Data Science
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Qualititative Data
Can be divided into different categories
Ex. What’s your favorite type of coffee?
Quantitative Data
Is a numerical data that can be counted or measured
Ex. How many cups of coffee did you drink today?
Variable
A name that stores a piece of data
Ex. greeting = “Hello, World!”
print(greeting)
Output: Hello, World!
var name = greeting
data type = string
value = “Hello, World!”
Naming Rules
Basic Guidelines
Use descriptive names
Underscores take the place of spaces
Only lower case letters
Cannot start with a number
Integer
A number can be positive, negative or zero w/o a decimal component
Ex. -5; 500; ;0
Float
A number can be positive, negative or zero w/ a decimal component
Ex. 3.2; 0.0; 4.5623
String
Contains sequence of letters, numbers, punctuations, spaces, etc.
Ex.”abcdehj”; “Hello, World!”
Character
Contains single character or punctuation
Ex. a; z; 1; !; #;
Boolean
Binary and evaluate to either true or false
Ex. True or false
==
equal to → 6 == 6
!= / ≠
not equal to → 6 != 7
>
greater than → 6 > 7
<
less than → 6 < 7
>=
greater than or equal to → 6 >= 7
<=
less than or equal to → 6 <= 7
and
is only true if both conditions are true
Ex. 6 > 7 and 6 > 3
* Print false because 6 is not greater than 7, only one statement is true not both
or
is only true if either condition is true
Ex. 6 > 7 or 6 > 3
* Print true because 6 is greater than 3. One statement is true, doesn’t require both statements to be true
not
negates the truth value of the condition
Ex. not (6 > 7)
* print true because 6 isn’t greater than seven, the statement is false
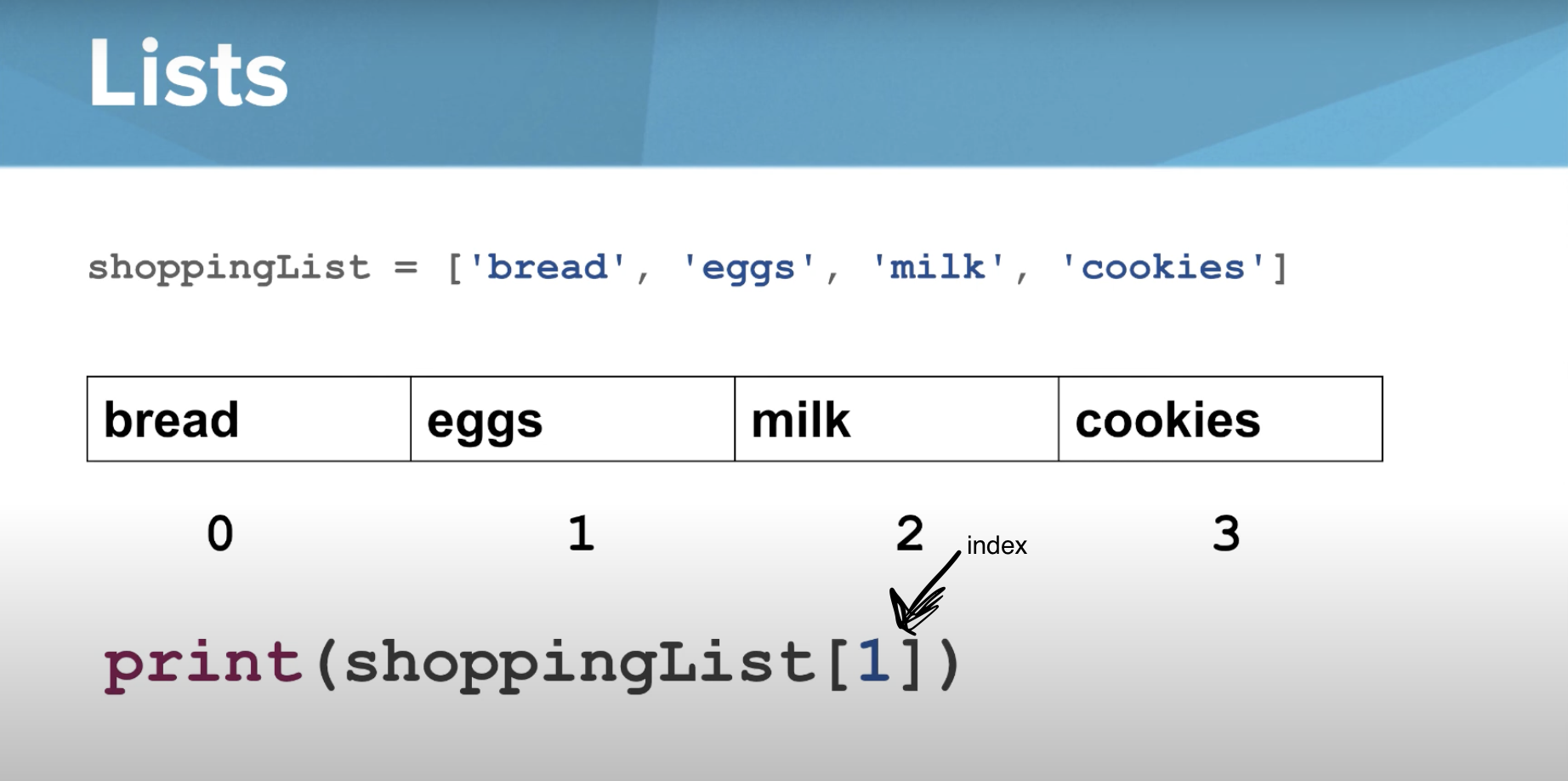
List
a collection of ordered items
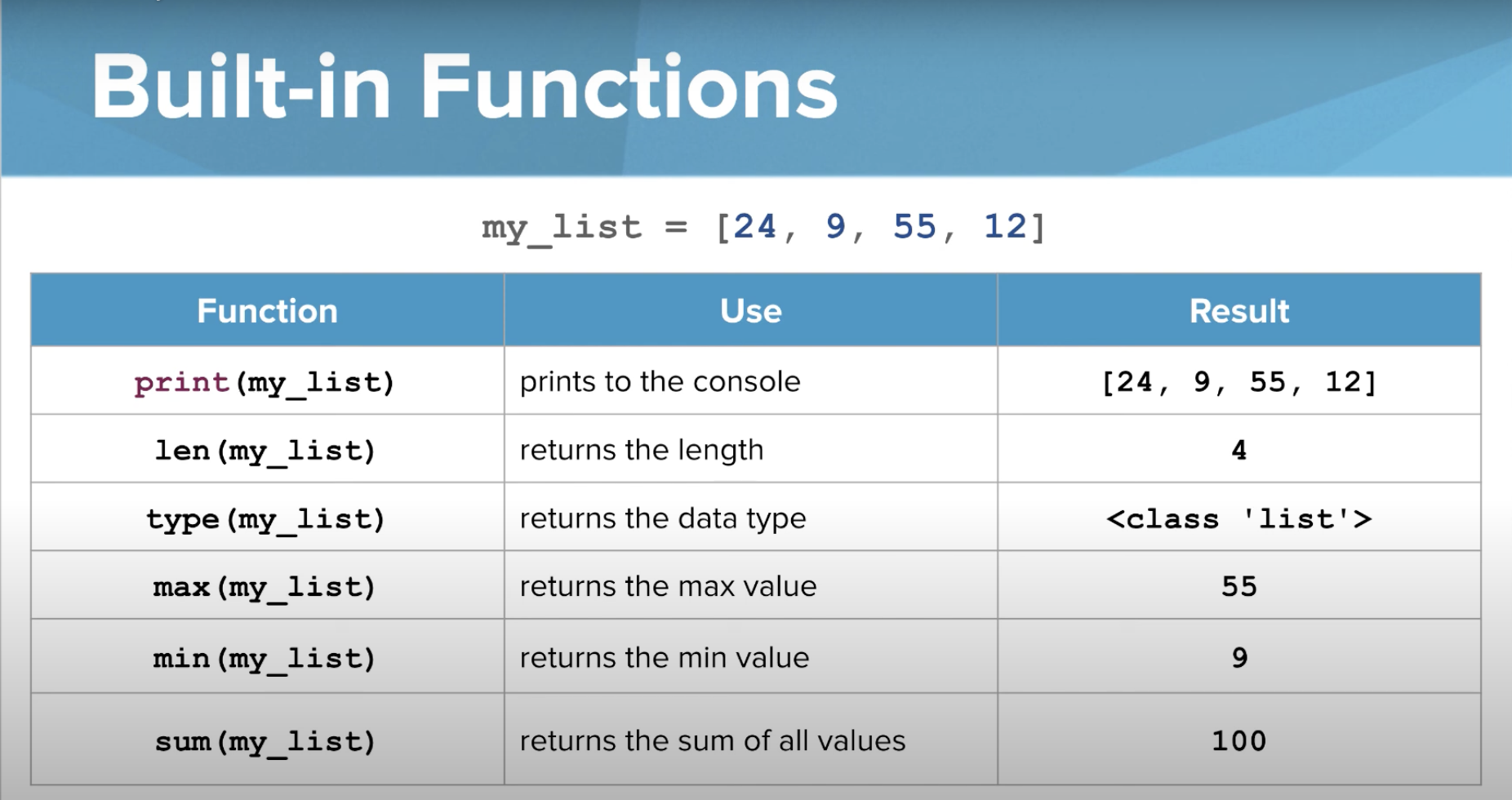
Built in functions
Python modules
Can be imported into your code
Contains predefined functions, variables and more
Helps build programs faster and w/ less difficulty
A package is a collection of related modules
A library is a collection of modules and packages
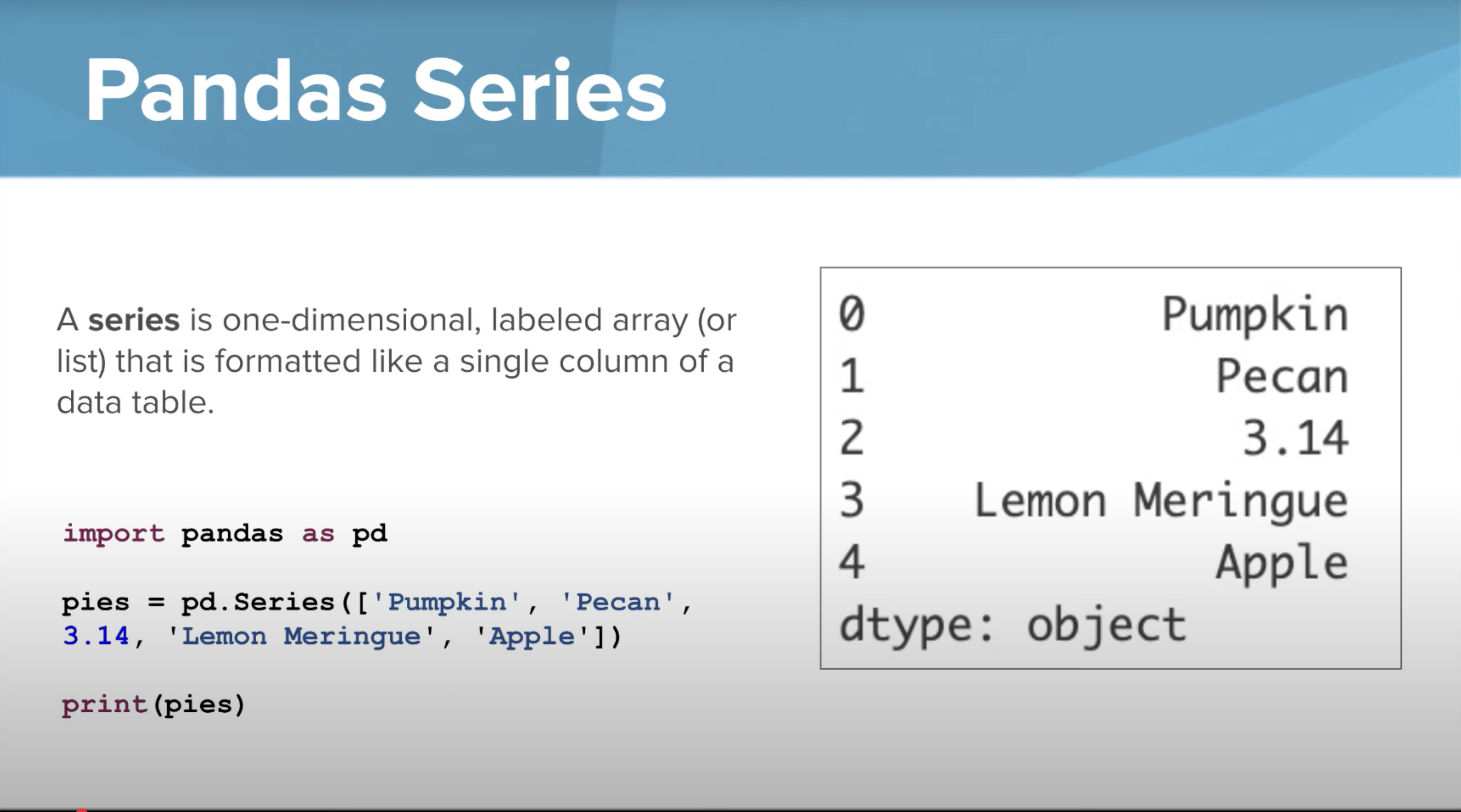
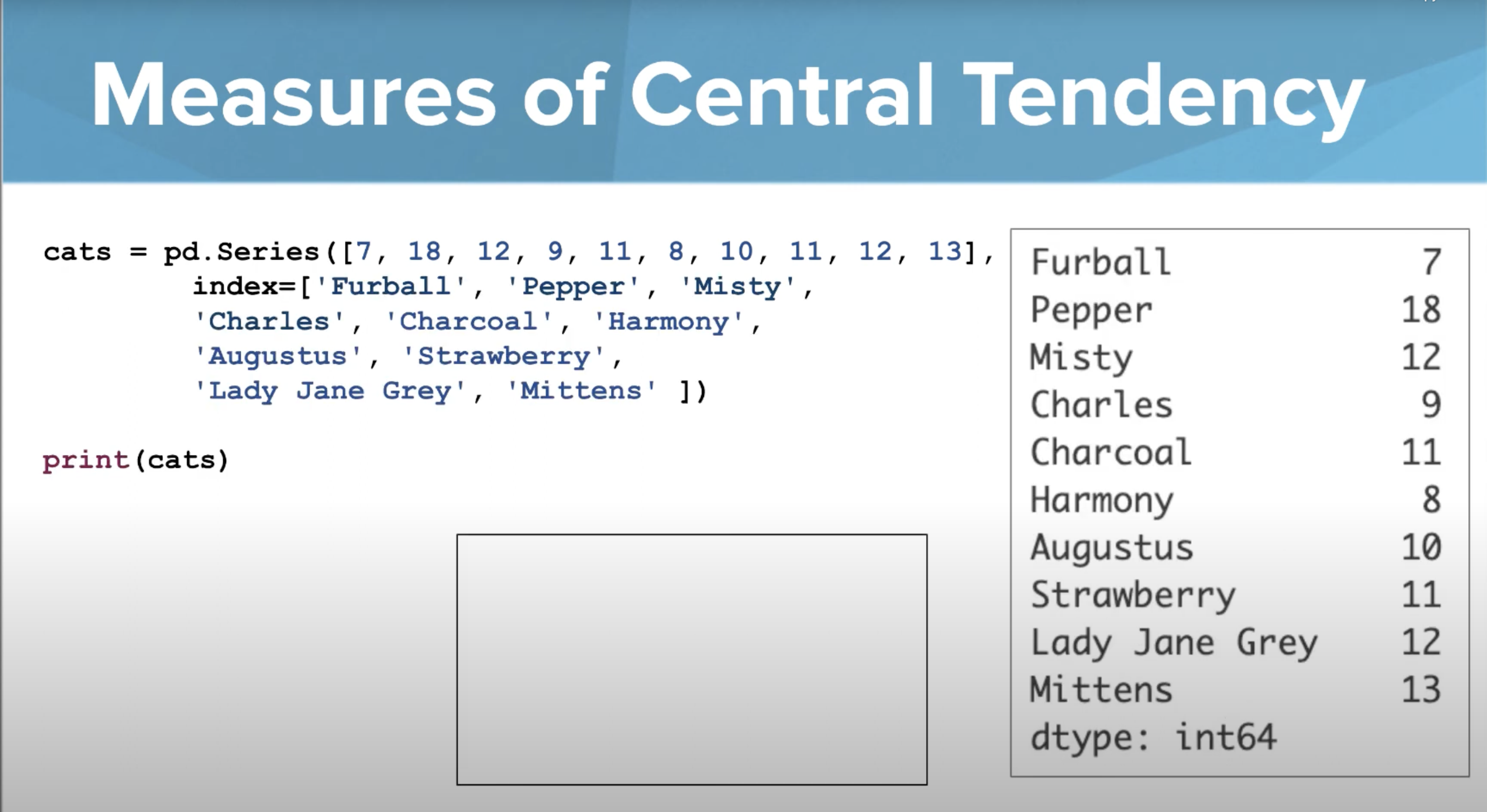
Series
One-dimensional labeled array or list that is formatted for like a single column of a data table.
Mean
Use when points aren’t too spread out and there aren’t any outliers.
Use to avoid outliers from negatively affecting data
Median
Use when there are extreme outliers or the data isn’t balanced well.
Mode
Use when there is only a few different data values
Documentation
A written set of instructions for using the python module or library.
Lists functions that are included
Directs how to use each function
Offers examples
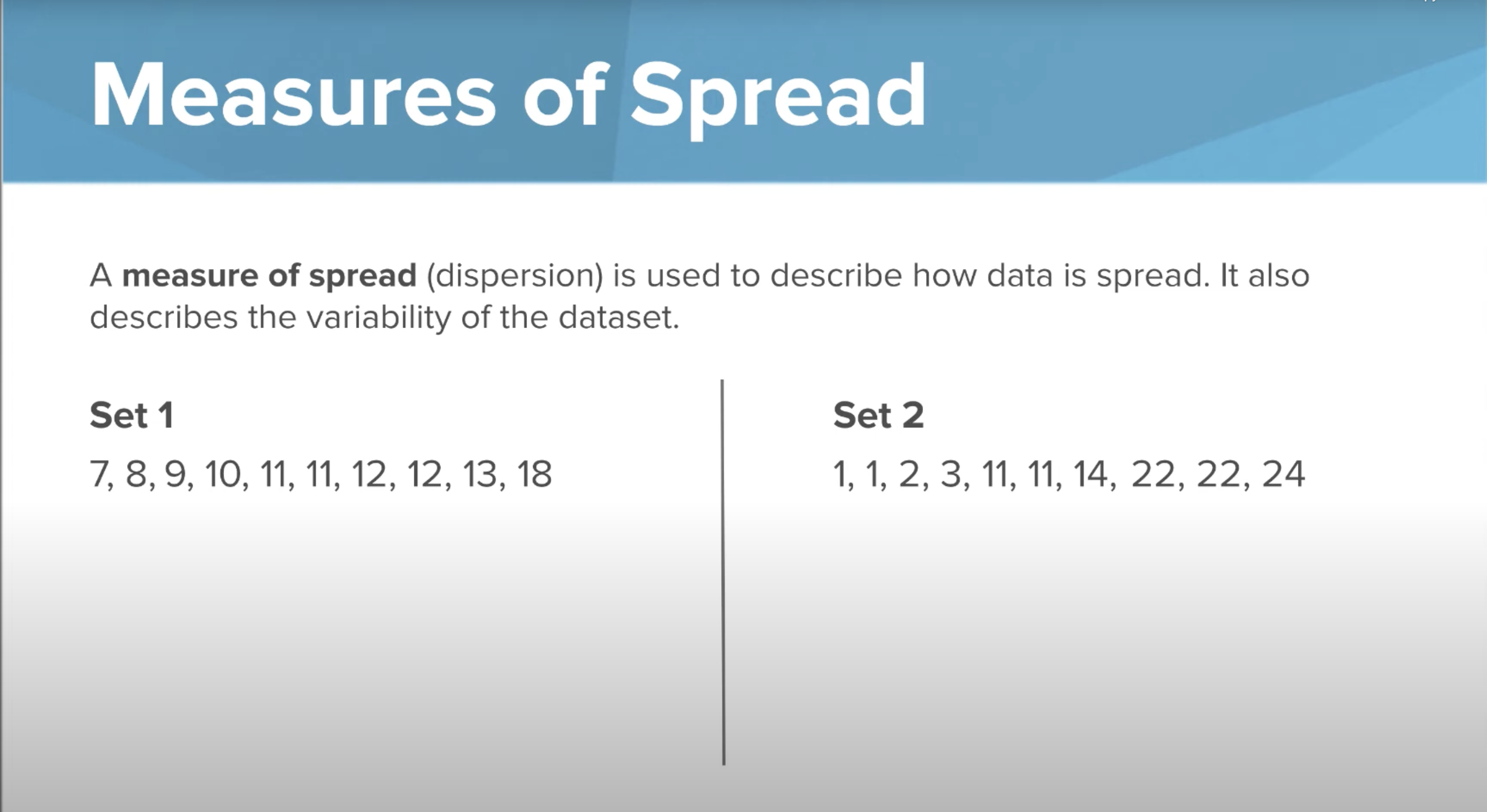
Measures of Spread
Indices
Assigns names to elements in the list
Dataframe
A data structure that stores and aligns data in a table using rows and columns
Essentially a collection of more than one series.
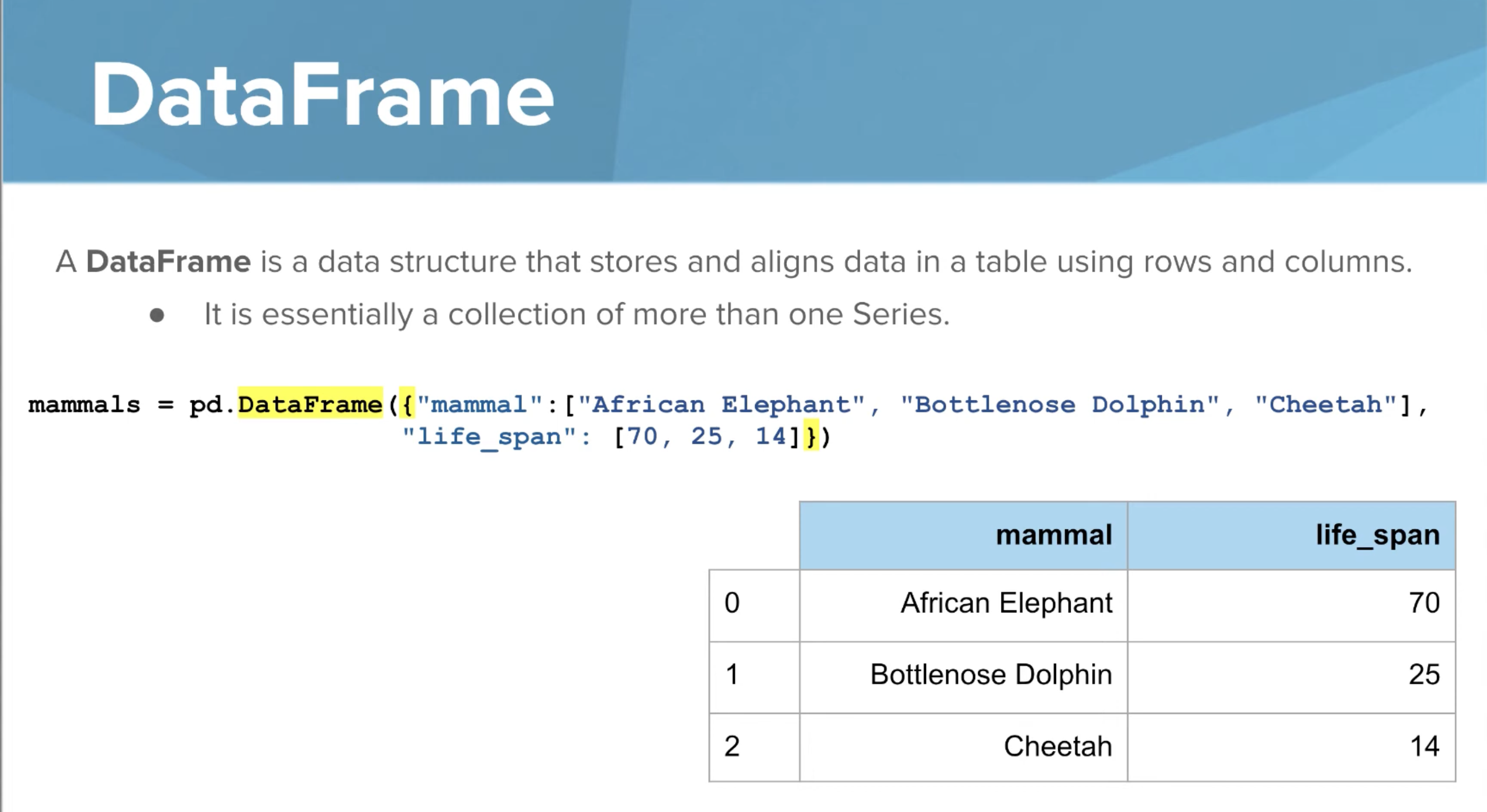
table.dtypes
Lists the datatypes used in each column in the Data Frame.
This one for examples print integers as a datatype because positive whole numbers are being used in the column.
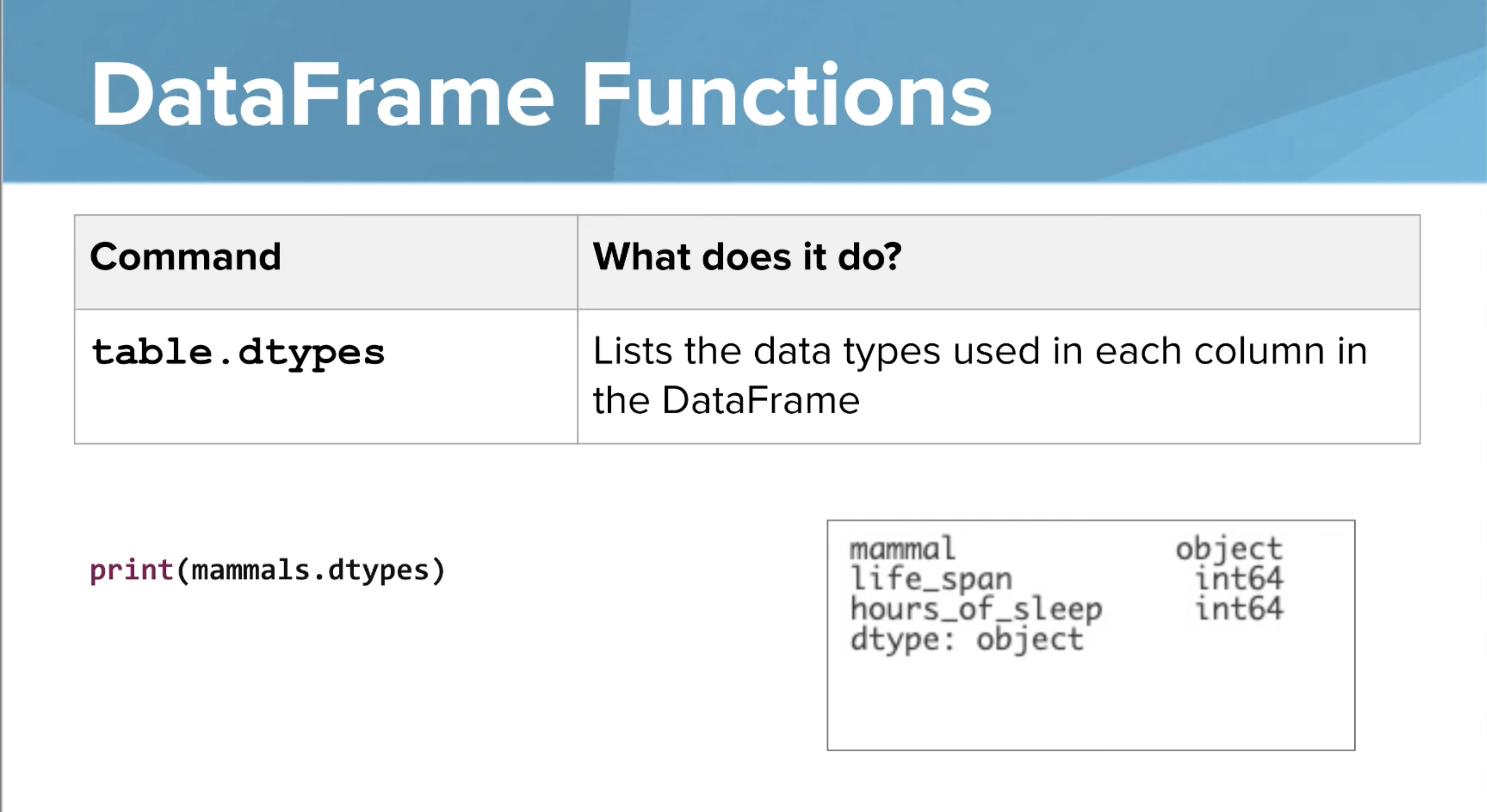
table.shape
Displays the # of rows and columns within the table

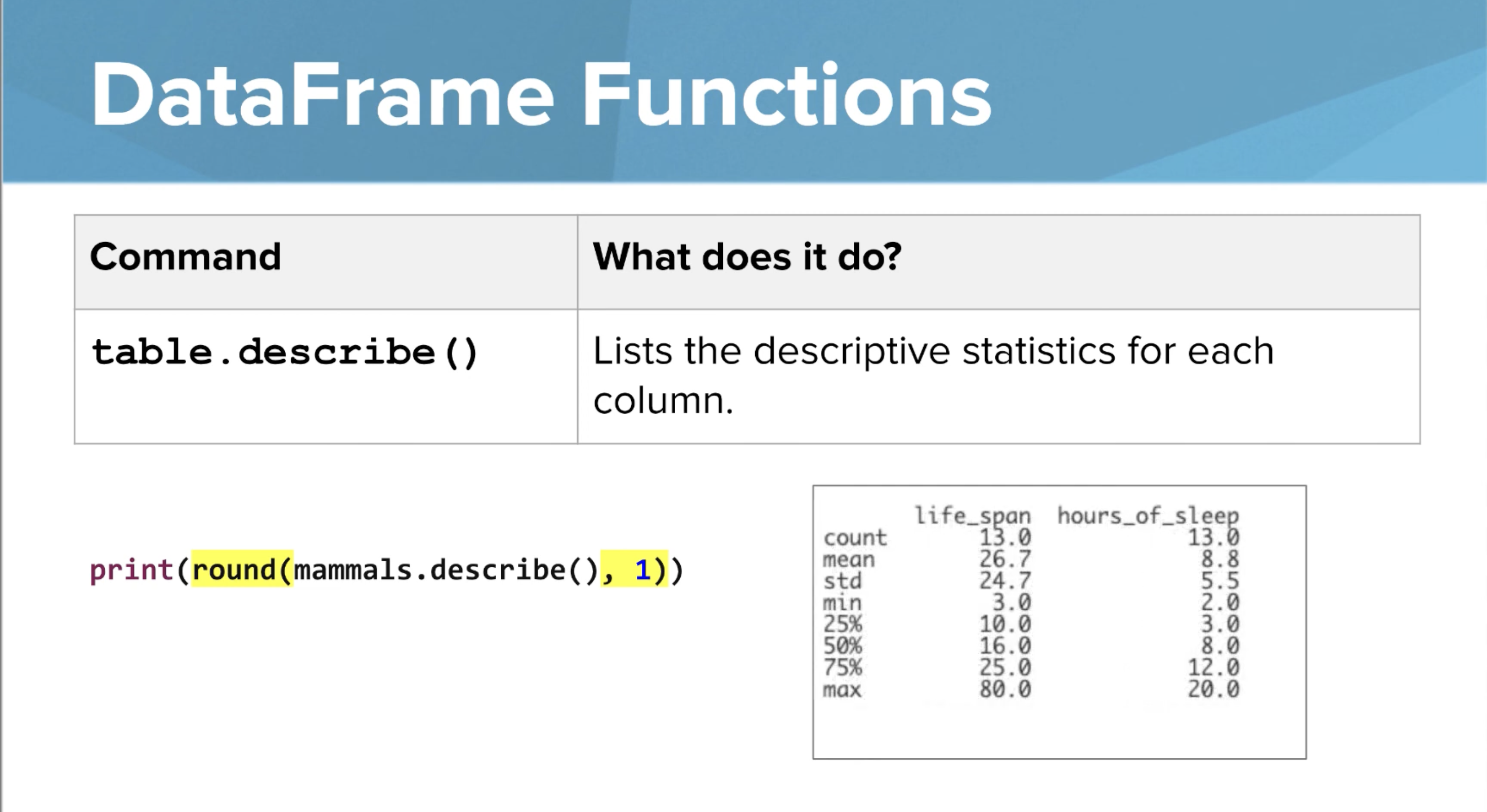
table.describe
Lists and describes all the specific statistics for each column
the round command rounds the decimal to whatever place the user inputs in this case, the decimal is rounded to 1 place.
Rows Commands
Determine which rows of the table are displayed, instead of displaying the entire table, useful for using big data tables.
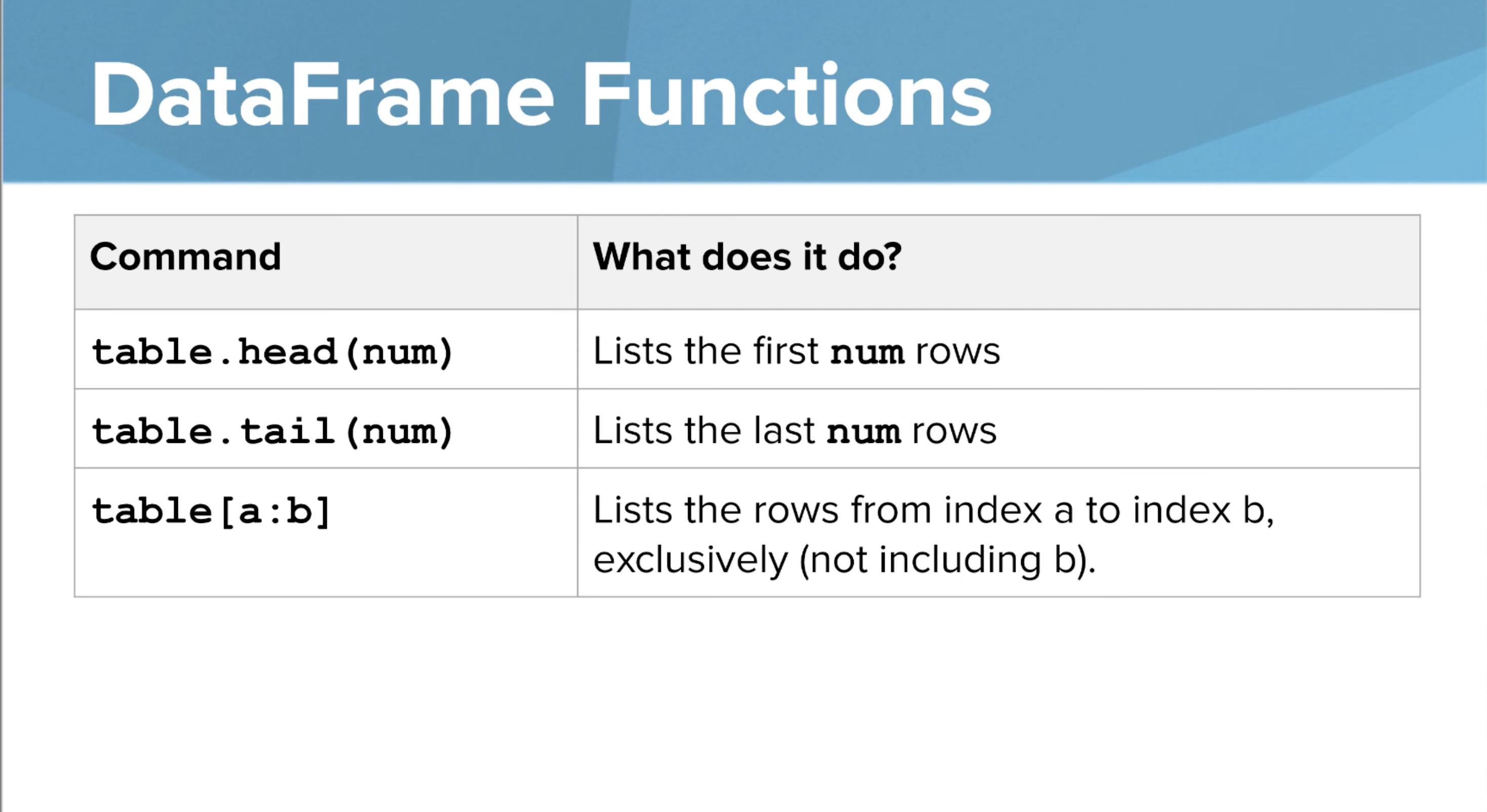
table.head / table.tail
displays the first or last few rows depending on which number is placed in the parentheses
* if there isn’t any number in the parentheses, the function will display the first / last five rows as a default.
table[a:b]
Choose a specific section of the table to display using brackets.
will list the rows using the indices from the first # to the last # EXCLUSIVELY
* Will not include the last #
Module
A python module:
Can be imported into your code
Contains predefined functions, variables, and more.
helps to build programs faster with less difficulty.
Package
A collection of related modules
Library
Is a collection of modules and packages that can be imported into a program