Photosynthesis
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What is photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae, and some photosynthetic bacteria convert solar light energy, into chemical energy stored in C bonds in glucose.
This process involves the fixation of carbon dioxide and splitting of water, with the release of oxygen as a byproduct.
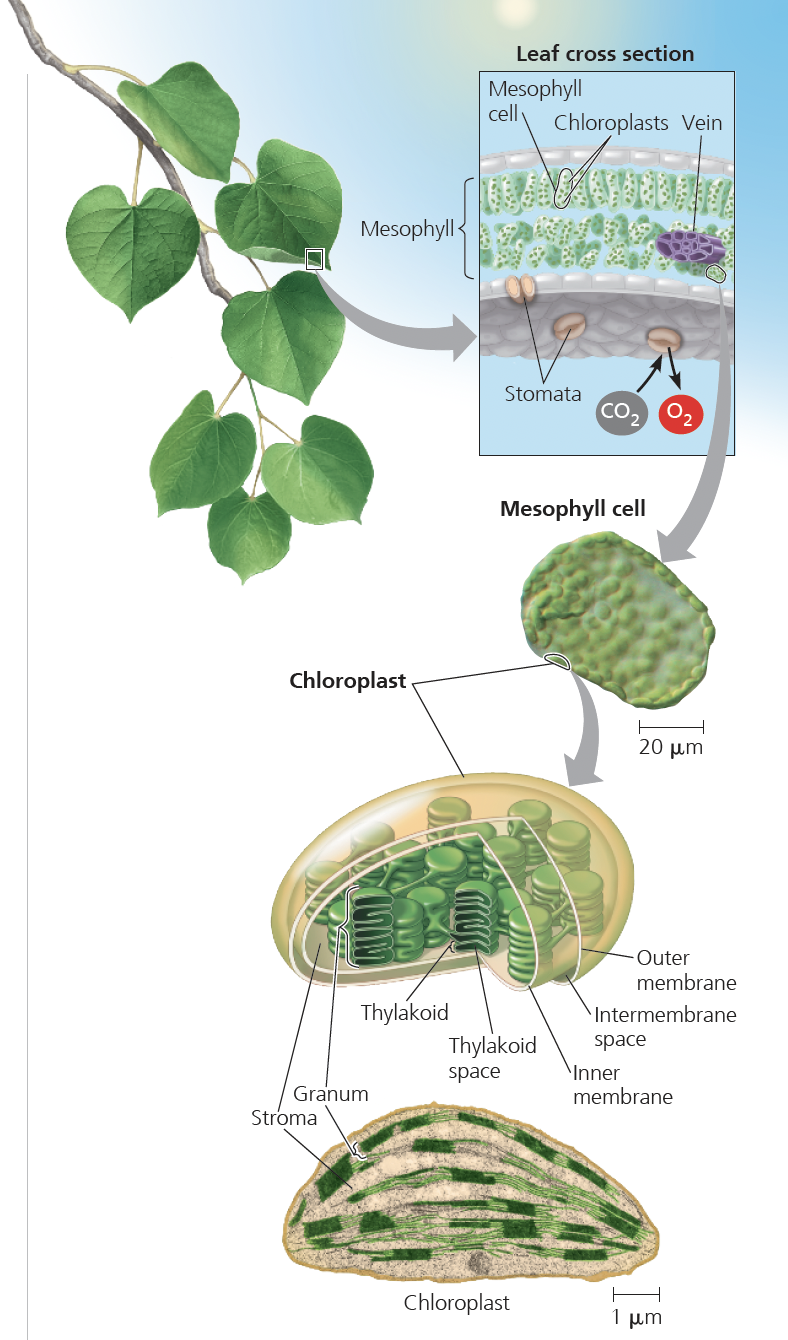
What is a chloroplast and its key structures?
A chloroplast is the double-membraned organelle where photosynthesis occurs found in the cells of the mesophyll of a leaf
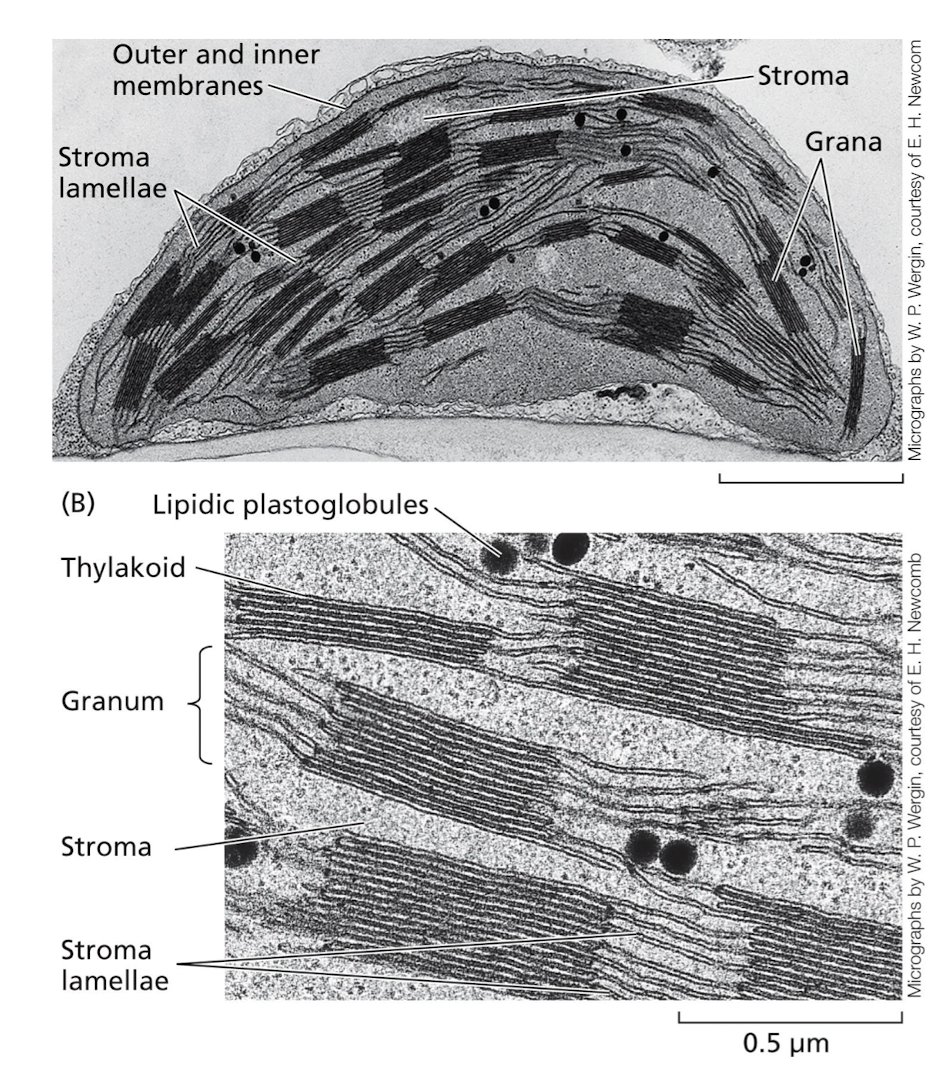
3 membranes: outer, inner, and thylakoid.
Thylakoids stack into grana and are surrounded by stroma.
Proteins and pigments (chlorophyll) that function in photosynthesis are embedded in the thylakoid membrane.
Adjacent grana are connected by unstacked membranes called stroma lamella (plural: lamellae)
where does photosynthesis take place? - more detailed
Most photosynthesis in plants occurs leaves
• Chloroplasts are found mainly in mesophyll cells, the interior tissue of the leaf
• CO2 enters and O2 exits the leaf through microscopic pores called stomata
• Veins transport water from the roots and export sugar to non-photosynthetic parts of the plant
how does photosynthesis act as a Redox process?
• Photosynthesis reverses the direction of electron flow compared to respiration
•Redox process in which H2O is oxidised and CO2 is reduced

*Energy in form of ATP
• It is an endergonic process; the energy boost is provided by light
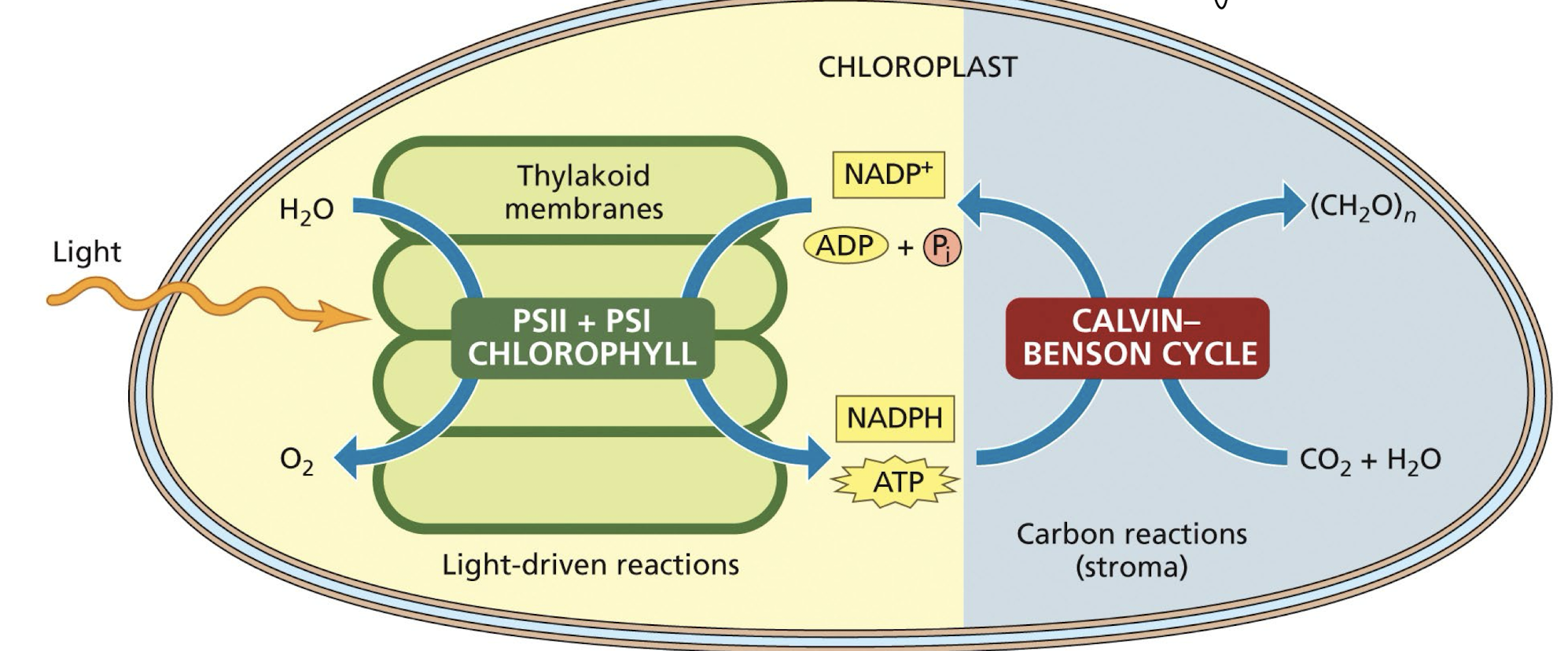
what are the 2 stages of photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis consists of the light reactions (photo part) and Calvin cycle (synthesis part)
The light reactions occur in the thylakoids + involves
• Split H2O, providing e- + (H+)
• Release O2 as a by-product
• Reduce the electron acceptor NADP+ to NADPH
• Generate ATP from ADP by photophosphorylation
The Calvin cycle occurs in the stroma + involves
C-fixation the incorporation of CO2 into organic molecules
Reduction
Regeneration of ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) to continue the cycle.
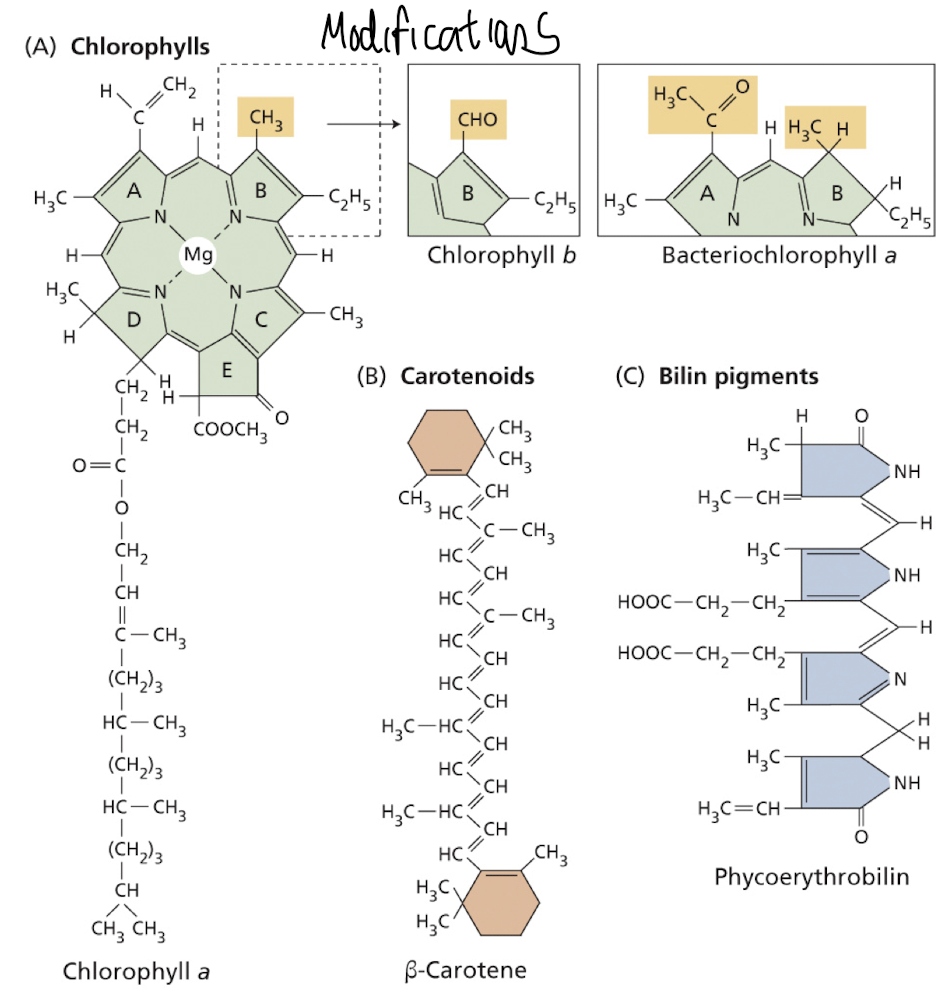
what are the main chlorophyll pigments found in photosyntheticorganisms?
Chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b are abundant in green plants
Chlorophylls c, d, and f are found in some protists and cyanobacteria.
Bacterio-chlorophyll a is the most widely distributed chlorophyll pigment in bacteria
All absorb photons of a particular wavelength
What is meant by electromagnetic radiation and the different wavelengths of light
Electromagnetic radiation refers to the range of all types of light energy, which includes visible light, ultraviolet, and infrared light.
Different wavelengths of light correspond to different colors and energies, playing a crucial role in photosynthesis by providing the energy needed for the light reactions.
why do plants look green?
Chlorophyll pigments absorb other wavelengths of light, such as red and blue, while reflecting green light.
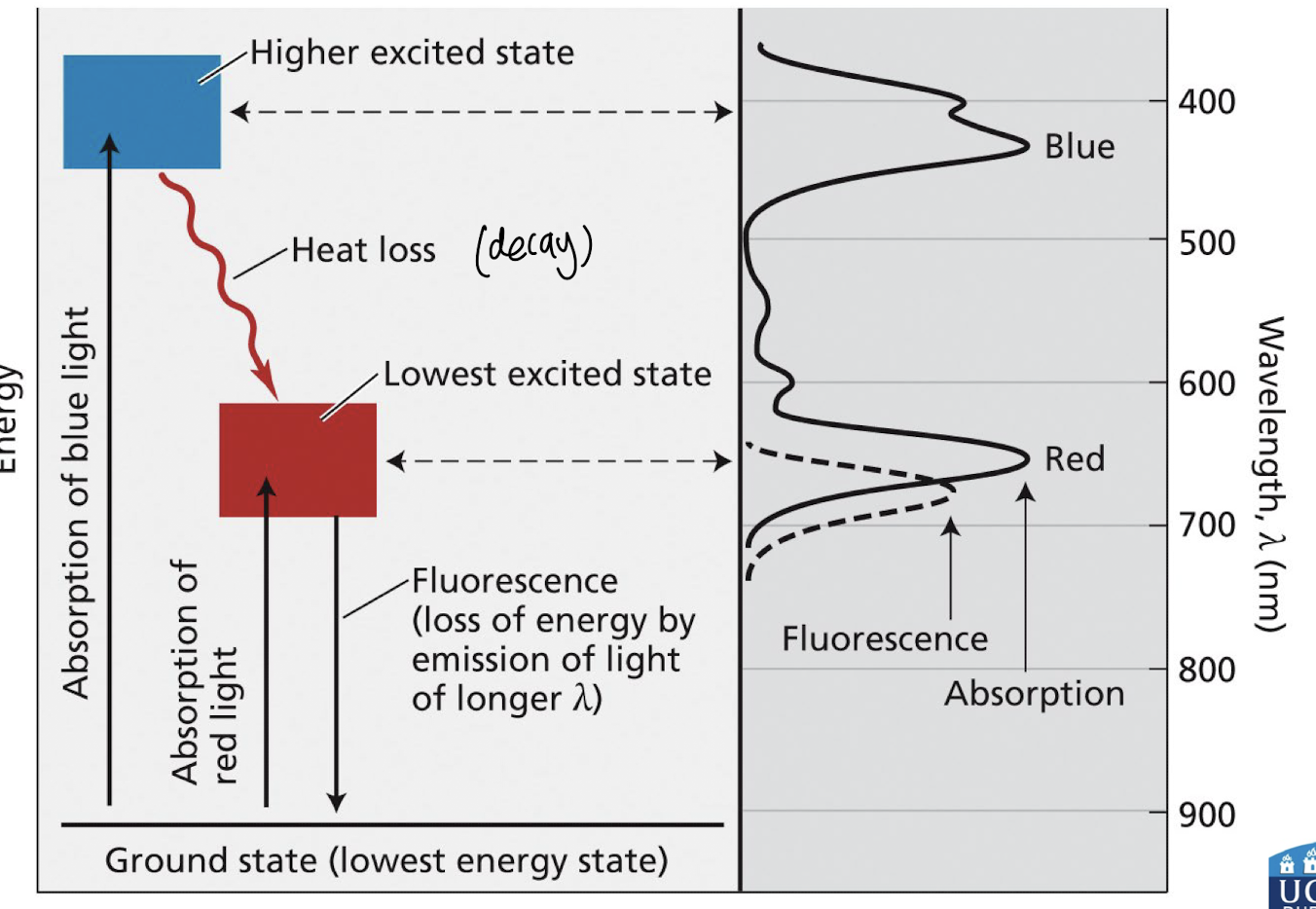
what happens when plants absorb blue light & its significance?
Absorption of light by chlorophyll results in the transition to a higher excited state.
Blue light absorbed by chlorophyll produces a high excited state – highly unstable
Rapid decay to lowest excited state → initiating light reactions
How can we describe the chemical structure of chlorophyll?
Complex ring structure
Chemically related to heme groups found in haemoglobin
The ring structure contains some loosely bound electrons that are involved in the electronic transitions and redox reactions.
The complex ring structure is connected to a hydrocarbon tail:
Hydrocarbon tail anchors the chlorophyll to the thylakoid membrane
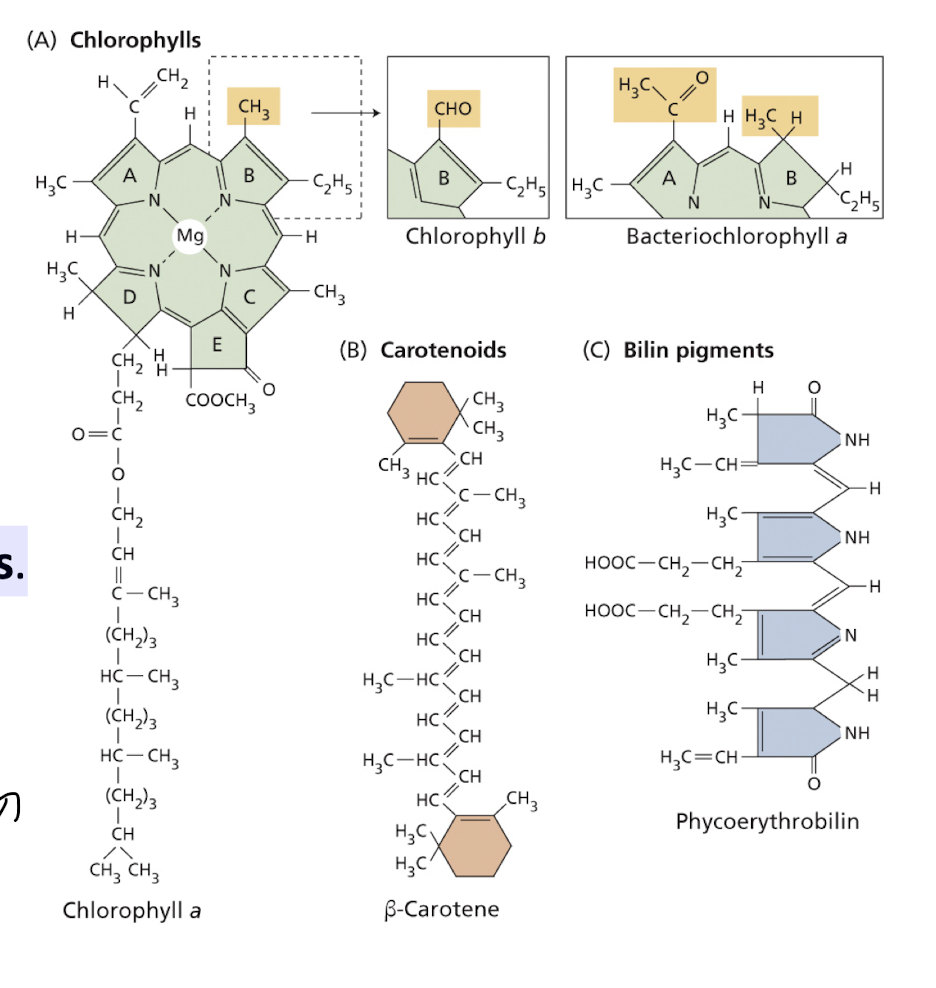
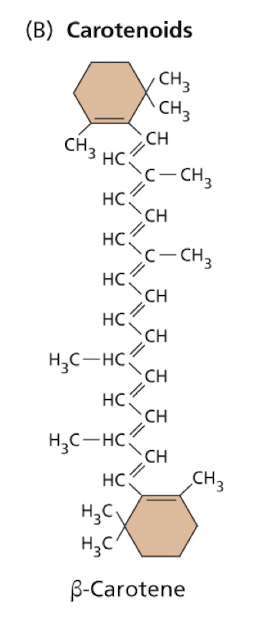
what are carotenoids + their function?
Carotenoids are found in all photosynthetic organisms – integral components of thylakoid membranes.
Light energy absorbed by carotenoids can be transferred to chlorophyll for photosynthesis –
Known as accessory pigments – also protect the organism from ‘damage’ by excessive light
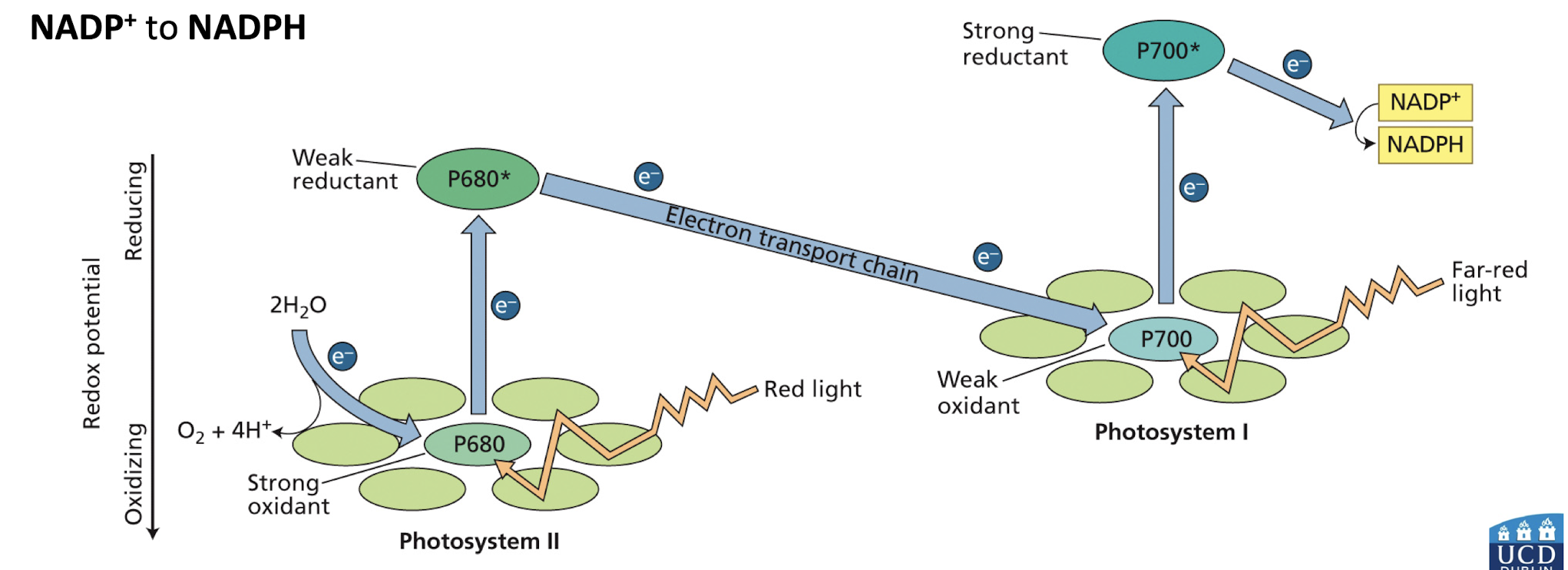
What are photosystems and how do they function?
Photosystems II (PSII) and I (PSI) are protein-pigment complexes that convert light energy into chemical energy
PSII splits water and transfers electrons
PSI uses light to reduce NADP+ to NADPH.
What is the reaction centre complex?
Special pair of chlorophyll a and a primary electron acceptor that can transfer an excited electron to an electron acceptor
• the primary electron acceptor accepts excited electrons + is reduced as a result
what is the difference between the special pair in PSII vs PSI?
The special pair in PSII is known for absorbing red light at 680 nm and facilitating photolysis by producing a very strong oxidant
while in PSI it absorbs far red light at 700 nm, aiding in the reduction of NADP+ by producing a very strong reductant
where is PSII and PSI located?
PS II is predominantly localised to the grana lamellae
PS I, proteins of the ETC, and ATP synthase enzyme are localised to the stroma lamellae and at the edges of the grana lamellae
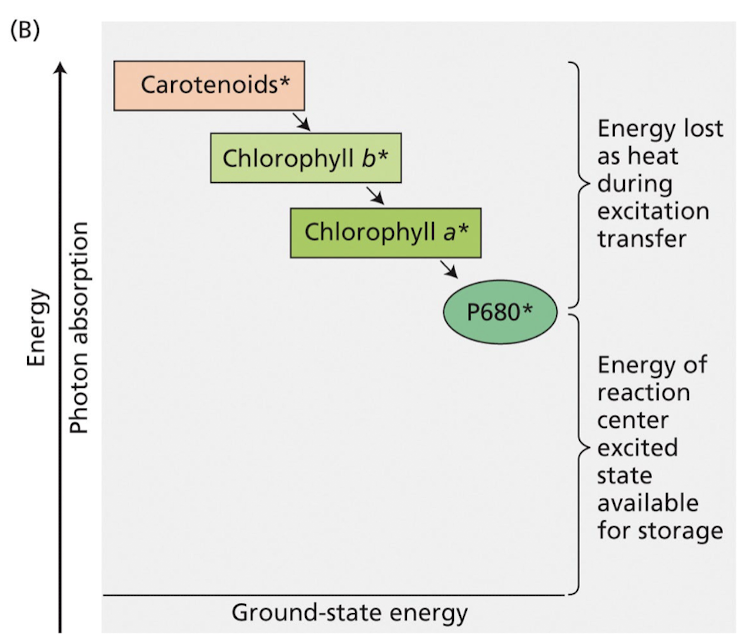
what are the LHC / antenna complexes?
Various chlorophyll pigment molecules bound to proteins i.e LHCII for PSII and LHC I for PSI
• Organised for efficient transfer of energy of photons to chlorophyll a molecules in the reaction-centre
The difference in the energy between _______ is lost as ____ during energy transfer it isn’t possible for _______
2 pigments, lost as heat, reverse transfer of energy
What is the Z-scheme in photosynthesis?
It represents the series of electron flow through PSII and PSI, resulting in:
Photolysis of H2O to produce O2 and H+
Production of NADH and ATP through the electron transport chain.
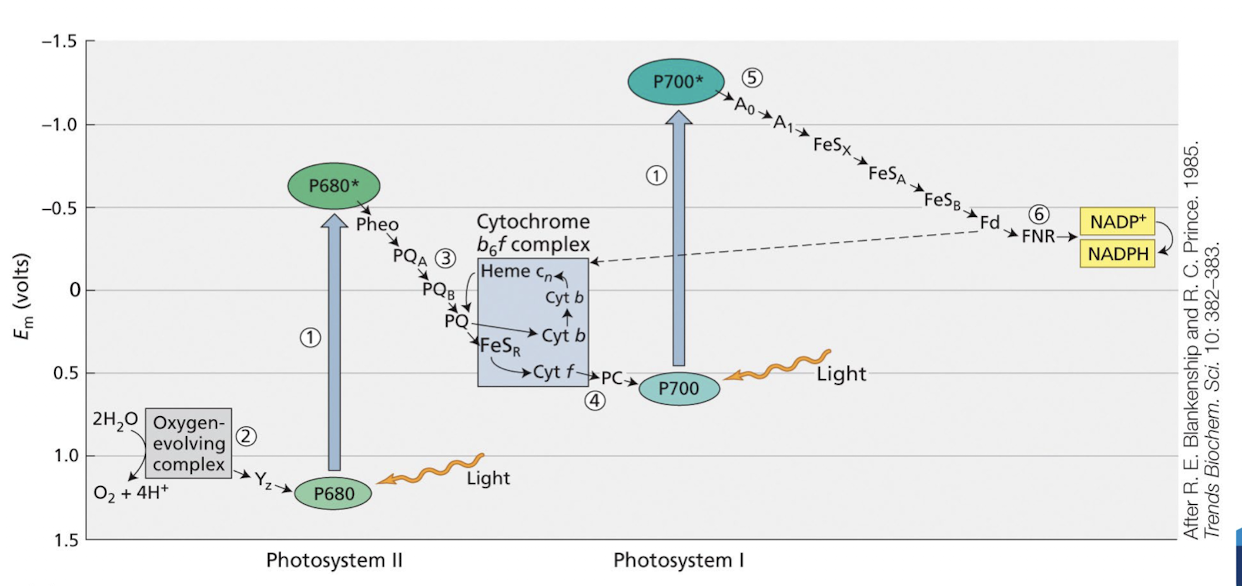
What are the 5 main steps of how e- are transferred in the Z scheme?
PQ is reduced to PQH2 (using H+ produced from splitting of H2O)
Cytochrome b6f complex oxidises PQH2 (complex process called the Q cycle), while transferring electrons to plastocyanin (PC)
PC transfers the electron to the reaction centre chlorophyll, P700 of PS I.
Excited P700+ transfers the electrons to a chlorophyll (A0) and a quinone (A1) followed by transfer to a series of iron-sulphur proteins (FeS) to ferrodoxin (Fd)
Fd and the flavoprotein, ferrodoxin-reductase (FNR) reduces NADP+ to NADPH
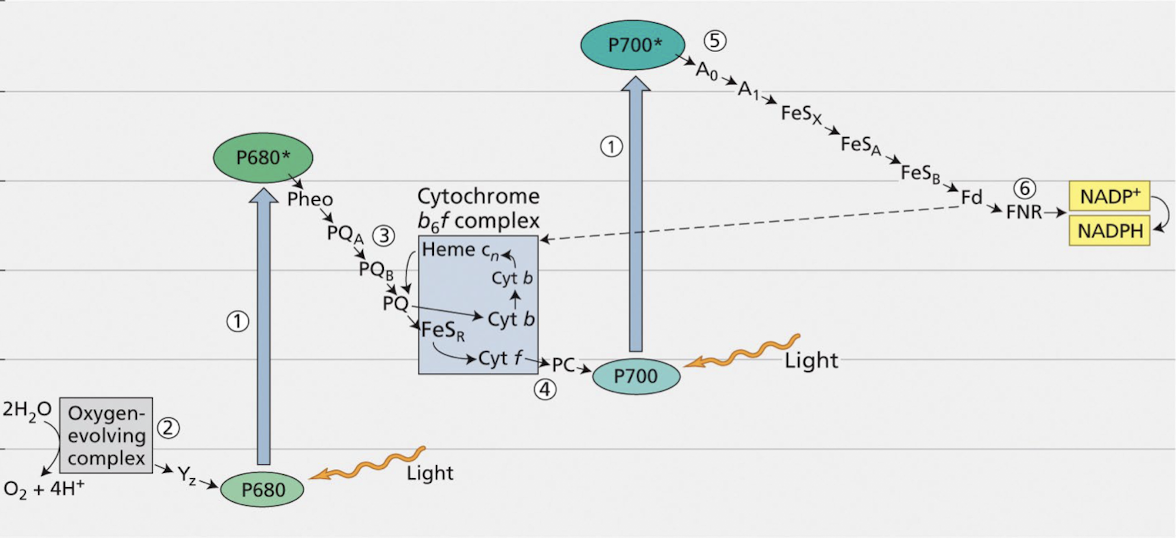
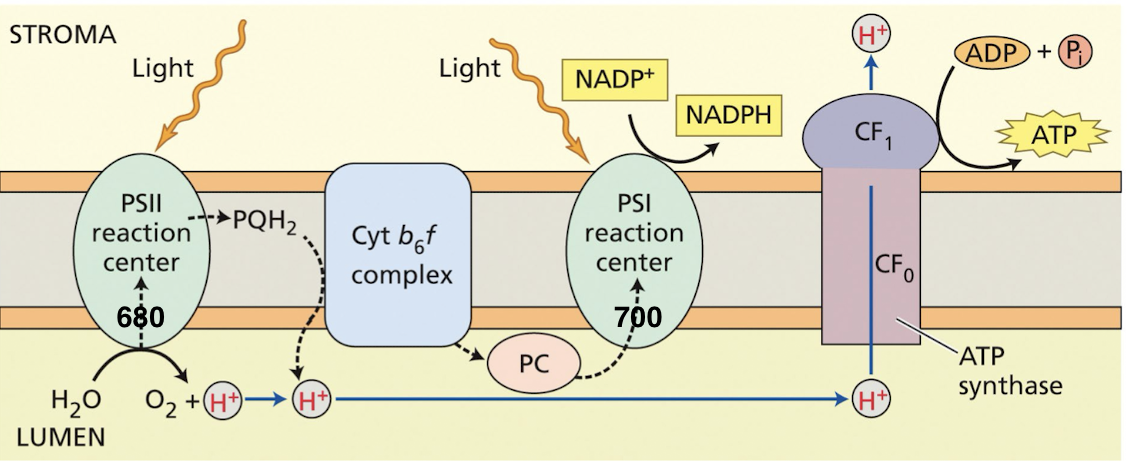
Q: What are the roles of plastoquinone (PQ), plastocyanin (PC), and ferredoxin (Fd)?
PQ shuttles electrons in PSII
PC transfers electrons to PSI
Fd helps reduce NADP+ to NADPH via FNR.
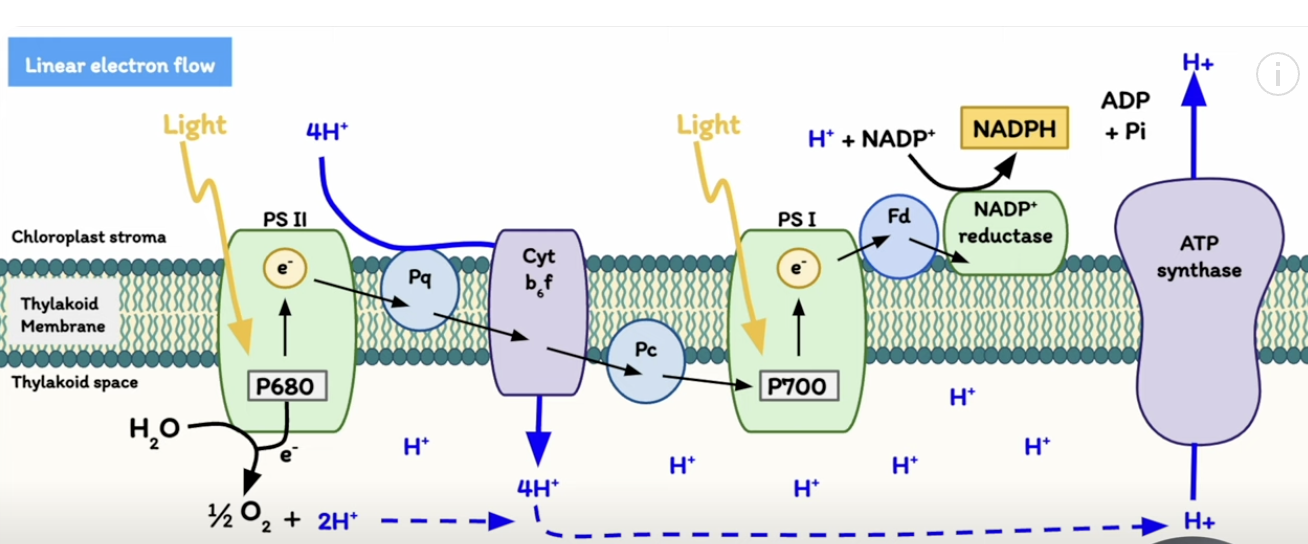
Protons (H+) produced from _____________ and the oxidation of _____ by the ________ complex is used for _________ by __________
splitting of H2O, oxidation of PQH2 by cytochrome b6f, ATP synthesis by ATP synthase
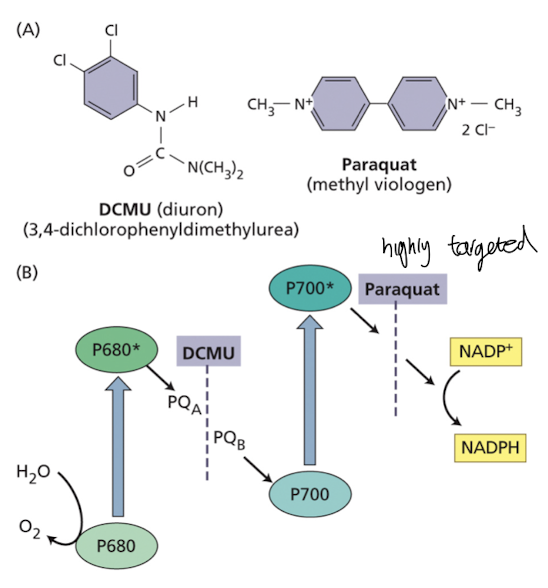
What herbicide blocks e- flow in light rxns of photosynthesis?
The herbicide DCMU inhibits electron transport by blocking the transfer of electrons from PSII to plastoquinone by competing for e-
Also competes for electrons from the early acceptors of PS I and then reacts with O2 to form superoxide → damaging to
chloroplast components
What is the Calvin-Benson Cycle?
It's the cycle that fixes CO2 into sugars using ATP and NADPH from the light reactions.
It occurs in three phases: carboxylation, reduction, and regeneration.
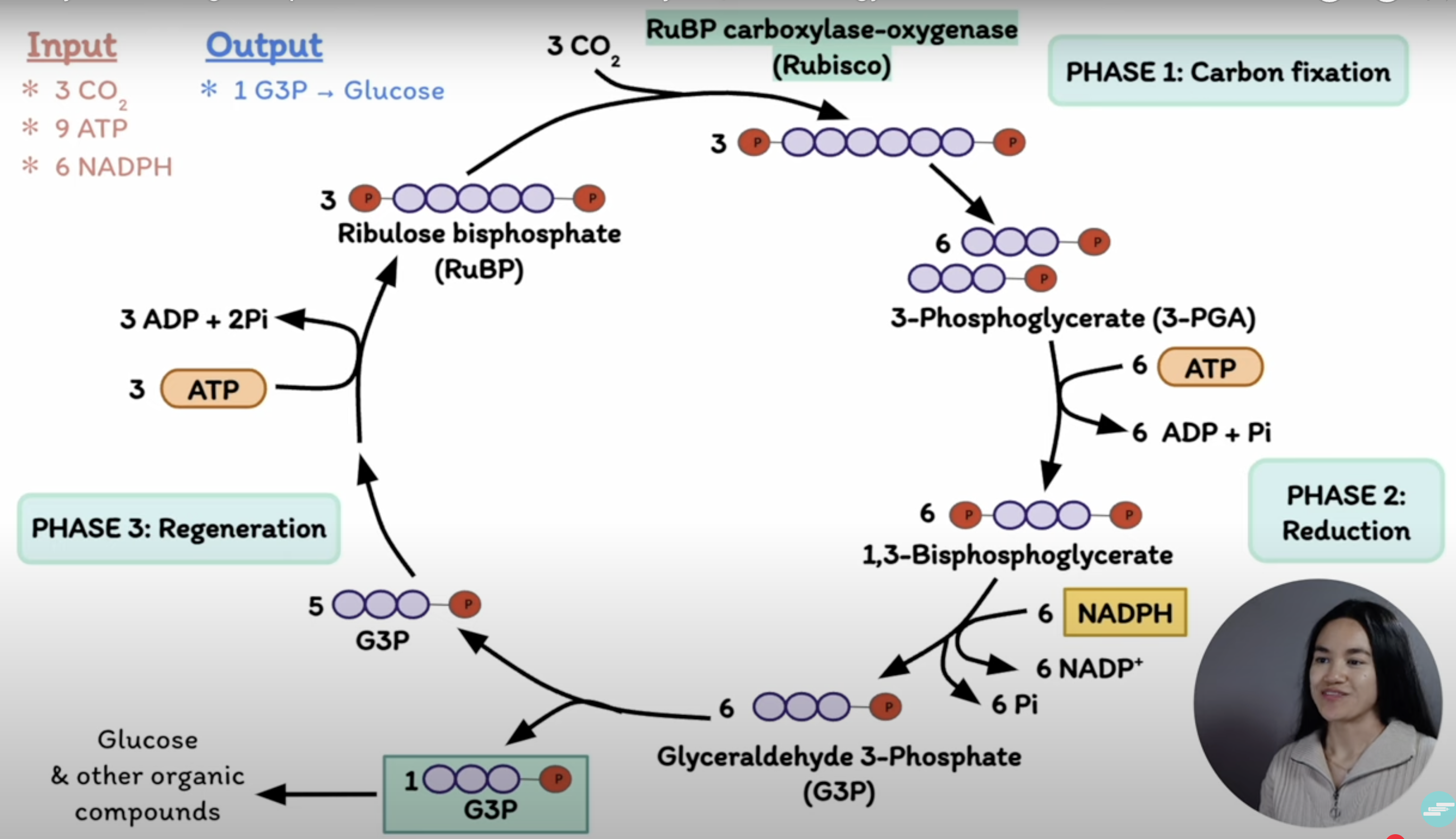
How does the Calvin-Benson cycle decrease the oxidation state of C?
It reduces CO2 (+4) to levels found in carbohydrates (i.e +2 in keto groups -(-CO=) to 0 in secondary alcohols (-CHOH-) using electrons from NADPH.
Hence also known as the reductive pentose phosphate cycle
what occurs in carboxylation?
CO2 is fixed to a 5-C acceptor molecule (ribulose bisphosphate RuBP)
Forming two molecules of 3-C intermediate (3 phosphoglycerate 3-PGA)
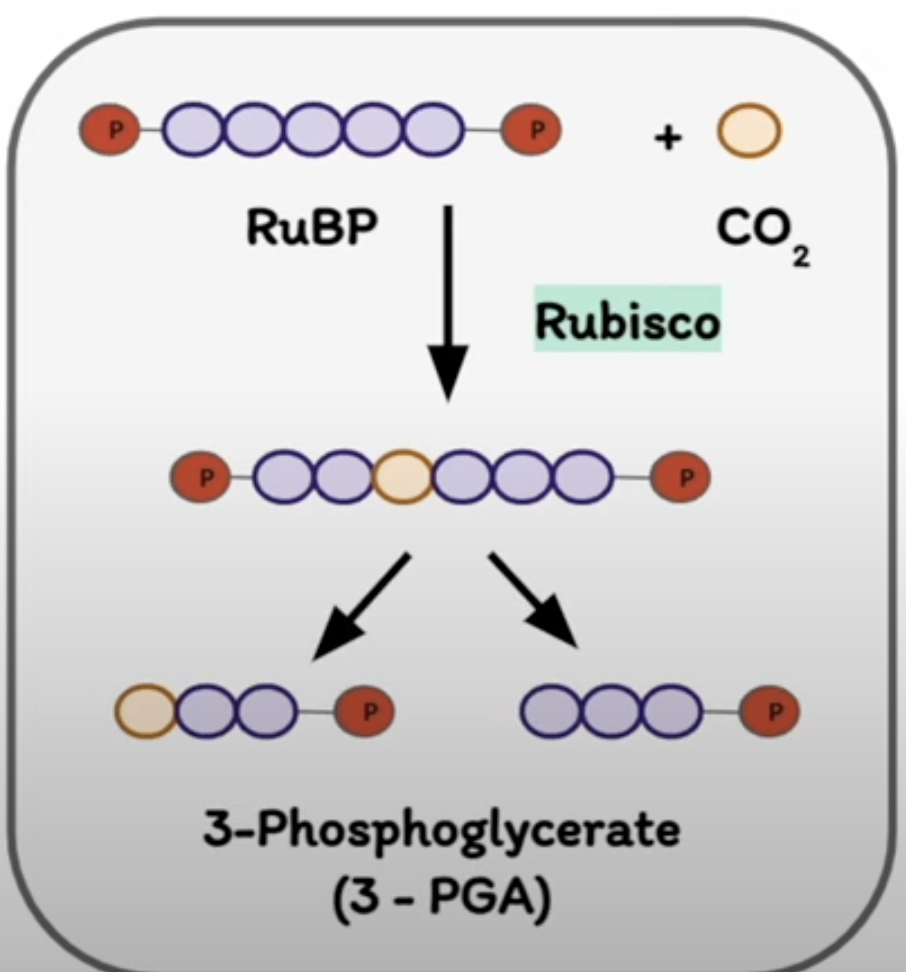
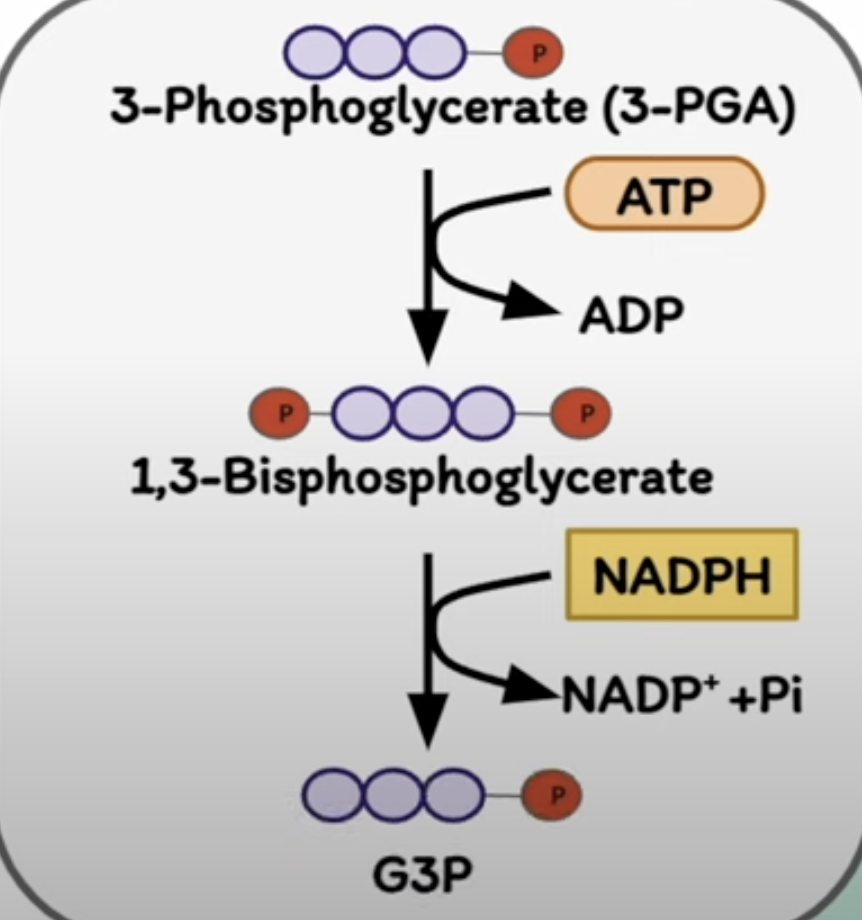
what occurs in reduction?
Reduction of 3PGA
Two successive enzymatic reactions phosphorylate and reduce 3PGA → triose phosphate (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate G3P) using ATP and NADPH generated from the light rxns
where does 3PGA go after the reduction step?
It can be converted into glucose i.e G3P + DHAP used to create starch or sucrose or used to regenerate RuBP in the Calvin cycle.
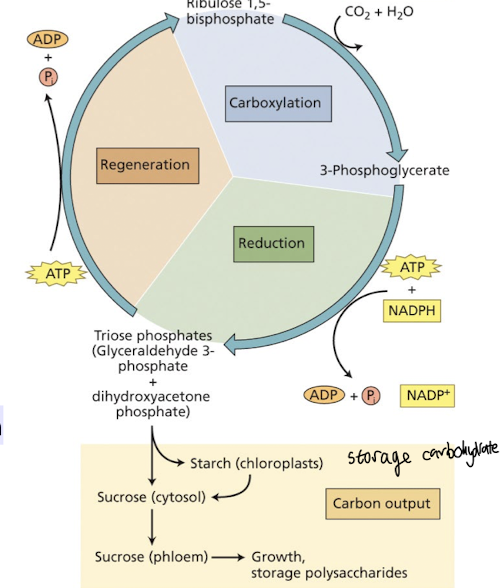
what occurs in regeneration?
Regeneration of the CO2 acceptor ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate RuBP – involves ten enzymatic reactions requiring ATP
What enzyme catalyses CO2 fixation?
Rubisco (ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase) catalyses the fixation of CO2 → RuBP.
Dual enzymatic activity involving carboxylase and oxygenase
Why is Rubisco significant yet problematic?
It's the most abundant enzyme on Earth (i.e makes up 30-50% of soluble protein in leaves) but slow and error-prone, often fixing O2 instead of CO2 when CO2 is limited,due to its flexibility leading to photorespiration
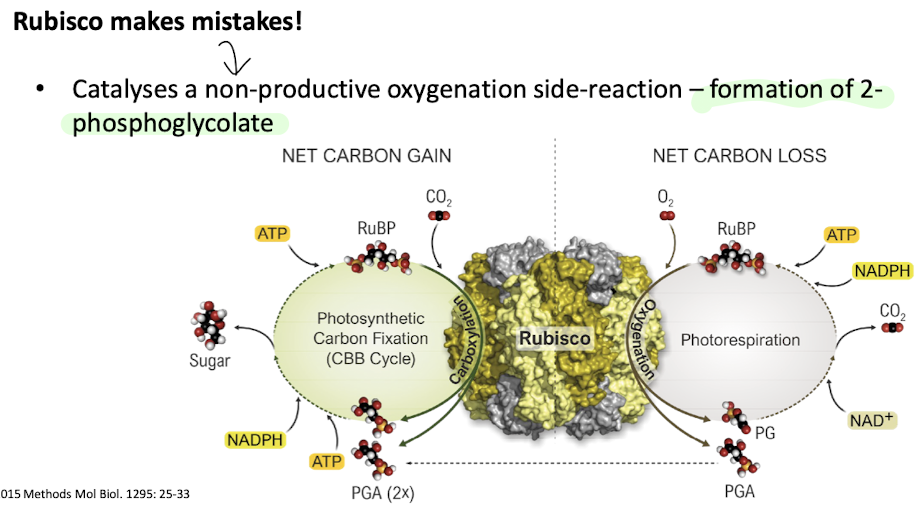
what is formed by the nonproductive oxygenation side rxn catalysed by Rubisco?
2-phosphoglycolate (2-PG), a toxic byproduct of photorespiration
what is photorespiration?
Metabolic process where O2 is consumed and CO2 is released in plants producing 2-phosphoglyolate, counteracting photosynthesis.
Energy inefficient as recycling it costs ATP
It occurs when Rubisco fixes oxygen instead of carbon dioxide, particularly under low CO2 or high light conditions.
Common in C3 plants when it is hot and stomata are closed as heat increases Rubisco’s O2 affinity
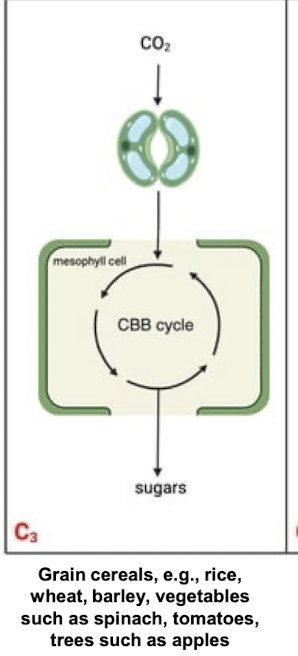
What is the C3 pathway?
It’s the most common pathway done by plants where the 1st product of CO2 fixation is a 3-C compound (3-phosphoglycerate). 3-PGA
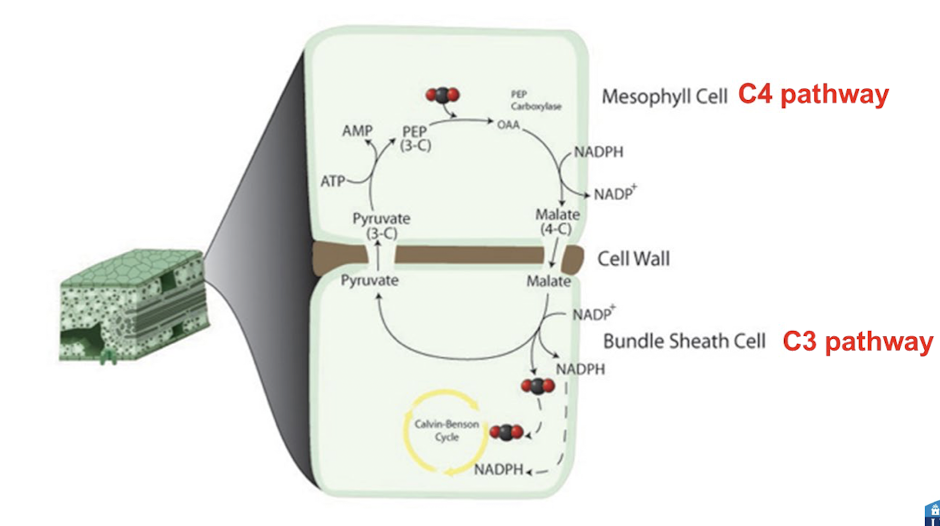
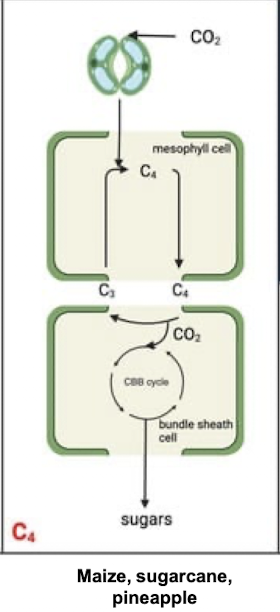
What is the C4 pathway?
Found in plants like maize, it uses PEP carboxylase to initially fix CO2 into a 4-carbon compound (malate) in mesophyll cells before passing it to Rubisco in bundle sheath cells.
PEP carboxylase has no oxygenase activity hence higher affinity for CO2
Spatial separation of C4 (mesophyll) and C3 (bundle sheath) pathway in C4 plants
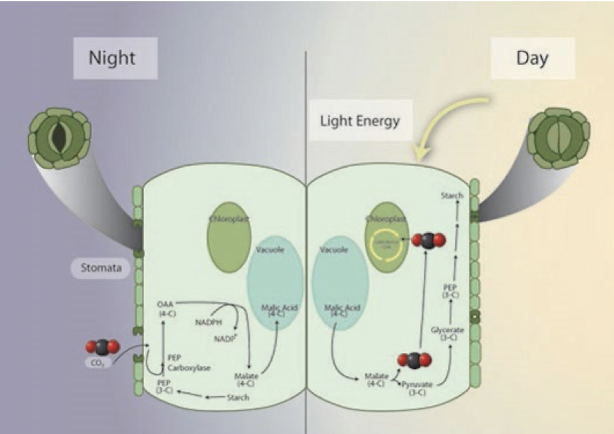
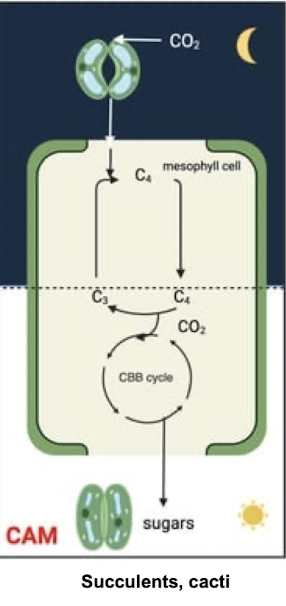
What is CAM photosynthesis?
(Crassulacean Acid Metabolism)
A water-conserving adaptation where plants like succulents fix CO2 at night, storing it as malic acid, and use it during the day for photosynthesis, uses temporal separation instead of spatial separation: