RAD 120 - Ch 11 Filtration - Key Terms & Definitions
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Added Filtration
any filtration that occurs outside the tube and housing before the image receptor
Compensating Filter
usually designed to solve a problem involving unequal subject densities
Compound Filter
the use of two or more materials to complement one another in their absorbing abilities; also known as K-edge filters
Filter
any material designed to selectively absorb photons from the x-ray beam
Half-Value Layer (HVL)
the amount of absorbing material that will reduce the intensity of the primary beam to half of its original value
Inherent Filtration
A result of composition of the tube and housing
K-edge Filter
the use of two or more materials to complement one another in their absorbing abilities; also known as compound filters
Thoraeus Filter
A type of compound filter consisting of tin, copper, and aluminum, in that order, typically used in radiation therapy.
Total Filtration
the sum of inherent and added filtration
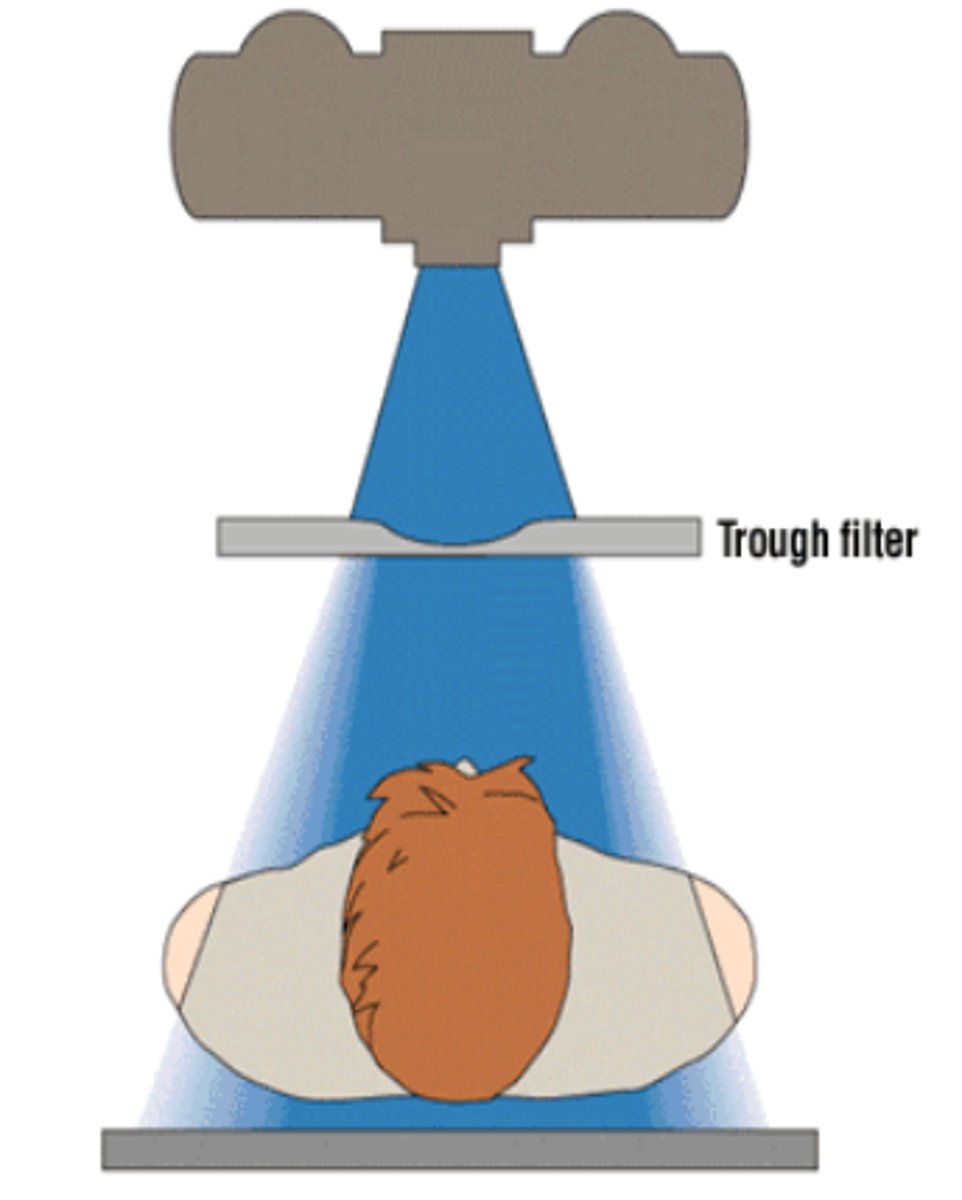
Trough Filter
A double wedge compensating filter added to the primary beam to produce more consistent exposure to the image receptor
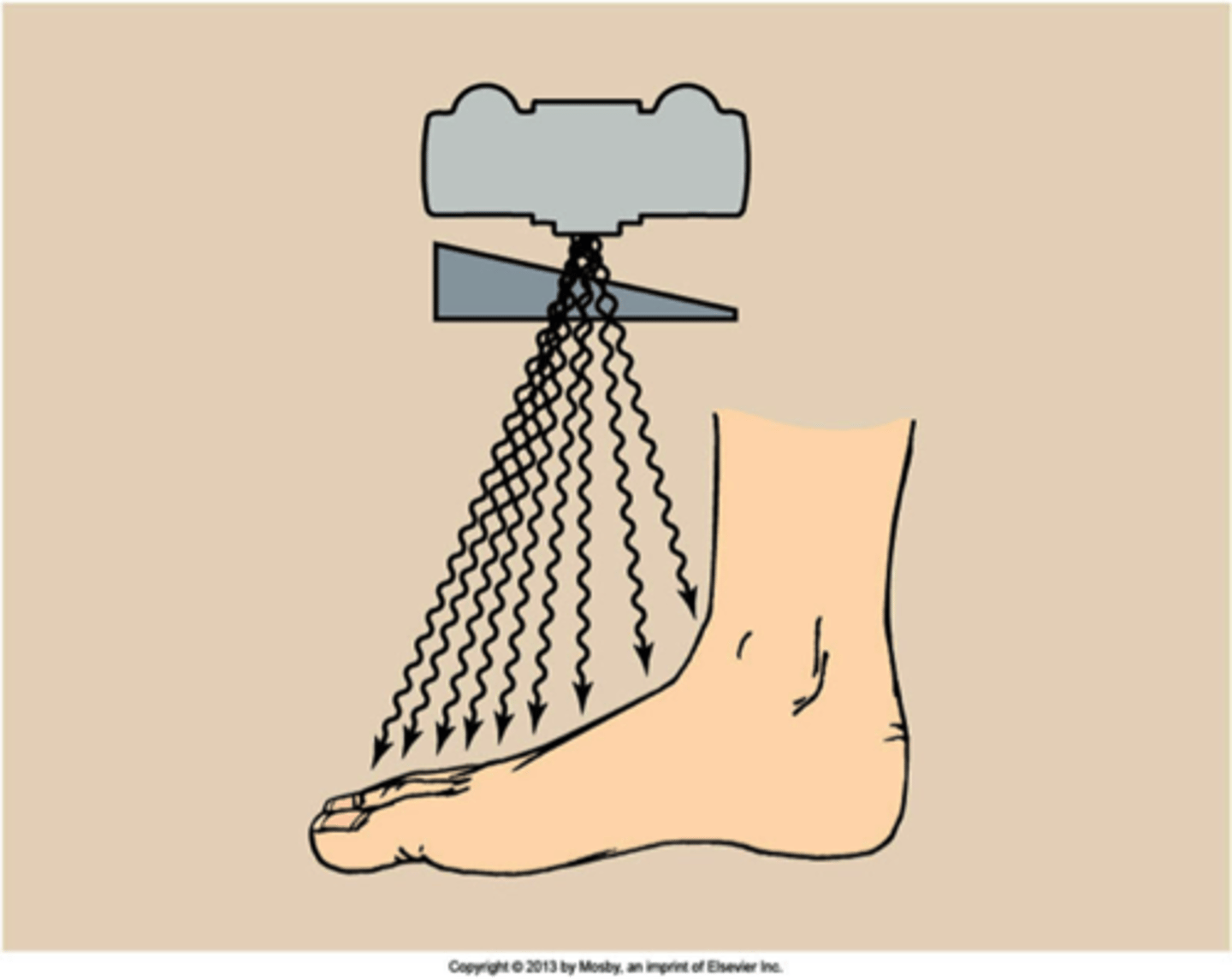
Wedge Filter
Most common kind of compensating filter which is used to radiograph body parts that vary considerably, such as the foot.
Filtration
eliminates the low-energy x-ray photons by inserting absorbing materials into the primary beam
Best range for significant soft tissue penetration
30-40keV
Filtration is expressed in terms of
Aluminum Equivalency (Al/Eq)
Filtrations Effect on Output
- filtration reduces patient exposure, but also removes a portion of useful beam affecting IR exposure
- To compensate for the loss of exposure when filtration is increased, technical factors must be increased to maintain the same image receptor exposure