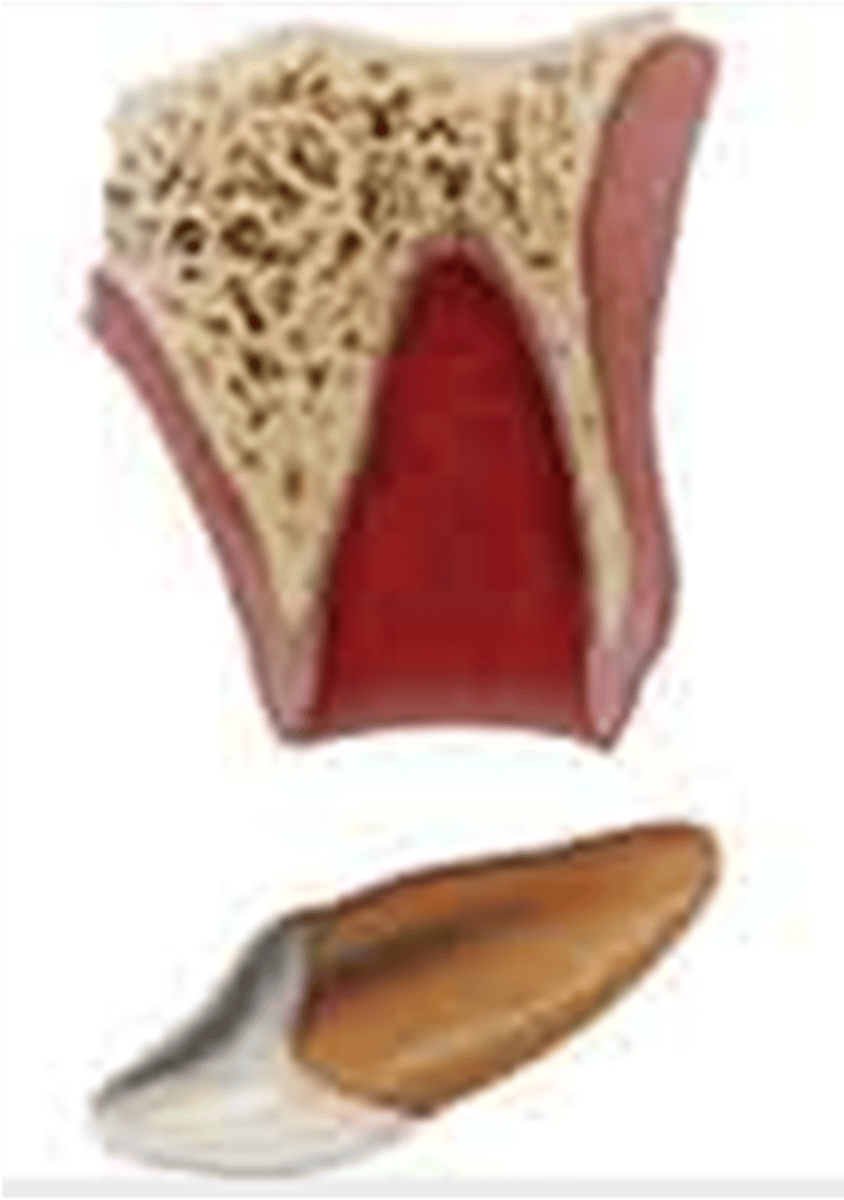
Severed neurovasculature, Crushed and torn pdl, Damage to the alveolar bone, cementum and gingival tissues, Viable PDL cells on most of the root surface
What occurs when a tooth is avulsed
Minimize extra-alveolar time (Immediate replantation = best prognosis)
what is the most critical factor in healing an avulsed tooth
maintain the PDL cells (prevent them from drying out)
what is the goal of the practitioner replanting an avulsed tooth?
Hank’s Balanced Salt Solution (HBSS)
What is the best form of avulsed tooth storage media?
Revascularization of the PDL, Splicing of ruptured Sharpey's fibers
How does a replanted tooth heal?
false, CROWN only
T or F: For first aid in an avulsed tooth, handle the tooth by the root only
revascularization of the pulp
In an open immature apex, the goal of the extra-oral dry time <60 mins it for...
for 1-2 weeks with Flexible wire of a diameter up to 0.016in or 0.4 mm
How long do you splint an open immature apex? What should the diameter be for the wire?
within 7-10 days
When should endodontic treatment be preformed for a closed mature apex?
poor prognosis
Does a delayed replantation have a poor or strong long term prognosis?
ankylosis related root resorption
What is the expected outcome in a delayed replantation?
4-6 weeks
For closed mature apex: extra oral dry time being greater than 60 minutes, how long would we splint the teeth
???
Possible exam question “Why are we applying fluoride?”
YES
For a Closed (mature) Apex that has been out of the mouth for >60 mins, Could you do the Endo before replanting?!
Tetracycline
what has the additional benefit of decreasing root resorption by affecting the motility of the osteoclasts and reducing the effectiveness of collagenase?
Nylon fishing line (0.13-0.25 mm)
What can be used to create a flexible splint?
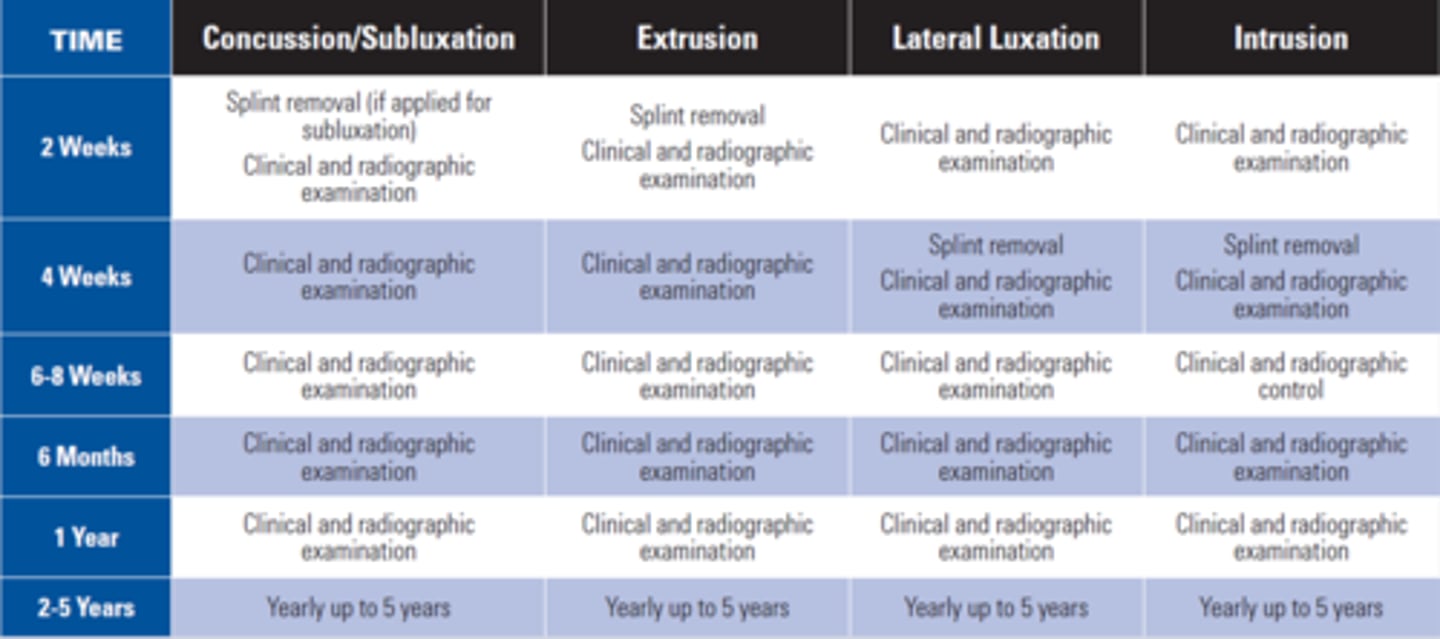
splinting time for various types of injuries
1-2 months
During the obturation of an avulsed/traumatized tooth, how long should Calcium Hydroxide be in place for?
<30mins
What extraoral dry time presents the best prognosis for an avulsed tooth?
33%
Teeth with immature apex have how much percent chance of revascularization?
tetracycline, stannous fluoride (NaF)
What are some root surface treatments for avulsed teeth?
c. Position in the arch (This type of fracture involves enamel, dentin, and pulp)
Which of the following factors does not need to be considered when evaluating a crown fracture with pulp exposure?
a. Extent of fracture
b. Stage of root development
c. Position in the arch
d. Time since the injury
c. 4 weeks (Initial treatment for root fractures should be of acute priority for best results)
How long should horizontal root fractures be splinted, if the Fracture is in the apical 1/3?
a. Splinting is not indicated
b. 7 -10 days
c. 4 weeks
d. 4 months
pulp necrosis, pulp canal obliteration, root resorption
What are some Complications Following Traumatic Injuries?
intrusion
Which has the worst prognosis of luxation injuries in terms of pulp survival?
no
Are pulpal necrosis and periapical disease a common complication of PCO?
yellow discoloration
what can be a common finding in teeth with pulpal obliteration but does not imply the presence of pulp or periapical disease
asymptomatic
>2/3 of teeth with pulpal obliteration are...
1% to 27%
The incidence of pulp necrosis following PCO is variable ranging from_____ ______, but is generally considered low
clinical symptoms and/or definite radiographic findings suggestive of periapical disease
When are root canal treatments indicated?
non-vital (Internal) bleaching
If root canal treatment is required and there are aesthetic concerns, which technique can be considered?
true
T or F: Teeth with Pulp Canal Obliteration requiring root canal treatment are challenging
root resorption
Loss of pre-cementum, cementoblasts and epithelial rest of Mallassez à denuded root surface à hard tissue resorbing cells remove damaged periodontal ligament and cementum
Internal root resorption
characterized by resorption of the internal aspect of the root by multinucleated giant cells
Surface resorption (Localized injury), Inflammatory root resorption, Replacement root resorption (Ankylosis)
External Root Resorption types
Surface Resorption (Localized injury)
Localized injury to PDL or cementum, Local inflammatory response, Periodontal healing and root surface repair will occur within 14 days, May or may not be radiographically visible, No treatment is required
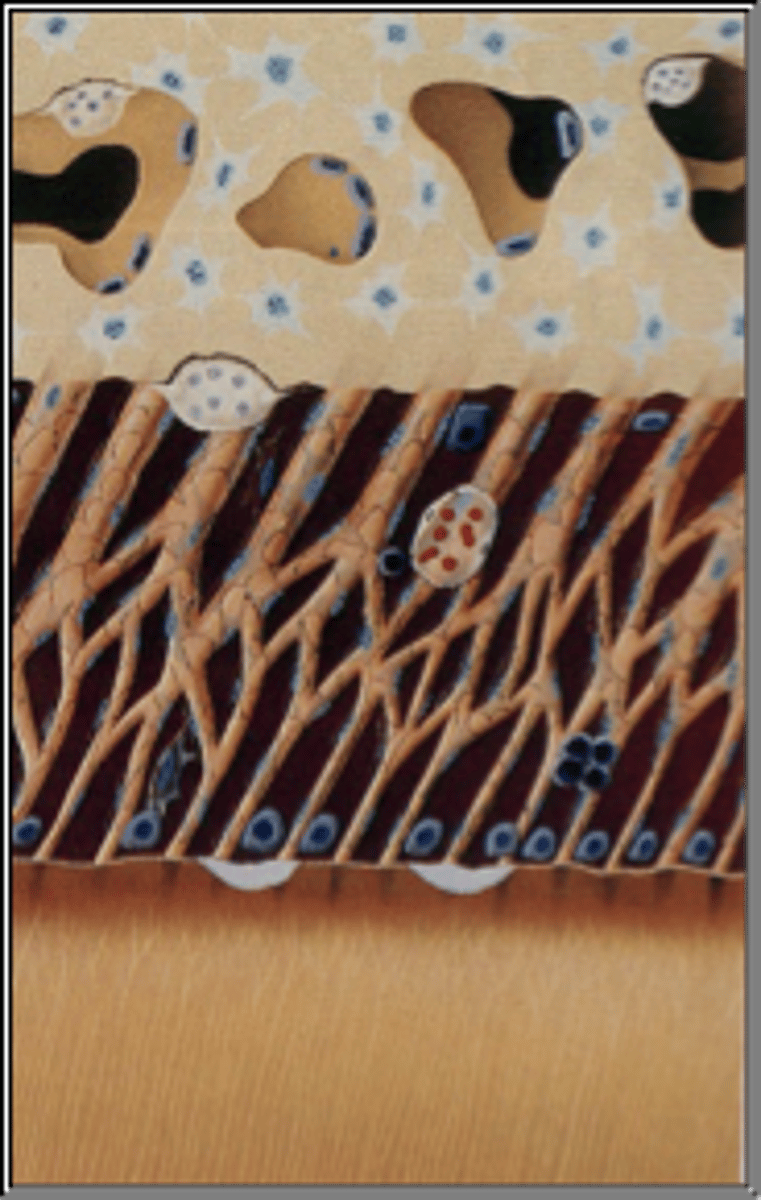
Surface Resorption (Localized injury)
Clinical evaluation:
-No significant signs
-Transient condition/ self limiting (no treatment needed!)
-Normal physiologic response, no significant inflammation
-Spontaneous destruction and repair process on root surface
Inflammatory Root Resorption
Clinical evaluation:
-Asymptomatic
-Necrotic pulp
-Progression: inward and lateral but leaving canal intact
-Resorption may begin 2-12 wks after trauma
-Transient/progressive (most likely requires RCT)
Inflammatory Root Resorption
•Damage of the periodontium
•Bacteria within tubules
•2-visit NS-RCT with Ca(OH)2 can arrest resorptive process and promote healing
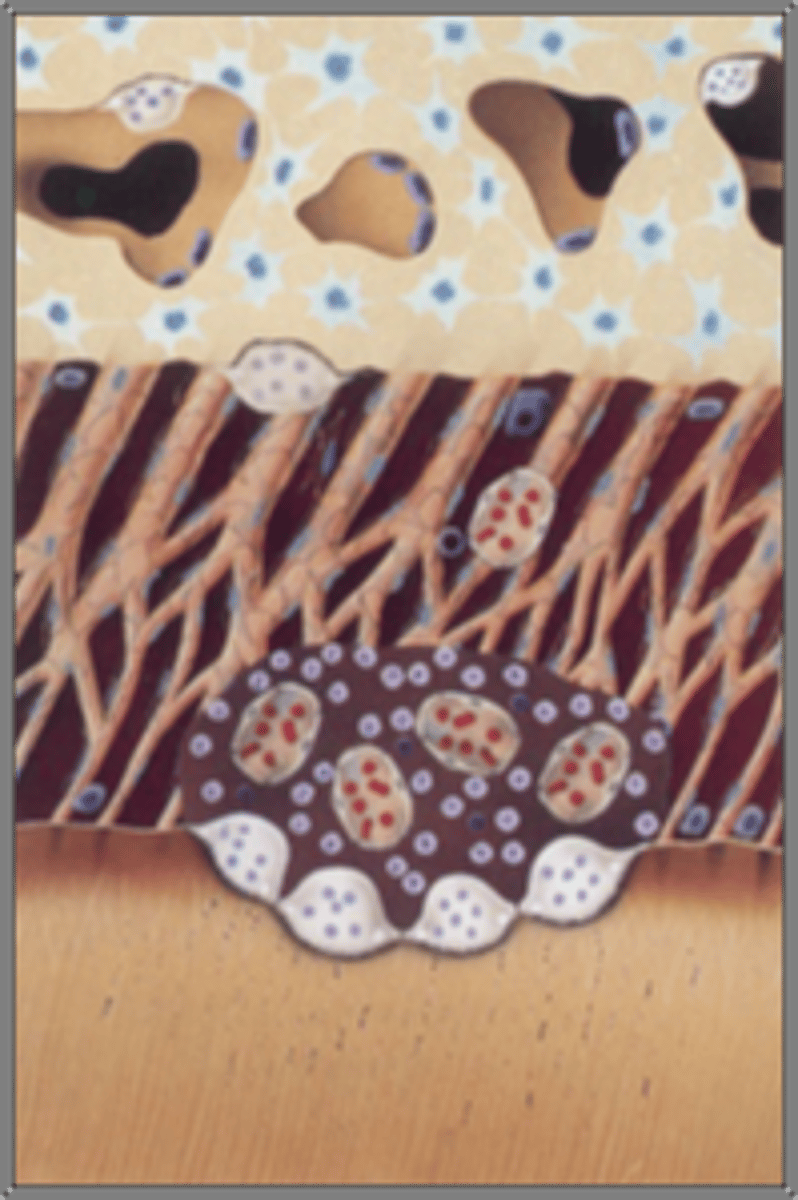
Replacement resorption (Ankylosis)
•Severe damage to the periodontium (Intrusion, Avulsion)
•“Fusion” of the tooth root with the adjacent alveolar bone
•Diagnosis:
-Tooth is immobile
-High percussive tone
-No visible PDL space
•Treatment:
-Cannot be arrested or repaired
•Survive for a number of years
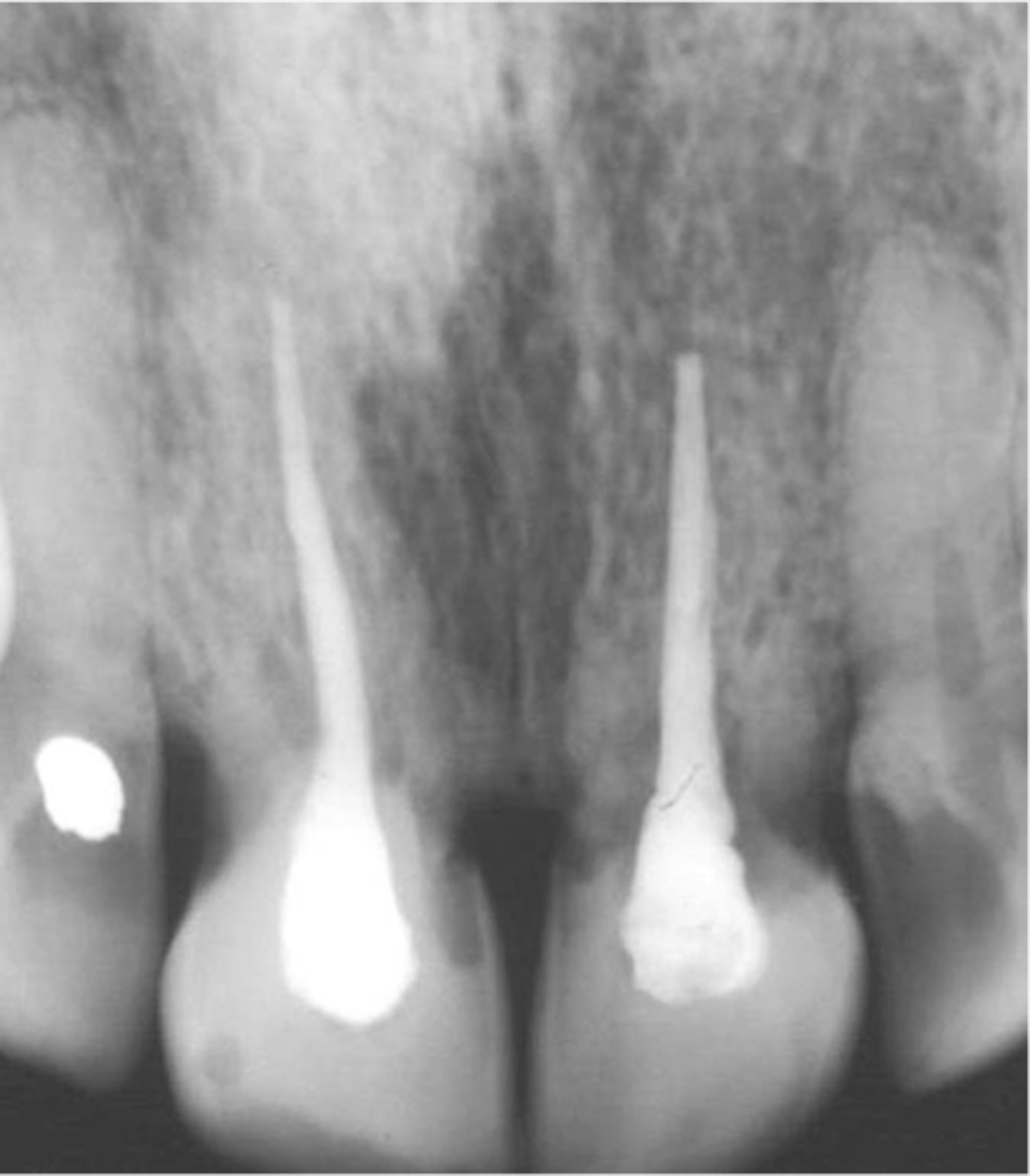
fusion of the alveolar bone and the root surface
In replacement resorption, Repair is accomplished with
disappearance of the normal PDL space
Radiographically Replacement Resorption is characterized by what and continuous replacement of root substance with bone?
d. All of the above
Which of the following traumatic events Can cause injury to the periodontium?
a. Concussion
b. Intrusion
c. Extrusion
d. All of the above