Chapter 27 - Amines, Amino Acids + Polymers
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
amines
-derived from ammonia
-primary, secondary + tertiary = refer to number of alkyl groups attached to nitrogen
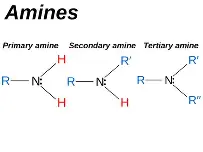
naming amines
-primary = when NH2 group is on end, suffix = -amine
-primary = when NH2 group is in middle, prefix = number + amino
-secondary + tertiary = same length side chains attached to nitrogen, ‘di’ or ‘tri’ alkylamine
-secondary + tertiary = different length side chains attached to nitrogen, prefix = shorter chain with N for position, longest chain = stem + amine e.g. N-methylbutylamine
properties of amines
-act as bases = lone pair of N can accept a H+ from a dilute acid to form a salt = neutralisation
-phenyl amine is a weaker base as the electrons in lone pair are partially delocalised into ring so not fully available to accept H+
if 3 groups bonded to N = neutral
if 4 things bonded to N = 1+ charge
preparation of PRIMARY amines (write equation of CH3Cl)
reagents = haloalkane + ammonia
conditions = ethanol + excess ammonia - needs to be in excess so the salt is more likely to form from the excess ammonia instead
CH3Cl + 2NH3 → CH3NH2 + NH4Cl
preparation of SECONDARY amines (write equation of CH3CH2Cl + 2CH3CH2NH2)
reagents = haloalkane + primary amine
conditions = excess primary amine + ethanol OR can then also use NaOH after
CH3CH2Cl + 2CH3CH2NH2 → (CH3CH2)2NH + CH3CH2NH3+Cl-
preparation of AROMATIC amines
reagents = nitrobenzene
conditions = Sn (tin) + conc HCl
-reduction reaction [H], heated under reflux, product collected using NaOH
NO2 is a 3,5 directing group while NH2 is 2,4 directing group
amides
-derived from acyl chlorides reacted with ammonia if primary or amine if secondary
-difference with amine - has C=O
-primary, secondary + tertiary = refer to the 1 alkyl group attached to carbon ADD number of alkyl groups attached to nitrogen
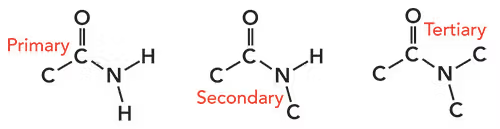
properties of amides
can react as they:
-have lone pair on ammonia/amine
-can behave as nucleophile
-have polar bond on acyl chloride
preparations of amides (write equation for CH3COCl)
reagents = acyl chloride + excess ammonia/amine
conditions = excess ammonia/amine
CH3COCl + 2NH3 → CH3CONH2 + NH4Cl
properties of amino acids (DRAW)
-can behave as acids due to -COOH group and as bases due to -NH2 group
-soluble in water as they can form hydrogen bonds with both groups
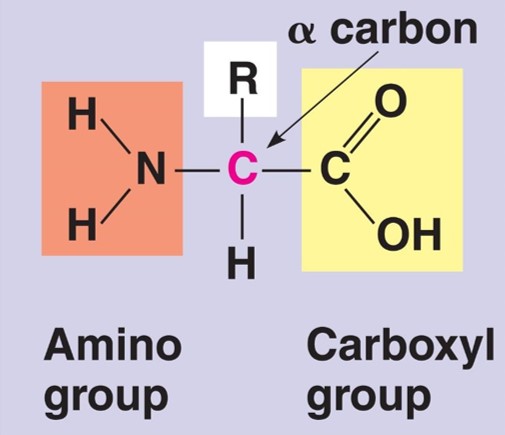
reactions of amino acids
with HCl = NH2 group reacts to make ammonium salt + halide ion
with NaOH = COOH group reacts to make carboxylate salt + water
with alcohol = COOH group reacts to make ester + water
(if there is a COOH or NH2 group on R group it can also react)
optical isomerism of amino acids (DRAW)
.
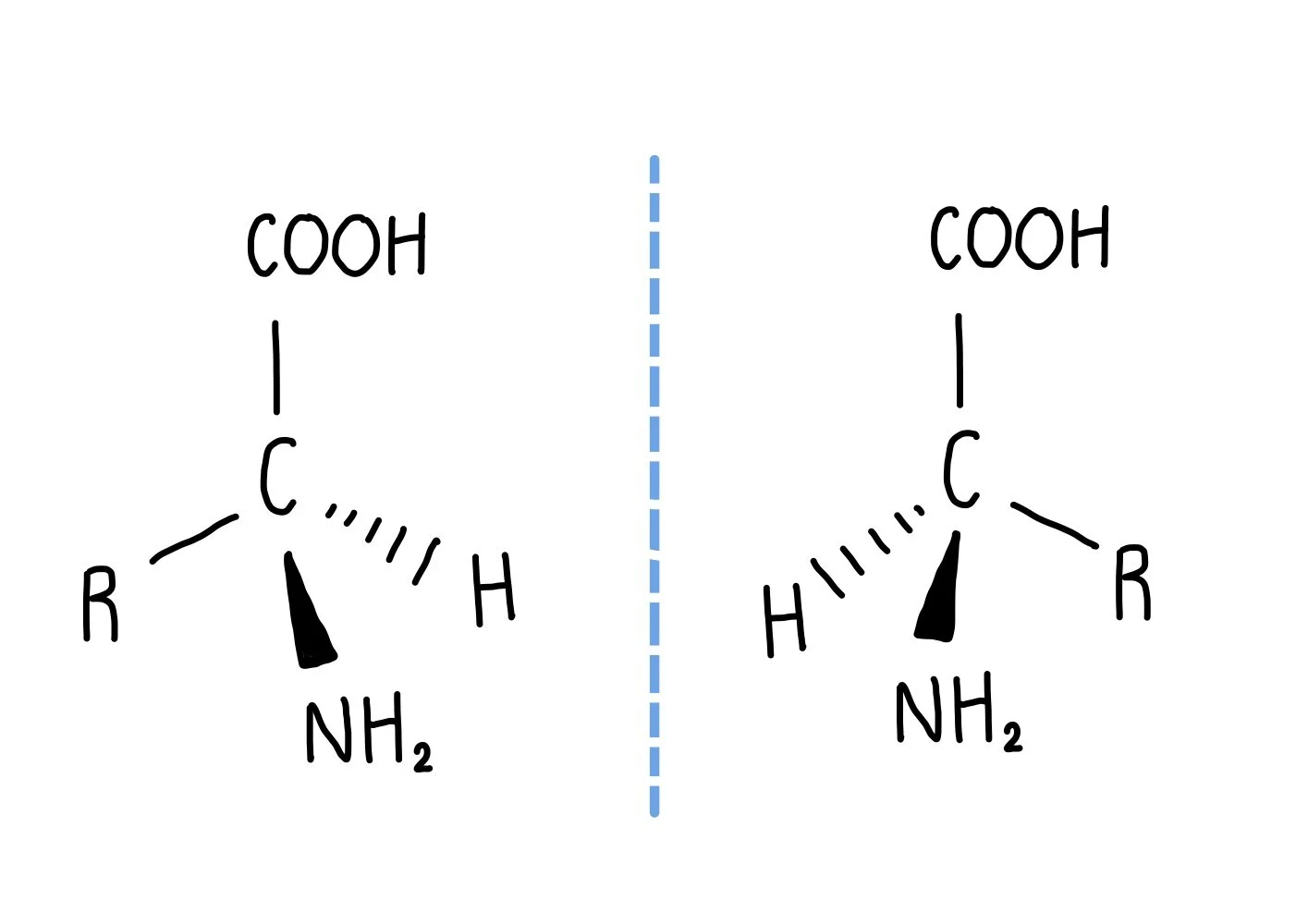
chiral carbons
-carbon has 4 different groups bonded to it
-pair of isomers for every chiral carbon
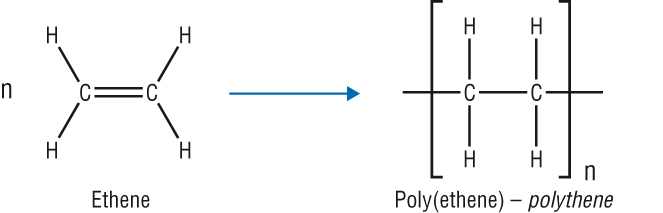
addition polymerisation (DRAW ethene → polyethene)
monomers containing alkene functional group are added together by breaking of double bond
condensation polymerisation - FUNCTIONAL GROUPS involved
-COOH or -COCl groups - the OH or Cl atoms are lost
AND
-OH or -NH2 groups - the H atom is lost
condensation polymerisation -PRODUCTS FORMED
-2 possible by products = H2O if COOH or HCl if COCl
-2 types of polymers = polyesters if OH or polyamides if NH2
-when writing balanced equations need to write (2n-1) H2O or HCl
hydrolysis of polymers
-breaking apart with water
-bond always breaks after C of C=O
in alkali: Na, O, H atoms added on, products = carboxylate salt + alcohol or amine
in acid: H, H, O atoms added on, products = carboxylic acid + alcohol or amine - but acid reacts with amine to form NH3+