Power of Water
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Steam Power
A form of power generated by converting water into steam using heat. Used to drive engines and machinery
Heat liquid water, volume increased, moving an object
Condensing steam to liquid decreased volume
Single and Double acting steam engines (power and work)
Single-acting steam engine:
Steam pushes the piston in one direction → 1 power stroke per cycle → less power.
Double-acting steam engine:
Steam pushes in both directions → 2 power strokes per cycle → more power and efficiency.
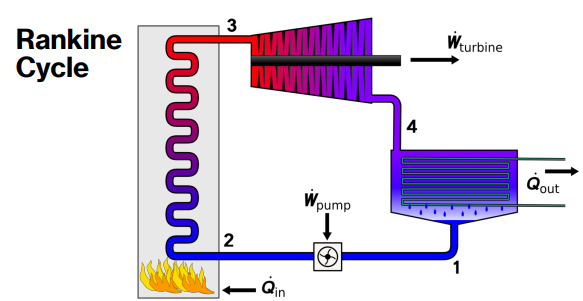
Rankine Cycle (4 main steps)
Pump (Compression)
Water (liquid) is pumped to high pressure.
Small input of energy.
Boiler (Heat Addition)
Water is heated → turns into high-pressure steam.
Turbine (Expansion)
Steam expands and spins the turbine → (makes power).
Condenser (Heat Rejection)
Steam cools down → turns back into liquid water at low pressure.
Geothermal Energy
heat from deep inside the Earth that can be used to produce electricity or provide heating by bringing hot water or steam to the surface.
Solar Water Heating
uses sunlight (solar energy) to heat water, usually through a solar collector and a storage tank.
Tidal Energy
energy generated from the movement of ocean water caused by the Moon’s gravity, especially during tides.
Wave Energy
power generated from the movement of ocean waves, caused by temperature differences and wind across the ocean surface.
Waterwheel
device that uses moving water to turn a wheel, which powers machinery through a rotating shaft.
Hydroelectric Power
electricity made by using flowing or falling water to spin a turbine, which powers a generator.
Steam Engine
uses steam from boiling water to push a piston or turn a turbine, creating mechanical energy to power machines.