Mechanics II
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
Formula for Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation
F=G(m1m2/d2)
What does F stand for in Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation?
Force (of gravity)
What does G stand for in Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation?
The Universal Constant of Gravitation
What does m1 stand for in Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation?
mass of first object
What does m2 stand for in Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation?
mass of second object
What does d stand for in Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation?
distance (between their centres)
Formula for gravity
g=GM/d2
What is weight?
The force of gravity. It’s measured in Newtons and depends on the planet you’re on.
Weighing Scales
Weighing scales measures your weight in N. But the mechanism inside it divides by 9.81 to show your mass in kg
Formula for weight
W=mg
Astronauts on the ISS
They appear to be floating but they’re actually falling towards Earth. They seem to be floating because they’re travelling so fast that as they fall towards Earth, the curvature of the Earth falls away underneath them
Formula for Angular Speed
ω = θ / t
What does the ω stand for?
angular speed
What does the θ stand for?
angular distance (angle)
What does the t stand for?
time
Unit for angular speed
rad s-1 or rad/s
What is a radian?
The angle subtended by an arc of length 1 radius
Radian and degree conversion base formula (note: manipulate this based on what you need)
180=π radians
Relationship between Linear speed and Angular speed (ω formula)
ω=v/r
Relationship between Linear speed and Angular speed (v formula)
v=rω
What does v stand for?
linear speed
What does the r stand for?
radius
centripetal acceleration (definition)
Acceleration experienced by an object travelling in a circular path. It always points towards the centre of the circular path
Formula for Centripetal acceleration (v version)
a=v2/r
Formula for Centripetal acceleration (ω version)
a=rω2
What does a stand for?
acceleration/centripetal acceleration
Unit for centripetal acceleration
m/s-2 or m/s2
Centripetal Force (definition)
The force required to keep an object moving. It always points towards the centre of the circular path
Explanation of “The Rotor”
In the fairground attraction, you feel like you’re being pushed against the wall, this is stopping you from falling, but it’s imaginary, the wall is actually pushing you in the back, creating a centripetal force
Centripetal force formula (v version)
F=mv2/r
Centripetal force formula (ω version)
F=mrω2
What does m stand for?
mass
What does F stand for?
Resultant Force/Centripetal force
Car going round the bend explanation
For a car to go around a bend a centripetal force must be applied. Supplied by the friction between the rubber wheels and the road, and we want it to be as small as possible
Option 1 for decreasing the centripetal force
Reduce m (impractical)
Option 2 for decreasing the centripetal force
Increase r (dangerous, wrong side of the road)
Option 3 for decreasing the centripetal force
Reduce v (most effective anyway, because halving your speed quarters the centripetal force)
Kepler’s Law (formula)
T2 = 4π2 d3/GM
What does T (tau) stand for?
periodic time
What does d stand for? (Kepler’s Law)
distance between their centres
What does M stand for? (Kepler’s Law)
mass of object being orbited
What happens to an astronaut’s weight as they travel from the Earth to the Moon? (diagram)
…
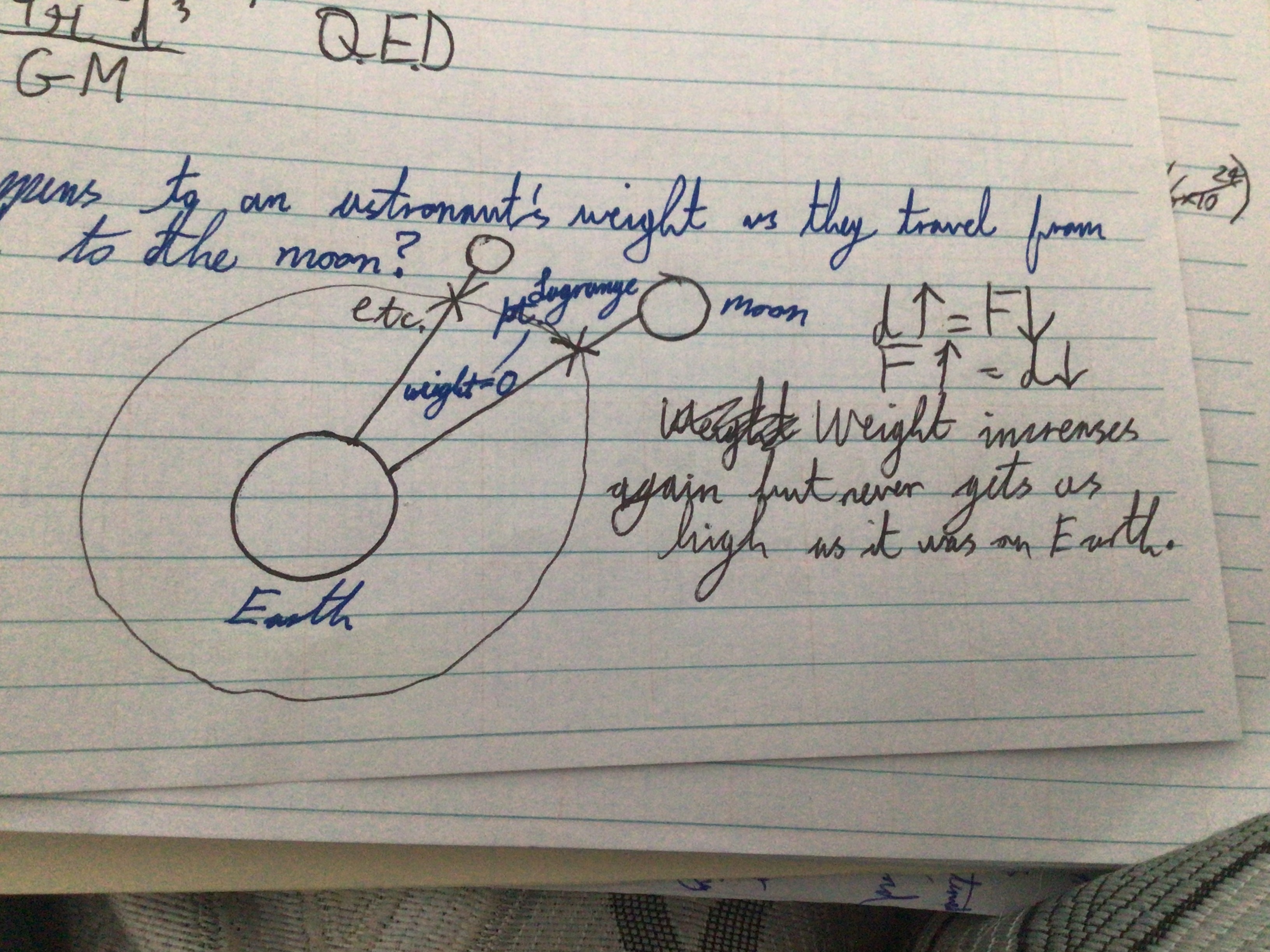
What happens to an astronaut’s weight as they travel from the Earth to the Moon? (explanation)
d increases = F/weight decreases. F/weight increases= d decreases. Weight increases again after passing the Lagrange point but never is as high as it was on Earth
What is the Lagrange point?
The point between a planet and a star or a planet and a moon where the force of gravity between the objects is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction so an object at that point would be effectively weightless
Lagrange point (Telescope)
James Webb space telescope is at the Lagrange point between the Earth and the Sun so that it’s stationary with respect to both those objects
Geosynchronous satellites (definition)
One which orbits the Earth in the same time the Earth rotates on its own axis (24hrs)
What do geosynchronous satellites provide us with?
GPS (Global Positioning System), satellite TV, instantaneous international TV broadcasts
Difference between Geosynchronous/Geostationary satellites
Both orbit the Earth in 24 hours. Geostationary satellites orbit the equator
Lever (definition)
A rigid object which is free to rotate around a fixed point or line called a fulcrum e.g. scissors, doors, can opener
Lever (diagram)
…

Moment/Torque (formula)
T=Fr
What does T stand for (torque)?
Moment
What does r stand for (moment formula)?
perpendicular distance between the force and fulcrum
Unit for Moments
Nm
What is a moment?
The twisting effect of a force
Density (formula)
ρ = m/V
Unit for density
kgm-3 or kg/m3
What does V stand for?
volume
What does ρ stand for?
density
Substances floating (density)
One substance will float in another substance if it has a lower density than it. This is why hot air balloons float
Pressure (formula)
p= F/A
What does A stand for?
area
What does p stand for?
pressure
Unit for pressure
Pascals (Pa)
Pressure paragraph (big p=big F/Small A, small p =Small F/Big A)
This is the reason why, an elephant wouldn’t damage a linoleum floor but a woman in heels would puncture it, snow shoes allow you to walk on soft snow, why sharp knives cut more easily than a blunt knife
What is a fluid?
A liquid or a gas
Pressure in fluids (formula)
p=ρgh
What does h stand for?
depth
Atmospheric pressure (definition)
Caused by the force of gravity acting on the Earth’s atmosphere
Atmospheric pressure (diagram)
..
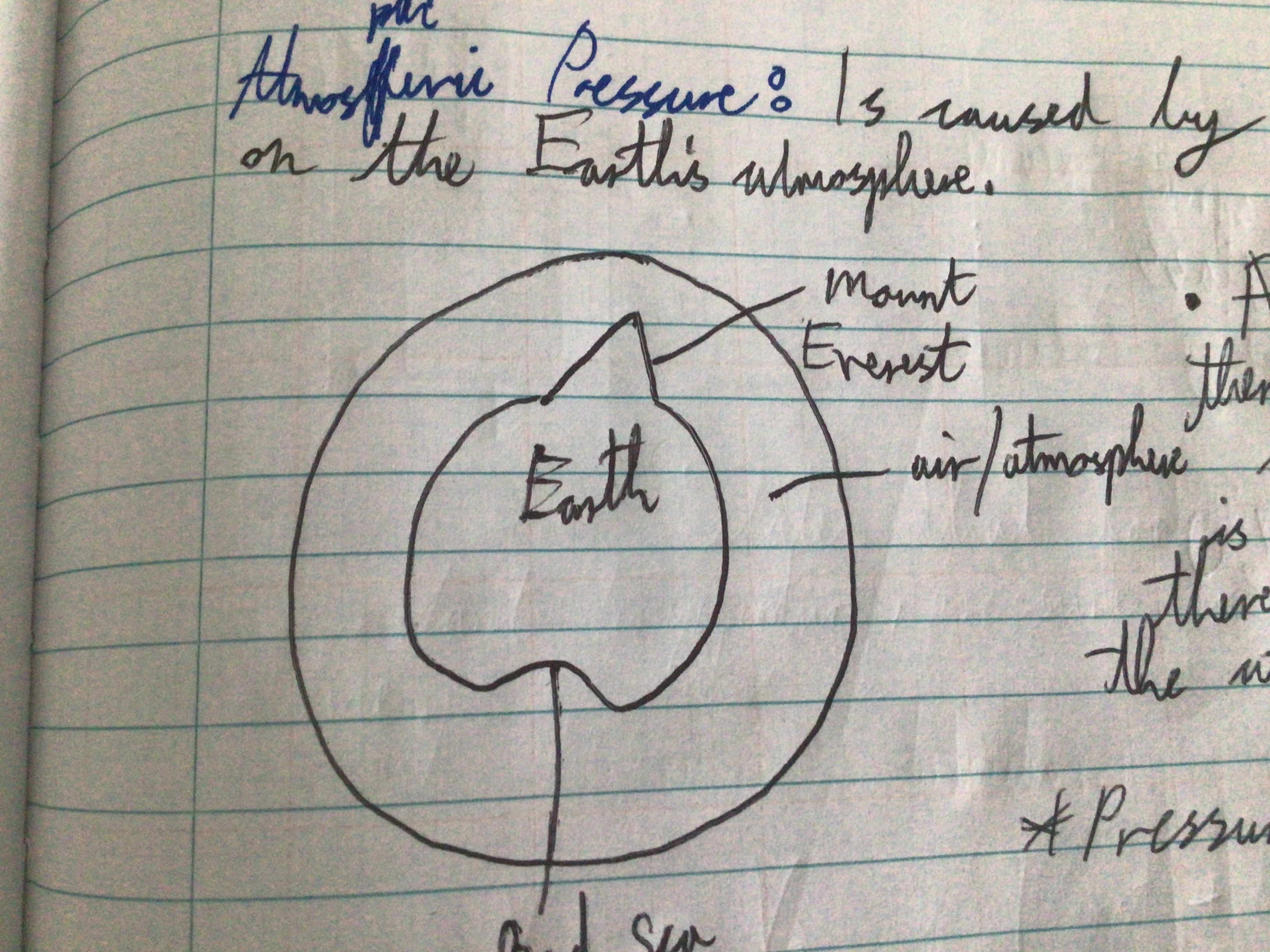
Atmospheric pressure diagram explanation
At the top of M.T. Everest there is less air above you so the atmospheric pressure is lower. At the dead sea, there is more air above you so the atmospheric pressure is higher
What does the pressure in fluid depend on?
depth
What does Melting point and boiling point depend on?
Pressure and purity. E.g. pressure cooker, why we salt the roads in winter, why tea tastes terrible on top of M.T. Everest (water boils at 80 degrees)
Water (purity + boiling point)
Water only boils at 100 degrees and freezes at 0 degrees if the water is pure and at one atmospheric pressure
What causes the “pop“ when you go down in an aeroplane?
Imbalance in atmospheric pressure
What do high/low atmospheric pressure cause?
High atmospheric pressure causes good weather, low atmospheric pressure causes bad weather
Draw the Boyle’s Law diagram
…
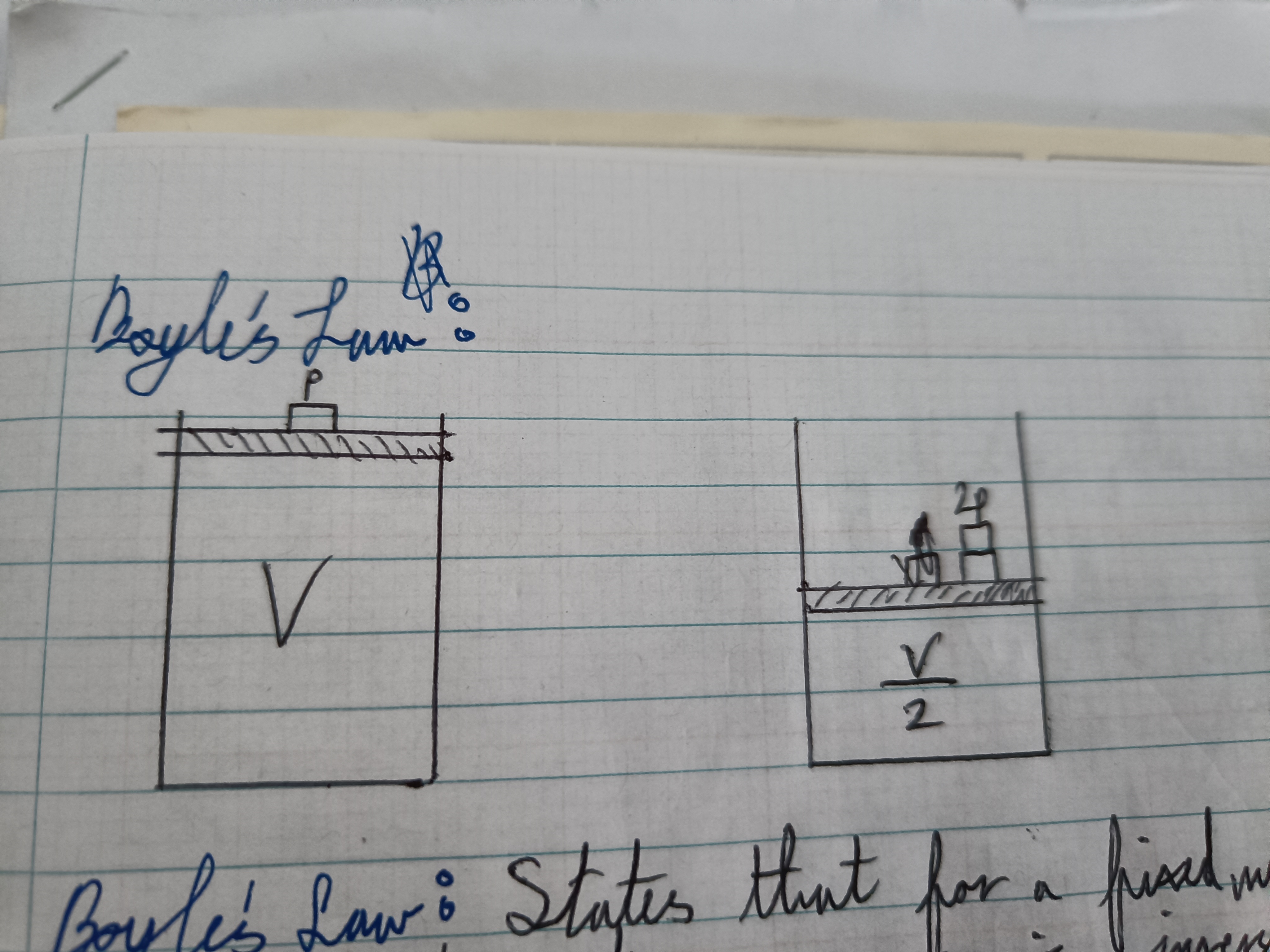
Boyle’s Law (definition)
States that for a fixed mass of gas, at constant temperature, pressure is inversely proportional to volume
Nitrogen Narcosis/”The Bends”
If a diver dives deep, nitrogen is forced into the blood, (unlike oxygen it doesn’t dissolve), as bubbles. If the diver comes up too quickly the nitrogen bubbles can’t get out of the blood quick enough and they expand because the pressure is too high. When these bubbles burst against the nerves they cause extreme pain or even death, known as nitrogen narcosis or “The bends“
Boyle’s Law formula
p1V1 = p2V2 if T const. and m const.
What does T stand for in Boyle’s Law?
temperature
Archimede’s Principle (definition)
States that when an object is partially or wholly immersed in a fluid, the upthrust is equal in magnitude to the weight of the fluid displaced
The Law of Floatation (definition)
States that the weight of the floating object is equal to the weight of fluid displaced
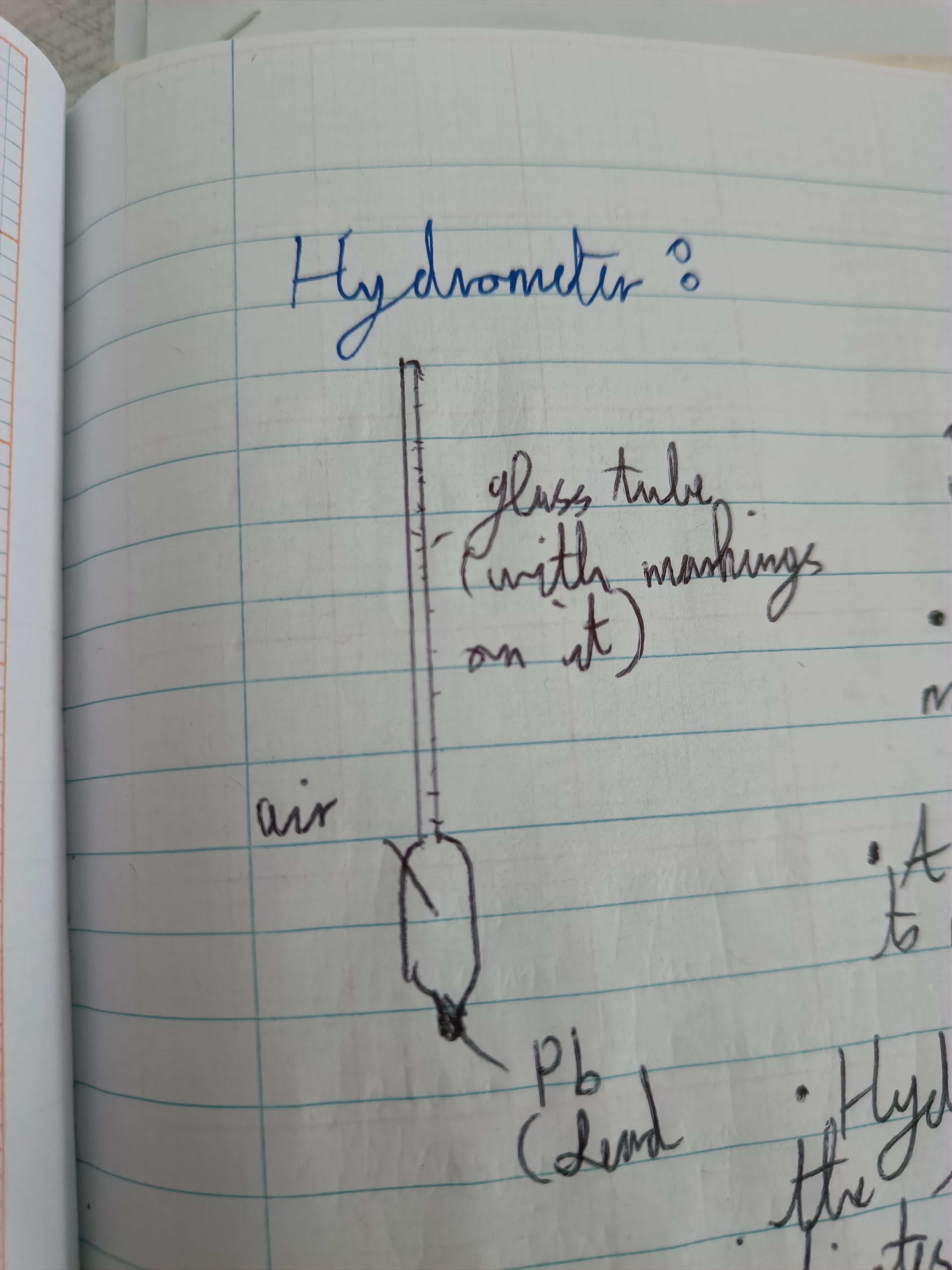
What is a hydrometer?
A device based on the law of floatation, which is used to measure the density of liquids
Lactometer (uses for the hydrometer)
Used in dairies to measure the amount of cream in milk
Saccharometer (uses for the hydrometer)
Used in wine-making to measure the sweetness
Mechanics (uses for the hydrometer)
Hydrometers used by mechanics to measure the density of the liquid in car batteries which indicates how charged it is
What is a couple?
A system of forces that produces rotation only
Formula for the moment of a couple
T=Fd
Draw a hydrometer
…