Human Anatomy and Physiology Review
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A series of flashcards covering key concepts of human anatomy and physiology for exam preparation.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What organ is responsible for most of the nutrient absorption in the body?
Small intestine
What type of joint is the elbow?
Hinge
How does serotonin affect the body?
It helps to regulate mood, anxiety, sleep, memory, and appetite.
Which type of tissue is most widely distributed throughout the body?
Connective tissue
Which chamber of the heart has the thickest muscular wall?
Left ventricle
What structure may have been injured in a mild car accident if a patient complains of sternum pain?
Xiphoid process
Which important minerals are stored within the skeletal system?
Calcium and phosphorous
Which muscles pull a body part away from the midline of the body?
Abductors
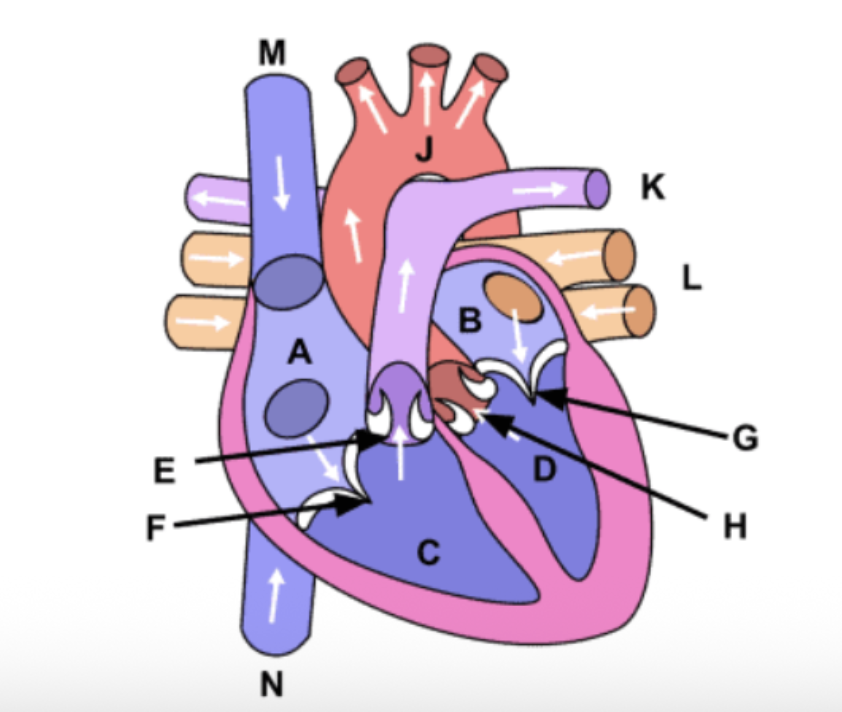
Which anatomical structure is designated by letter B in the provided image?
Left atrium
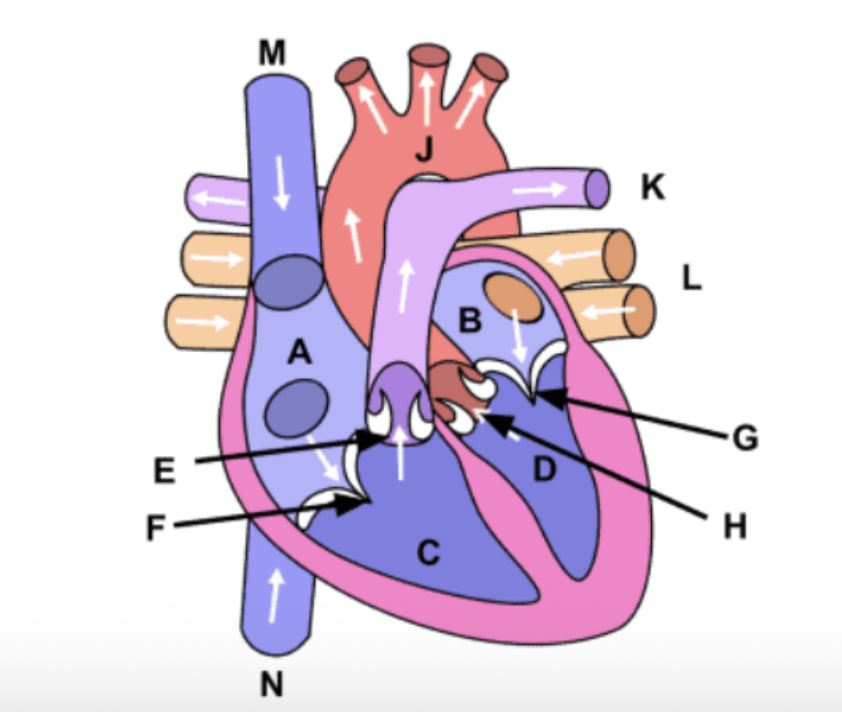
What is the function of the mitral valve?
Lets blood flow from the left atrium to the left ventricle.
In which reproductive structure does fertilization of an ovum occur?
Fallopian tube
Which structure is part of the upper respiratory system?
Pharynx
Where is the tibialis anterior located?
The front of the lower extremities
How does urine travel from the kidney to the urinary bladder?
Through the ureter.
What is located in the thoracic cavity?
The mediastinum.
Which part of the brain processes auditory information?
Temporal lobe.
What molecule carries genetic instructions for organisms?
DNA.
Which nerve is likely compromised if a patient has decreased sensation in the distal arm and inability to adduct and abduct fingers?
Ulnar nerve.
Which plane divides the body into left and right sides?
Sagittal.
What are the layers of the epidermis from most superficial to deepest?
Stratum corneum, stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum, stratum germinativum.
Which statement about the endocrine system is false?
The hypothalamus is commonly known as the 'master gland.'
What is the function of sebaceous glands?
To secrete oil that lubricates the skin and prevents drying.
What type of connection do ligaments create?
Bone to bone.
Where are the malleus, incus, and stapes located?
In the ear.
What is the primary function of hemoglobin?
Carries oxygen to tissues and organs.