Chemistry Final Ultimate Review Study Guide
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/127
Earn XP
Description and Tags
1-28: Notes: Bonding Basics 29-43: Notes: Electron Configuration 1-3 44-47: Notes Making of an ion
Last updated 3:23 PM on 5/31/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
1
New cards
Define electronegativity (EN)?
A measurement of how much an atom wants the electron from another electron
2
New cards
Define Pauling Scale?
A scale used to measure how much an atom wants the electrons from another atom. The smaller the number less the atom wants more
3
New cards
Where are Valence Electrons found and what is there role?
They are found in the outside energy level and is involved in making of ionic and covalent bonds
4
New cards
Define Polar Covalent Bond?
The electrons are not shared equally. The atom with the greater En shares the electrons longer and will be partially negative
5
New cards
Define Nonpolar Covalent Bond?
The electrons are shared equally and there is not is partial negative and positive end
6
New cards
Define Electrostatic Force?
A fore produced when a negative and positive are attracted
7
New cards
Define Ionization Energy?
The energy required to remove an electron is added to an atom
8
New cards
Define Electron Affinity Energy?
The energy released when an electron is added to an atom
9
New cards
Define Crystal Lattice?
A crystal formed in ionic compounds when are arranged in an ordered and 3 dimensional way. The atom occur in a pattern and regular intervals
10
New cards
Define Lattice Energy?
The energy given off when positive on negative ions come together to form an bond
11
New cards
How can you tell if it an ionic bond?
* Forms between an metal and nonmetal
* EN difference between the atoms is greater than EN on the Pauling scale
* Are usually found far apart on the periodic table
* EN difference between the atoms is greater than EN on the Pauling scale
* Are usually found far apart on the periodic table
12
New cards
Steps to forming an ionic bond - step 1: A -------- with a low ---------- gives away ------ so the outer ------- level is full and stable
metal, EN, electrons, energy
13
New cards
Steps to forming an ionic bond - step 2: When ------- are ------- a cation is formed. ------- energy is needed to remove the electrons
electrons, lost, ionization
14
New cards
Steps to forming an ionic bond - step 3: A ------ with a high -------- takes enough ------- to fill the outer ------ level
nonmetal, EN, electron, energy
15
New cards
Steps to forming an ionic bond - step 4: When ------ are ------- an anion is formed. When the ------ are added ------ is released
electron, gained, electrons, electron affinity energy
16
New cards
Steps to forming an ionic bond - step 5: The ------ and ------ are attracted to each other
cation, anion
17
New cards
Steps to forming an ionic bond - step 6: An ------ force holds ------ together in a repeating pattern
electrostatic, anion
18
New cards
Steps to forming an ionic bond - step 7: When the ionic bond is formed into a crystal lattice, the --------- energy is released
Lattice
19
New cards
Define Covalent Bond?
A bond where electrons are shared
20
New cards
How can you tell if it an covalent bond?
* Formed between two nonmetals or nonmetal and metalloid
* EN difference between two atoms is less than 1.7 on the Pauling scale
* Are found close together on periodic table
* EN difference between two atoms is less than 1.7 on the Pauling scale
* Are found close together on periodic table
21
New cards
Steps in forming a covalent bond - step 1: There are two atoms that have the same --------, but can each atom needs ------- to obtain a stable energy level
EN, electrons
22
New cards
Steps in forming a covalent bond - step 2: The ------- will be attracted to the ------ in the nucleus
Valence electrons, protons
23
New cards
Steps in forming a covalent bond - step 3: Each electron moves around the energy level space of BOTH the atoms. Neither one of the atoms “keeps” the ------ longer so the bond has no charge so it is a ------ bond
electrons, nonpolar
24
New cards
Steps in forming a covalent bond - step 4: If the two atoms have ---- then the shared ----- will move around the ------ space to BOTH the atoms
EN, electrons, energy level
25
New cards
Steps in forming a covalent bond - step 5: The atom with the ----- EN will “keep” the ----- longer. In this same atom the protons in the nucleus have a slightly greater attraction to the -----. That will cause a partial ------ end and a partial ------ end. This is a ------ covalent bond
Higher, electrons, electrons, negative, positive, polar
26
New cards
How does polarity affect bonds?
* Greater polarity causes a stronger bond
* Greater EN the more polar the bond and the more like an ionic bond
* Greater EN the more polar the bond and the more like an ionic bond
27
New cards
What the weakest bonds to strongest
* Most gases have nonpolar covalent bonds
* Many liquid have polar covalent bonds.
* A few solids have polar covalent bonds. Most solids are held together by ionic bonds at room temperature
* Gas, liquid, solid
* Many liquid have polar covalent bonds.
* A few solids have polar covalent bonds. Most solids are held together by ionic bonds at room temperature
* Gas, liquid, solid
28
New cards
What is symbol used to show that there is a partial charge?
d+ d-
29
New cards
Define Electron Configuration?
The organization of the electrons in an atom
30
New cards
What is in each energy level in Electron Configuration?
In each energy level there are orbitals. An orbital represent the area around the nucleus of an atom where there is the greatest probability of locating an electron
31
New cards
What are symbol of the 4 different types of orbitals?
s, p, d, f
32
New cards
What are some important points energy level and orbitals
* Only 2 electrons can be in orbital
* Every energy level starts with s orbital
* There is a maximum a of 1 s-orbital with 2 electrons
* There is a maximum of 3 p-orbital with 2 electrons in each for a total of 6 electrons
* There is a maximum of 5 d-orbitals with 2 electrons in each for a total of 10 electrons
* Every energy level starts with s orbital
* There is a maximum a of 1 s-orbital with 2 electrons
* There is a maximum of 3 p-orbital with 2 electrons in each for a total of 6 electrons
* There is a maximum of 5 d-orbitals with 2 electrons in each for a total of 10 electrons
33
New cards
What is Hund’s Rule?
Electrons occupy all different orbitals within the same sub-orbital before doubling up the orbital. Example: the p-orbital can have 3 suborbitals. There must be 1 electrons in each of the 3 suborbitals before adding the second electron to each
34
New cards
Now do you know how to write orbital diagrams. How do you write Orbital notation?
2s^2
2 = Energy level
s = Type of orbital
^2 = # of electrons
2 = Energy level
s = Type of orbital
^2 = # of electrons
35
New cards
What must happen in order for chemical reaction to occur and how does electron configuration play an role?
For a chemical reaction to occur there must be energy, and the loss or gain of electrons. Thus electrons need to be loss or gain to be round down or round up to nearest full energy level
36
New cards
What is formed when electrons are lost
An cation (+) is formed
37
New cards
What is formed when electrons are gained
An anion (-) is formed
38
New cards
Where are all of the noble gas on periodic table?
He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn
39
New cards
Why are valence electrons important and their role?
As we know valence are the electrons that do most of the work during an chemical reaction and can participate in the formation of chemical reactions
40
New cards
What do the “leftovers” electrons in s and p orbitals represent?
Valence electrons
41
New cards
How do you draw valence dot diagrams?
1. Each side of the square can only have 2 electrons
2. You must put 1 electron on each side of the square before adding the second (Hund’s rule)
3. The electrons are put on each side in a clockwise direction
4. Maxim number of electrons around the square is 8 because the maxim number of valence electrons is 8
42
New cards
What are some major properties of ionic compound properties compared to covalent compound properties?
1. Ionic compound properties
* Strongly attracted to each other
* They are harder and less flexible
* Tend to be less flammable
* Ions are needed to conduct electricity in an aqueous solution
* Dissolve well in water
43
New cards
What are some major properties of covalent compound properties compared to ionic compound properties?
1. Covalent compound properties
* Can be separated from each other when a lower amount of energy is added to them
* Has lower enthalpy of fusion (melting point) and vaporization (boiling point) than ionic compound
* Tend to be soft and flexible
* Are more flammable than ionic compound bonds
* They don’t conduct electricity
* Don’t dissolve well in water
44
New cards
Will Sulfur electron configuration lose or gain electrons? 1s^2, 2s^2, 2p^6, 3s^2, 3p^4
The atom on the third energy level has 6 valence electrons and gain 2 electrons to fill the third energy level. This will form all anions S^-2
45
New cards
Will Potassium electron lose or gain electrons? 1s^2, 2s^2, 2p^6, 3s^2, 3p^6, 4s^1
The atom on fourth energy level has 1 valence electrons and will lose 1 electrons to full third energy level. This makes a cation K^+1
46
New cards
Why do ions form? Cation (+) and anion (-) are both ions
The path that requires least amount of energy to make the unstable atom more stable ions
47
New cards
What are names of periodic table families and their location?
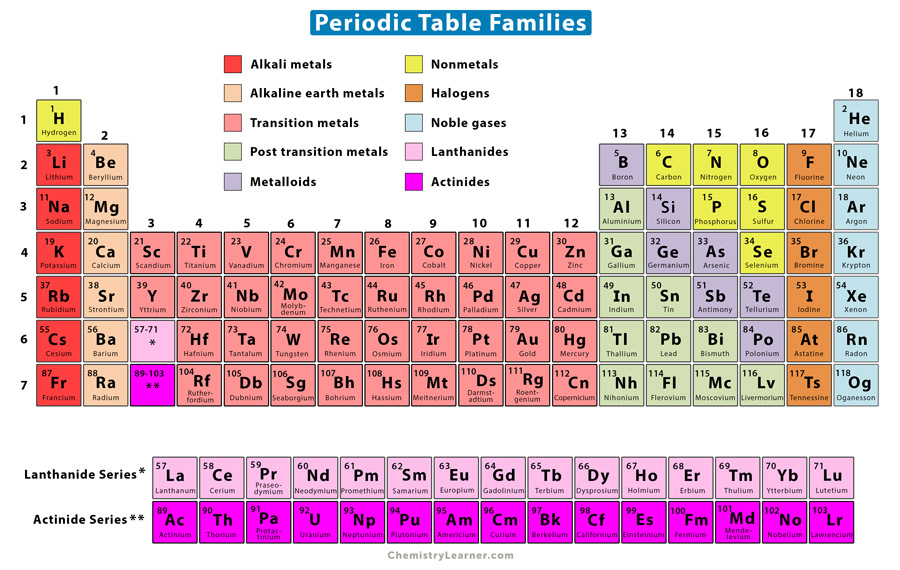
48
New cards
What does Coulomb’s Law explain?
It used to explain the relative strength of the ionic attraction between cation and anion
49
New cards
How can you find the relative strength of an ionic bond?
* Charge of ions: An the charge (+) or (-) goes up relative strength
* Distance between two ions: Smaller the distance (smaller radius) relative strength increase
* The charges are the most important factor for determining the strength of the bond
* You look at distance only when the charges are similar
* Distance between two ions: Smaller the distance (smaller radius) relative strength increase
* The charges are the most important factor for determining the strength of the bond
* You look at distance only when the charges are similar
50
New cards
What is the trend down family and across period for EN and atomic radius?
Down family: Reduce EN, Gained Atomic radius
Across period: Gained EN, Reduce Atomic radius
\
Across period: Gained EN, Reduce Atomic radius
\
51
New cards
Define Delocalized Electrons?
The electrons from the valence shell of a group of metallic atoms. These electrons can move freely and are attracted to the metallic cations
52
New cards
Define Malleable?
The ability to be pounded into sheet. Aluminium foil is an example
53
New cards
Define Ductile?
the ability to be pulled into wire. Copper wire is an example
54
New cards
Define Luster?
Having a shiny surface. Many metals are described as lustrous
55
New cards
Define Molten?
The state described after energy is added to a substance. The substance is a solid at room temperature. Metals will become “melted” or molten when energy is added
56
New cards
How are metallic bonds formed?
They are formed when a sea of delocalized electrons are electrostatically attracted to the positive nuclei of metal cations
57
New cards
Metallic bonds are usually considered strong. There are three factors that affect the strength?
* When there are more delocalized electrons in the sea of electrons then there is a greater attraction between the nuclei and the electrons
* Higher the positive charge for an element. The stronger the metallic bond
* Smaller ionic radius will allow more atoms to be packed together. This allows greater electrostatic attraction between the valence electrons and the metallic cations
* Higher the positive charge for an element. The stronger the metallic bond
* Smaller ionic radius will allow more atoms to be packed together. This allows greater electrostatic attraction between the valence electrons and the metallic cations
58
New cards
Coulomb law: A set of rules to explain the strength of attractive and/or repulsive forces
* Greater the charge means a greater electrostatic force
* Smaller distance (smaller radius) greater electrostatic force
* Smaller distance (smaller radius) greater electrostatic force
59
New cards
Ionic compounds are usually harder to melt: They have stronger attractive forces. Why?
* Greater EN
* Transfer of valence electrons
* Cations and anion are formed
* Electrostatic force produced
* Transfer of valence electrons
* Cations and anion are formed
* Electrostatic force produced
60
New cards
Covalent compounds are usually easier to melt. They have weaker attractive forces. Why?
* Smaller EN
* Sharing the electrons equally or unequal
* Nuclear charges (protons) and valence electrons (electrostatic force)
* Shielding effect
* Sharing the electrons equally or unequal
* Nuclear charges (protons) and valence electrons (electrostatic force)
* Shielding effect
61
New cards
What is general rule about solubility?
Polar covalent usually dissolves polar solutes, like water. Nonpolar solvents usually dissolve nonpolar solutes
62
New cards
What do the prefixes endo- and exo mean?
Endo = inside (absorb)
Exo = leave (release)
Exo = leave (release)
63
New cards
How do you identify the central atom in a compound?
Has the lowest EN - Distance from F
64
New cards
What elements are usually central atoms?
Cl, Si, Ge, As, P, S, Se
65
New cards
What element is always the central atom?
C
66
New cards
Which elements are never the central atom?
F, H
67
New cards
How many electrons can go around most elements and bonds?
8 electrons = 4 bonds
68
New cards
How many electrons can hydrogen have going around it?
2 electrons = 1 bond
69
New cards
If there are too many electrons in this structure that means you will have double and triple bonds. More of the electrons will have double or triple bonds?
1. C and N can have single, double, and triple
2. C should ALWAYS have 4 bonds
3. P, S, and O can have single or double bonds
4. O will only have a triple bond if there is no other structure possible
5. The halogens will never have double or triple bonds
70
New cards
What does TBU stand for?
T = Total pairs
B = Bond pairs
C = Unbonded pairs
B = Bond pairs
C = Unbonded pairs
71
New cards
Molecular geometry is determined by a process called VSEPR. It stands for: Valence Shell Electrons Pair Repulsion
\
72
New cards
What do linear-linear, trigonal planar-trigonal planar, tetrahedral-tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal-trigonal bipyramidal, and octahedral-octahedral have in common?
They are nonpolar, and anything beside those polar (except linear and square planar. That are nonpolar)
73
New cards
Define Resonance Structure?
One of two or more lewis structure representing a single molecule with bonding that cannot be described fully with only one lewis structure
74
New cards
What the purpose of formal charge?
When more than one resonance structure is possible, the determination of the best structure can be made based on the formal charges in the structure
75
New cards
What the equation for formal charge?
Valence electrons in \[element\] - 1/2 bonding electrons - lone pair electrons = \[formal charge\]
\
Example
BF3
Valence electrons in B seven - 1/2 six bonding electrons - zero lone pair electrons = 0
Valence electrons in F seven - 1/2 two bonding electrons - six bonding electrons = 0
\
Example
BF3
Valence electrons in B seven - 1/2 six bonding electrons - zero lone pair electrons = 0
Valence electrons in F seven - 1/2 two bonding electrons - six bonding electrons = 0
76
New cards
Polarity is determined by two important characteristics?
Electronegativity and molecular geometry?
77
New cards
What makes the element either partially negative or partially positive?
The greater EN shares the electron longer and has a partial (-) charge. The smaller EN it shares the electron less and has partial (+) charge. In other words electrons are shared unequally
78
New cards
What do partial negatives and partial positives serve as?
Partial negative and partial positives are both attracted due electrostatic force. Thus both of them are attracted to each other, but since partial negative has greater EN. That means that the partial negative holds the electrons longer than partial positive. Partial negative and positive are found intermolecular forces, but no intramolecular forces
79
New cards
How can you determine if the bond is polar or nonpolar?
1. Nonpolar
* If ALL of the bonds are nonpolar and there are no lone electrons then the molecule has to be nonpolar
* If all of the polar bond forces equal zero then the bond is nonpolar
2. Polar
* If ALL the bonds are polar then the molecule could be polar or nonpolar
* If all the forces are greater than zero the molecule is polar
\
\
\
\
\
80
New cards
What are the Intramolecular forces?
They hold atoms together in molecules and polyatomic ions. There are three them. Ionic and covalent and metallic
81
New cards
What are the intermolecular forces?
They hold molecules together as a solid, liquid, or gas. There are four them. Dispersion and dipole-dipole and hydrogen forces and ion-dipole
82
New cards
Why are intramolecular forces stronger than intermolecular forces?
Intramolecular forces hold full charges for positive and negatives, but intermolecular forces form only partial positive and negative charges?
83
New cards
What factors affect strength of IMF (intermolecular forces)?
Size of the charge and distance
84
New cards
Define Coulomb Law?
The larger charge the greater force, the larger distance the smaller the force
85
New cards
Define instantaneous dipole?
There are hundreds of thousands of atoms and molecules that make up a substance. At any time one or more the electrons that are in these atom or molecules will instantaneously be found concentrated on one side. They are also known as London Dispersion forces
86
New cards
What is induced dipole?
That dipole can influence the atoms or molecules around them and cause the electrons to move to one side. This can passed through a substance and is called an induced dipole. They are temporary and do not last long. The strength of this type of LMF is determined by the number of electrons and the shape. More electrons mean a higher chance of moving to one side and shape can determine area the interactions can take place
87
New cards
Define polarizability?
This ability to shift electrons is called the polarizability of the atom. The more electrons the greater polarizability
88
New cards
Where do intermolecular forces originate?
They originated from electrostatic forces
89
New cards
What causes London Dispersion forces?
Temporary dipoles
90
New cards
What causes dipole-dipole?
Permanent dipoles
91
New cards
What elements form diatomic molecules?
H2, N2, F2, O2, I2, Cl2, and Br2
92
New cards
What are hydrogen forces?
Stronger than dipole-dipole. They have small atomic radius and have an high EN. Forms with Hydrogen and paired with F, O, or N
93
New cards
What is viscosity?
How thick an substance is
94
New cards
What are physical properties influence by IMF?
Surface tension, viscosity, melting point, boiling point, vapor pressure, cohesion, and adhesion
95
New cards
Define adhesion?
The attraction between the same type of molecule
96
New cards
Define cohesion?
The attraction between the different types of molecules
97
New cards
The stronger the intermolecular force the:
* Higher the boiling point
* higher the melting point
* Higher the surface tension
* Lower the vapor pressure
* higher the melting point
* Higher the surface tension
* Lower the vapor pressure
98
New cards
Define exothermic?
A chemical reaction that releases energy
99
New cards
Define endothermic?
A chemical reaction that absorb energy
100
New cards
How do you know if it an composition (synthesis) - syn
1. 2 or more substance combine to produce a fewer substance
2. Sometimes redox
Example and Practice
* H2 + O2 = 2 H20
* CO + O2 = 2 CO2
* K + Cl2 = 2 KCl