Quiz 7 - Animal Reproduction
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
The process of parturition is…
–a complex cascade of events that must occur in a short amount of time.
What causes the stimulus that causes parturition to begin?
is when the fetus reaches the physical space limits of the uterus
How does the fetus stimulate parturition?
•When the fetus reaches the physical space limits of the uterus, this causes the fetus to be stressed, which causes the fetus to release cortisol (i.e. cortisol is the stress hormone)
•Fetal cortisol is transferred from the fetal blood supply to the maternal blood supply, which triggers the parturition cascade.
–The parturition cascade:
•Fetal cortisol causes the release of four hormones from the dam that are important for parturition to occur
estrogen, PGF 2 alpha, relaxin, oxytocin
What does estrogen stimulate after released from fetal cortisol?
»Starts early contractions of the muscles surrounding the uterus
»Stimulates the cervix and vagina to produce mucus for lubrication
What does PGF 2 alpha stimulate after released from fetal cortisol?
»Causes the removal of the corpus luteum (CL) or corpora lutea (CLs)
What does relaxin stimulate after released from fetal cortisol?
»Causes the cervix to relax and also causes the ligaments in the pelvis to relax which allows more space for the fetus to move through the pelvis
•It is not well understood if relaxin is important in the bovine
What does oxytocin stimulate after released from fetal cortisol?
»Causes the final and most forceful contractions of the muscles surrounding the uterus which expel the fetus.
What does the forceful muscular contractions caused by oxytocin cause the fetus to do?
feet and head of the fetus to put pressure on the fetal membranes, which causes the fetal membranes to rupture
What specific fetal membrane ruptures?
•the amnion and the chorioallantoic membrane
When the amnion and chorioallantoic membranes rupture, what does the fluid do?
•provides additional lubrication to the birth canal (i.e. the cervix and the vagina)
The cervix and the vagina will also produce some mucus to provide lubrication.
What are three basic stages of parturition?
1.Dilation of the cervix and muscle contractions of the uterus
–During this stage the fetus is positioned for the parturition process
2.Expulsion of the fetus
3.Expulsion of the fetal membranes.
•Length of stages of parturition by species
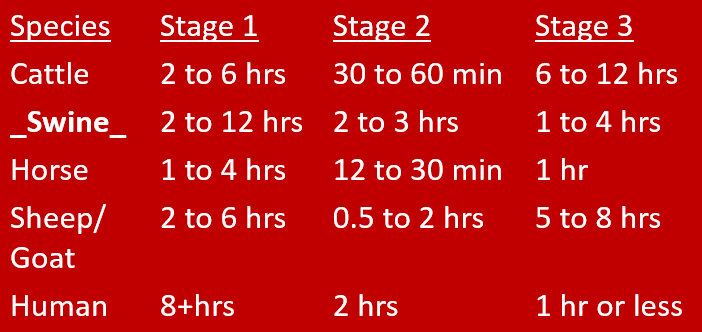
What is the normal presentation of the fetus for birth for cattle, sheep, goats, and horses?
•The fetus should be resting on its abdomen with the front feet and nose at the cervix
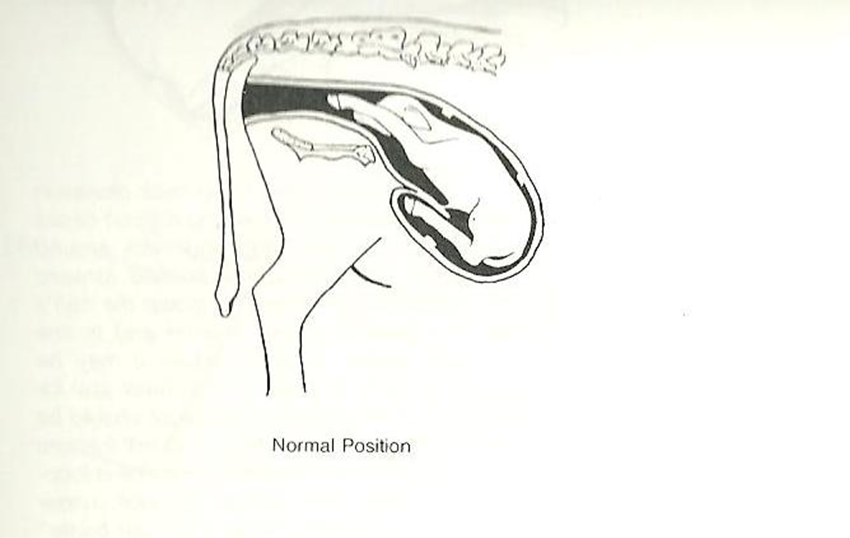
What is the normal presentation of the fetus for birth for swine?
•The sow can usually deliver piglets that are presented at the cervix backwards as well as those presented in the normal forward position
–The normal forward position of pigs is also somewhat different because the front feet are normally back against the body, rather than pointing at the cervix.
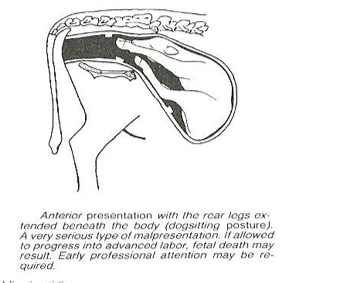
What is dystocia?
difficult parturition or difficulty in birthing (i.e. abnormal parturition)
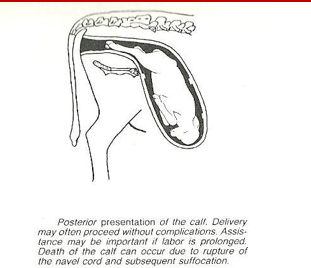
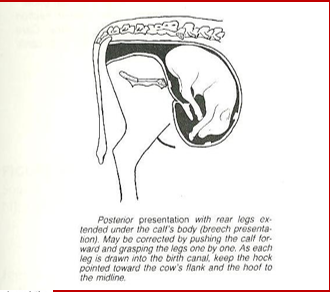
What is uterine involution?
Following parturition the uterus will slowly return to its original size through a process
When does uterine involution begin?
immediately after parturition during stage 3 with the expulsion of the fetal membranes caused by the contractions of the muscle layers surrounding the uterus
Is complete uterine involution required before ovarian activity and estrous cycles can resume?
•In most species, resumption of the estrous cycle is dependent on the length of ‘lactational anestrous’ and not on uterine involution
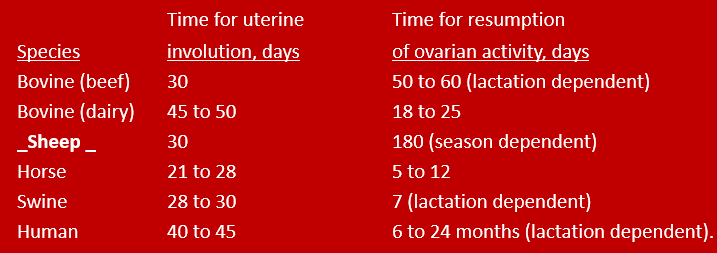
–Time required for complete uterine involution and resumption of ovarian activity after parturition
What is lactation?
•production, secretion and removal of milk during suckling from the mammary gland
What are two hormones important for lactation
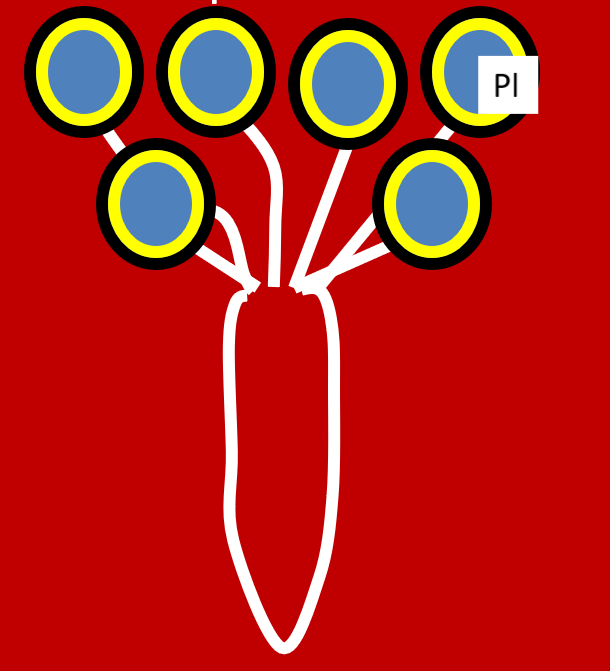
1.Prolactin (Pl)
2.Oxytocin (Ot)
What does prolactin do?
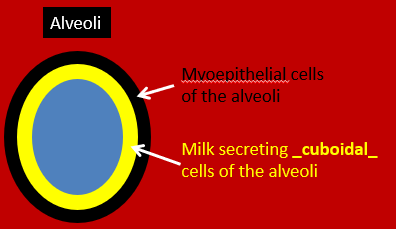
responsible for causing the milk secreting cuboidal cells of the alveoli tissue of the mammary gland to produce milk
»Remember, the prolactin released during suckling will stimulate the production of milk for the next lactation, not the current lactation.
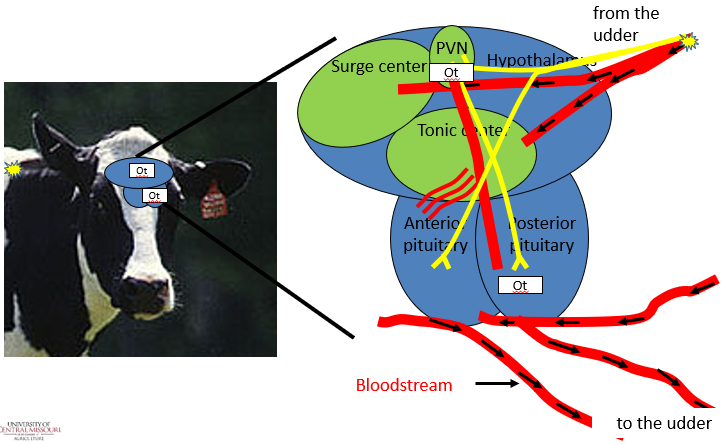
Where does prolactin come from?
–produced and released from the anterior pituitary in response to suckling of the teat by the neonatal offspring
What does oxytocin do?
responsible for causing the myoepithelial cells_ of the alveoli tissue of the mammary gland to contract and secrete milk into the gland cistern and then the teat cistern.
Where does oxytocin come from?
–produced in the PVN (paraventricular nucleus) of the hypothalamus and then is stored in, and then released from, the posterior pituitary
Real animal perspective for reproduction using the cow – positive feedback loop
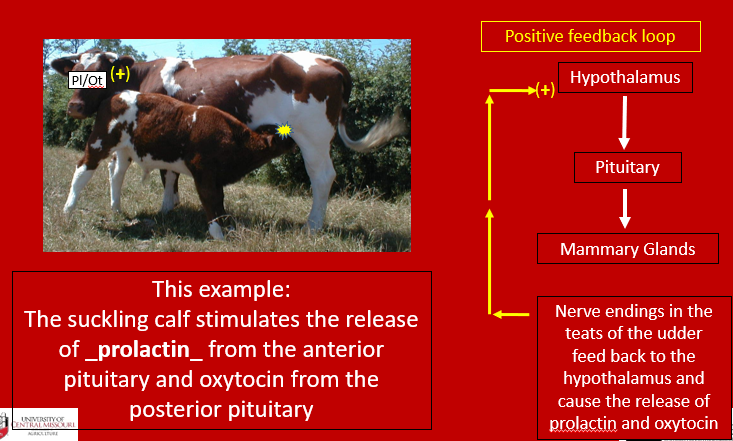
Real animal perspective for reproduction using the cow – positive feedback loop for prolactin
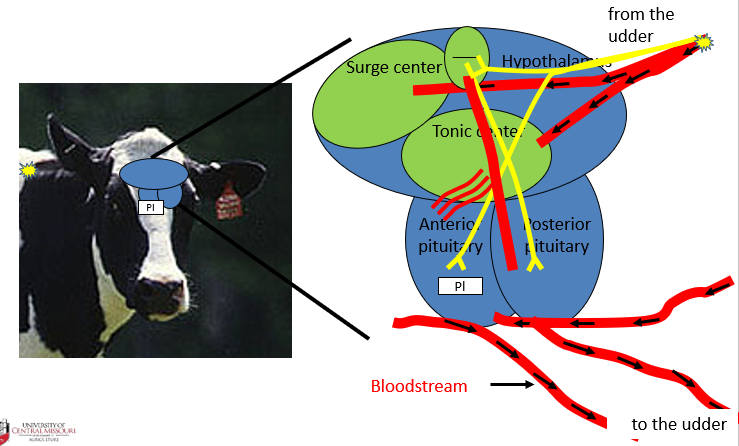
Real animal perspective for reproduction using the cow – positive feedback loop for oxytocin
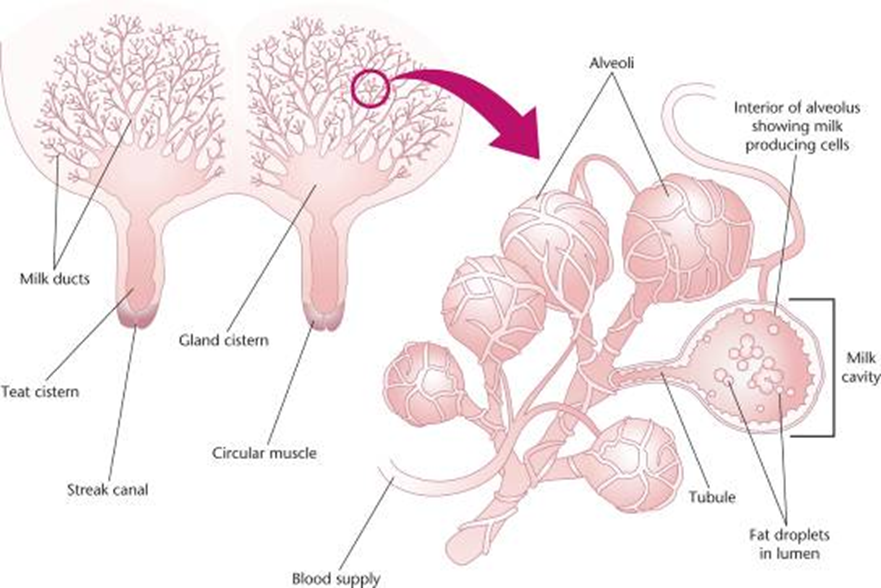
–The basic components of the mammary gland
Animation process of prolactin and oxytocin working
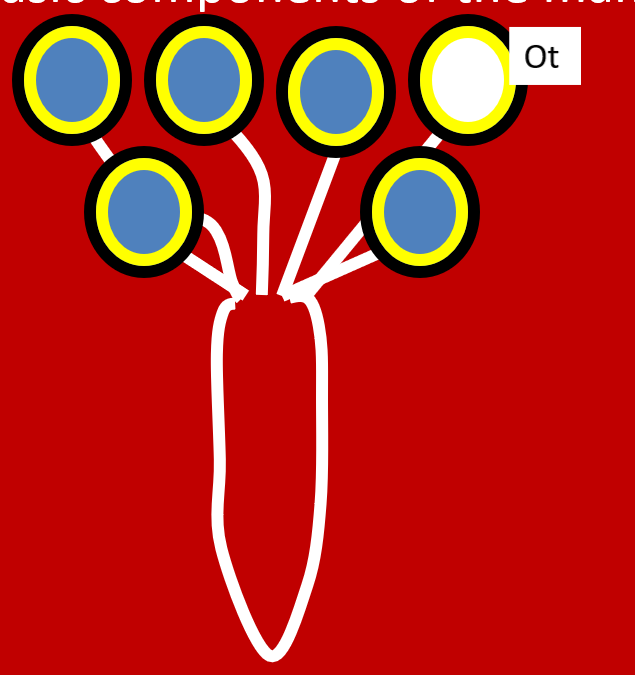
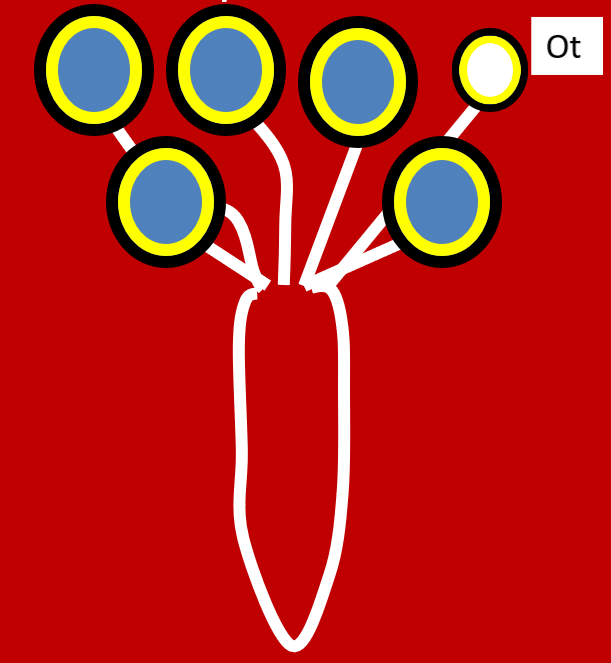
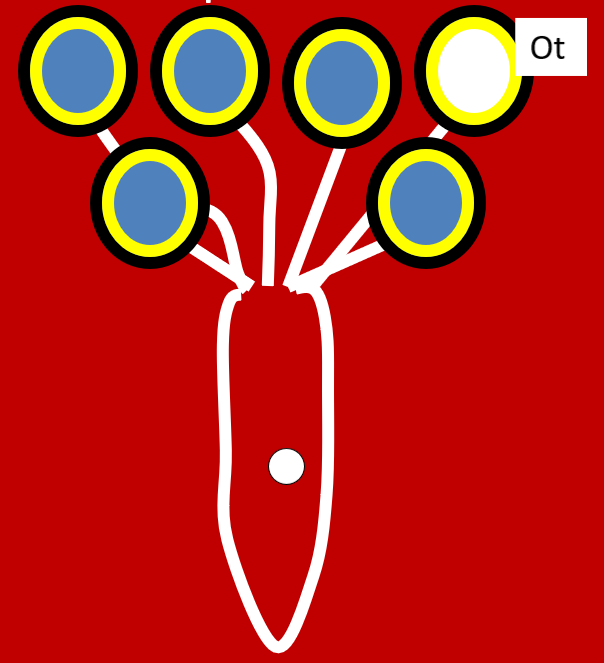
For swine, location on the body and number of mammary glands (i.e. teats) for the livestock species.
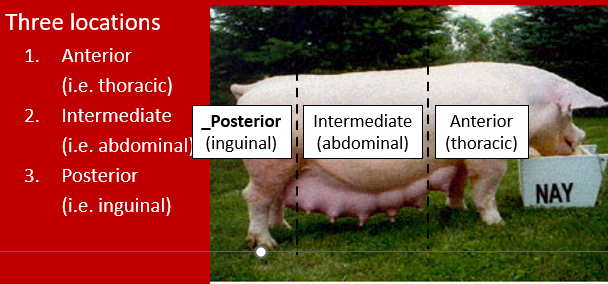
Swine need 6-7 functioning teats per side so 12-14 in total
–Location on the body and number teats for the livestock species

–Remember, the prolactin released during suckling will stimulate the production of milk for the next lactation, not the currentlactation_
–So, what stimulates the milk to be produced for the first suckling after parturition?
•Depending on the species, the placenta will produce a hormone called placental lactogen, which is thought to stimulate the mammary glands to begin to produce milk prior to parturition
–Depending on the species, this milk production will begin a few weeks to a few days before parturition.
What is colostrum?
–first milk produced by the dam following parturition
When is colostrum produced?
within first 24 to 48 hour after parturition
What does colostrum contain?
•high levels of antibodies produced by the dam and nutrients that the neonatal animal can use to fight infectious pathogens
–antibodies consumed in the colostrum by the neonate are absorbed directly from the small intestine into the bloodstream
–The colostrum is also very high in nutrients, especially protein, which also helps the neonatal animal to fight infectious pathogens.
–what stimulates the mammary tissue to produce the colostrum only at the time of parturition
•Research suggests that the placental lactogen may play a role in colostrum production.
what is ‘Anestrous’ or ‘Anestrus’?
•describe when the female animal does not show estrous cycles
What is lactational anestrous?
–when the female does not show estrous cycles during lactation
What is seasonal anestrous?
–when the female does not show estrous cycles because of the season of the year.
What causes lactational anestrous?
–specific causes of lactational anestrous are not well understood
•It was thought that stimulation of the nerve ending_ of the teats during suckling caused a negative feedback effect on the release of GnRH and subsequent release of FSH and LH
–However, research in cattle has shown that suckling alone is not responsible for causing lactational anestrous.
Factors that cause lactational anestrous?
–Suckling of the teats by the offspring
–Sight of the offspring
–Smell of the offspring
–Sounds of the offspring
–Other physical contact with the offspring.
–Sheep and goats are ____ day seasonal breeders which means they show estrous cycles beginning in the fall of the year in the USA as the day-light length gets shorter
•Therefore, during the spring and summer of the year, when day-light length is longer, sheep and goats are in seasonal anestrous
short
–Horses are ____ day seasonal breeders which means they show estrous cycles beginning in the spring of the year in the USA as the day-light length gets longer
•Therefore, during the late fall and winter of the year, when day-light length is shorter, horses are in seasonal anestrous
long
–What causes sheep and goats to be short-day breeders?
–Decreasing day-light stimulates the photoreceptors of the retina in the eyes of sheep and goats
–The stimulated photoreceptors cause the pineal gland to release a hormone called melatonin
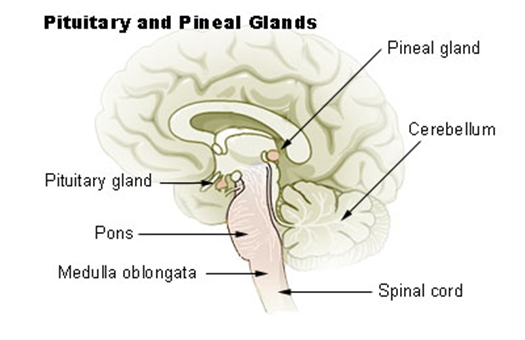
–Melatonin increases in the body in response to the decrease in day-light length
–The increase in melatonin stimulates reproductive activity in sheep and goats
»Specifically, melatonin stimulates the hypothalamus to release GnRH, which stimulates the anterior pituitary to release FSH and LH, which causes the females to begin estrous cycles
–During the spring and summer, melatonin decreases in the body in response to the increase in day-light length
»The lack of melatonin prevents the hypothalamus from releasing GnRH in sheep and goats.
Where is the pineal gland located?
located just below the brain, and just behind the hypothalamus.
–What causes horses to be long-day breeders?
•In long-day seasonal breeders a decrease in melatonin appears to stimulate reproductive activity
–It is not understood why a decrease in melatonin stimulates reproductive activity in long-day seasonal breeders
–Remember, this is completely opposite as to what happens in sheep and goats.