Unit 3: Work-Energy
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
kinetic energy equation
K = 1/2mv²
Ugrav (at surface of planet) equation
Ugrav = |mgh|
work equation
W = Fd = Fdcos(x)
power equation
P = W/t = Fdcos(x)/t
Us equation
Us = 1/2kx²
Hooke’s Law
Fs = -kx
why is hooke’s law negative?
because force is always in the opposite direction of displacement
K units
J
m units
kg
v units
m/s
g units
m/s²
h units
m
U units
J
k units
N/m
d units
m
F units
N
W units
J
t units
s
P units
W
vector or scalar: K
scalar
vector or scalar: m
scalar
vector or scalar: v
vector
vector or scalar: g
vector
vector or scalar: h
scalar
vector or scalar: U
scalar
vector or scalar: d
vector
vector or scalar: F
vector
vector or scalar: W
scalar
vector or scalar: t
scalar
vector or scalar: P
scalar
principle of conservation of energy
the total amount of energy in the Universe is conserved. This is a wonderful property of our Universe: Energy can be transformed from one type to another and transferred from one object to another, but the total amount is always the same.
what is energy?
ability to do work to organize or change matter
what is K?
energy associated with the state of motion; if something moves, it can do work
K depends on which 2 variables
m and v
what is U?
energy associated with an object’s position
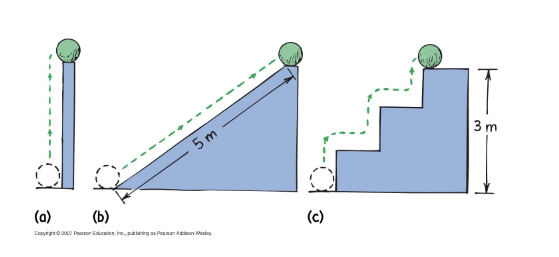
which 10 N ball has the greatest Ug?
they are all the same
why is spring force a variable force?
force increases as displacement increases, so it is not constant acceleration; CANNOT use F=ma
what is mechanical energy?
sum of all K and U (including Ugrav and Us)
T/F: energy can be transformed into other types of energy
T
If F and d are in the same direction, W is
positive
If F and d are NOT in the same direction, W is
negative
what does + W do to the TME of the system?
increases it
what does - work do to the TME of the system?
it decreases it
One group member holds out a hand, palm up, supporting the mass. They do not move their hand. Are they doing work?
no, there was no energy change due to no displacement
A different group member holds out a hand, palm up, supporting the mass, not moving. They should lift the mass 1.0000 m, then stop. Are they doing work?
yes
Same group member holds out a hand, palm up, supporting the mass, not moving. They should lower the mass 1.0000 m, then stop. Is work positive or negative?
negative
A different group member sets the mass on the table, pushes gently on the mass without moving it, then stops pushing. Is work done on the mass?
no
A different group member sets the mass on the table, pushes the mass horizontally across the table, then stops. There are four forces acting on the mass: pushing force, kinetic friction, normal force, force of gravity. Which ones do work?
Fpush and Ffr
can friction do positive work?
no; any friction, including air resistance, does negative work because it transfers energy away from the object and to the surroundings in the form of heat (thermal energy transfer).
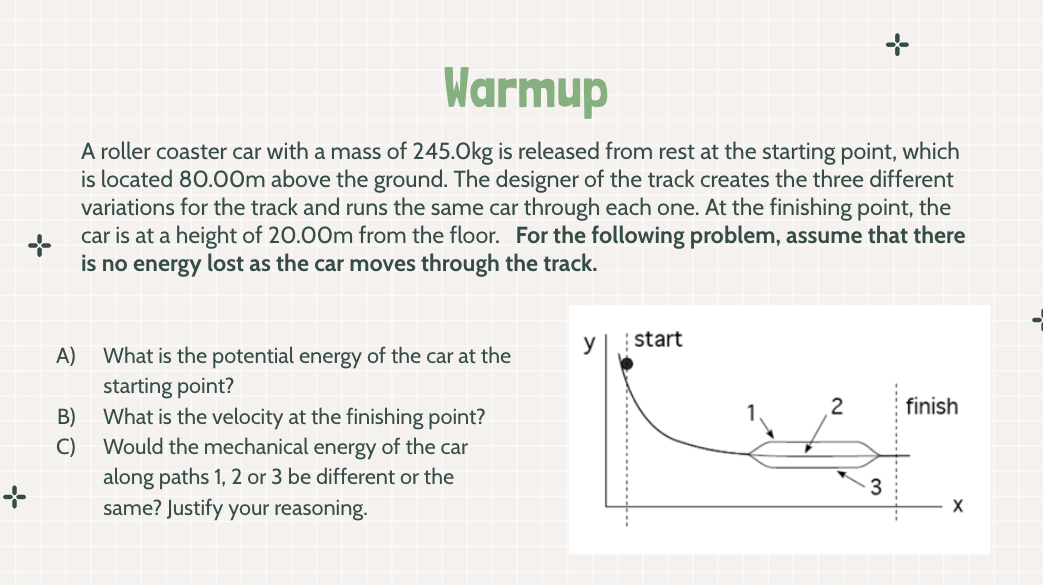
a. 1.921×10^5 J
b. 34.29 m/s
c. same - conservation of energy
what are conservative forces?
forces that act on a body or system without changing the total energy in that system.
Gravitational force acting on a box at the top of a frictionless ramp will cause the box to slide down the ramp, converting gravitational potential energy to kinetic energy without changing the total mechanical energy in the box-ramp-Earth system. Is this a conservative or non-conservative force?
conservative
what are non-conservative forces?
forces that act on a body or system causing the total energy in that system to change.
Friction force acting on a box at the top of a rough-surfaced ramp will cause part of the total mechanical energy in the box-ramp system to be “lost” to thermal energy in the ramp, air around the ramp, etc. Thus, the total mechanical energy of the system is not conserved. Is this a conservative or non-conservative force?
non-conservative
slope of a F v. position graph is
k
area under the curve of a F vs. position graph is
W
1000. kg car starts from rest, and takes 2.00 seconds to reach velocity of 5.00 m/s.
What is the power output by the engine?
6250 W
A pump is to lift 8.00 kg of water per minute through a height of 3.50 m. What output rating (watts) should the pump motor have?
4.57 W
A test car and its driver, with a combined mass of 600 kg, are moving along a straight, horizontal track when a malfunction causes the tires to stop rotating. The car skids to a halt with constant acceleration, leaving skid marks on the road during the whole time it skids. Which two of the following measurements, taken together, would allow engineers to find the total mechanical energy dissipated during the skid? Select two answers.
A. The length of the skid marks
B. The contact area of each tire with the track
C. The coefficient of static friction between the tires and the track
D. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the tires and the track
A and D
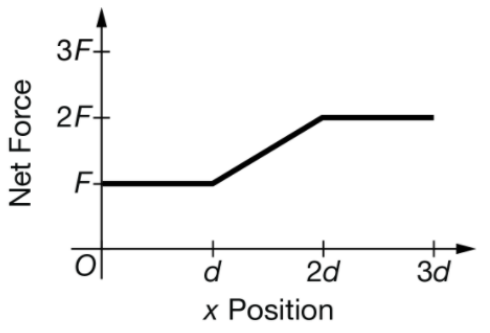
A graph of the net force F exerted on an object as a function of x position is shown for the object of mass M as it travels a horizontal distance 3d . Which expression represents the change in the kinetic energy of the object?
A. 3Fd
B. 3.5Fd
C. 4.5Fd
D. 6Fd
C
A block on a horizontal surface of negligible friction is placed in contact with an ideal spring. The block is moved to the left so that the spring is compressed a distance x from equilibrium and then released from rest. The block has kinetic energy K1 when it separates from the spring. When the spring is compressed a distance 2x and the block is released from rest, the kinetic energy of the block when it separates from the spring is
A. ½ K1
B. K1
C. √2K1
D. 2K1
E. 4K1
E
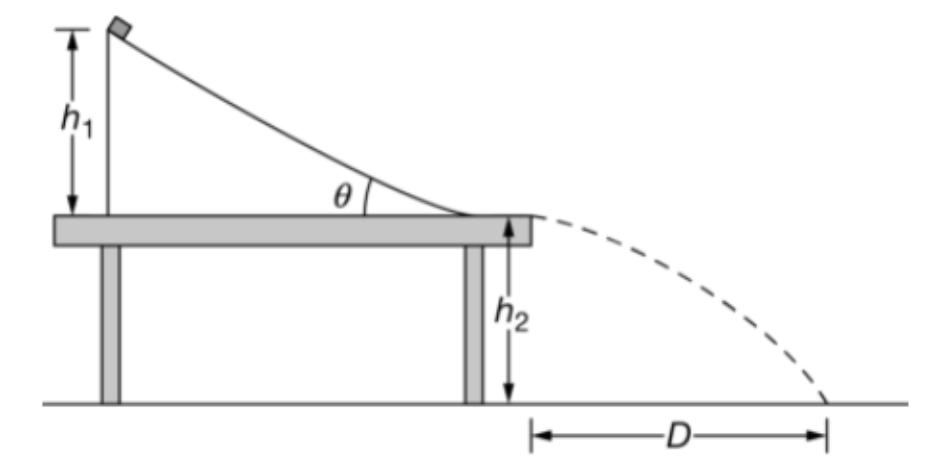
An inclined track is secured to a table. The height of the highest point of the track above the tabletop is h1. The height from the tabletop to the floor is h2. A block of mass M is released from rest and slides down the track such that all frictional forces are considered to be negligible. The block leaves the track horizontally and strikes the ground at a distance D from the edge of the track as shown. Which of the following statements is correct about the scenario? Select two answers.
A. If the block is released from a height 2h1, the block will land at a distance 2D away from the end of the track.
B. If the block’s mass is increased to 2M, the block will land at a distance 2D away from the edge of the track.
C. The total mechanical energy of the system containing only the block increases from the moment of release to the moment it strikes the ground.
D. The total mechanical energy of the block-Earth system remains constant.
C and D
Ms. Zhou stands stationary, holding her coffee thermos in her hand. The thermos is not moving. The upward force Ms. Zhou exerts on the coffee thermos does
A. + W
B. no W
C. - W
B
Ms. Zhou pushes a box to the left (negative velocity) with an acceleration of -1 m/s2 (negative acceleration) across the classroom. Her pushing force does ____ work.
A. +
B. -
C. no
+
The slope of a Force vs. displacement graph can represent
A. U
B. k
C. P
D. W
E. K
k
Suppose you have a pendulum, and you have defined the pendulum-Earth as the system you are studying. You pull back the pendulum with your hand. In the pendulum-Earth system, the force of your hand is
A. a conservative force
B. a non-conservative force
B
A spring oscillates continuously without air resistance. At its equilibrium position (in the middle position, amplitude=0), the spring has maximum
A. Ugrav
B. Us
C. K
C
Calculate the kinetic energy for a pendulum with:
mass = 66.7 grams
velocity = 1.24 m/s
0.0513 J