Hydrometeorological Hazards - DRRR 4Q
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Hydrometeorological Hazards
Processes or phenomena of atmospheric, hydrological, or oceanographic in nature that can cause loss of life, damage to properties, socio-economic disruption, and environmental damage.
Typhoon
Intense low-pressure system with a minimum sustained wind velocity of 35 kph.
Tai Fung
The word "typhoon" is probably derived from the Chinese term "_____."
Tropical cyclone
A type of storm system that forms over warm ocean waters in tropical and subtropical regions. It is characterized by a low-pressure center, strong winds, and heavy rain.
Warm ocean water of at least 26.5C; Moist air; Low vertical wind shear; Coriolis effect
Enumerate four (4) conditions of formation for a tropical cyclone:
WMLC
Eye
Area of lowest atmospheric pressure in the tropical cyclone. Appears eerily calm.

Eye wall
Region immediately surrounding the tropical cyclone's center. Has strongest winds and heavy rains.
Rain bands
Spiraling strips of cloud in the fringes of tropical cyclones which are associated with rainfall.
Coriolis effect
Deflection of an object's motion due to the Earth's rotation about its axis.
Tropical depression
A wind velocity of 61 KPH or less.
Tropical storm
A wind velocity of 62-88 KPH.
Severe tropical storm
A wind velocity of 89-117 KPH.
Typhoon
A wind velocity of 118-220 KPH.
Super typhoon
A wind velocity of more than 220 KPH.
Hurricanes
Typhoons are typically referred to as _____ in the U.S. and Caribbean (Northeast Pacific and North Atlantic).
Cyclone
Typhoons are typically referred to as _____ in South Asia (Southwest Pacific Ocean and Indian Ocean).
East Asia
The term "typhoon" is typically heard throughout _____ (Northwest Pacific Ocean).
Willy-willies
Typhoons are typically referred to as _____ in Australia.
Storm surge
Sudden rise of sea level above the normal level on the coast due to a drop in atmospheric pressure and the force of the wind as a tropical cyclone approaches the coast.

Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA)
Country's official weather bureau. It monitors storms, typhoons, and other weather disturbances in the country.
Public Storm Warning Signals (PSWS)
PAGASA releases warning signals for hazards in the form of _____.
PSWS 1
Has a lead time of 36 hours and indicates no damage or very light damage.
PSWS 2
Has a lead time of 24 hours and indicates light to moderate damage.
PSWS 3
Has a lead time of 18 hours and indicates moderate to heavy damage.
PSWS 4
Has a lead time of 12 hours and indicates heavy to very heavy damage.
PSWS 5
Has a lead time of 12 hours and indicates very heavy to widespread damage.
Philippine Area of Responsibility
PAR stands for _____.
Thunderstorm
Localized storm cloud that produces lightning and thunder and often brings heavy rain showers and strong winds. Five kilometers in diameter and lasts an average of 30 minutes.

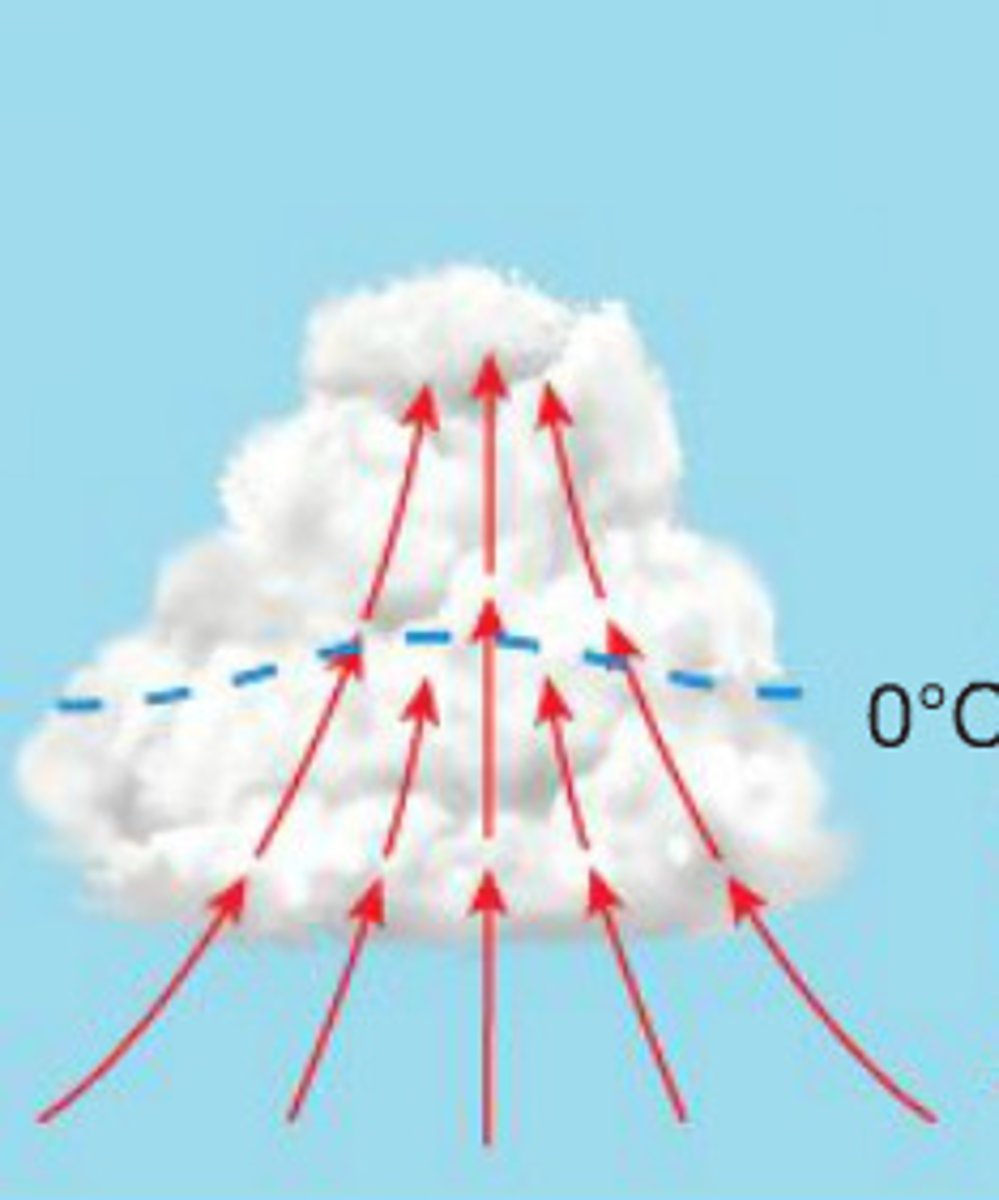
Developing stage
First stage of a thunderstorm where:
- Towering cumulus cloud indicates rising air
- Usually little if any rain during this stage
- Lasts about 10 minutes
- Occasional lightning
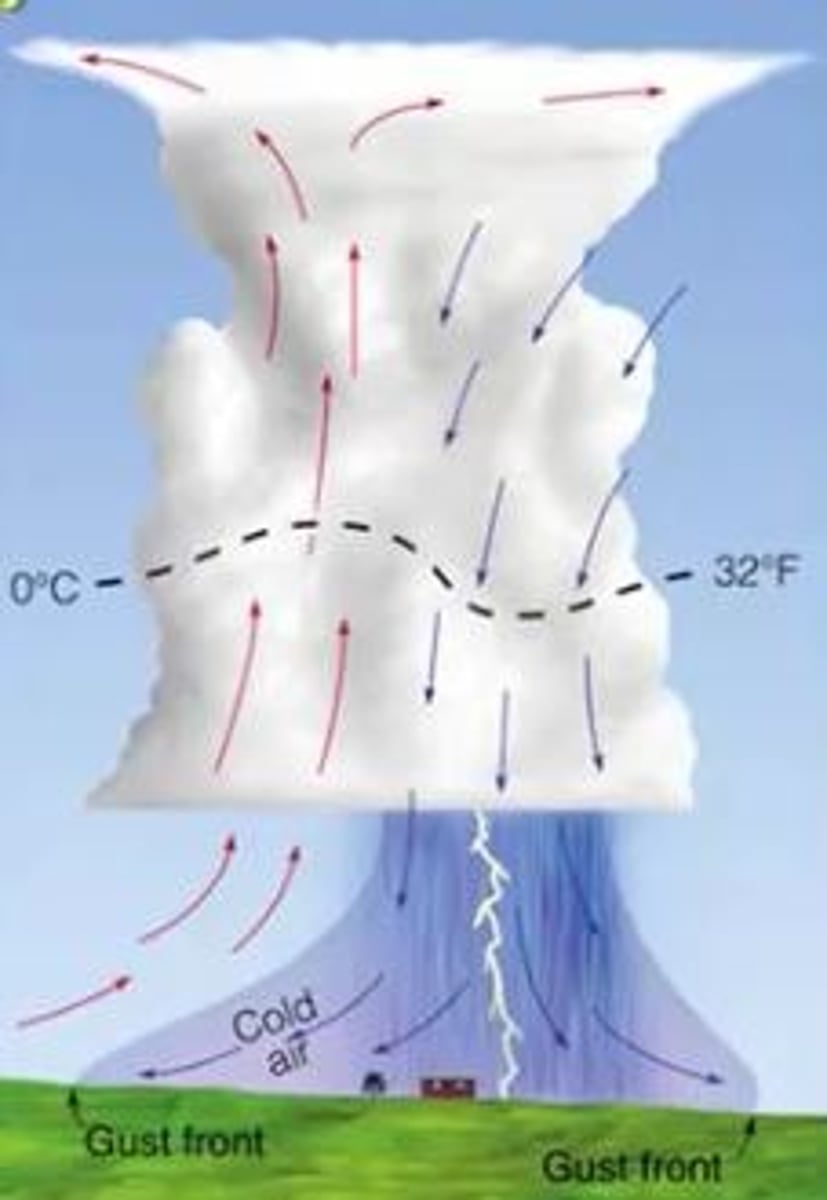
Mature stage
Second stage of a thunderstorm where:
- Most likely time for hail, heavy rain, frequent lightning, strong winds, and tornadoes
- Storm occasionally has a black or dark green appearance
- Lasts an average of 10 to 20 minutes but some storms may last much longer
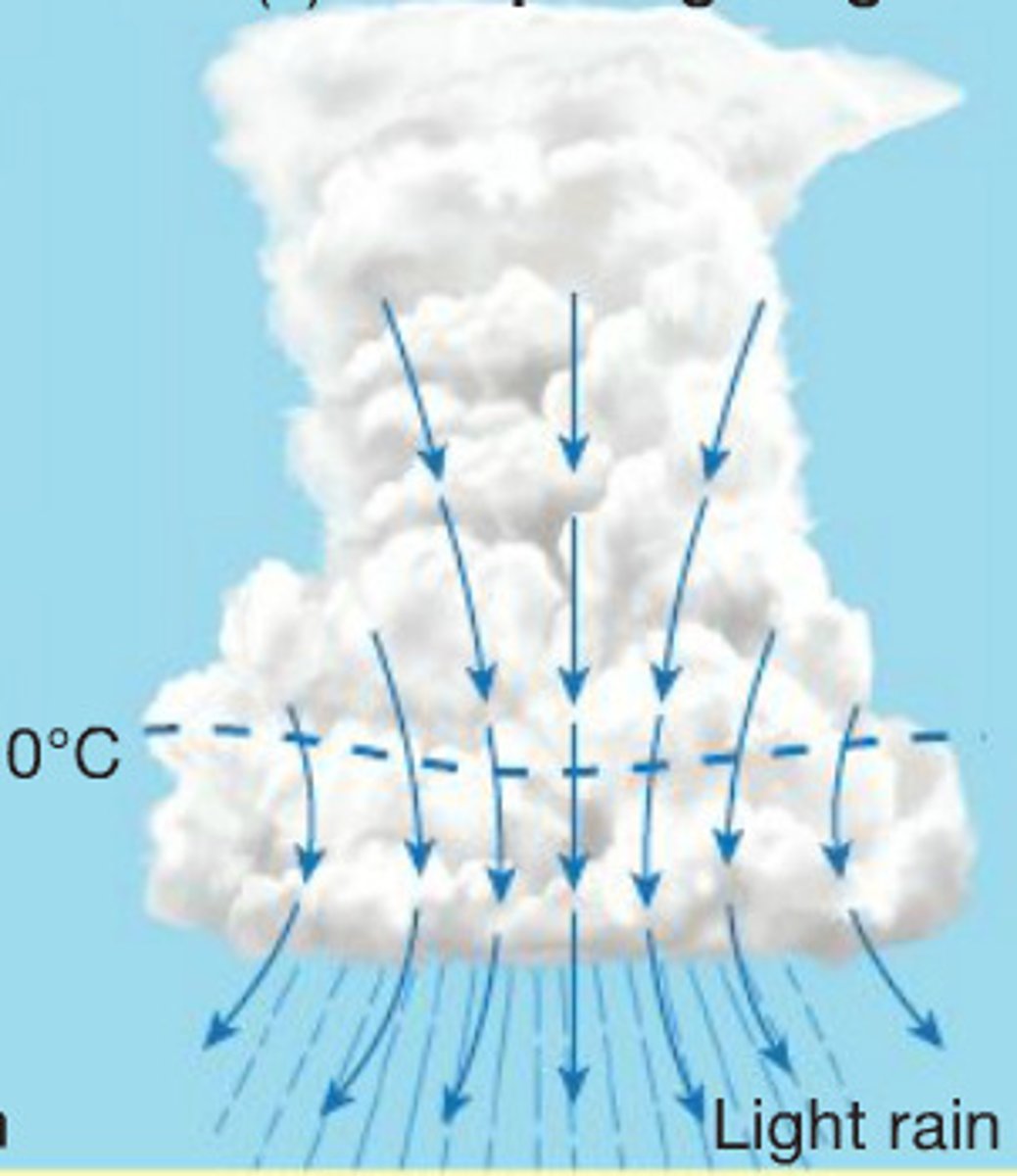
Dissipating stage
Third stage of a thunderstorm where:
- Downdrafts, downward flowing air, dominate the storm
- Rainfall decreases in intensity
- Can still produce a burst of strong winds
- Lightning remains a danger
Lightning
Abrupt, natural, visible high-voltage electrical discharge that takes place when positive and negative charges join within a cloud, between clouds, or between a cloud and the ground.
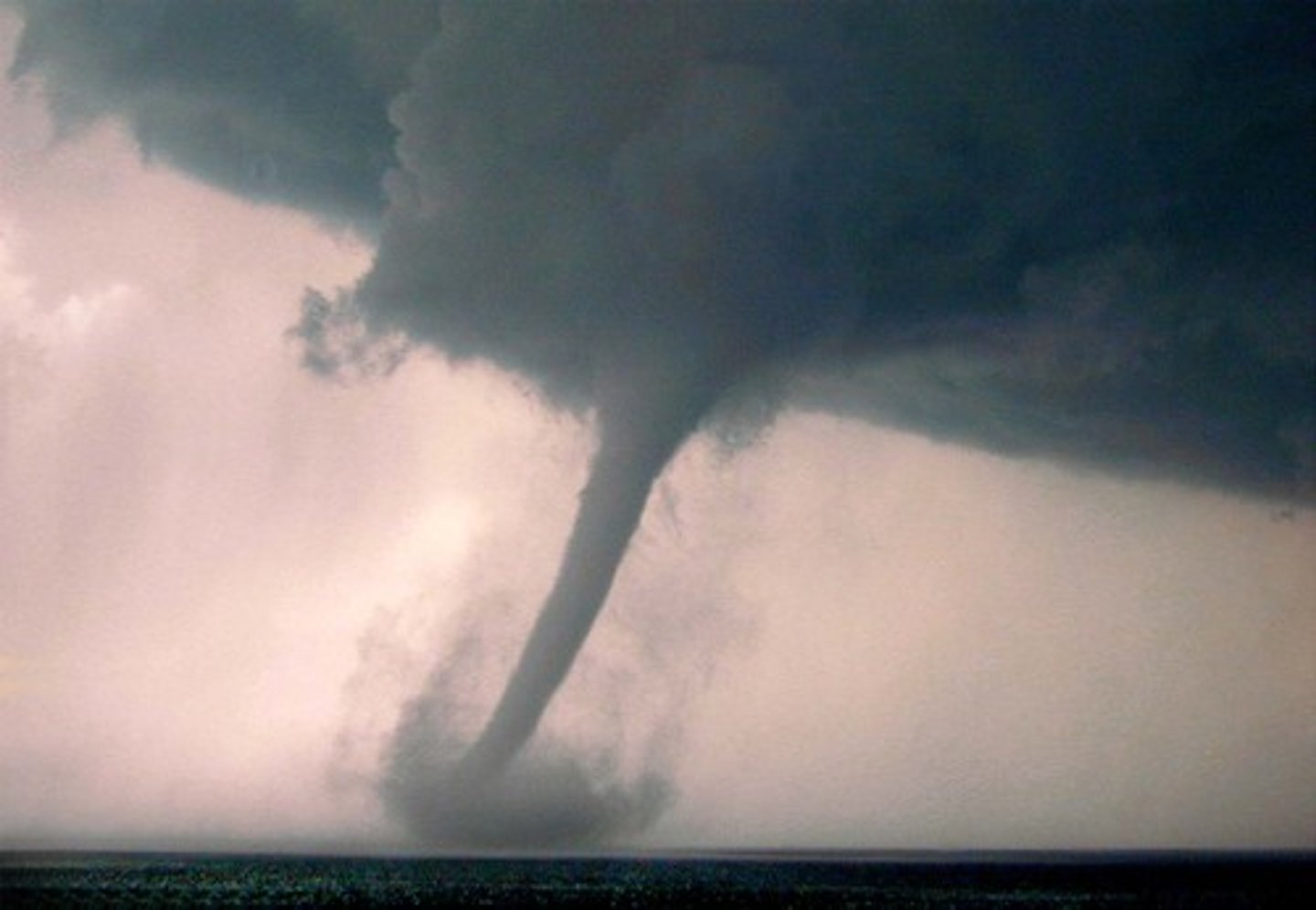
Tornadoes
Narrow, funnel- or cylindrical-shaped, and intensely rotating columns of wind that form during powerful thunderstorms and extend from the base of a cumulonimbus cloud down to Earth's surface.

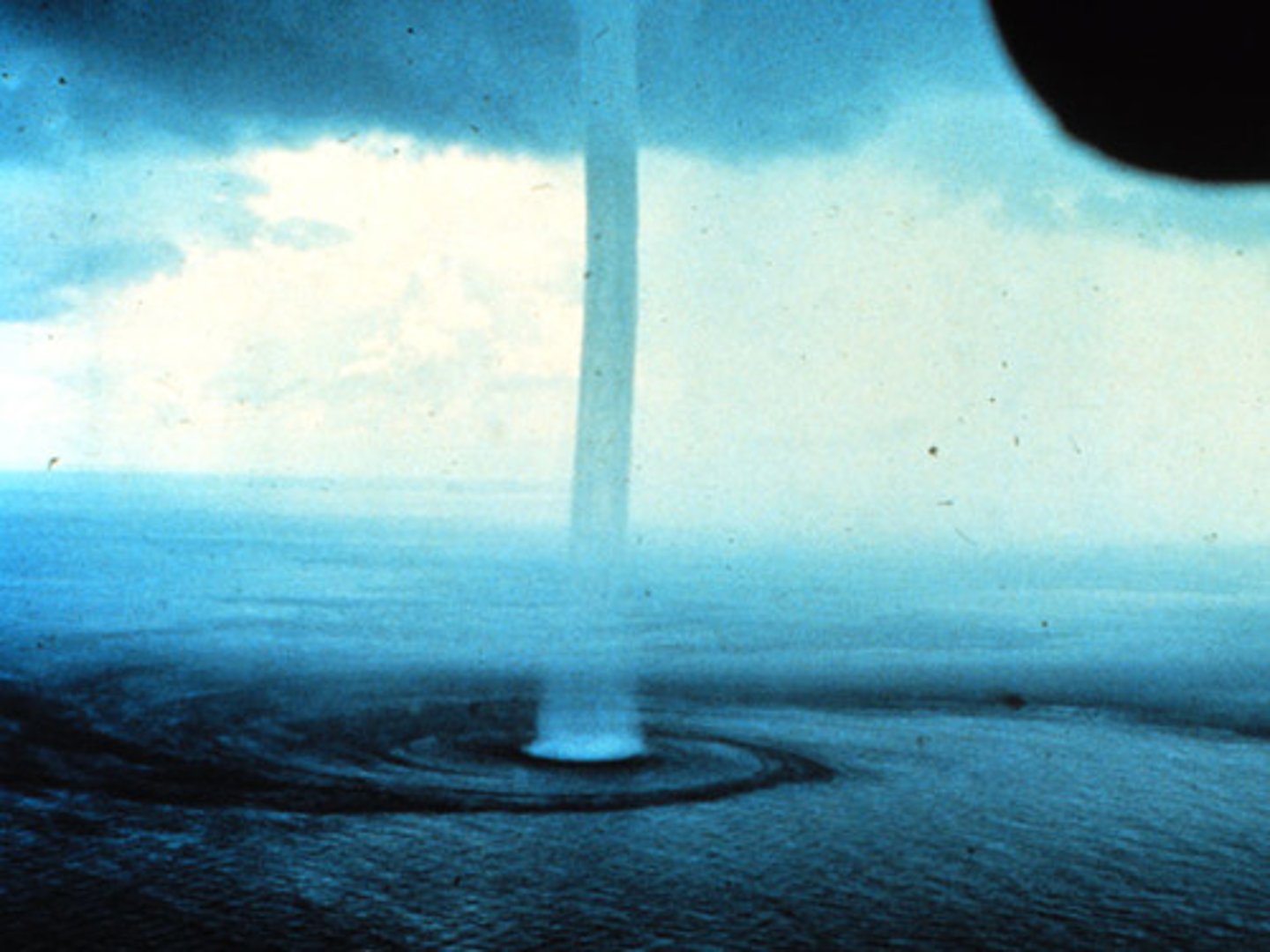
Waterspouts
A tornado that moves over a body of water.

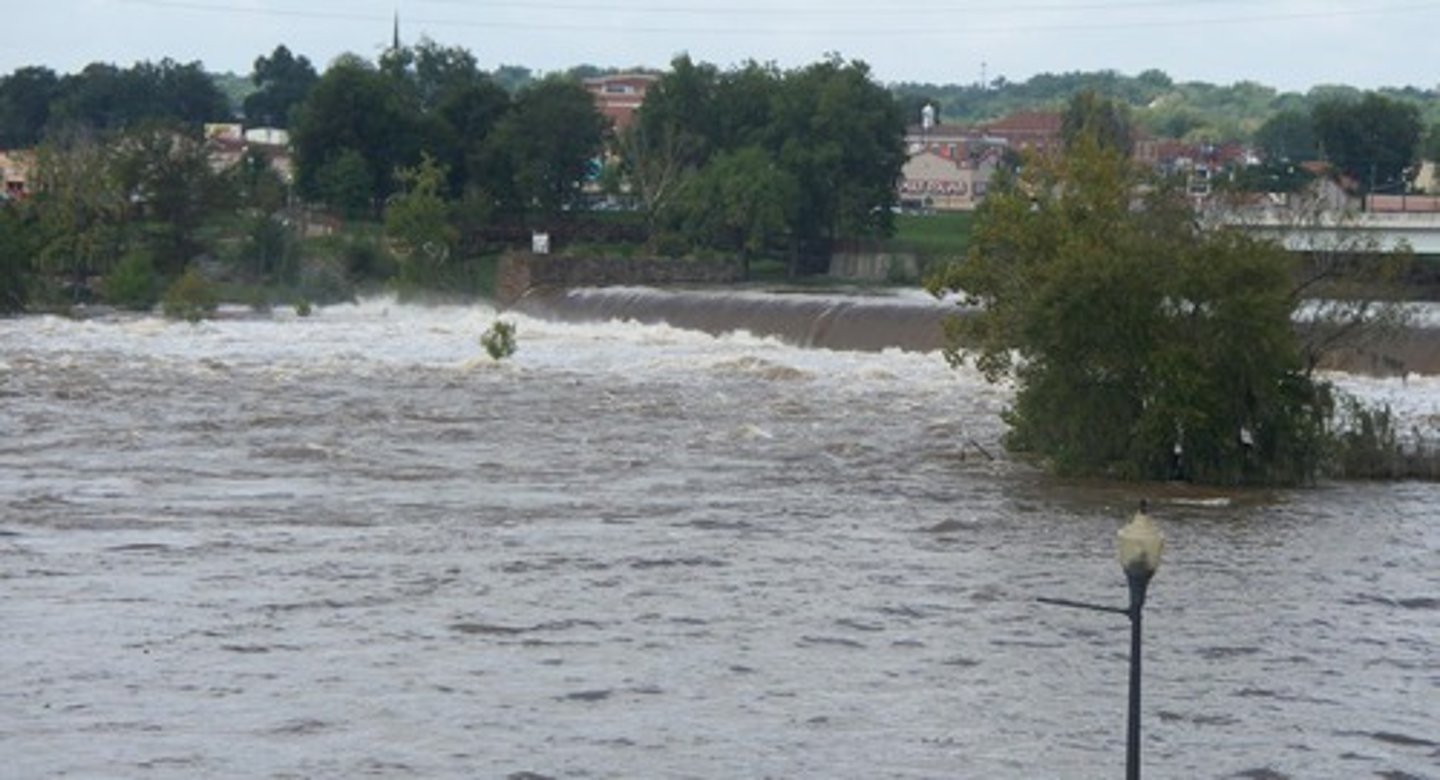
Flooding
Abnormal progressive rise in the water level of a stream; may result in the overflowing by the water of the normal confines of the stream.

Riverine
A type of flooding wherein the level of water flowing through rivers increases and goes beyond average water level, or worse, further encroaches levees.
Estuarin and coastal flooding
A type of flooding that occurs when seawater encroaches upon low-lying land that is usually still above sea level. May be a result of storm surges.
Urban flooding
A type of flooding usually occurs in highly populated, developed areas set on relatively low-lying areas like valleys and plains.
Catastrophic flooding
A type of flooding that may result from ground failure and/or major infrastructure failure.
Flash flood
Rapid, short-lived, and violent arrival of a large volume of water which can be caused by a very short period of heavy rainfall on land that is saturated or unable to absorb water. Most deadly because they happen without warning.
El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO)
Climatic phenomenon characterized mainly by cyclic fluctuations of warm and cold sea surface temperatures and atmospheric pressure in the central and eastern Pacific.
El Nino
Warm phase with warm water and weak trade winds. Prolonged unusual warming of sea surface temperatures in the central equatorial Pacific and eastern equatorial Pacific. Usually lasts for nine months up to two years.
La Nina
Cold phase with cool water and strong trade winds. Caused by strengthening of easterly trade winds which blow more warm water toward the west and allows the upwelling of cold water in the east.