Attending notes
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Pulmonary function test interpretation
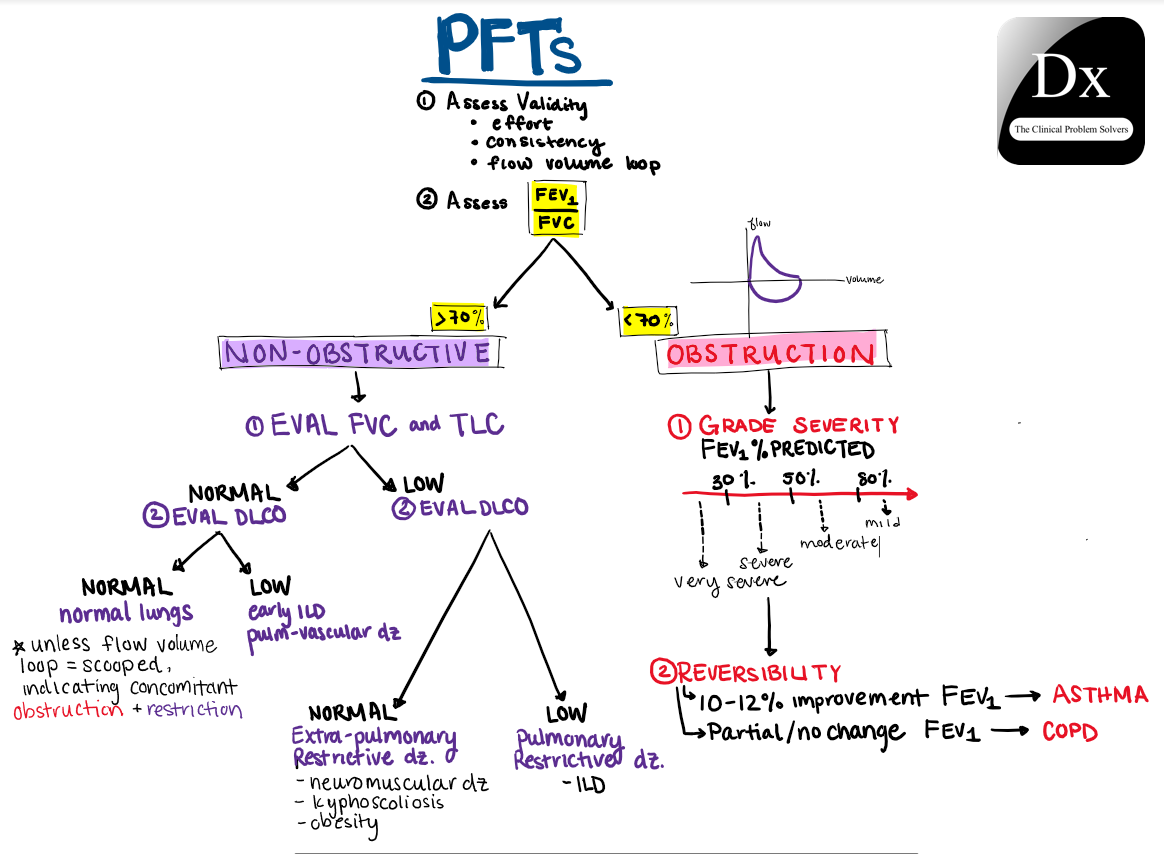
Light’s criteria
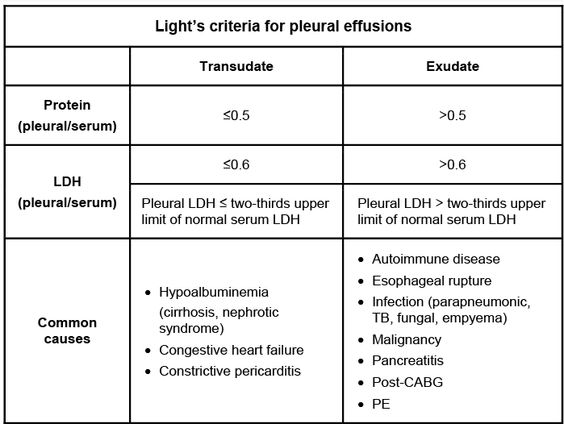
SAAG
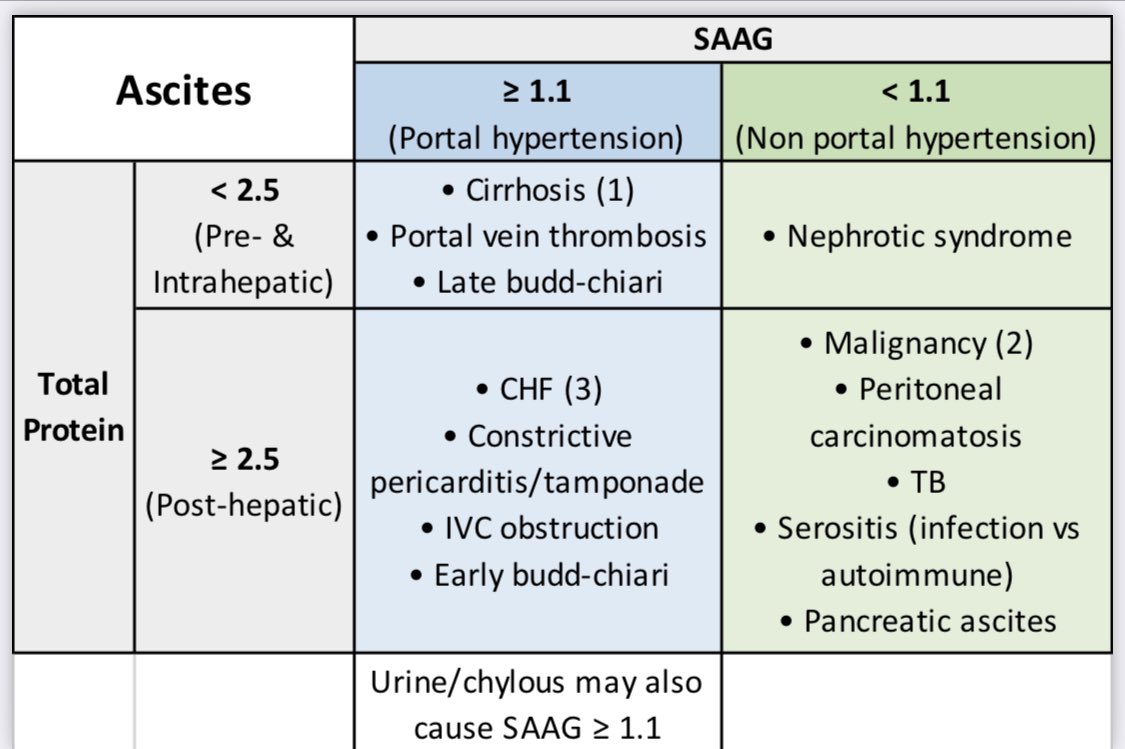
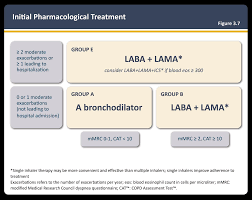
COPD Gold treatment 2025 categories
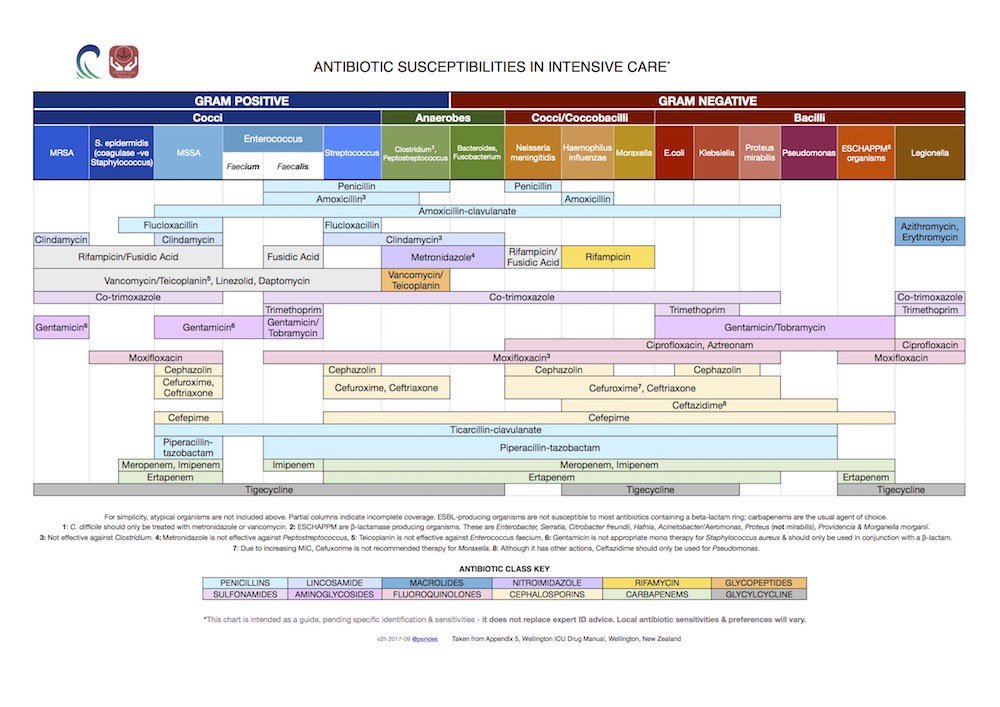
Antibiotic chart
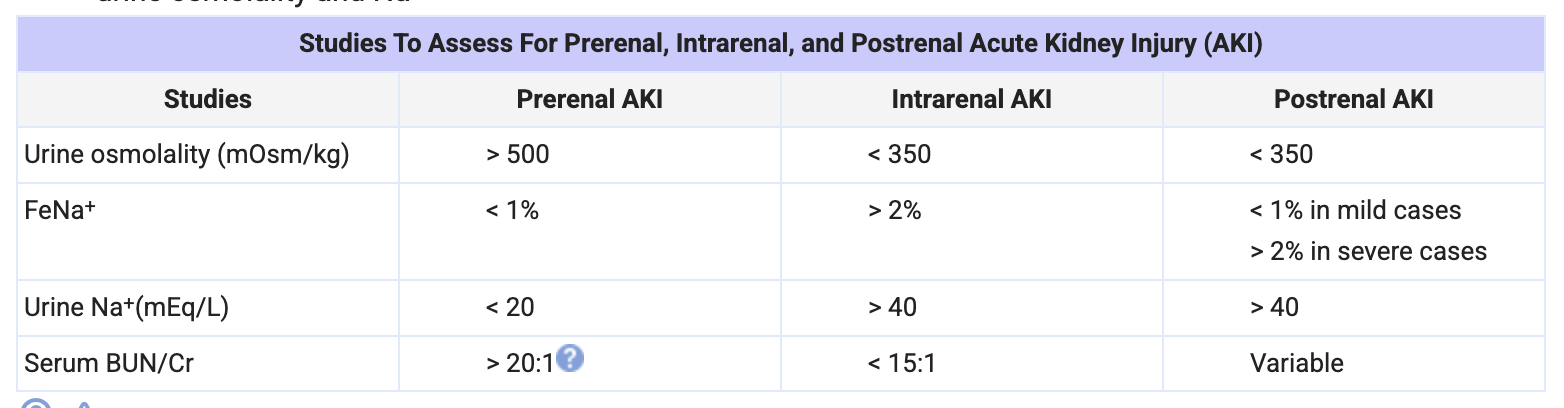
AKI
Classification of asthma
step up therapy for asthma
COPD classification and treatment
Pack years
packs smoked per day x number of years smoked = pack years
> 30 = higher risk and can do annual screening
Cholestatic vs hepatic liver injury
Cholestatic - ALT + AST < ALP
Hepatic - ALT + AST > ALP
stable vs unstable angina - diagnosis and treatment
diagnostic criteria and treatment for STEMI vs NSTEMI
How much albumin do you give after paracentesis? How many liters do you remove before giving the albumin?
How much albumin do you give in albumin challenge?
What is the difference between alcoholic hallucinosis and delirium tremens?
Alcoholic hallucinosis refers to hallucinations that develop within 12 to 24 hours of abstinence and typically resolve within 24 to 48 hours (which is the earliest point at which DT typically develops). Hallucinations are usually visual, although auditory and tactile phenomena are also described. Patients are aware that they are hallucinating and often very distressed. However, in contrast to DT, alcoholic hallucinosis is not associated with global clouding of the sensorium, only with specific hallucinations, and vital signs are usually normal Delirium tremens (DT) presents with confusion, disorientation, and severe autonomic instability after prolonged alcohol use, often requiring medical intervention.
Hepatic vs cholestatic LFTs
R factor for liver injury
The R-factor (or R ratio) helps interpret liver injury by classifying it as hepatocellular, cholestatic, or mixed, based on the ratio of elevated ALT (liver cell damage enzyme) to ALP (bile duct/cholestasis enzyme) compared to their normal limits. An R-value > 5 indicates hepatocellular damage (more ALT), < 2 suggests cholestatic injury (more ALP), and 2-5 points to a mixed pattern, guiding diagnosis, especially in cases like drug-induced liver injury (DILI) where causes differ significantly.
Definition of AKI
S Cr >/= 0.3 over 48 hr or >/= 1.5 x bCr over 7d
Urine protein:Cr ratio interpretation
Classes of antiarrhythmic medications