AP Human Geo - Unit 1 Thinking Geographically
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Human Geography
One of the two major divisions of geography; the spatial analysis of human population, its cultures, activities, and landscapes.
Time-space compression
The rapid innovation of communication with transport technologies associated with globalization that transforms the way people think about space and time.
Distance decay
The effect of distance on interaction, generally the greater the distance, the less interaction.
Scale of analysis
How zoomed in or out you are when looking at geographic data.
Reference maps
Show locations of places and geographic features.
Political maps
Show countries, provinces, or other political borders.
Physical maps
natural features, landforms (mountains, rivers, deserts)
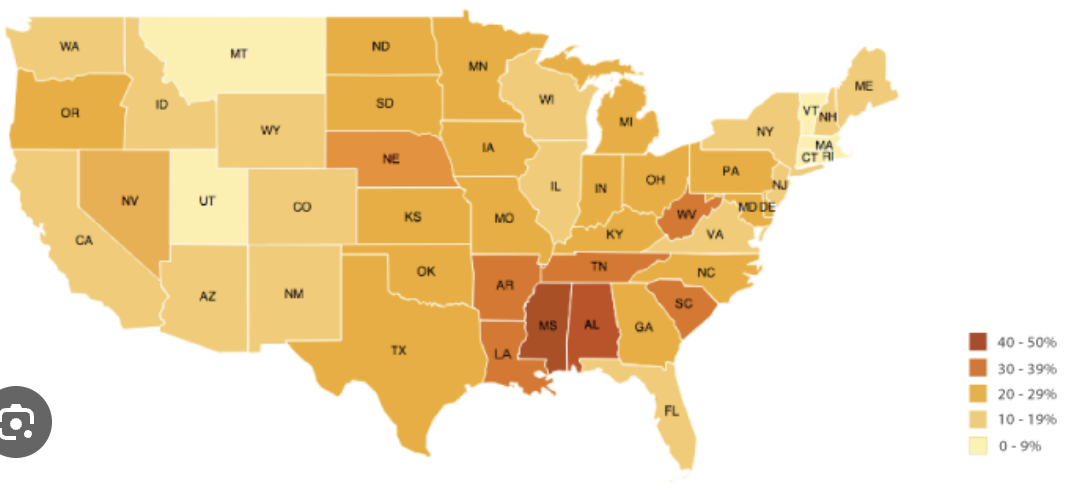
Choropleth map
A thematic map that uses tones or colors to represent spatial data as average values per unit area.
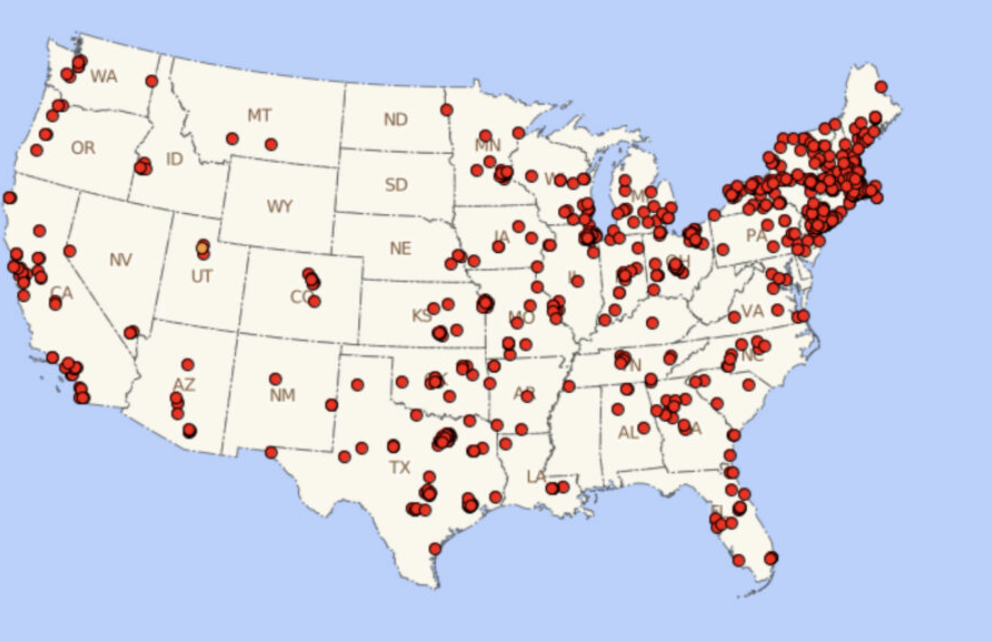
Dot distribution map
A map where dots are used to demonstrate the frequency or intensity of a particular phenomena (think: population density maps).
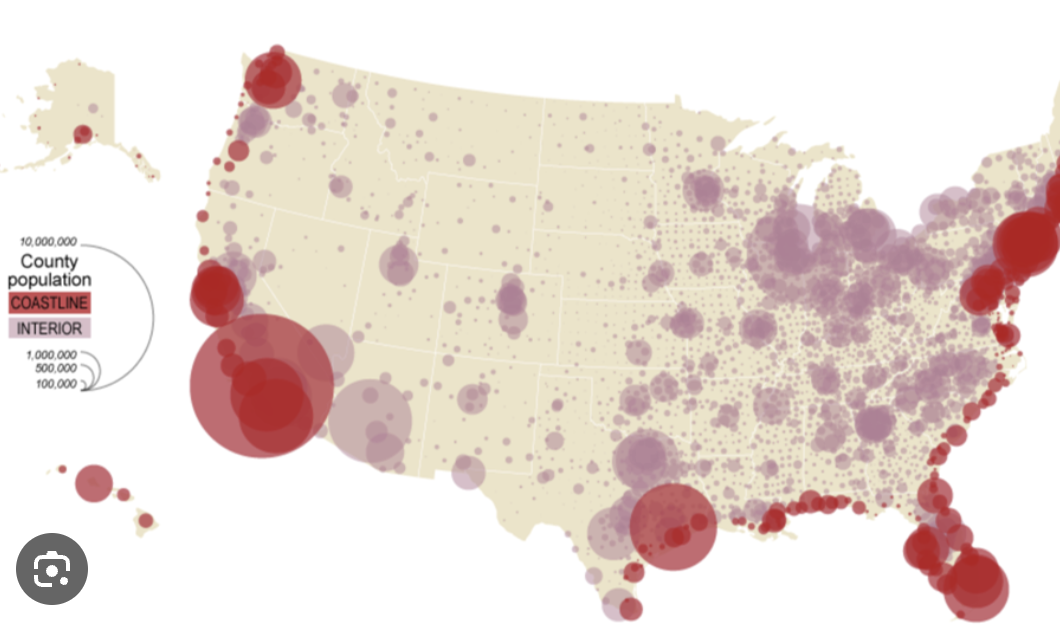
Graduated symbol map
A map with symbols that change in size according to the value of the attribute they represent.
Isoline map
Map displaying lines that connect points of equal value; for example, a map showing elevation.
Cartogram map
A map in which the size and shape is distorted in order to demonstrate a variable such as travel, population, or economic production.
Cartographic scale
Refers to the way the map communicates the ratio of its size to the size of what it represents.
Small scale map
Shows fewer details, focuses on a larger area (region, world).
Large scale map
Shows more details, focuses on a smaller area (city, town).
Latitude
The numbering system used to indicate the location of parallels drawn across the globe and measuring distance north and south of the equator.
Longitude
Distance east and west of the prime meridian, measured in degrees.
Prime meridian
The meridian, designated at 0 longitude, which passes through the Royal Observatory at Greenwich, England.
International date line
An arc that for the most part follows 180° longitude, although it deviates in several places to avoid dividing land areas. When you cross the International Date Line heading east (toward America), the clock moves back 24 hours, or one entire day. When you go west (toward Asia), the calendar moves ahead one day.
Equator
0 degrees latitude
Relative location
Where a place is located in relation to another place
Absolute location
The exact position of an object or place, measured within the spatial coordinates of a grid system.
Remote sensing
The scanning of the earth by satellite or a high flying aircraft in order to obtain information about it (changes in landforms, weather patterns, etc).
Global positioning system (GPS)
Satellite based system for determining the absolute location of places or geographic features.
Geographic information system (GIS)
A computer system that can capture, store, query, analyze, and display geographic data (layering data sets together to create geographic models of a place).
Projection
The system used to transfer locations from earth’s surface to a flat map.
Mercator projection
A projection of a map of the world onto a cylinder in such a way that all the parallels of latitude have the same length as the equator, used for navigation.
Peters projection
An equal area projection purposely centered on Africa in an attempt to treat all regions of earth equally.
Distortion
A change in the shape, size, or position of a place when it’s shown on a map.
Friction of distance
A measure of how much absolute distance affects the interaction between two places.
Topynym
The place name of geographic location.
Environmental determinism
A doctrine that claims that all cultural traits are formed and controlled by environmental conditions.
Possibilism
The physical environment may limit some human actions, but people have the ability to adjust to their environment.
Formal region
An area within which everyone shares in common one or more distinctive characteristics.
Functional region
An area organized around a node or focal point.
Perceptual(Vernacular) Region
How people think about or percieve a region (ex: “the south”).