Key Concepts in Global Politics and Power Dynamics
1/176
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
177 Terms
Legitimacy
The belief that an institution, party or leader has right to exert control and power.
Sovereignty
The ability of the state to exert ultimate control over a defined territory within its borders.
Global Interconnectedness
Refers to the interactions and interdependencies that link countries, societies and individuals around the world.
Global actors
States, Regional Groupings, IGGs, Non-state actors (nations, TNCs, NGOs and illegal groups).
State
A political actor defined by a permanent population, defined territory, a government able to exert control within those boundaries and international recognition of sovereignty from other states.
Nation
A community of people who share a particular identity, through common bonds such as ethnicity, religion, language, culture or history.
Political Perspectives
The positions from which political actors see and understand their interests. Ideologies, ideas, events and values create these perspectives.
National Interests
The objectives and priorities that states need to safeguard, such as security, economic property, regional relationships and regional standing.
Unilateral
The state acts independent, and alone in its best interests.
Bilateral
Two states coordinating national policies in partnership.
Multilateral
Three or more states working together to reach a shared objective.
Multilateral…
Promotes an 'elastic' idea of sovereignty, where states will transcend national/regional boundaries to solve challenges.
International cooperation
Challenges such as global pandemic, climate change, and terrorism require international cooperation and coordination.
International Norms and Expectation
Sovereignty is dependent on the behaviour of the state, and states who significantly deviate from norms are subject to the interference of other states.
State & Representing its Citizens Abroad
States represent their citizens abroad through their memberships in IGGs, regional groupings, the ratification of international law and regional agreements, and participating in bilateral and multilateral initiatives.
Foreign Policy
The government decisions and strategies that concern global political actors beyond their own territories.
Domestic Policy
The government decisions and strategies in dealing with its own population and within its own territory.
Legitimacy & Coercive Power
In democracies, legitimacy derives from the consent of the governed, and all states are considered to have the right to have a monopoly on the use of violence within their own borders.
Social contract
It is assumed that for the people to accept the coercive nature of the state, the state must advance them in the pursuit of their interests, which revolve around security, freedom, welfare, order and justice.
State's Relationship with other Global Actors
All global actors, to a degree, have the ability to challenge the states' 'supremacy', and the state can exert their power to assert that they are supreme.
Institutions of Global Governance (IGGs)
IGGs seek to exist as a platform that can facilitate and encourage the cooperation and communication between states.
IGGs and States
Tensions can arise in IGGs if they are perceived to be encroaching on the autonomy of a state.
Individuals
Individual's relationship with the state varies, ranging from patriotism to anti-government mentalities and a rejection of the state's legitimacy itself.
Non-Government Organisations (NGO)
Independent organisations that cooperate with states and oversee government actions, influencing them through research, lobbying, and public involvement.
Interstate Relations
The interactions between states that can be characterized by cooperation or competition, including unilateral, bilateral, and multilateral relations.
Regional Groupings
A grouping of states organized under shared priorities and political interests, such as the EU, NATO, and ASEAN.
Cooperation
A process where member states pursue mutual benefits without the obligation to homogenize their domestic laws and international actions.
Integration
The binding of member states to common rules enforced by a supranational entity.
Tension
Rifts that develop between member states of a regional grouping when policies breach their autonomy.
Level 1: Free Trade
The removal of all trade barriers between member states, allowing each state to decide its own trade policy regarding non-members.
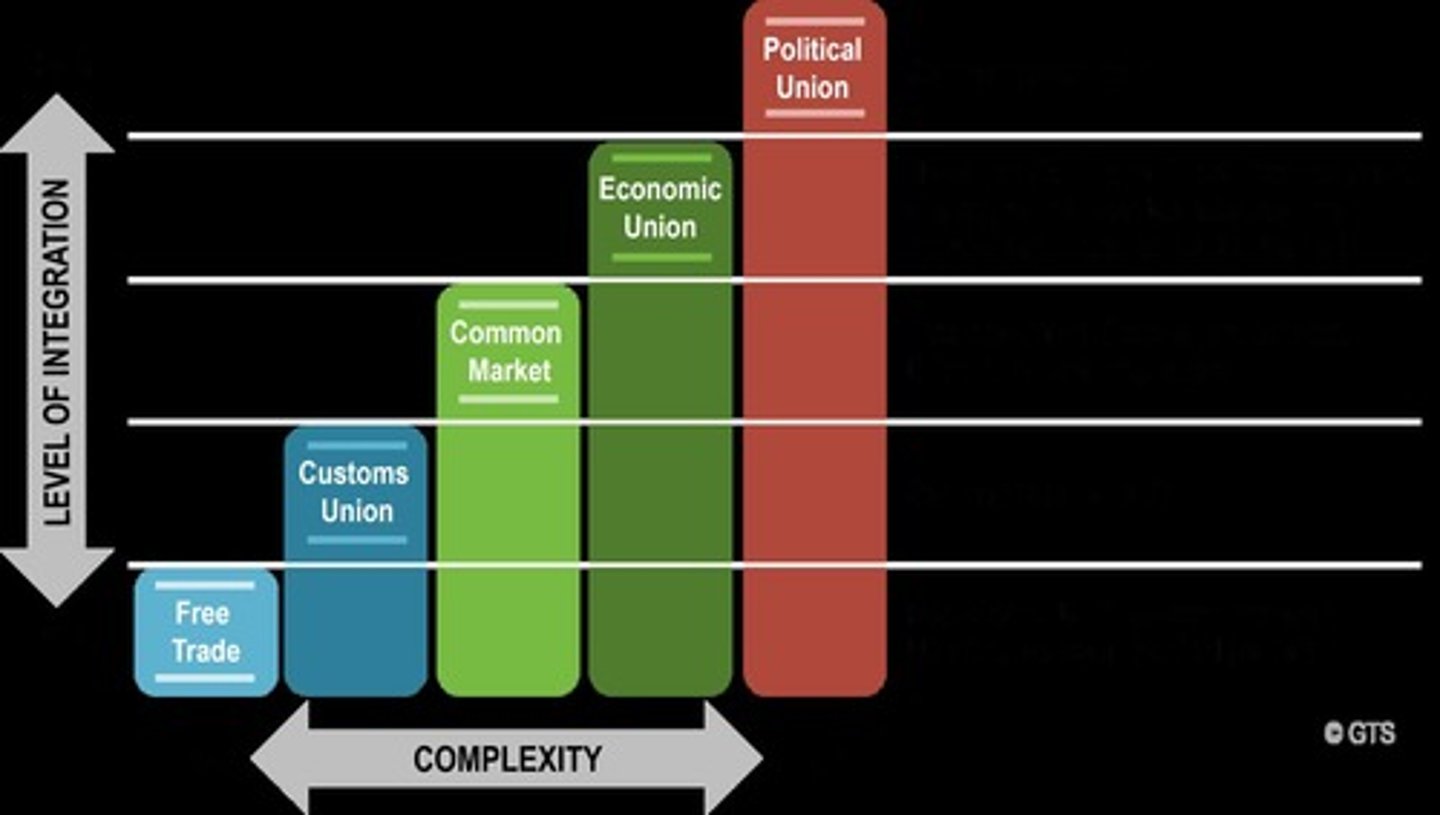
Level 2: Customs Union
A system where trade barriers between member countries are abolished, and a common external trade policy is determined.
Level 3: Common Market
An arrangement where there are no barriers to trade between member communities, and factors of production can move freely between members.
Level 4: Economic Union
A union where a common currency is adopted, tax rates are harmonized, and a common monetary and fiscal policy is implemented.
Level 5: Political Union
A union where a common government coordinates social and foreign policies of all member states.
Evaluating Economic Integration - Pros
Benefits include trade creation, employment opportunities, and consensus & cooperation.
Evaluating Economic Integration - Cons
Drawbacks include trade diversion, employment shifts and reductions, loss of national sovereignty, and rising crime rates associated with immigration.
European Union (EU)
An economic and political union of 28 member states that has developed a single internal market through standardized law.
Schengen Area
A zone where citizens can travel freely within member states due to the abolishment of passport controls.
Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)
A regional grouping aimed at promoting economic growth and political stability in Southeast Asia.
Hard Power
Power exercised through coercion or economic incentives.
Soft Power
Power exercised by influencing the preferences of others and appealing to shared cultural and political values.
Political Power
The power that states and governments wield with the law, aligning with government ideologies and enforcing societal values.
Separatism
A political/social movement that advocates for the independence of a region from a larger political entity, that seeks to establish its own government.
Establishment of a New State
A new state can be formed on the separation of territory from an existing state, but only with the consent of Parliament and upon international recognition.
Civil War
A war between organised groups who are within the same state, and seek to control the entirety of the country.
Military Power
Military power can be wielded by illegal groups, social movements, transnational corporations (private military companies), formal military (coups), and international governmental organizations (e.g., UN peacekeeping forces).
Illegal Groups & Military Power
Groups that do not accept the legitimacy of the state's power, and will endeavour to defy that power and seize it through violence and intimidation.
Terrorism
States seek to counter and destroy terrorist groups, as they pose a threat to their security and legitimacy.
Criminal Networks
Groups focused on controlling economic power through the sale of illegal products sold on the black market, challenging the state's monopoly on violence.
Economic Power
Economic power is directly associated with states and transnational corporations; however, it is also wielded by individuals and illegal groups.
Individuals (Economic Power)
$1.6 trillion is annually laundered.
Illegal Groups (Economic Power)
$1 trillion is spent on bribes each year.
Transnational Corporations & Economic Power
Powerful economic institutions that can influence states to achieve their preferred outcomes, and are thus agents of global change.
Pros of TNCs
States consider economic prosperity to be a key interest, and TNCs can offer employment and foreign investment, acting as attractive partners for states.
Cons of TNCs
TNCs can exert power on governments to relax laws concerning working regulations and tax exemptions to maximise their own profits.
State Capture
Corporations can lobby and influence the state's decision making to receive benefits that serve their private interests, which come at the detriment of the social community.
Diplomatic Power
Almost exclusively associated with the state, diplomatic power prioritizes and employs negotiation, bilateral/multilateral agreements, representing citizens abroad with regional agreements and IGGs, and diplomatic coercion.
IGGs & Diplomatic Power
By encouraging cooperation they enable states to diplomatically manage their relationships with one another.
Cultural Power
The exercise of power through the transfer and exchange of culture; the ability to influence a situation or achieve political aims by exhibiting behaviours or values that will appeal to others.
Example of Cultural Power
The Nordic Model in Denmark and Finland, has allowed them to exert power over Europe.
Technological Power
Technological innovation is a resource through which states can exert power by obtaining information and thus acquiring an 'edge' over others, which is primarily employed by states and TNCs.
NGOs & Technological Power
In 2016, Amnesty International used satellite imagery to virtually enter Sudan to investigate their report ('Scorched Earth, Poisoned Air: Sudanese Government Forces Ravage Jebel Marra, Darfur').
Nationalism
Argues that the nation is the most important political identity, and thus, one should support the state's interests, particularly to the detriment of other states.
Pros of Nationalism
Strengthens a country's values and national identity (unification), cultivates a commitment to state ideals and principles, supports and protects national companies and businesses.
Cons of Nationalism
Excludes minorities, does not value multiculturalism, promotes anti-immigration policies, and fosters 'us before them' attitudes leading to racism.
Ideology
A series of interconnected ideas that are organised into a worldview of specific philosophical perspectives, together, they form an entity of principles, beliefs and core values.
Example of Ideology
Greenpeace is determined by environmentalism and pacifism.
Humanitarian Concerns
Human life is valued as the most important principle, and as such political actors should assist each other to improve the conditions of humanity for moral and unselfish reasons.
Examples of Humanitarian Organizations
Red Cross, Doctors Without Borders, Human Rights Watch.
Global Influence
The ability of political actors to operate beyond a state's border by extending their influence to regional and global counterparts.
Pros of Global Influence
Sharing knowledge and information (e.g., COVID vaccine), forums to discuss global concerns (e.g., Paris Summit), managing global crises.
Cons of Global Influence
Controlling/manipulating prices of products worldwide, the actions of a significant global actor will affect others, lobbying with foreign local authorities for specific benefits, corruption and bribery.
COVID-19 Pandemic Response
The response to the COVID-19 pandemic by global actors can be analysed through the political perspective of global influence.
Globalisation
A system that embraces a global scale of diffused actors, thus, decision consider the exchange of goods, services, transportations and people into a variety of socioeconomic, technology and environmental scenarios.
States
National interests: security, economic prosperity, regional relationships and regional standing.
IGGs
Promote cooperation and multilateralism by facilitating interstate relationship and establishing international norms and laws.
NGOs
Raising awareness and advocating for particular causes (eg. human rights, environment).
TNCs
Maximising profits to create value for stakeholders.
Cosmopolitanism
All human beings are members of a single moral community that transcends national boundaries, and thus they prioritise cooperation to reach common goals and confront challenges faced by the global community.
Global Citizens
People are considered 'global citizens' and are expected to act responsibly, ethically and sustainably to one another.
Cosmopolitan Theories
Framework for peacekeepers in post war societies; human rights are a universal principle, that belong equally to all; people must be protected from prejudice and discrimination.
Liberalism
The idea that international institutions, open market, liberal democracies and market can, and should cooperate for global security.
Realism
The idea that global actors will prioritise their own interests over the needs of others, seeking to maximise their own power to safeguard their survival.
Anarchic State
A concept in realism where it is every man for himself, with no supreme authority in the global arena.
Power in Realism
Realists are concerned with power, equating power to security as the only thing that matters.
Impact of Globalisation on States
Globalisation has been associated with the decline of the states power, and their ability to dominate other actors.
Economic Interconnectedness
Increased economic interconnectedness has caused the chance of war to decline.
Self-Reliance
Countries who are not economically connected will either become increasingly self-reliant or form relationships with other isolated states.
IGGs & Globalisation
Coordinate and monitor the organisation of globalisation and develop coordinated actions and responses to global crisis (eg. global pandemic).
NGOs & Globalisation
Create channels, with citizens, to guide and input the decisions/actions of states and can scrutinise the actions of states.
TNCs & Globalisation
Aspire to integrate global politics into the global economy to reap economic benefits, leading to a dramatic increase in their power.
Globalisation Issues
Includes mass migration crisis, such as the US and Mexico border, and the decline of employment in Mexico.
Economic Ties
25% of EU's oil imports are from Russia, and thus criticism of Russia jeopardises their income resources.
Globalisation Benefits
Globalisation is beneficial in moderation, but can concentrate the world's wealth.
Syrian Refugee Crisis
The political significance of key global political actors in at least one global issue, including the sources and forms of their power, their perspective and legitimising narratives about contributions to political stability and change, their competing interests and the consequences of the actions taken.
Power
The ability to influence outcomes within a system
Power is never static
Power flows
Power is a compound
Tangible Power
(eg. fighter plane, weightlifter, army)
Intangible Power
(dominant figures, advertising, celebrities)