Cerebellum
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
4th ventricle is ___ to cerebellum
ventral
peduncles are ___ to cerebellum
ventral
cerebellum sits ___ tentorium cerebelli with ___ ____
beneath, posterior fossa
4th ventricle is between which 2 structures?
pons and cerebellum
cerebellum sits on which structure that can press on spinal cord?
foramen magnum-cerebral tonsil
3 lobes of cerebellum
anterior, posterior, flocculonodular
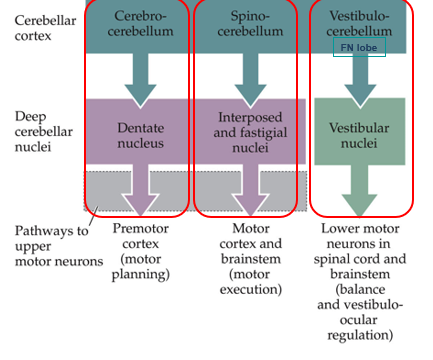
3 functional area of cerebellum
spinocerebellum, cerebrocerebellum, vestibulocerebellum
spinocerebellum includes
anterior lobe, vermis, paravermis
cerebrocerebellum includes
most of posterior lobe
vestibulocerebellum includes
flocculus and nodule
3 cerebellar peduncles
superior, middle, inferior cerebellar peduncle
3 nucleus of deep cerebellar nuclei
fastigial, interposed, and dentate nucleus
where does input arrive in cerebellum?
cerebellar cortex
where does information project to in the cerebellum?
deep nuclei
what does the deep nuclei do in the cerebellum?
provide cerebellar output
transverse organization of cerebellum
anterior, posterior, flocculonodular lobe
longitudinal organization of cerebellum
vermis, paramedian, lateral
function of vermis
body posture
function of paravermis
regulates gross movements of ipsilateral extremities (walking)
lateral zone
regulates skilled movements of ipsilateral extremity (tying your shoe)
what divides the posterior and anterior lobe of cerebellum?
primary fissure
function of flocculonodular lobe
eye movement and body posture
function of anterior lobe
regulates movements of legs
function of posterior lobe
regulars movements of arms
the 3 nuclei of deep cerebellar receive what kind of signal?
both inhibitory and excitatory signals from other parts of brain
function of dentate nucleus
largest, communicates through cerebellar peduncle
coordinate fine limb movements
emboliform/globose (intermediate nucleus
regulate ipsilateral extremity (grosser movement)
fastigial nucleus function
regulates body posture via flocculonodular lobe
inputs to cerebellum ( 2 pathways)
pons → middle cerebellar peduncle → cerebellar cortex
inferior olive or spinal cord or vestibular nuclei → inferior cerebellar peduncle → cerebellar cortex
what is the main input of cerebellum?
middle cerebellar peduncle
output from cerebellum to cerebral cortex (pathway)
cerebellar cortex → deep cerebellar nuclei → superior cerebellar peduncle → VL complex (thalamus) → primary motor and premotor cortex
output target of cerebellum
3 layers cerebellar cortex
molecular layer, purkinje layer, granular layer
inputs to cerebellar cortex
climbing and mossy fibers
climbing fibers originate in
inferior olive (medulla)
mossy fibers originate in
all other cerebellar afferents tracts
what does climbing fibers do?
excite purkinje cells
what do mossy fibers do?
excite granule cells
what do granule cells do?
excite purkinje cells
what do basket interneurons do?
inhibit purkinje cells
what do purkinje cells do?
tonicly inhibit cerebellar nuclei
purkinje cells and neurodegeneration
extremely susceptible to it
primary function of cerebellum
control posture
correct rapid movements, initiated by cerebral cortex
motor learning
process of motor control
cerebellum receive intention to move from motor cortex
proprioception and visual signals inform cerebellum of body position
cerebellar cortex calculates best way for a movement
blueprint of coordinated movement is sent to cerebral motor cortex
error are noted and sent to cerebellum for correction
nystagmus
jerky eye movements
ataxia
lack of coordination
dysarthria
speech difficulties
intention tremor
tremor upon movements
titubation
body wavering
dysdiadochokinesia
clumsy alternating movements
dysmetria
undershooting/overshooting
what does flocculonodular regulates
balance and eye movements
flocculonodular lobe receive vestibular inputs from
semicircular canals and vestibular nuclei
flocculonodular lobe receive visual inputs from
superior colliculi and visual cortex
lesion in FNL
disturb eye tracking, balance, and gait
paravermal region coordinates
limb movements
paravermal receive proprioceptive input from
spinal cord, trigeminal nerve, visual and auditory system
paravermal region send fibers to ____
deep cerebellar nuclei, which project to cerebral cortex to modulate descending motor system
paravermal region contains
sensory maps (tracks position of body parts i nspace
paravermal region use proprioceptive input to
predict future position of a body part during movement
function of lateral cerebellum
plan movement
lateral cerebellum receive input from
cerebral cortex via pontine nuclei
lateral cerebellum sends fibers to
thalamus (connected to premotor and primary motor cortex) and red nucleus
how does lateral cerebellum send fibers to red nucleus?
via inferior olivary nucleus, which links back to cerebellar hemisphere)
posterior lobe syndrome
intention tremor
dysmetria
dysdiadochokinesia
scanning speech (slow separation of syllables)
anterior lobe syndrome
ataxia (lower limbs)
alcoholic degeneration of purkinje cells
flocculonodular syndrome
truncal ataxia (titubation)
midline tumors in infants
dysmetria
irregular, wavering course of overshooting, overcorrecting, then overshooting again toward intended goal
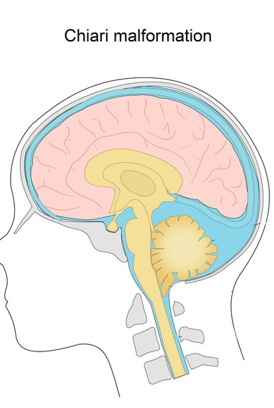
what is this?
chiari malformation
characteristics of Dandy-Walker Malformation
enlargement of 4th ventricle
complete absence of cerebellar vermis
cause variety of levels of disability
can cause increase intracranial pressure
purkinje cell is an output of
cerebellar cortex