Muscle physiology
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
Three muscle types
skeletal, cardiac, smooth
structure of cells
body location
function
how activated to contract
How do muscles differ
elongated muscle cells (muscle fibers)
contraction dependent on microfilaments (Actin and myosin)
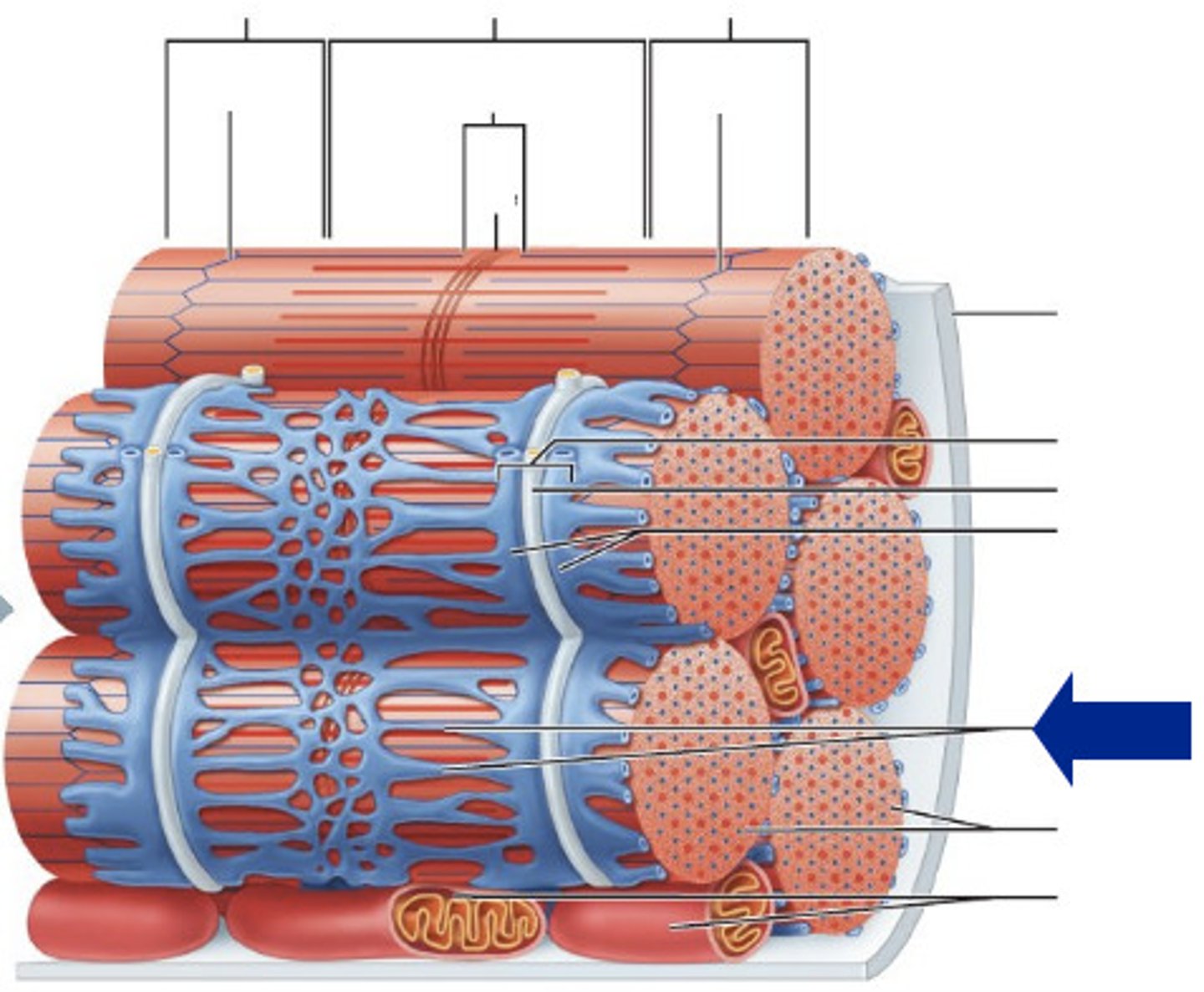
sarcolemma
sarcoplasma
how are muscles similar
sarcolemma
plasma membrane of a muscle fiber
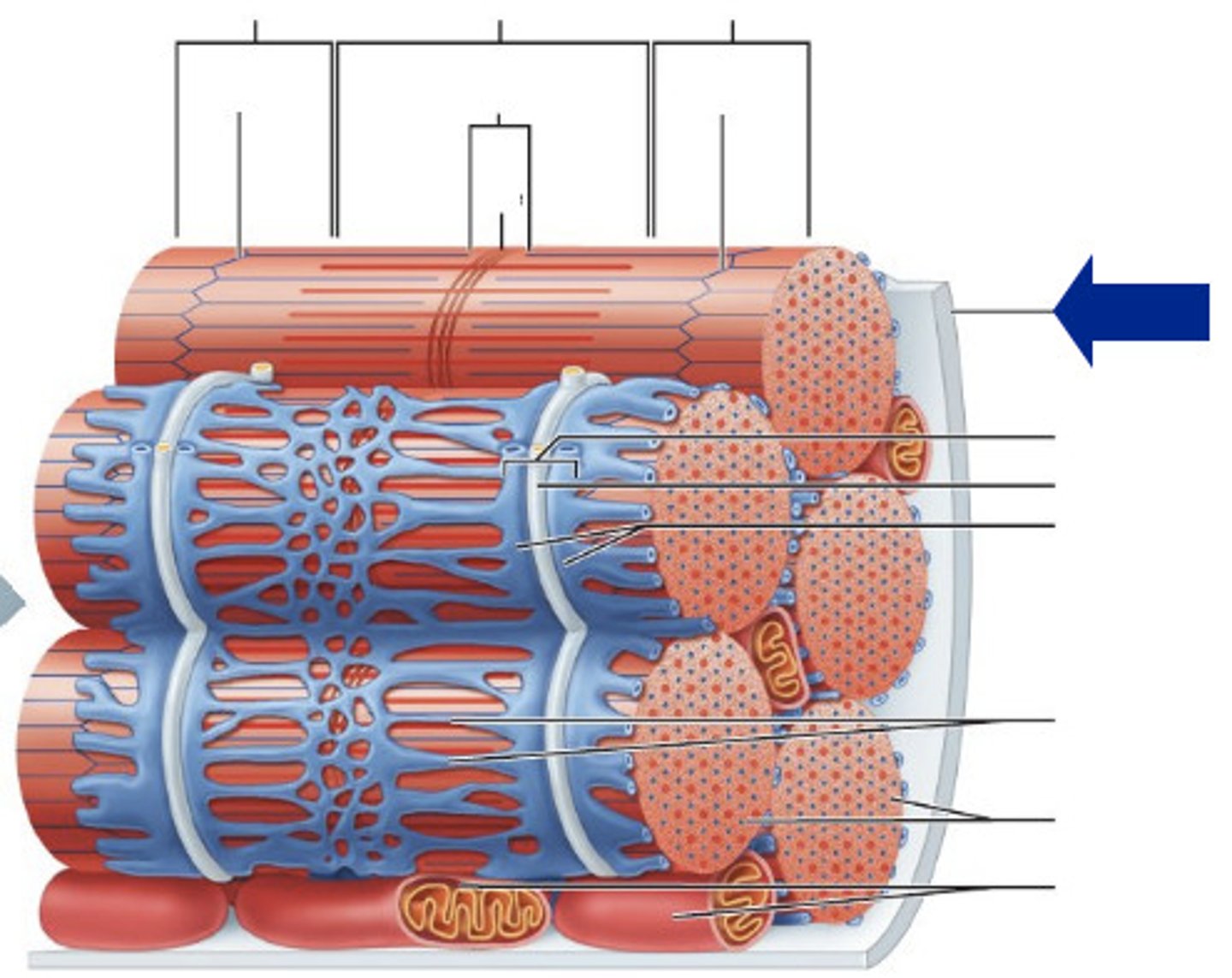
sarcoplasm
cytoplasm of a muscle fiber
Skeletal muscle
A muscle that is attached to the bones of the skeleton and provides the force that moves the bones.
1. attach/cover bones
2. longest fibers
3. multinucleated
4. striations
5. voluntary
6. contract rapidly
7. tires easily
8. adaptable
9. wind-up toy- runs down
Skeletal muscle overview
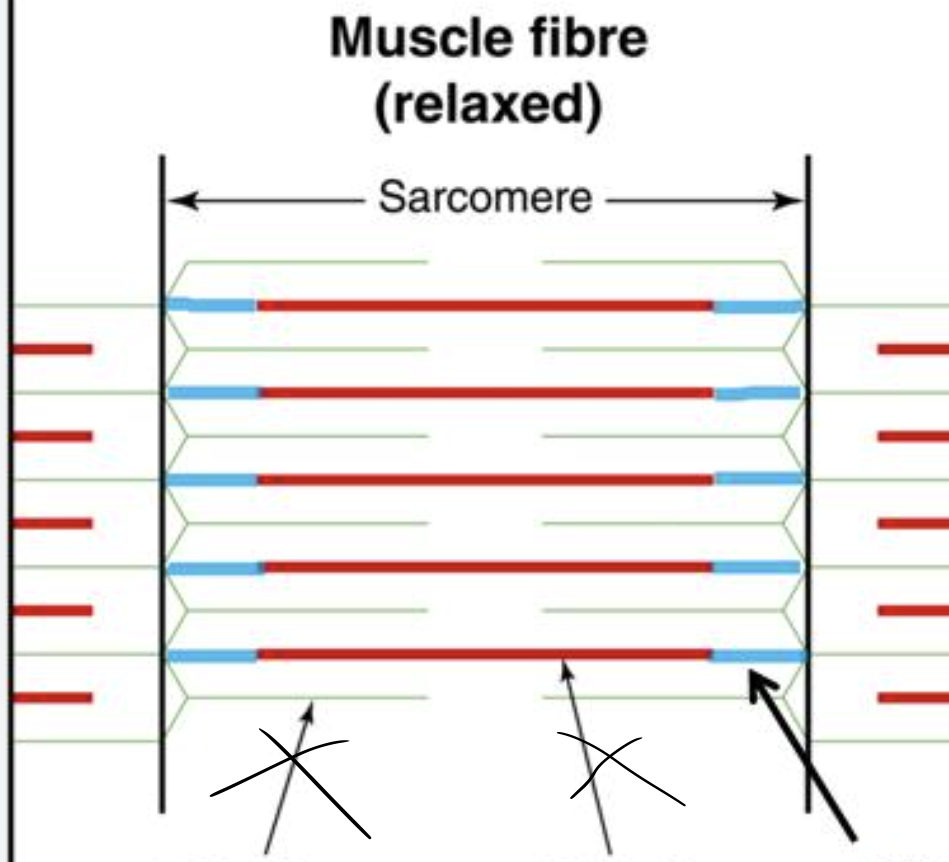
sarcomere
Contractile unit of a muscle fiber
true or false: there are multiple sarcomeres per muscle fiber
true
where does a sarcomere run from
Z disc to Z disc
what filaments are in a sarcomere
thin (actin) and thick (myosin)
titin filament
connect myosin to z disc
why does skeletal muscle tire easily
it needs rest after a short period of activity it quickly uses ATP resources and has a slow vs fast twitch
Why can't mature skeletal muscle cells divide?
They are specialized cells that have lost the ability to go through cell division
How do skeletal muscles grow if they can't divide?
Muscle growth happens through hypertrophy, which is stimulated by hormones and exercise
What are satellite cells in skeletal muscle
stem cells located around muscle fibers that can regenerate or repair damaged muscle tissue by forming new fibers
1. only in heart walls
2. striations- thick + think filaments
3. involuntary- ANS + pacemaker cells
4. Steady rate
5. coordinated rhythm
cardiac muscle overview
Automatic Nervous System cells are found in
smooth and cardiac muscle (involuntary)
Pacemaker cells are
found in cardiac muscle
coordinated rhythm of cardiac muscle
contracts smooth steady pattern to keep blood flow properly
1. walls of hollow organs
2. no striations (still have thick + thin filaments)
3. involuntary
4. slow contractions
5. last long time
6. steady engine going along
smooth muscle overview
unique properties of smooth muscle
excitability, contractility, extensibility, elasticity, conductivity
excitability
ability to receive and respond to stimuli (can be chemical)
response of smooth muscle
make and transmit electrical currents (Action potentials) along the sarcolemma, causing the muscle to contract and produce movement
neuromuscular junction
The connection between motor neuron and muscle fiber where the nerve impulse signal is transmitted to muscle to trigger contraction
action potential
An electrical signal that travels along the sarcolemma, initiating the process that leads to muscle contraction
contract
shorten when stimulated
extensibility
the ability to be stretched or extended
elastic
resume to resting length
conductivity
The ability of a muscle to carry an electrical signal so the whole muscle can contract together
wave of excitation
levels of organization from largest to biggest
epimysium
bicep brachii
perimysium
fascicle
endomysium
sarcolemma
microfibril (organelle)
sarcomere
myofilaments
actin and myosin
Muscle fibers
long cells with multiple flattened nuclei inside the cell membrane
what is the sarcolemma
muscle cell membrane with tunnel-like infolding called tubules that carry signals into the cell
what is found inside the sarcoplasm
myofibrils, glycogen for energy storage, and myoglobin for binding oxygen
what does the sarcoplasmic reticulum do
(smooth ER) around myofibrils that store and release calcium to trigger muscle contraction
what makes up a triad in muscle cells
T-tubule and two terminal cisternae
What happens when calcium floods out of the sarcoplasmic reticulum
it triggers muscle contraction
what are thick filaments made of
contractible protein myosin
what do thick filaments do
Bind to actin and cause contraction (uses lots of ATP)
what are thin filaments made of
globular (G) actin with active sites and tropomyosin and troponin proteins
tropomyosin
blocks actin's active sites when the muscle is relaxed
troponin
regulatory protein that binds to actin, and moves tropomyosin off actin's active sites for contraction
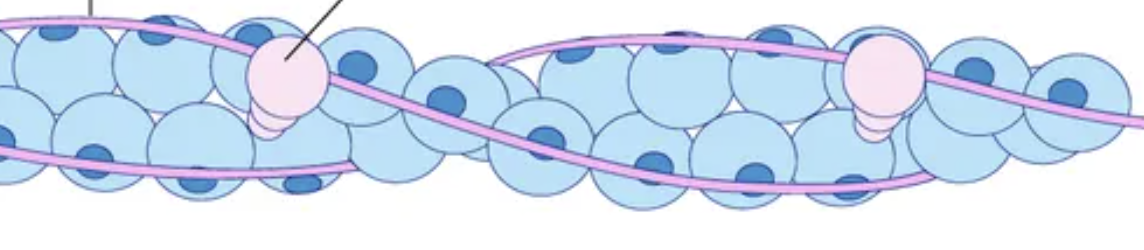
what are elastic filaments made of and function
springy proteins called titin, they anchor thick filaments to the Z disc to prevent overstretch of sarcomere
main contractile proteins
myosin and actin
what proteins regulate contraction
troponin and tropomyosin
how does calcium trigger contraction
calcium binds to tropoinin which moves tropomyosin which then exposes actin active sites
what causes muscle striations
alternating dark A and light I bands in the sarcomere
what is a sarcomere
the segment from one Z disc to the next- functional unit of muscle
what happens when a muscle contracts
sarcomeres shorten as Z discs are pulled closer together; filaments slide
how is skeletal muscle activated
by a nerve signal
what are somatic motor neurons
nerve cells whose axons stimulate skeletal muscle fibers
motor unit
A motor neuron and all of the muscle fibers it innervates
small motor units
fine degree of control
large motor units
for strength
What is a neuromuscular junction
point of contact between a motor neuron and a skeletal muscle cell
what neurotransmitter is released at the NMJ
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Main components of the NMJ
Synaptic knob, synaptic cleft, basal lamina
synaptic knob
swollen end of nerve fiber that releases ACh
synaptic cleft
tiny gap between nerve and muscle cells
basal lamina
thin layer of collagen and glycoprotein over all of muscle fiber
what do cholinesterase inhibitors do
prevent breakdown of Ach; cause spastic paralysis
what is tetanus
blocks glycine release, which causes overstimulation of muscles; spastic paralysis
flaccid paralysis
a state in which the muscles are limp and cannot contract
what happens when there is a polarized muscle cell
a difference in charge- more Na+ outside and more K+/anions in the cell
what is the resting membrane potential
Difference in electrical charge across the membrane at rest; The muscle cell’s charged-up resting state before any signal arrives.
what happens when the muscle cell is stimulated
Ion gates open, Na+ diffuses in, K+ rushes out which causes quick voltage change called an action potential
What happens when a nerve signal reaches the synaptic knob
Voltage-gated calcium channels open, calcium enters, and triggers exocytosis of ACh into the synaptic cleft
What happens when Ach binds to receptors on the muscle fiber
Ligand- gated sodium and potassium channels pop open and sodium rushes in, which activates the action potential
How is action potential created from the end plate potential
voltage-gated channels open and sodium rushes in first and an action potential spreads across muscle fiber
What happens when the action potential spreads across the sarcolemma
It travels down the T-tubules
How is calcium released inside the muscle fiber
Action potential triggers the sarcoplasmic reticulum to release Ca+
What does calcium bind to during contraction
troponin, which shifts tropomyosin revealing actin active sites
What activates the myosin heads?
Myosin ATPase hydrolyzes ATP "cocking" the head into position
Why is ATP important for cross bridge formation
Myosin must bind ATP to release its old position, then bind actin and form a new cross bridge
whats the power stroke
myosin releases ADP and Phosphate and pulls actin toward the center, shortening the sarcomere
how does the myosin head reset
A new ATP molecule binds, detaches, and prepares for the next stroke
how does stimulation stop
nerve signals stop and acetylcholinesterase removes Ach from receptors
What happens to calcium during relaxation
it is pumped back into the SR using ATP and bound to calsequestrin
calsequestrin
molecule that binds calcium within the sarcoplasmic reticulum
how do actin sites get re-covered
loss of Ca+ allows troponin/tropomyosin to block active sites again
what helps the muscle return to resting length
elastic recoil and antagonistic muscle action
why does rigor mortis occur
no ATP is available to release attached actin and myosin molecules
isometric contraction
no shortening; muscle tension increases but does not exceed load
isotonic contraction
muscle shortens because muscle tension exceeds load
concentric
tension while shortening
eccentric
tension while lengthening