Exam 1 applied physics
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:57 AM on 2/10/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
1
New cards
1)"Physics" could best be described as the study of
B) the general principles underlying natural phenomena.
2
New cards
2)A primary reason for you to learn science, according to the textbook's opening section, is
C)to increase your awareness.
3
New cards
3)Our primary reason for studying the theories of Ptolemy, Copernicus, and Kepler in this course is
C)to learn about the methods and the validity of science.
4
New cards
4)If you observe the night sky in the direction of the North Star, you will observe that
D)the other stars near the north star move along counterclockwise circles around the north starduring the night.
5
New cards
5)In Ptolemy's theory,
E)the planets move in circles-within-circles \["loop-the-loops"\] around Earth.
6
New cards
6)The ancient Greeks, including Ptolemy, thought that the stars were
A)fixed to the inside surface of a large sphere that enclosed the universe.
7
New cards
7)The very earliest Greek cosmological theory, several centuries before Ptolemy, stated that
C)the planets go in simple circles around Earth.
8
New cards
8)The Greeks abandoned their earliest cosmological theory (planets moving in simple circles aroundEarth) because
A)it did not agree with their observations of the planets.
9
New cards
9)The greatest astronomer of antiquity \[that is, of the time before the Middle Ages\] was
B)Ptolemy.
10
New cards
10)The ancient Greeks noted that the planets
C)wandered around among the stars.
11
New cards
11)One ancient Greek scientist, Aristarchus, had a theory about the layout of the universe that wasquite different from the other Greek theories. According to Aristarchus's theory,
C)the sun is at the center and other objects, including Earth, move around the sun in simplecircles.
12
New cards
12)How did ancient Greeks such as Aristotle know that Earth is round?
C)By noting that ships drop below the horizon as they go out to sea.
13
New cards
13)Venus is usually either the "evening star" or the "morning star" because
D)its orbit around the sun is inside Earth's orbit.
14
New cards
14)Copernicus proposed his theory because
B)he thought that Ptolemy's theory was too messy and that his was more "fitting."
15
New cards
15)The most significant difference between the astronomical theories of Ptolemy and Copernicus is
C)Ptolemy's theory is sun-centered, whereas Copernicus's is Earth-centered.
16
New cards
16)In Ptolemy's theory, retrograde planetary motion is explained as
B)the backward part of the planet's loop-the-loop orbits around Earth.
17
New cards
17)Who originated the idea that planets go inellipses around the sun?
D)Kepler
18
New cards
18)A scientific theory \[or scientific principle\] could best be described as
A)an idea that explains a large collection of observations of the natural world.
19
New cards
19)Is it possible to prove, for certain, that a scientific theory is true?
E)No, because it is always possible that a future experiment will disagree with the theory.
20
New cards
20)How is the sun situated in the universe?
E)The sun is just one of a large number of stars, and is located on the fringes of the Milky Waygalaxy, which itself is just one galaxy among many galaxies.
21
New cards
21)A defining feature of "pseudoscience" is
A)it does not use proper scientific methodology.
22
New cards
22)The "father" of atomic materialism was
A)Democritus.
23
New cards
23)Roughly how many different elements are there?
A)100
24
New cards
24)The number of atoms in the glucose molecule, C6H12O6, is
B)24.
25
New cards
25)How many atoms are in the alcohol molecule C2H5OH?
A)9
26
New cards
26)The number of atoms in the sulfuric acid molecule, H2SO4, is
C)7.
27
New cards
27)Chemically, helium is
D)an element.
28
New cards
28)The distance to the sun is about 150 million km. Expressed in powers of ten, this is
A)1.5× 108 km.
29
New cards
29)Which is smallest?
B)the sun
30
New cards
30)According to the philosophy of Democritus,
A)the color red is not "real" but is instead just humans' "conjecture" or imagination.
31
New cards
31)Democritus said that, although we imagine many things, "in reality, there are only atoms and thevoid." This idea could best be classified as
D)materialism.
32
New cards
32)According toAristotle, which of these is a "natural" or "unforced" motion?
C)Both of the above.
33
New cards
33)A book is given a brief shove along a table top and released so that it slides a short distance andcomes to rest.Galileo would say that the book stopped because
B)of friction.
34
New cards
34)A stone is lifted and released so that it falls to the ground. According toAristotle, it fell because
B)its natural motion is to fall.
35
New cards
35)A stone is lifted and released so that it falls to the ground. According toGalileo, it fell because
E)of gravity.
36
New cards
36)What, if any, evidence did Galileo have for the law of inertia?
A)A smooth ball slows down when rolling uphill, and speeds up when rolling downhill, so itshould maintain an unchanging speed on a level surface.
37
New cards
37)According to Newtonian physics, an object with no forces acting on it must
E)either be at rest or have constant velocity.
38
New cards
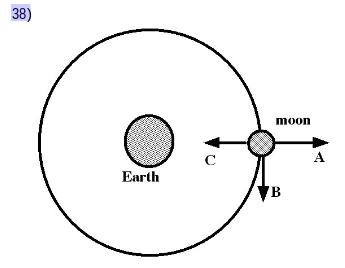
In the figure, the moon is moving clockwise in a circular orbit around Earth. Imagine that gravitywas suddenly shut off, throughout the solar system, at the instant when the moon is in the positionshown in the figure. How would the moon move, after gravity was shut off?
A)In the direction of arrow B, in a straight line.
39
New cards
39)A ball is moving at 20 m/s. If no forces act on it, then 5 seconds later the ball's speed will be
C)20 m/s.
40
New cards
40)You ride a motor scooter 8 km in 15 minutes. Your \[average\] speed is
A)32 km/hr.
41
New cards
41)Mary passes Mike from behind while bicycling. As she passes him,
B)the two have different speeds and different velocities
42
New cards
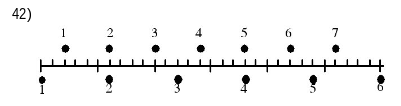
The figure represents a multiple-flash photo of two balls moving to the right, and shows both ballsat several numbered times. The time between flashes is 0.20 s, and thelarge divisions on themeasuring rod are centimeters. The speed of the lower ball is
D)6 cm/s.
43
New cards
43)It is 6 km to Centerville, and you bicycle there in 20 minutes. Your speed is
D)18 km/hr.
44
New cards
44)Is it possible for an object to accelerate but without changing its speed?
B)Yes, for example when a car turns a corner while maintaining an unchanging speed.
45
New cards
45)Edgar Jones, angry at having purchased a tasteless pizza, drops his pizza off the Brooklyn bridge.As it falls, Edgar's pizza has a constant \[or unchanging\]
A)acceleration.
46
New cards
46)An object is dropped from rest on the planet Jupiter. At the end of 1 second, it has fallen 8 m and ismoving at 16 m/s. What was its average speed during the entire first second \[i.e., from t=0 until t=1sec\]?
A)8 m/s
47
New cards
47)Suppose you are on the moon and you drop a rock and a feather at the same time. You will findthat
B)the two fall at the same speed, but this speed is slower than a rock would fall on Earth.
48
New cards
48)On the planet Venus, a Venusian picks up a stone and drops it into a deep hole. If it falls 3 m in 1second, how far will it fall in 2 seconds? You can neglect Venusian air resistance.
B)12 m
49
New cards
49)Galileo's principle of falling is limited by the condition that
A)air resistance must be negligible.
50
New cards
50)A rock is dropped from rest off of a high cliff on another planet, planet X. There is no atmosphere,and thus no air resistance, on planet X. At the end of 1 second, the rock is moving at a speed of 6m/s. At the end of 2 seconds, it is moving at 12 m/s. How fast will the rock be moving at 4 secondsafter being dropped?
A)24 m/s
51
New cards
51)The accelerationdue to gravity is 10 m/sec2. If an object falls from rest, its instantaneous speed atthe end of the fifth second is (neglecting air resistance)
D)50 m/sec.
52
New cards
52)Which of the following best describes the meaning of "force"?
D)A body exerts a force on another body when the first body causes the second body toaccelerate.
53
New cards
53)Object A has twice as much mass as object B. If you exert the same force on these two objects, howdo their accelerations compare?
A)Object A has half as much acceleration as object B.
54
New cards
54)Regarding the relation between acceleration, force, and mass, an object's acceleration is
E)proportional to the force on it and inversely proportional to the object's mass.
55
New cards
55)Which of the following is the basic \[and most accurate\] meaning of "mass"? An object's "mass" is
D)the amount of inertia it contains.
56
New cards
56)The main point of Newton's law of motion is that forces cause
A)acceleration.
57
New cards
57)You push your 2 kg physics book along a tabletop, pushing it with 10 newtons of force. If the bookis greased so that friction is negligible, the book's acceleration is
D)5 m/s2.
58
New cards
58)You push your 2 kg physics book along a tabletop, pushing it with 10 newtons of force. Thefrictional force on it is 4 newtons. The book's acceleration is
E)3 m/s2.
59
New cards
59)A girl lifts a ball by means of a string attached to the ball. The string exerts a 20 newton force on theball. The ball weighs 8 newtons. The net force on the ball is
D)12 newtons.
60
New cards
60)A girl lifts a ball by means of a string attached to the ball. The string exerts a 30 newton force on theball. The ball weighs 20 newtons and has a mass of 2 kilograms. The acceleration of the ball is
B)5 m/s2.
61
New cards
61)Forces of 8 N and 3 N act on an object. If the two forces act in opposite directions, the net force onthe object is
B)5 N.
62
New cards
62)The law of inertia says that
E)if there is no force on a body, the body will have no acceleration.
63
New cards
63)A rocket taking off straight upward develops a thrust of 10,000 newtons. The rocket weighs 2,000newtons. Thenet force on the rocket, neglecting air resistance, is
E)8,000 newtons.
64
New cards
64)You would be richest if your hunk of gold had amass of one kilogram
C)Actually it wouldn't make any difference.
65
New cards
65)You would be richest if your hunk of goldweighed 10 newtons
A)on the moon.
66
New cards
66)Would you be richer if you had a hunk of gold whose weight is 1 newton on the moon, or onewhose weight is 1 newton on Earth, and why?
B)1 newton on the moon, because then the gold's mass would be larger.
67
New cards
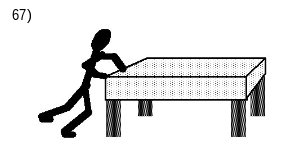
Mary pushes horizontally on a large, heavy table, which is standing alone in the middle of a room,and notes that the table does not move despite the fact that she is pushing on it (see the figure). Whydoesn't the table move?
D)Frictional forces by the floor on the table legs acted in the opposite direction to produce a netforce of zero.
68
New cards
68)An auto travels down a straight, level road at constant speed. One force that acts on the auto is
A)the road pushing upward on the auto.
69
New cards
69)An object's "momentum" is defined as
B)its mass times its velocity.
70
New cards
70)A stationary firecracker explodes, breaking into two parts of equal mass. One part is moving northat 20 m/s. The velocity of the other part is
A)southward at 20 m/s.
71
New cards
71)Which of the following principles explains why guns recoil?
A)Conservation of momentum.
72
New cards
72)A pool ball moving at 3 m/s collides head-on with an identical pool ball that's initially at rest. Justafter the collision, the second ball moves away at 2 m/s while the first ball
E)moves at 1 m/s in the same direction as the second ball.
73
New cards
73)A 39-kg girl standing at rest on slippery (frictionless) ice catches a 1-g ball moving at 10 m/s. Justafterward, the girl is
The right answer
74
New cards
74)A hypothesis is
A)an unconfirmed suggestion
75
New cards
75)A theory is
A)a well confirmed framework of ideas that explains what we observe.