L2: pH Measurement and Buffer Preparation
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
1
New cards
pH
a measure of how acidic/basic a solution is.
2
New cards
0-14
pH range goes from ___ __to__ __
3
New cards
acidic
If pH < 7, then the solution is __________
4
New cards
neutral
If pH = 7, then the solution is _______________
5
New cards
**basic**
If pH > 7, then the solution ______________
6
New cards
C
A solution has a pH of 9. What can be inferred about the nature of this solution?
A) The solution is acidic.
B) The solution is neutral.
C) The solution is basic.
D) The solution is both acidic and basic.
A) The solution is acidic.
B) The solution is neutral.
C) The solution is basic.
D) The solution is both acidic and basic.
7
New cards
A
A solution has a pH of 4.5. What does this pH value indicate about the solution?
A) The solution is acidic.
B) The solution is neutral.
C) The solution is basic.
D) The solution is neither acidic nor basic.
A) The solution is acidic.
B) The solution is neutral.
C) The solution is basic.
D) The solution is neither acidic nor basic.
8
New cards
potential of hydrogen
The letters pH stand for _______________
9
New cards
pH
_______ is a measure of the hydrogen ion (H+) concentration in an aqueous solution
10
New cards
pH
__________ is also expressed as the negative of base 10 logarithm of the hydrogen-ion concentration.
11
New cards
potential of Hydroxide
pOH stands for _________________
12
New cards
\-log \[H+\]
pH = formula
13
New cards
\-log \[OH-\]
pOH = formula
14
New cards
pOH
It is a measure of hydroxide ion (OH–) concentration
15
New cards
pOH
It is expressed as the negative of the base 10 logarithm of the hydroxide-ion concentration.
16
New cards
7\.8-8.4
Nemo (clownfish) requires a pH between ________________
17
New cards
chemical reactions and processes are affected by the hydrogen ion concentration
The control of pH is important in organism and their cells because ____________________
18
New cards
acid
a compound that can donate a hydrogen ion.
19
New cards
base
a substance that accepts hydrogen ions.
20
New cards
hydrogen
low pH; Acids
21
New cards
hydroxide
high pH; Alkalis
22
New cards
B
What does the pH value represent in an aqueous solution?
A) The concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-)
B) The concentration of hydrogen ions (H+)
C) The concentration of oxygen ions (O2-)
D) The concentration of sodium ions (Na+)
A) The concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-)
B) The concentration of hydrogen ions (H+)
C) The concentration of oxygen ions (O2-)
D) The concentration of sodium ions (Na+)
23
New cards
D
What does the term "pOH" represent in a solution?
A) The concentration of hydrogen ions (H+)
B) The concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-)
C) The negative logarithm of the hydrogen-ion concentration
D) The negative logarithm of the hydroxide-ion concentration
A) The concentration of hydrogen ions (H+)
B) The concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-)
C) The negative logarithm of the hydrogen-ion concentration
D) The negative logarithm of the hydroxide-ion concentration
24
New cards
6
Approx ___ mmol of H+ is produced by metabolism everyday
25
New cards
4; 100000
Approx 6mmol of H+ is produced by metabolism everyday if all of this were to be diluted in the extracellular fluid \[ECF\] (=14L), \[H+\] would be __mmol/L , or__ __ times ==**more acidic than normal!**==
26
New cards
TRUE
Efficient urine excretion of H+ produced ensures that this does not happen; as a result, urine is profoundly acidic.
\
T/F
\
T/F
27
New cards
Carbon dioxide (CO2).
Metabolism also produces ________________.
28
New cards
H2CO3, carbonic acid
In solution the CO2 converts to weak acid (H2CO3, ___________).
29
New cards
acid-base balance
The large amount of CO2 produced by cellular activity each day could upset __________________
30
New cards
lungs
But under normal circumstances large amount of CO2 is to be excreted via _______.
31
New cards
B
Approximately how many millimoles (mmol) of H+ ions are produced by metabolism every day?
A) 60 mmol
B) 6 mmol
C) 600 mmol
D) 16 mmol
A) 60 mmol
B) 6 mmol
C) 600 mmol
D) 16 mmol
32
New cards
B
What is the primary reason for the excretion of carbon dioxide (CO2) via the lungs, which is produced as a result of metabolism?
A) To increase the oxygen content in the bloodstream
B) To prevent the buildup of carbonic acid (H2CO3) in solution
C) To enhance the production of bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) in the blood
D) To lower the overall acidity of the body's extracellular fluid
A) To increase the oxygen content in the bloodstream
B) To prevent the buildup of carbonic acid (H2CO3) in solution
C) To enhance the production of bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) in the blood
D) To lower the overall acidity of the body's extracellular fluid
33
New cards
Chemists
_____________ have tried to define acids and bases in relation to their compositions and molecular structures
34
New cards
Svante Arrhenius
defines **acids** as substances that produce H+ ions in aqueous solution while **bases** are substances that produce OH- ions in aqueous solution
35
New cards
Gilbert N. (G.N.) Lewis
Mentioned that **acids** are electron-pair acceptors and **bases** are electron-pair donor.
36
New cards
Johannes Bronsted and Thomas Lowry
the most useful and accepted definition of acids and bases nowadays are those proposed by ____________ __and__ __________________
37
New cards
Bronsted-Lowry theory
the most useful and accepted definition of acids and bases nowadays are those proposed by Johannes Bronsted and Thomas Lowry, and it is known as the _______________
38
New cards
acid
HCl (Hyrochloric acid) is an _______ because it donates a proton making Cl- (Chloride)
39
New cards
base
water is a ____ because it accepts a proton making H3O+.
40
New cards
Bronsted-Lowry theory
the theory explains that for every acid-base reaction, there is a creation of conjugate acid-base pair.
41
New cards
TRUE
Cl- is the conjugated base of HCl and H3O+ is the conjugated acid of water as shown below.
\
T/F
\
T/F
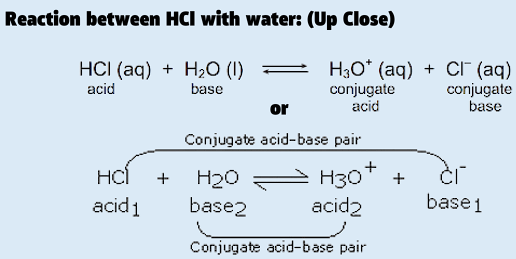
42
New cards
Soren Peter Lauritz Sorensen (S.P.L.) Sorensen
introduced the pH scale that measures the strength of an aqueous acidic or basic solution.
43
New cards
pH = -log \[H+\]
It converts the H+ concentrations to pH using the formula.
44
New cards
pH
The precise definition of _______ is "the negative common logarithm of the activity of hydrogen ion in solution
45
New cards
C
According to the definition, how are acids and bases distinguished based on their behavior in aqueous solutions?
A) Acids produce OH- ions, while bases produce H+ ions.
B) Acids and bases both produce H+ ions.
C) Acids produce H+ ions, while bases produce OH- ions.
D) Acids and bases both produce OH- ions
A) Acids produce OH- ions, while bases produce H+ ions.
B) Acids and bases both produce H+ ions.
C) Acids produce H+ ions, while bases produce OH- ions.
D) Acids and bases both produce OH- ions
46
New cards
A
In the given rationale, why is HCl considered an acid?
A) HCl donates a proton, forming Cl- (Chloride).
B) HCl accepts a proton, forming Cl- (Chloride).
C) HCl donates an electron, forming Cl- (Chloride).
D) HCl releases an electron, forming Cl- (Chloride)
A) HCl donates a proton, forming Cl- (Chloride).
B) HCl accepts a proton, forming Cl- (Chloride).
C) HCl donates an electron, forming Cl- (Chloride).
D) HCl releases an electron, forming Cl- (Chloride)
47
New cards
A
According to the rationale, what is the conjugated base of HCl?
A) Cl-
B) HCl
C) H3O+
D) OH-
A) Cl-
B) HCl
C) H3O+
D) OH-
48
New cards
C
Which mathematical expression represents the calculation of pH using the hydrogen ion concentration \[H+\]?
A) pH = \[H+\]
B) pH = log \[H+\]
C) pH = - log \[H+\]
D) pH = 10^-\[H+\]
A) pH = \[H+\]
B) pH = log \[H+\]
C) pH = - log \[H+\]
D) pH = 10^-\[H+\]
49
New cards
A
If a solution has a pH of 6.75, what is the pOH of the solution?
A) pOH = 7.25
B) pOH = 7.30
C) pOH = 7.75
D) pOH = 7.80
A) pOH = 7.25
B) pOH = 7.30
C) pOH = 7.75
D) pOH = 7.80
50
New cards
Buffers
________ prevent changes in pH
51
New cards
Buffers
__________ resist changes in the pH even when acids or bases are added.
52
New cards
**Buffers**
**_______ are a** **mixture of a weak acid or alkali and one of its salts**
53
New cards
Le Chatellier's principle.
The ability of buffers to resist large changes in pH is governed by the ________________
54
New cards
La Chatellier's Principle
A principle of equilibrium shift due to changes in buffer conditions.
55
New cards
carbonic acid
In our blood, ____________ is the most important buffer.
56
New cards
carbonic acid
This solution maintains our blood pH to facilitate transport of oxygen from the lungs to the cells
57
New cards
C
What is the primary role of buffers in a solution?
A) To increase the pH of the solution
B) To decrease the pH of the solution
C) To prevent changes in pH
D) To enhance the reactivity of the solution
A) To increase the pH of the solution
B) To decrease the pH of the solution
C) To prevent changes in pH
D) To enhance the reactivity of the solution
58
New cards
D
How do buffers resist changes in pH when acids or bases are added to a solution?
A) By neutralizing the acids or bases
B) By releasing hydrogen ions (H+) or hydroxide ions (OH-)
C) By converting the acids or bases into water
D) By maintaining a balance between weak acid and its conjugate base
A) By neutralizing the acids or bases
B) By releasing hydrogen ions (H+) or hydroxide ions (OH-)
C) By converting the acids or bases into water
D) By maintaining a balance between weak acid and its conjugate base
59
New cards
D
**How does carbonic acid function as a crucial buffer in our blood, and what role does it play in maintaining blood pH?**
**A) Carbonic acid helps in digestion by breaking down complex molecules.**
**B) Carbonic acid supports bone health by facilitating calcium absorption.**
**C) Carbonic acid prevents the accumulation of lactic acid during exercise.**
**D) Carbonic acid maintains blood pH to enable efficient oxygen transport from the lungs to the cells.**
**A) Carbonic acid helps in digestion by breaking down complex molecules.**
**B) Carbonic acid supports bone health by facilitating calcium absorption.**
**C) Carbonic acid prevents the accumulation of lactic acid during exercise.**
**D) Carbonic acid maintains blood pH to enable efficient oxygen transport from the lungs to the cells.**
60
New cards
Litmus Test
a simple test to check if a substance is acidic or basic using a _________ paper
61
New cards
acidic
Blue litmus paper turns red for _______ pH
62
New cards
basic
Red litmus paper turns blue for _______ pH
63
New cards
neutral
No color change for ___________ pH
64
New cards
Indicator paper
is impregnated with organic compounds that change their color at different pH values.
65
New cards
Indicator paper
The color shown by the paper is then compared with a color standard usually provided by the manufacturer.
66
New cards
pH meter
should be calibrated first before being operating the device
67
New cards
pH 7, pH 4, and pH 10
The standard procedure for calibrating a pH meter is to calibrate it at three different pHs (pH ___, pH _, and pH _).
68
New cards
electrodes
After calibration, all that needs to be done is to insert the ___________ of the pH meter into the solution to be tested and read the pH flashed on the screen.