4a coastal changes and conflict
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
wave definition
the wind blowing over the ocean (friction with the surface water creates ripples which become waves)
what does the size of the wave depend on
the strength of the wind blowing over the sea
how long the wind blows for (time)
the length of water the wind blows over of fetch (distance)
fetch definition
the distance a wave has travelled towards coastline over open water
the stronger the wind and the longer the fetch, the bigger and more powerful the waves
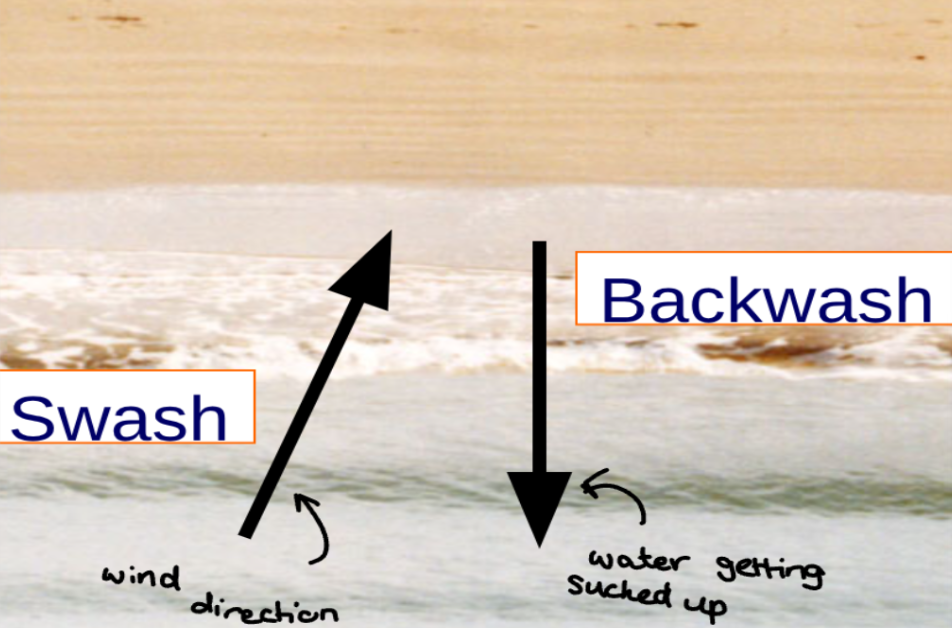
swash and backwash definition
swash = the rush of seawater up the beach after the breaking of a wave
backwash = backward flow of water after the breaking of a wave
what are and what are the characteristic of contructive waves
small waves, low wave height, long wavelength
occurs in calm conditions, without much wind
strong swash, weak backwash
strong swash brings sediment to build up the beacj
backwash not strong enough to remove sediment
low waves and further apart

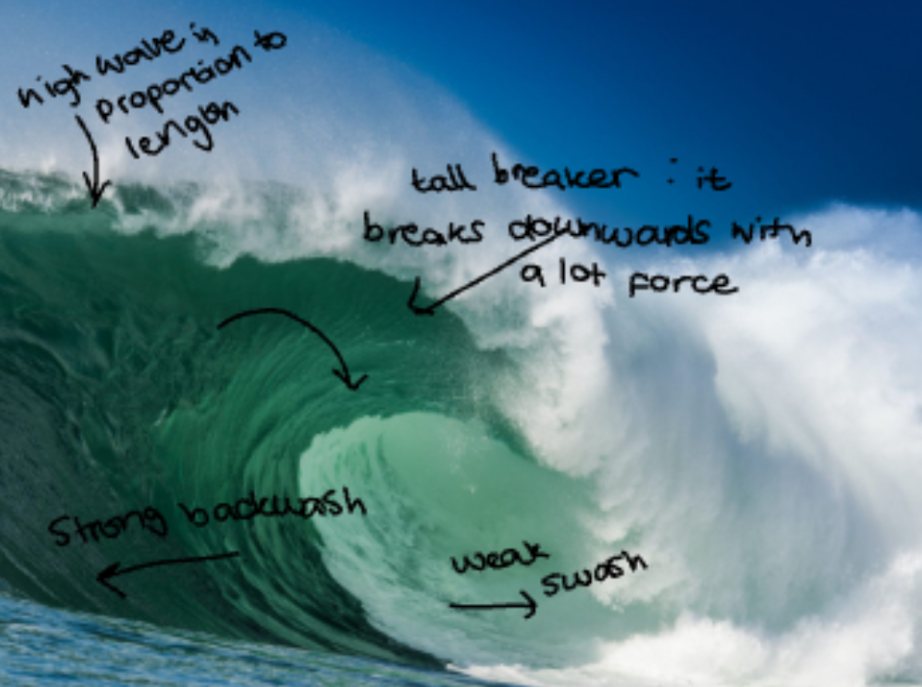
what are and what are the characteristic of destructive waves
weaker swash and strong backwash
occurs in stromy conditions with strong winds
strong backwash remove sediment from beach
waves steep and close together
tall waveswith short wavelength
arrive quickly and have high frequency - a ot come in short period of time
what are concordant coasts
bands of resistant and less resistant rock that run at parrallel to the coastline. the rock is the same type
the hard rocks acts as a barrier but can be breached on lines of weaknesses such as faults and joints creating a cove, a circular area of water with a narrow entrance from the sea
what are discordant coasts
bands of resistant or less resistant rocks that run at right angles to the coastline. headlands are formed on discordant coast because the harder rock resists erosion for a longer time standing out as headlands. the softer rock erodes quicker forming bays
4 main types of erosion which can be affected by: (and explained)
seasons = low pressure in winter and strong winds leads to more erosion from high energy destructive waves
storm frequency = areas susceptable to stron storms are likely to suffer with more erosion
prevailing winds = mainly from the south - west bringing warm moist air and frquent rainfall, this leads to more wetahering and erosion
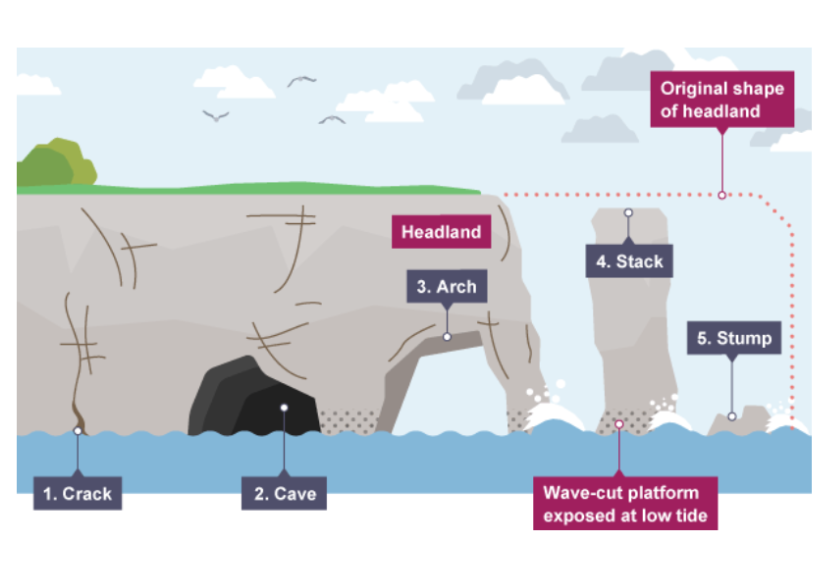
how an arch and stack are formed
large crack opened up by hyrdaulic action
the crack grows into a cave by hydraulic action and abrasion
the cave becomes larger
cave breaks through the headland forming natural arch
the arch is eroded and collapses
this leaves a tall rock stack
the stack is eroded forming a stump
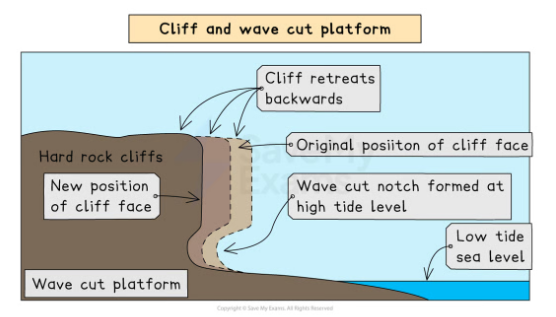
cliff and wave cut platform
key areas of erosion
climate change effect
process
key areas of erosion : wave cut notch, base of cliff (occurs by undercutting)
climate change can make the process faster and the wave cut notch will be clearer and higher
the rock will overhang the notch. the overhang will collapse and the cliff will retreat. this will create a wave cut notch platform which is visible during low tide and submerged during high tide
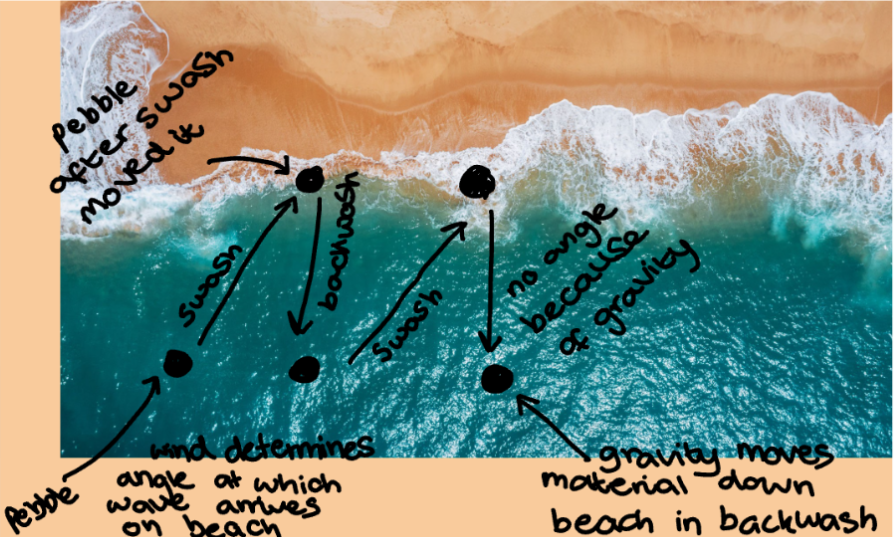
what is longshore drift
the movement of material along a beach transported by wave direction
the pebble moves with the swash in the prevailing wind direction and comes back with the backwash by gravity
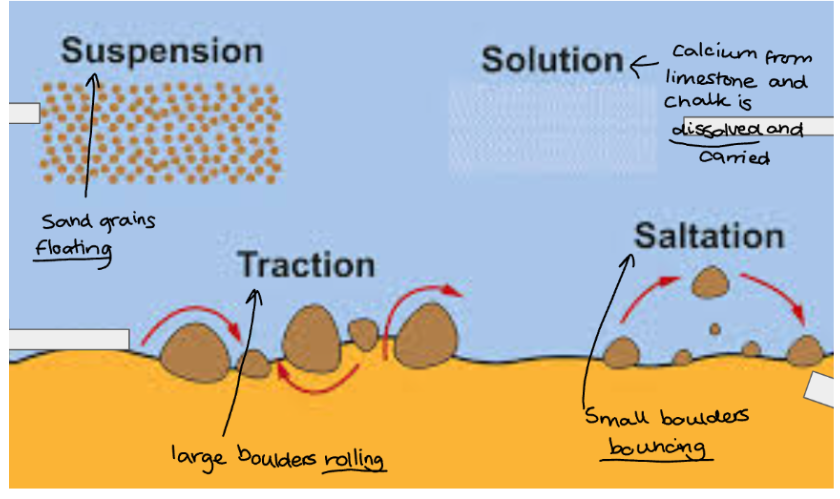
types of transportation in coasts
suspension = sand grains floating
traction = large boulders rolling
saltation = small boulders bouncing
solution = calcium from limestone and chalk is dissolved and carried
the formation of a beach
destructive waves erode cliffs and beaches. eroded material is transported by longshore drift. constructive waves deposit eroded material along the coastline. the largest waves deposit boulders and shingle at the top of the beach. the smallest material is deposited nearest the sea.
deposition definition
the laying down of sediment carried by wind, flowing water, the sea or ice
how are straight / curved beaches formed
beaches can be straight or curved. curved beaches formed by waves refracting or bending as they enter a bay. they can be sandy or pebbly (shingle). shingle beaches are found where cliffs are being eroded. ridges in a beach parallel to the sea are called berns and the one highest up the beach shows where the highest tide reaches
how spits are formed
narrow projections of sand or shingle that are attached to the land at one end. they extend across a bay or where the coastline changes direction. they are formed by longshore drift powered by strong prevailing wind. the area behind the spit is sheltered where slt and mud is depositev creating a saltmarsh

how is a bar formed
form in the same way as spits, with longshore drift depositing material away from the coast until a long ridge is built up. however, bars grow right across the bay cutting off the water to form a lagoon. a bar is attached at both ends and a spit is at one

what are sub-aerial processes
land based processes that weaken cliffs and occur above the high tide line. they include weathering and mass movement
weathering definition
the wearing down or breaking of rocks while they are in place. weathering can be biologicak, chemical or physical
different types of weathering definitions
physical / mechanicak (freeze thaw) = when temperature gets higher the snow melts and water gets in cracks of rock. when the temperature gets below 0.c the water in the crack freezes and expands about 9% making the crack larger. as the proccess is repeated the crack gets larger and pieces of the rock break
chemical (acid rain) = slightly acidic rainfall reacts with weak minerals causing them to dissolve and decay
biologic = the roots of plants grow in cracks and split the rocks apart same as burrowing animals
mass movement definition
the downhill movement of rock and soil under the force of gravity
different mass movement processes
rock falls = pieces of rock fall from cliff, happens when the base of cliff has been undercut
slumping = happens after long periods of rainfall, rock slides down a steep slopem
sliding = movement of material along flat surface, large amounts of soil and rock moving downslope rapidly
what are the 4 types of erosion
abrasion = load is dragged by water wearing away the cliffs and sea bed (causing more erosion)
attrition = load collides with loads and breaks up/wears down
solution = weak acid dissolves rock like limestone
hydraulic action = sheer force of water trapping air in crack fracturing the rock in cliffs and sea beds
positives and negatives of development, agriculture, industry, coastal management and tourisms on coasts
development positiive = more interest in protecting coastal landscapes
negative = weight of buildings on cliffs increases vulnerability. increased saturation due to changes in drainage
agriculture positive = wildlife habitats may be created
negatives = increased soil erosion
industry positive = brings jobs to an area
negative = increases soil, air and water pollution. destroys natural habitats
coastal management positive = helps reduce risk of coastal flooding. can protect sand dunes, bars and spits
negative = can increase erosion further along the coast
tourism = more money for an area. education about coastal landscapes
negative = increased development, increased pollution
holderness case study basic info
erosion happening
town names
popultion
location
holderness coast is the fastest eroding coastline in europe
erodes at rate of 2m/year
4 main towns - mappleton, hornsea, skipsea, withernsea
population of around 25,000 people
north east cost of england in east yorkshire
what are the physical causes of erosion
rock type = cliffs made from less-resistant boulder clay (made from sand & clay)
powerful waves = waves at holderness travel long distances over the north sea so have long fetch - means that they will increase in energy
longshore drift (transportation process) = moves material away from cliffs leaving cliffs unprotected
coastal management
Sea walls: Structures built along the coast to absorb wave energy and protect against erosion.
Groynes: Structures built at a right angle to the coast to trap sediment and reduce longshore drift.